Unlike other programming languages, Python doesn’t allow us to work with Date objects directly. To work with date and time objects in python, you have to import datetime module.
This Python datetime module holds different classes to work with dates or to manipulate dates and times, format them, timedelta, strptime, strftime classes with practical examples.
The syntax of this Python datetime object has Year_Number, Month_Number, Day_Number, Hours, Minutes, and Seconds arguments.
Python datetime examples
Let me show you the list of available methods in this Python datetime module. For this, you have to use the dir function argument.
import datetime print(dir(datetime))
List of available methods in this module.
['MAXYEAR', 'MINYEAR', '__all__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__',
'__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'date',
'sys', 'time', 'timedelta', 'timezone', 'tzinfo']Python datetime class
This class has attributes of year, month, and day. Here, the first print statement extracts and returns the Year from the current date. The next two print statement returns the Month number and Day. Notice that, we assigned and used the alias name to this class as gm.
import datetime as gm
today = gm.date.today()
print('Today\'s Date = ', today)
print('Year = ', today.year)
print('Month = ', today.month)
print('Day = ', today.day)
Today's Date = 2021-05-03
Year = 2021
Month = 5
Day = 3The MAXYEAR returns the maximum(highest) year supported by the module, i.e., 9999. The MINYEAR returns the smallest allowed year, i.e., 1.
print('Maximum Year = ', gm.MAXYEAR)
print('Minimum Year = ', gm.MINYEAR)
Maximum Year = 9999
Minimum Year = 1Python datetime today and now
This Python module has now function and it also has the today function, which returns the current date and time.
dt = gm.datetime.now()
print(dt)
print('Today\'s Dt = ', dt)
print()
dt = gm.date.today()
print('\nToday\'s Dt = ', dt)
2021-05-03 16:03:25.186286
Today's Dt = 2021-05-03 16:03:25.186286
Today's Dt = 2021-05-03Python datetime class attributes
Until now, we are using the basic import option, which is why we are using the keyword twice and method_name. However, if we use the below import technique, we can eliminate that extra.
This example displays the list of all the available attributes in Python datetime class. They are Year, Month, Day of Month, hour, minute, second, microsecond, and weekday.
We have also shown the available functions to extract and return the date and time from the current.
from datetime import datetime as syd
dt = syd.now()
print('Date = ', dt)
print('Short Date = ', dt.date())
print('Year = ', dt.year)
print('Month = ', dt.month)
print('Day = ', dt.day)
print('Time = ', dt.time())
print('Hour = ', dt.hour)
print('Minute = ', dt.minute)
print('Second = ', dt.second)
print('Microsecond = ', dt.microsecond)
print('Weekday Number = ', dt.weekday())
Date = 2021-05-03 16:00:39.908339
Short Date = 2021-05-03
Year = 2021
Month = 5
Day = 3
Time = 16:00:39.908339
Hour = 16
Minute = 0
Second = 39
Microsecond = 908339
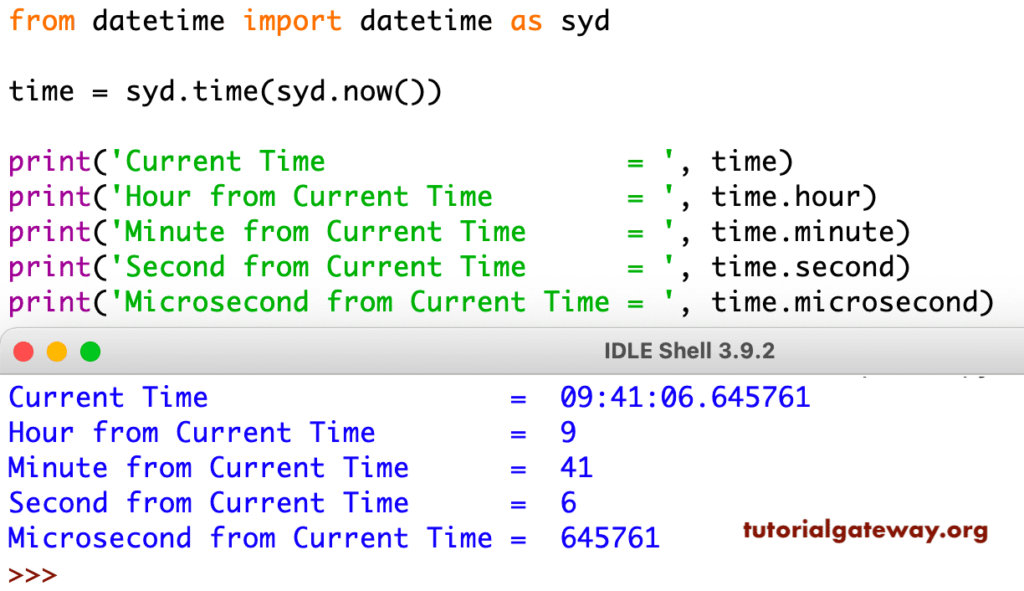
Weekday Number = 0The Python datetime module has the time class used to work or manipulate time values. Here, we used the time class to write the time from the current date and time. Next, we used the print statement to return the time parts using the available attributes hour, minute, second, and microsecond.
time = syd.time(syd.now())
print('Current Time = ', time)
print('Hour from Current Time = ', time.hour)
print('Minute from Current Time = ', time.minute)
print('Second from Current Time = ', time.second)
print('Microsecond from Current Time = ', time.microsecond)
Python datetime isoformat
This Python datetime class has the isoformat, which returns a string representation of a date in ISO 8601 format of YYYY-MM-DD
print(syd.now()) print(syd.now().isoformat())
2021-05-03 16:05:47.074065
2021-05-03T16:05:47.103824Create a Date and Time using Python datetime module
Here, we are using this function to create a custom date object that accepts year, month, day, hour, minute, second, and microsecond. The first statement creates a custom dt with zero hours or no time. The fourth one creates dt, and the fifth return the microseconds.
dt1 = syd(2017, 12, 31) print(dt1) dt4 = syd(2014, 12, 31, 22, 33, 44) print(dt4) dt5 = syd(2016, 12, 31, 22, 33, 44, 123456) print(dt5)
2017-12-31 00:00:00
2014-12-31 22:33:44
2016-12-31 22:33:44.123456datetime timestamp function
The Python datetime timestamp function returns the POSIX timestamp. And The utcfromtimestamp method returns the UTC from the given timestamp. Here, we are using both these functions to return the current timestamp and the UTC.
print("--- timestamp Result---")
dt = syd.now()
print(dt)
print(dt.timestamp())
print("\n---utcfromtimestamp Result---")
tm_stamp = syd.utcfromtimestamp(123456789)
print(tm_stamp)
tm_stamp2 = syd.utcfromtimestamp(482056789)
print(tm_stamp2)
tm_stamp3 = syd.utcfromtimestamp(19023456789)
print(tm_stamp3)
tm_stamp4 = syd.utcfromtimestamp(12761456789)
print(tm_stamp4)
--- timestamp Result---
2021-05-03 17:39:20.605253
1620043760.605253
---utcfromtimestamp Result---
1985-04-11 08:39:49
2572-10-29 21:33:09
2374-05-25 01:06:29Python datetime replace
The Python datetime replace function replaces the date and time parts with new values. The syntax of this replace is
repalce(year = self.year, month = self.month, day = self.day, hour = self.hour, minute = self.minute, second = self.second, microsecond = self.microsecond, tzinfo = self.tzinfo)
We replaced hours, minutes, seconds, and microseconds.
dt = syd.now() print(dt) dt_replace = dt.replace(hour = 2) print(dt_replace) dt_replace2 = dt.replace(minute = 59) print(dt_replace2) dt_replace3 = dt.replace(second = 4) print(dt_replace) dt_replace4 = dt.replace(microsecond = 7) print(dt_replace4)
2021-05-03 17:38:03.697423
2021-05-03 02:38:03.697423
2021-05-03 17:59:03.697423
2021-05-03 17:38:04.697423
2021-05-03 17:38:03.000007The following are the list of all the other attributes and functions available in this class.
dt = syd.now()
print('Replace = ', dt.replace(hour = 2))
print('Tzinfo = ', dt.tzinfo)
print('Tzname = ', dt.tzname())
print('Timetz = ', dt.timetz())
print('Timestamp = ', dt.timestamp())
print('Time = ', dt.ctime())
print('isoweekday = ', dt.isoweekday())
print('astimezone = ', dt.astimezone())
print('utcoffset = ', dt.utcoffset())
print('Daylight Saving = ', dt.dst())
Replace = 2021-05-03 02:37:16.992139
Tzinfo = None
Tzname = None
Timetz = 17:37:16.992139
Timestamp = 1620043636.992139
Time = Mon May 3 17:37:16 2021
isoweekday = 1
astimezone = 2021-05-03 17:37:16.992139+05:30
utcoffset = None
Daylight Saving = NonePython datetime combine
The combine function returns a new object by combining the given date value and time. The syntax of this combine is
combine(date, time, tzinfo = self.tzinfo)
First, we declared a custom date and a custom time. Next, we used the combine function to combine those objects and return the date and time. From that, we are returning dt parts using the available attributes.
We use the time function in this example without providing the second’s value. Next, we used the combine function that combines the dt.
import datetime as syt
dt = syt.date(2018, 12, 31)
tm = syt.time(23, 59, 58)
tm2 = syt.time(23, 0)
combine_dt = syt.datetime.combine(dt, tm)
combine_dt2 = syt.datetime.combine(dt, tm2)
print('Date = ', dt)
print('Time = ', tm)
print('Time2 = ', tm2)
print('Date and Time = ', combine_dt)
print('Date and Time2 = ', combine_dt2)
print('Year = ', combine_dt.year)
print('Month = ', combine_dt.month)
print('Day = ', combine_dt.day)
print('Hour = ', combine_dt.hour)
print('Minute = ', combine_dt.minute)
print('Second = ', combine_dt.second)
print('Microsecond = ', combine_dt.microsecond)
Date = 2018-12-31
Time = 23:59:58
Time2 = 23:00:00
Date and Time = 2018-12-31 23:59:58
Date and Time2 = 2018-12-31 23:00:00
Year = 2018
Month = 12
Day = 31
Hour = 23
Minute = 59
Second = 58
Microsecond = 0Python datetime date class
This module has the date class useful for manipulating dates or work. It has three important attributes.
- min: It returns the earliest or minimum representable date.
- max: Latest or maximum representable date.
- resolution: The smallest possible difference between continuous dates.
date class attributes
In all our previous examples, we are working with the current dt using now or today. However, you can use the date function to create a custom date. Here, we are using it and returning it in iso format.
from datetime import date dt = date(2018, 1, 31) print(dt) print(dt.isoformat())
2018-01-31
2018-01-31We use the Python datetime today method to return the current date and then use those three attributes.
This example shows the list of date attributes available. Here, the year attribute returns the year from the current local date, month = month number, day = day of the month, and weekday = weekday.
dt = date.today()
print('Today\'s Date = ', dt)
print('Year = ', dt.year)
print('Month = ', dt.month)
print('Day = ', dt.day)
print('Weekday Number = ', dt.weekday())
print('\nMinimum = ', date.min)
print('Maximum = ', date.max)
print('Resolution = ', date.resolution)
Today's Date = 2021-05-03
Year = 2021
Month = 5
Day = 3
Weekday Number = 0
Minimum = 0001-01-01
Maximum = 9999-12-31
Resolution = 1 day, 0:00:00It also has the date function to create a custom date from the year, month, and day of the month. The fromtimestamp function accepts the POSIX timestamp value as an argument and returns the date from it.
dt = date(2018, 1, 31)
print(dt)
print("\n---fromtimestamp Result ---")
tm_stamp = date.fromtimestamp(123456789)
print(tm_stamp)
tm_stamp2 = date.fromtimestamp(412056789)
print(tm_stamp2)
tm_stamp3 = date.fromtimestamp(9123456789)
print(tm_stamp3)
tm_stamp4 = date.fromtimestamp(8761456789)
print(tm_stamp4)
2018-01-31
---fromtimestamp Result ---
1973-11-30
1983-01-22
2259-02-10
2247-08-22time class
The Python datetime object has the time class, which helps us to work with time and manipulate them. It has the following 3 important attributes.
- min: It returns the earliest or minimum representable time.
- max: Latest or maximum representable time object.
- resolution: The smallest possible difference between time.
The first statement uses the time method to return 00:00:00. In this second statement, we are using the function to construct or create a time of 10 hours, 22 minutes, and 33 seconds. Next, we use those important attributes.
from datetime import time
tt = time()
print(tt)
print()
tt2 = time(10, 22, 33)
print(tt2)
print('\nMinimum = ', time.min)
print('Maximum = ', time.max)
print('Resolution = ', time.resolution)
00:00:00
0:22:33
Minimum = 00:00:00
Maximum = 23:59:59.999999
Resolution = 0:00:00.000001time attributes
This example shows the list of available time attributes. Here, the hour attribute returns the Hour from a given, minute, second, and microsecond.
tt = time(10, 50, 33)
print('Time = ', tt)
print('Hours = ', tt.hour)
print('Minutes = ', tt.minute)
print('Seconds = ', tt.second)
print('Microseconds = ', tt.microsecond)
Time = 10:50:33
Hours = 10
Minutes = 50
Seconds = 33
Microseconds = 0Create Time in Python datetime
This time example is an extension of the above. Here, we are using the microseconds and the argument names as well.
from datetime import datetime as syd, time
tme = syd.time(syd.now())
print('Current Time = ', tme)
tt = time()
print(tt)
tt1 = time(10, 22, 45)
print(tt1)
tt2 = time(11, 34, 49, 890765)
print(tt2)
tt3 = time(hour = 17, minute = 11, second = 33)
print(tt3)
tt4 = time(hour = 17, minute = 22, second = 55, microsecond = 223344)
print(tt4)
Current Time = 16:12:24.490551
00:00:00
10:22:45
11:34:49.890765
17:11:33
17:22:55.223344Python datetime timedelta, strftime and strptime
The timedelta object predicts or returns the past and future dates. In this example, we are returning the date and time after one year and two years before. Refer to timedelta.
The strftime method formats the date in the specified format, and returns the same as a string. Here, %Y-%m-%d’ means Year-Month-Day (2019-01-31). Refer to strftime.
The strptime converts the string representation of the date to a regular date and time, a string to dt Here, strptime(dt_str, ‘%d %B %Y’) means string date passes in Day Month_Name Year format. Refer strptime.
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
dt = datetime.now()
print('Dt = ', dt)
future_dt = dt + timedelta(days = 365)
print('Future = ', future_dt)
past_dt = dt - timedelta(days = 730)
print('Past = ', past_dt)
print("\n-----strftime Results----")
dt2 = dt.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
print(dt2)
dt3 = dt.strftime('%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S %p')
print(dt3)
dt4 = dt.strftime('%B %d, %Y %I-%M-%S %p')
print(dt4)
print("\n-----strptime Results----")
dt_str = '31 December 2017'
dt_value = dt.strptime(dt_str, '%d %B %Y')
print(dt_value)
dt_str2 = '15/8/17 22:33:55'
dt_value2 = dt.strptime(dt_str2, '%d/%m/%y %H:%M:%S')
print(dt_value2)
Dt = 2021-05-03 16:10:47.540318
Future = 2022-05-03 16:10:47.540318
Past = 2019-05-04 16:10:47.540318
-----strftime Results----
2021-05-03
2021/05/03 16:10:47 PM
May 03, 2021 04-10-47 PM
-----strptime Results----
2017-12-31 00:00:00
2017-08-15 22:33:55