Python does support File handling. I mean, Python provides various functions that allow us to create a file, open it, read the data, and write data to it.
Unlike other languages, Python programming language handles files differently. It treats Files as text or binary based on the data, and each line has to terminate with an End Of Line character like a newline, comma, etc.
Python provides an important function called open to work with files. The File open function accepts two parameters, and they are file_name and mode. The syntax of this file open function is
f_open = open(“File_Name”, “mode”)
In the above Python file handling syntax, the mode is an optional argument. There are four different modes for opening a file.
- r – It means Read Mode, which is the open file’s default mode. It opens an existing one for reading if there is no such document, then it throws an error.
- r+ – This is for both reading and writing modes.
- a – Means Append. If it exists, it opens that one and appends the data to the existing content. If there is none, it creates a new one with the specified name.
- w – Means Write mode. Python opens a file in write mode to handle and overrides the existing content with new content. It creates a new one if it doesn’t exist.
- x – Use this to create a new one. It throws an error if it already exists.
- Apart from these modes, you can also specify the type of data that the file has to handle. I mean binary data or text mode
- t – Text Mode, which is the default mode.
- b – Binary mode.
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt")
The above file handling code is equal to f_open = open(“PythonSample.txt”, “rt”)
Table of contents
Python File Operations Examples
The following list of Python examples helps to Create a New File, Open, Rename it, and Delete it. Next, write text to it, close, append, write, and read available options. To demonstrate most of these file methods, including reading and writing, we use the below txt text sample.
Python listdir function to show all files in a current directory
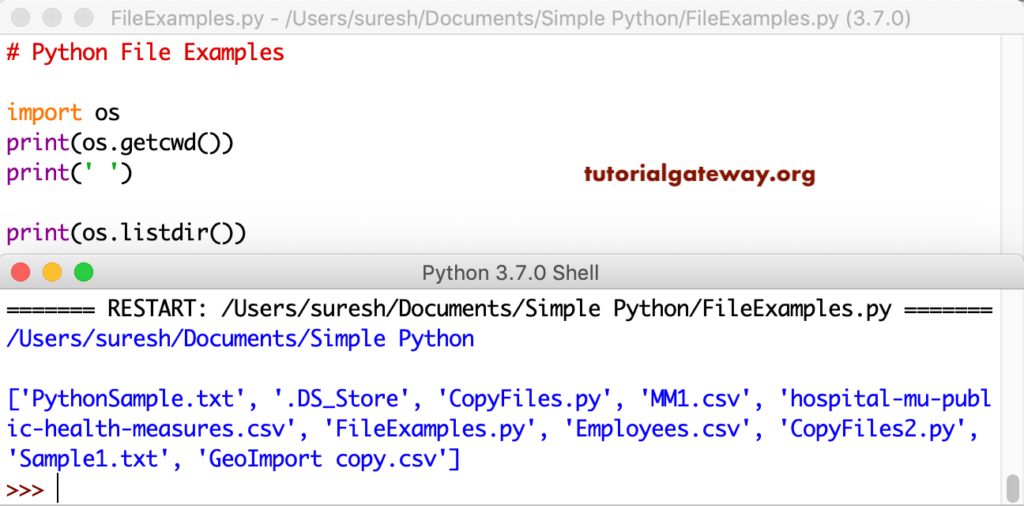
In this language, you can open a file specifying the name or the full path. The full name opens it in the current working directory. However, you can access documents using the full path in any directory. Before we start, let me use the listdir function to get the list in the current directory.
import os
print(os.getcwd())
print(' ')
print(os.listdir())
Python Open File
You can open a file in this Python programming language specifying the name or the full path.
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt")
Or use the full path
f_open = open("C:/users/Document/PythonSample.txt")
Python read file
The file read function is to read the data inside it. It is a simple Python example, which opens a sample txt in the read mode. Next, we used the read function to read data inside that txt.
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read())
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File Examples
file read function with Parameters
While working with string data, you can use the Python file read function with a parameter to restrict the number of characters returned by it. For example, read(5) reads the first five characters or read(10) read the first 10 characters.
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read(5))
print(f_open.read(2))
Reading required characters output
Hello
WoThe first read statement prints the first five characters. Next, read is printing the next two. If you want to print the first 10, then you have to close and reopen it.
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read(5))
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read(8))
Hello
HelloWorPython read file using For Loop
You can also use loops to read all the data in a sequence. For instance, the example below uses For Loop to read each line available in this txt.
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
for char in f_open:
print(char)
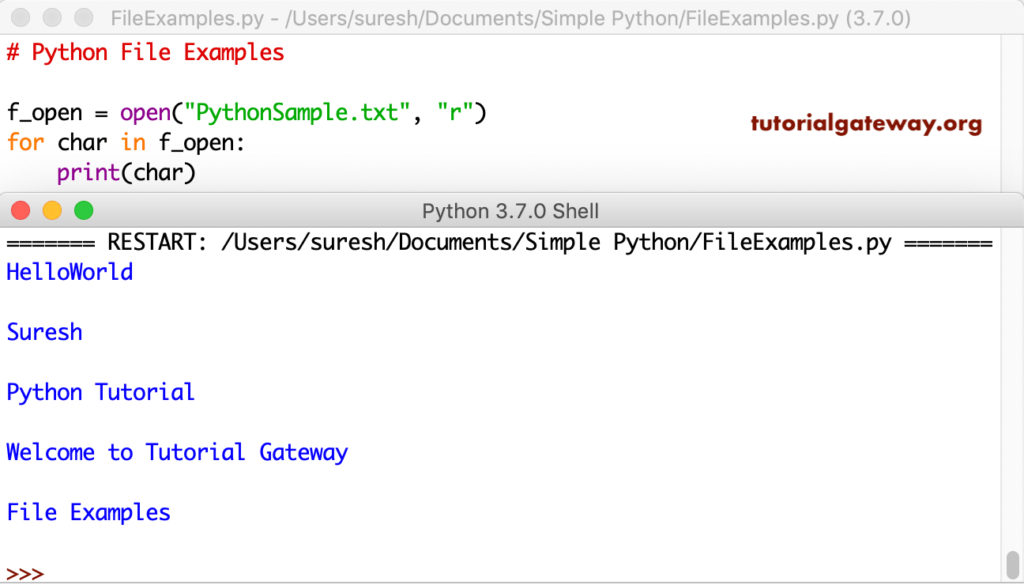
In this file read example, the Python for loop over the complete text in the sample text and prints each and every line.
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
for line in f_open:
print(line, end = '')
For Loop to read opened.
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File Examples
Python file readline function
The readline function reads the complete line before the end of the line character. This example opens a file and reads the first line from it.
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline())
HelloWorld
>>> If you want to read two lines, then call the readline function twice, and so on. Let me print three lines.
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline())
print(f_sample.readline())
print(f_sample.readline())
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python TutorialYou can use this readline function to read or print the required line. The below Python readline function code prints the second line from a text file. If you use the readline function along with an argument, then it behaves the same as the read function with a parameter. I mean, readline(2) = read(2)
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline(2))
print()
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.read(2))
File readline vs read function output
He
HePython read File using readlines function
In this language, we have one more function called readlines(). It reads data from the given text and prints all the data in a list format. It separates each line with a proper separator.
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readlines())
['HelloWorld\n', 'Suresh\n', 'Python Tutorial\n', 'Welcome to Tutorial Gateway\n', 'File Examples\n']Python close file function
The close file function closes an already opened one. Although it has a Garbage Collector to close them, you should not rely entirely on this. It is always a good practice to close the open one. Here, we opened it, read a single line, and then closed that.
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline())
f_sample.close()
HelloWorld
Let me print another line from that closed txt.
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.readline())
f_sample.close()
print(f_sample.readline())
You can notice the error thrown by the shell.
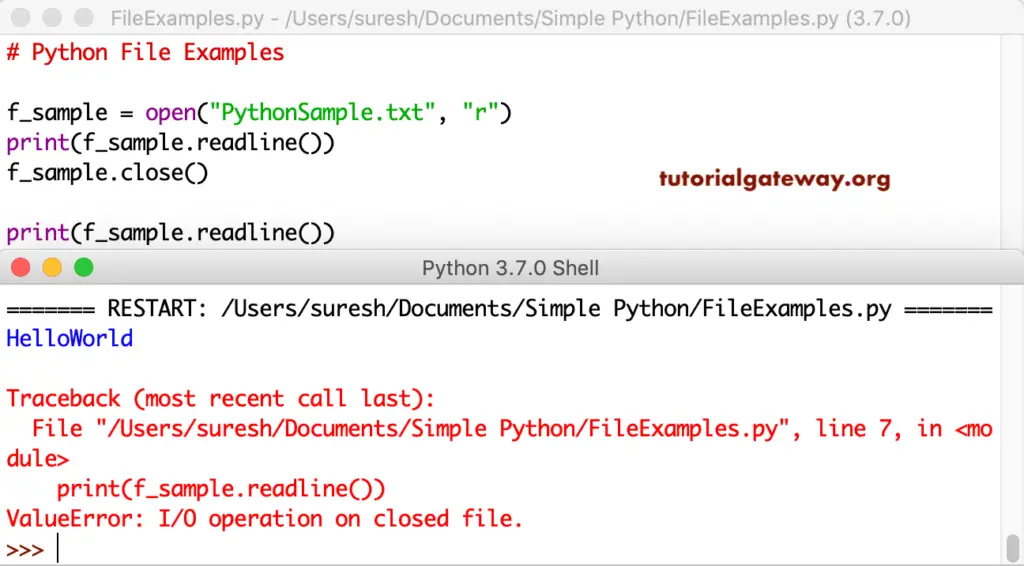
The above program shows the use of the close method. However, it is not advisable to use the way that we showed above.
In real-time, you have to use with statement to close the open properly. Or, some people say, we can go with try finally block. We will show you both.
Using try finally in Python File Operations
try:
f_sample = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.read())
finally:
f_sample.close()
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File ExamplesPython File with Statement
The Python with statement makes sure that every file opened by this closed irrespective of the errors.
with open("PythonSample.txt", "r") as f_sample:
print(f_sample.read())
f_sample.close()
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File ExamplesThe with statement is not about closing the file object. You can use this Python with to open a file in any mode. I mean, you can use this to read data, write methods to data so on.
Most importantly, we use this in the case of manipulations, where we have to execute multiple statements. This statement holds them in a block so that we can write multiple statements such as read and write files in that block.
with open("PythonSample.txt", "w") as f_sample:
f_sample.write("First Line")
f_sample.close()
with open("PythonSample.txt", "r") as f_sample:
print(f_sample.read())
f_sample.close()
HelloWorld
Suresh
Python Tutorial
Welcome to Tutorial Gateway
File Examples
>>>Python Write File
It provides the write method to write content or data to a file. Before we get into the write function example, I assume you remember what I said earlier. You have to use either a mode for append or w for write mode.
This example opens the Sample text in writing mode and writes a welcome message. Next, we opened that to print the data.
f_demo = open("PythonSample.txt", "w")
f_demo. write("Welcome to Tutorial gateway")
f_demo.close()
# Let me open and check
f_demo = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_demo.read())
Welcome to Tutorial gatewayThis time, we write multiple lines of code using the write method.
f_writedemo = open("PythonSample.txt", "w")
f_writedemo. write("Python")
f_writedemo. write("\nTutorial gateway")
f_writedemo. write("\nHappy Coding!")
f_writedemo. write("\nHi \nHello \nCheers")
f_writedemo.close()
# Let me open it and check
f_writedemo = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_writedemo.read())
Python
Tutorial gateway
Happy Coding!
Hi
Hello
Cheers
>>>We have been working on this txt from the beginning. However, this write function erased everything and returned this Welcome message.
The write method accepts a list as an argument, so you can write a list of items in one go. I mean, without using multiple write functions.
f_writelinesdemo = open("PythonSample.txt", "w")
text = ["First Line\n", "Second Line\n", "Third Line\n", "Fourth Line"]
f_writelinesdemo. writelines(text)
f_writelinesdemo.close()
# Let me open and check
f_writelinesdemo = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_writelinesdemo.read())
First Line
Second Line
Third Line
Fourth Line
>>>append File
We are opening a file in append mode and checking what happens after writing a hello message.
f_demo = open("PythonSample.txt", "a")
f_demo. write("\nHell World!")
f_demo.close()
# Let me open the file and check
f_demo = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_demo.read())
First Line
Second Line
Third Line
Fourth Line
Hell World!
>>>How to Write to a File using For Loop in Python?
You can also use the for loop to write multiple lines of information. Here, we are sampling writing 10 lines in a Sample10 text.
f_loopdemo = open("Sample10.txt", "w")
for i in range(1, 11):
f_loopdemo.write("This is the %d Line\n" %(i))
f_loopdemo.close()
# Let me open the file and check
f_loopdemo = open("Sample10.txt", "r")
print(f_loopdemo.read())
Write to it using a for loop output
This is the 1 Line
This is the 2 Line
This is the 3 Line
This is the 4 Line
This is the 5 Line
This is the 6 Line
This is the 7 Line
This is the 8 Line
This is the 9 Line
This is the 10 Line
Create a New File in Python
Until now, we are working with the existing one. However, you can create your own using the read method. For this, you have to use either x to create a new, a mode, or w mode. These three modes create a new one, but the last two are different.
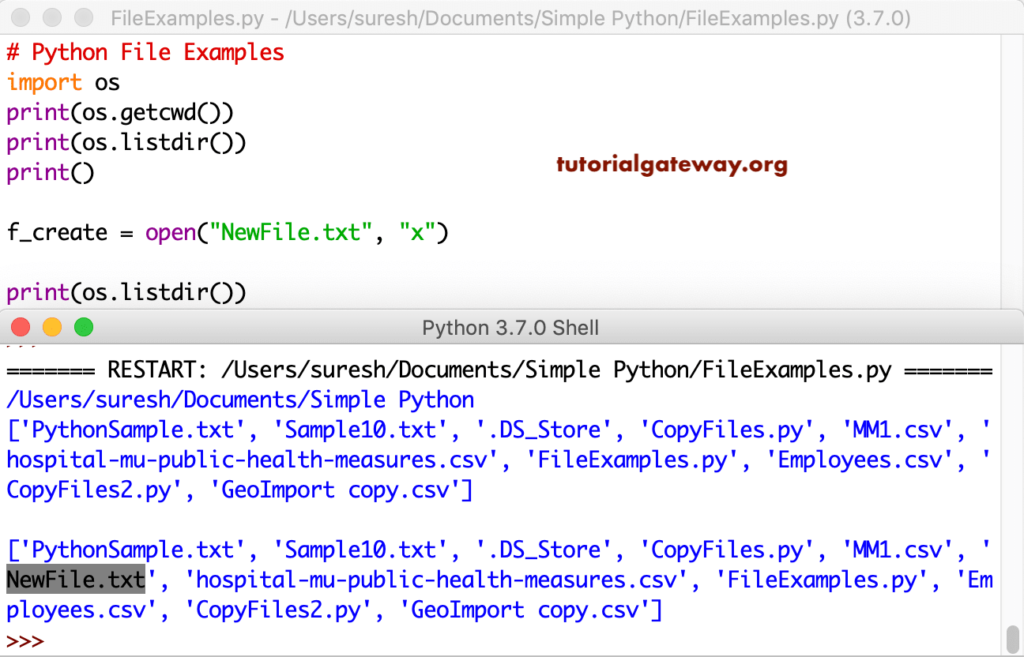
f_create = open("NewFile.txt", "x")
Let me create another file and write something to it. So, you can see the new one along with the text. This program creates a Sample1 text, writes a string, and closes it. Next, we opened that one in the read mode and printed the data from it.
f_create = open("Sample1.txt", "x")
f_create.write("Python Program")
f_create.close()
# Open the Sample1 file
f_create = open("Sample1.txt", "r")
print(f_create.read())
It uses the w for write mode to create a new and writes something to it.
f_wcreate = open("Sample2.txt", "x")
f_wcreate.write("Python Tutorial")
f_wcreate.close()
# Open the Sample1
f_wcreate = open("Sample2.txt", "r")
print(f_wcreate.read())
Python Program
>>>The open function along with a mode – append mode.
f_acreate = open("Sample3.txt", "x")
f_acreate.write("Tutorial Gateway")
f_acreate.close()
# Open the Sample1
f_acreate = open("Sample3.txt", "r")
print(f_acreate.read())
Tutorial Gateway
>>>How to rename a file in Python?
You must import the os module to rename the one within a directory. Within the os module, we have a function that helps us rename existing ones in a directory.
Let me use this file rename function in Python to rename Sample2.txt to NewSample.txt. Next, we opened that renamed one to see the data inside that.
import os
os.rename("Sample2.txt", "NewSample.txt")
f_sample = open("NewSample.txt", "r")
print(f_sample.read())
Python Tutorial
>>>How to Delete a File in Python?
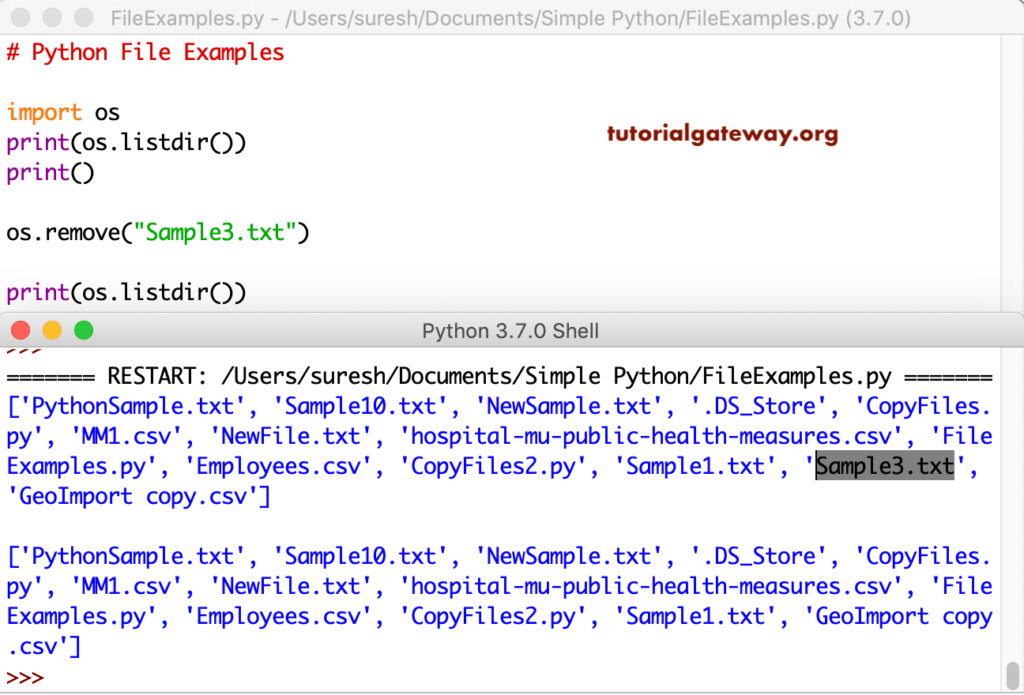
To delete a document from a directory, you have to import the os module. Within the os module, we have a remove function that helps us to remove files from a directory. Let me use this file remove function in Python to delete the Sample3.txt that we created before.
import os
os.remove("Sample3.txt")
It works like a charm; however, if you try to delete a file that doesn’t exist, throw an error. Let me remove the Sample3.txt that we deleted before.
When you run, it throws an error: FileNotFoundError:[Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘Sample3.txt’. To avoid these kinds of errors, it is advisable to check whether it exists or not.
import os
if os.path.exists("Sample3.txt"):
os.remove("Sample3.txt")
else:
print("Hey! No such file exists")
Hey! No such file exists
>>>Python File seek and tell Functions
These are the two functions to find the pointer position.
- tell(): It tells you the current pointer position.
- seek(): To set the pointer position to a specific position.
with open("PythonSample.txt", "r") as f_sample:
print("Pointer Initial Position : ", f_sample.tell())
print(f_sample.read())
print("Current Pointer Position : ", f_sample.tell())
f_sample.seek(22)
print("\n Current File Position : ", f_sample.tell())
f_sample.close()
Pointer Initial Position : 0
First Line
Second Line
Third Line
Fourth Line
Hell World!
Current Pointer Position : 57
Current File Position : 22
>>>Python File Attributes
Python provides the following file attributes to get the information about them that you are working with.
- name: It returns its name of it.
- mode: On what mode do you open? For instance, r mode, w mode, etc.
- closed: returns True if the given one is closed otherwise, False.
f_open = open("PythonSample.txt", "r")
print(f_open.read())
print('\nName = ', f_open.name)
print('Mode = ', f_open.mode)
print('closed? = ', f_open.closed)
f_open.close()
print('\closed? = ', f_open.closed)
Pointer Initial Position : 0
First Line
Second Line
Third Line
Fourth Line
Hell World!
Name = PythonSample.txt
Mode = r
closed? = False
closed? = True
>>>