The Python math Library provides various Functions and Constants / Properties, which allows us to perform mathematical functionality. Unlike other global objects, Properties, and Functions inside the Python math library object are static. So, we can access the math properties as pi and function as abs(number).
Object Properties
The list of Properties or Constants is available in the Python math library module.
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| math.e | It returns the Euler’s Number e, approximately equal to 2.71828 |
| math.pi | It returns the Pie Value, approximately equal to 3.14 |
| math.inf | This property returns the Positive Infinity. You can use -math.INF to return the Negative Infinity. |
| math.nan | It returns Not A Number as output. |
Python math Functions
The list of Python mathematical Functions is available in the math Library. Please follow these links to view the tutorial on the available methods.
| Python math Functions | Description |
|---|---|
| ceil(x) | It returns the smallest integer, which is greater than or equal to the specified expression or a number. |
| copysign(x) | This function finds the Absolute value of the first argument. It returns the absolute value and the sign specified in the second argument. |
| fabs(x) | The absolute value of a Given number |
| factorial(x) | It finds the factorial of a specified expression or a specific number. |
| floor(x) | The largest integer value is less than or equal to the specified number. |
| fmod(x, y) | This Python math function calculates the Module of the specified given arguments. |
| frexp(x) | It returns the mantissa and exponent of x as pair (m, e) where m is a float value, and e is an integer value. |
| fsum(Iterable) | Calculates and returns the sum of iterates (Tuples and Lists) |
| gcd(x, y) | This function returns the greatest common divisor of two given arguments. |
| isclose(x, y) | Returns TRUE, If the two arguments are close to each other otherwise, it returns FALSE |
| isfinite(x) | Used to check whether the given number/expression is neither Infinity (both Positive or Negative) nor NaN. It returns TRUE If the given number is neither Infinity nor NaN (Not a Number) otherwise, FALSE. |
| isinf(x) | Checks whether the given number is Infinity (both Positive or Negative) or not. It returns TRUE If the number is Infinity otherwise, FALSE |
| isnan(x) | This Python math function checks whether the given number is NaN (Not a Number) or not. It returns TRUE if the given number is NaN otherwise, FALSE |
| round(x) | It is a regular one (not a Math module fmethod). It rounds the specified expression or a specific number to the nearest integer. |
| ldexp(x, i) | This built-in method Returns x * (2**i). It is also called the inverse of the frexp method. |
| modf(x) | Divides the given value into two arguments: Fractional Part as the first argument and integer value as the second argument. |
| trunc(x) | Removes the decimal values from the specified expression and returns the integer value |
Python math Power and Logarithmic Functions
The following is the list of Power and logarithmic functions available in the Python math Library.
| Power and Logarithmic Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| exp(x) | It calculates the power of E, Where E is Euler’s number approximately equal to 2.71828. |
| expm1(x) | It calculates the power of E (Where E is Euler’s number approximately equal to 2.71828) and subtracts one from it. |
| log(x, base) | This Power and logarithmic function find a number’s log value with base E. |
| log2(x) | Logarithmic value of a number with base E. |
| log10(x) | Logarithmic value of a given number with base E. |
| pow(x) | This Power and logarithmic function calculate the Power of the specified expression |
| sqrt(x) | The square root of a specified Python expression or an individual number |
Python Trigonometric math Functions
The following is the list of Trigonometric functions available in the Python math Library.
| Trigonometric Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| acos(x) | It returns the Arc Cosine value of a given number |
| asin(x) | This Trigonometric function returns the Arc Sine value of a given number |
| atan(x) | Arc Tangent value of a number |
| atan2(y, x) | It returns the angle (in radius) from the X-Axis to the specified point (y, x). |
| cos(x) | This Trigonometric function returns the Cosine value of a number |
| hypot(x, y) | It extracts the characters from a string based on the specified indices |
| sin(x) | Sine value of a given number |
| tan(x) | Tangent value of a given number |
Python Hyperbolic math Functions
The Python Hyperbolic trigonometric functions allow us to perform the following math functions on Hyperbolic instead of Circles.
| Hyperbolic Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| acosh(x) | It returns the Hyperbolic Arc Cosine (inverse Hyperbolic Cosine) value of a given number |
| asinh(x) | This Hyperbolic Function returns the Hyperbolic Arc Sine (inverse Hyperbolic Sine) value of a given number |
| atanh(x) | Hyperbolic Arc Tangent (inverse Hyperbolic Tangent) value of a given number |
| cosh(x) | Hyperbolic Cosine value of a given number |
| sinh(x) | It returns the Hyperbolic Sine value of a given number |
| tanh(x) | Hyperbolic Tangent value of a given number |
Python Angular math Functions
The following is the list of Angular functions available in the Python math Library.
| Angular Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| degrees(x) | It converts the specified angle from Radians to Degrees. |
| radians(x) | This Angular function converts the specified angle from Degrees to Radians. |
Python Special math Functions
The following is the list of Special functions available in the Python math Library.
| Special | Description |
|---|---|
| erf(x) | It returns the error at a specified value. |
| erfc(x) | This Special function returns the complementary error function. OR we can simply say, 1 – erf(x) |
| gamma(x) | It returns the Gamma at a specified value. |
| lgamma(x) | This Special function returns the Natural Logarithm of the Gamma function at a specified value. |
Python math Functions Examples
The following examples help you to understand these math functions.
constants Example
In this constants example, we use the list of available constants in the math library. They are pi, e, tau, inf, and nan.
import math as td
print('pi Constant - Pi = ', td.pi)
print('pi Constant - Degrees of Pi = ', td.degrees(td.pi))
print('\ne Constant - e = ', td.pi)
print('e Constant - Degrees of e = ', td.degrees(td.e))
print('\ntau Constant - tau = ', td.tau)
print('tau Constant - Degrees of tau = ', td.degrees(td.tau))
print('\ninf Constant - Positive Infinity = ', td.inf)
print('inf Constant - Negative Infinity = ', -td.inf)
print('\nNaN Constant - Not a Number = ', td.nan)
pi Constant - Pi = 3.141592653589793
pi Constant - Degrees of Pi = 180.0
e Constant - e = 3.141592653589793
e Constant - Degrees of e = 155.74607629780772
tau Constant - tau = 6.283185307179586
tau Constant - Degrees of tau = 360.0
inf Constant - Positive Infinity = inf
inf Constant - Negative Infinity = -inf
NaN Constant - Not a Number = nanPython math Functions – fabs, ceil, floor, factorial
In this example, we will use the fabs to find the absolute value and copysign to change the sign. Next, we used the ceil and floor to find the Ceiling and Floor values. Within the last statement, we used the factorial func to find the factorial of a given value.
import math as mh
x = 10.98
y = 30.22
z = -40.95
print('FABS - Absolute Value of z = ', mh.fabs(z))
print('FABS - Absolute Value of -124.897 = ', mh.fabs(-124.897))
print('\ncopysign of x, z = ', mh.copysign(x, z))
print('copysign of z, x = ', mh.copysign(z, x))
print('\nCEIL - Ceiling of x = ', mh.ceil(x))
print('CEIL - Ceiling of y = ', mh.ceil(y))
print('\nFLOOR - Floor of x = ', mh.floor(x))
print('FLOOR - Floor of y = ', mh.floor(y))
print('\nFactorial of 3 = ', mh.factorial(3))
print('Factorial of 5 = ', mh.factorial(5))
FABS - Absolute Value of z = 40.95
FABS - Absolute Value of -124.897 = 124.897
copysign of x, z = -10.98
copysign of z, x = 40.95
CEIL - Ceiling of x = 11
CEIL - Ceiling of y = 31
FLOOR - Floor of x = 10
FLOOR - Floor of y = 30
Factorial of 3 = 6
Factorial of 5 = 120Python math Functions – fmod, frexp, fsum, gcd
In this example, we used fmod, frexp, fsum, and gcd with different values.
import math as gm
print('FMOD - Mod of 2 and 3 = ', gm.fmod(2, 3))
print('FMOD - Mod of 225.55 and 5.5 = ', gm.fmod(222.55, 5.5))
print('\nFREXP - Mantissa and Exponent Value of 5 = ', gm.frexp(5))
print('FREXP - Mantissa and Exponent Value of -9 = ', gm.frexp(-9))
print('\nFSUM - Sum of Tuple Items = ', gm.fsum((10, 20, 30, 40)))
print('FSUM - Sum of List Items = ', gm.fsum([5, 22, 35, 9]))
print('\nGCD of two 10 and 2 = ', gm.gcd(10, 2))
print('GCD of two 100 and 15 = ', gm.gcd(100, 15))
FMOD - Mod of 2 and 3 = 2.0
FMOD - Mod of 225.55 and 5.5 = 2.5500000000000114
FREXP - Mantissa and Exponent Value of 5 = (0.625, 3)
FREXP - Mantissa and Exponent Value of -9 = (-0.5625, 4)
FSUM - Sum of Tuple Items = 100.0
FSUM - Sum of List Items = 71.0
GCD of two 10 and 2 = 2
GCD of two 100 and 15 = 5Python math functions – round, ldexp, modf, trunc, remainder
In this math Functions example, we used round, ldexp, mode, trunc, and remainder.
import math as at
print('ROUND - Rounded Number 100.98763 = ', round(100.9876, 2))
print('ROUND - Rounded Number 125.932832 = ', round(125.932832, 3))
print('\nLDEXP - LDEXP (FREXP inverse) Number of 4, 5 = ', at.ldexp(4, 5))
print('LDEXP - LDEXP (FREXP inverse) Number of -9, 2 = ', at.ldexp(-9, 2))
print('\nMODF - Modf (Divided 1 to 2) Number of 100 = ', at.modf(100))
print('MODF - Modf (Divided 1 to 2) Number of 120.98 = ', at.modf(120.98))
print('\nTRUNC - Truncated Number 100.98763 = ', at.trunc(100.9876))
print('ROUND - Truncated Number 125.932832 = ', at.trunc(-125.932832))
print('\nRemainder of 29 and 5 = ', at.remainder(20, 5))
print('Remainder of 10 and 3 = ', at.remainder(10, 3))
ROUND - Rounded Number 100.98763 = 100.99
ROUND - Rounded Number 125.932832 = 125.933
LDEXP - LDEXP (FREXP inverse) Number of 4, 5 = 128.0
LDEXP - LDEXP (FREXP inverse) Number of -9, 2 = -36.0
MODF - Modf (Divided 1 to 2) Number of 100 = (0.0, 100.0)
MODF - Modf (Divided 1 to 2) Number of 120.98 = (0.980000000000004, 120.0)
TRUNC - Truncated Number 100.98763 = 100
ROUND - Truncated Number 125.932832 = -125
Remainder of 29 and 5 = 0.0
Remainder of 10 and 3 = 1.0Logarithmic Functions Example
In this Python Logarithmic functions example, we use the math exp, expm1 to get exp values. Next, we used the log, log2, and log10 to get the natural logarithmic value, base 2 Logarithmic value. And base 10 logarithmic values. Then we used the pow to find x raised to the power of y and sqrt to find the square root of a number.
import math as th
print('exp of 5 = ', th.exp(5))
print('exp of -3 = ', th.exp(-3))
print('\nexpm1 of 8 = ', th.expm1(8))
print('expm1 of -5 = ', th.expm1(-5))
print('\nLOG - logarithmic of 5 = ', th.log(5))
print('LOG - logarithmic of 100 Base 2 = ', th.log(100, 2))
print('\nLOG2 - logarithmic of 120 Base 2 = ', th.log2(120))
print('\nLOG10 - logarithmic of 150 Base 10 = ', th.log2(150))
print('\nPOW - 2 Power 3 = ', th.pow(2, 3))
print('POW - 5 Power 4 = ', th.pow(5, 4))
print('\nSQRT - Square Root of 25 = ', th.sqrt(25))
print('SQRT - Square Root of 19 = ', th.sqrt(19))
exp of 5 = 148.4131591025766
exp of -3 = 0.049787068367863944
expm1 of 8 = 2979.9579870417283
expm1 of -5 = -0.9932620530009145
LOG - logarithmic of 5 = 1.6094379124341003
LOG - logarithmic of 100 Base 2 = 6.643856189774725
LOG2 - logarithmic of 120 Base 2 = 6.906890595608519
LOG10 - logarithmic of 150 Base 10 = 7.22881869049588
POW - 2 Power 3 = 8.0
POW - 5 Power 4 = 625.0
SQRT - Square Root of 25 = 5.0
SQRT - Square Root of 19 = 4.358898943540674Trigonometric cos, sin, tan, acos, asin, atan, atan2, hypot Functions
In this Python Trigonometric math functions example, we will use the sin, cos, and tan to find the Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Values. Next, we used the acos, asin, atan, and atan2 to find the Arc cosine, Arc Sine, and Arc Tangent values. Within the last statement, we used the hypot
import math as mt
print('COS - Cosine of 10 = ', mt.cos(10))
print('COS - Cosine of -15 = ', mt.cos(-15))
print('\nSIN - Sine of 3 = ', mt.sin(3))
print('SIN - Sine of -5 = ', mt.sin(-5))
print('\nTAN - Tangent of 9 = ', mt.tan(9))
print('TAN - Tangent of -3 = ', mt.tan(-3))
print('\nACOS - Arc Cosine of 1 = ', mt.acos(1))
print('ACOS - Arc Cosine of -0.78 = ', mt.acos(-0.78))
print('\nASIN - Arc Sine of 1 = ', mt.asin(1))
print('ASIN - Arc Sine of -2 = ', mt.asin(-0.42))
print('\nATAN - Arc Tangent of 0.72 = ', mt.atan(0.72))
print('ATAN - Arc Tangent of -2.71 = ', mt.atan(-2.71))
print('\nATAN2 - Tangent of 2, 5 = ', mt.atan2(2, 5))
print('\nHYPOT - Hypot Value of 2, 3 = ', mt.hypot(2, 3))
COS - Cosine of 10 = -0.8390715290764524
COS - Cosine of -15 = -0.7596879128588212
SIN - Sine of 3 = 0.1411200080598672
SIN - Sine of -5 = 0.9589242746631385
TAN - Tangent of 9 = -0.4523156594418099
TAN - Tangent of -3 = 0.1425465430742778
ACOS - Arc Cosine of 1 = 0.0
ACOS - Arc Cosine of -0.78 = 2.4654621440291318
ASIN - Arc Sine of 1 = 1.5707963267948966
ASIN - Arc Sine of -2 = -0.43344532006988595
ATAN - Arc Tangent of 0.72 = 0.6240230529767569
ATAN - Arc Tangent of -2.71 = -1.2172930308235297
ATAN2 - Tangent of 2, 5 = 0.3805063771123649
HYPOT - Hypot Value of 2, 3 = 3.6055512754639896Python math Trigonometric cosh, sinh, tanh, acosh, asinh, atanh Functions
In this Python math example, we use the Hyperbolic trigonometric functions. First, we used the cosh, sinh, and tanh to find the Hyperbolic Cosine, Sine, and Tangent Values. Next, acosh, asinh, and atanh find the Hyperbolic Arc cosine, Arc Sine, and Hyperbolic Arc Tangent values.
import math as ma
print('COSH - Hyperbolic Cosine of 2 = ', ma.cosh(2))
print('COSH - Hyperbolic Cosine of -1 = ', ma.cosh(-1))
print('\nSINH - Hyperbolic Sine of 3 = ', ma.sinh(3))
print('SINH - Hyperbolic Sine of -5 = ', ma.sinh(-5))
print('\nTANH - Hyperbolic Tangent of 1 = ', ma.tanh(1))
print('TANH - Hyperbolic Tangent of -3 = ', ma.tanh(-3))
print('\nACOSH - Hyperbolic Arc Cosine of 10 = ', ma.acosh(10))
print('ACOSH - Hyperbolic Arc Cosine of 30.78 = ', ma.acosh(30.78))
print('\nASINH - Hyperbolic Arc Sine of 15 = ', ma.asinh(15))
print('ASINH - Hyperbolic Arc Sine of -25 = ', ma.asinh(-25))
print('\nATANH - Hyperbolic Arc Tangent of 0.57 = ', ma.atanh(0.57))
print('ATANH - Hyperbolic Arc Tangent of -0.71 = ', ma.atanh(-0.71))
COSH - Hyperbolic Cosine of 2 = 3.7621956910836314
COSH - Hyperbolic Cosine of -1 = 1.5430806348152437
SINH - Hyperbolic Sine of 3 = 10.017874927409903
SINH - Hyperbolic Sine of -5 = -74.20321057778875
TANH - Hyperbolic Tangent of 1 = 0.7615941559557649
TANH - Hyperbolic Tangent of -3 = -0.9950547536867305
ACOSH - Hyperbolic Arc Cosine of 10 = 2.993222846126381
ACOSH - Hyperbolic Arc Cosine of 30.78 = 4.119748326708938
ASINH - Hyperbolic Arc Sine of 15 = 3.4023066454805946
ASINH - Hyperbolic Arc Sine of -25 = -3.9124227656412556
ATANH - Hyperbolic Arc Tangent of 0.57 = 0.6475228448273728
ATANH - Hyperbolic Arc Tangent of -0.71 = -0.8871838632580928Angular and Special Functions – degrees, radians, gamma
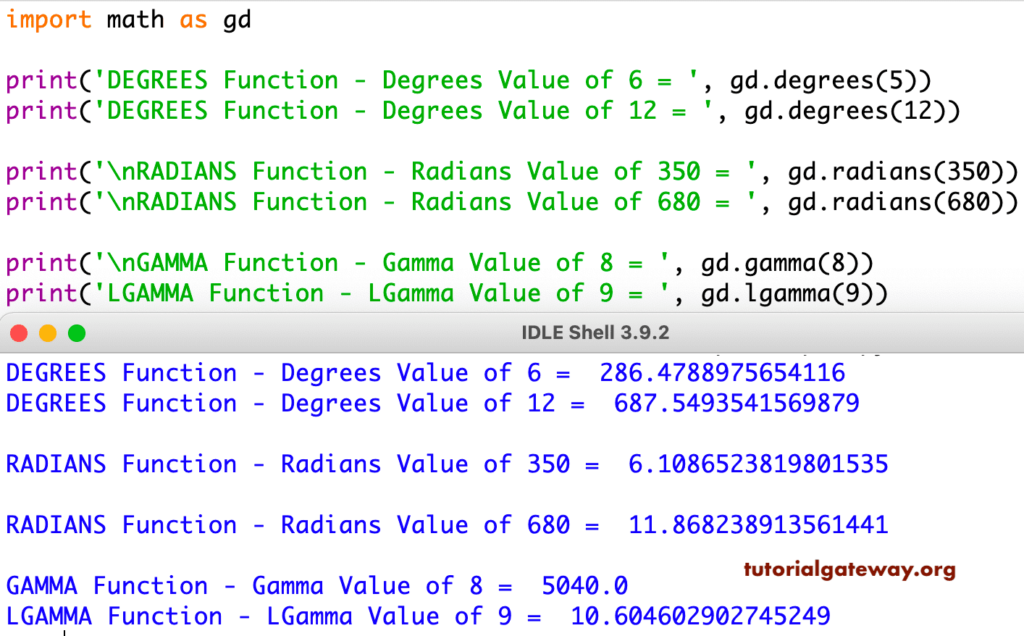
In this Python math Angular functions example, we used the degrees and radians to convert degrees to radians and vice versa. Next, we used gamma and lgamma to return the gamma values.
import math as gd
print('DEGREES Function - Degrees Value of 6 = ', gd.degrees(5))
print('DEGREES Function - Degrees Value of 12 = ', gd.degrees(12))
print('\nRADIANS Function - Radians Value of 350 = ', gd.radians(350))
print('\nRADIANS Function - Radians Value of 680 = ', gd.radians(680))
print('\nGAMMA Function - Gamma Value of 8 = ', gd.gamma(8))
print('LGAMMA Function - LGamma Value of 9 = ', gd.lgamma(9))