Python Function is a piece of code or any logic that performs a specific operation. In real-time, a Python function may define with or without parameters, and it may or may not return a value. It entirely depends upon the user’s requirements. In this article, we explain to you the types of functions in Python Programming language with examples.
We have already seen some methods until now, and you may not notice them. For instance, print(), factorial(), round(), etc., are a few of the built-in Python functions.
Let us see the definition, declaration, syntax, and example of using functions in Python Programming language. There are two types of functions:
- We don’t have to bother about the logic inside the Library or built-in functions in this Python Programming Language. In our previous articles, We used many library methods such as print(), factorial(), round(), etc.
- User Defined: Instead of relying on built-in, it allows us to create user-defined functions. For example, if we want to implement some mathematical calculations, put them in separate methods with the correct name. Then we can call that method multiple times.
In Python programming, as per our requirement, We can define the User defined functions in multiple ways. The following is the list of available types of functions in Python.
- With no argument and no return value.
- With no argument and with a Return value.
- Argument and No Return Value.
- With argument and return value.
From the above, 1 and 3 types of functions in Python do not return any value when they are called. So, while defining them, we can avoid the return keyword. When we call the 2 and 4 types of functions, they return some value. So, we have to use the return keyword.
Python Define Functions Syntax
The syntax to define the Functions in Python Programming language is as follows.
def FName (Parameters):
Local Variable Declaration
Programming Logic
Executable Statement 1
……
return
- def: Keyword def is the introduction to the definition. Remember, the Python def keyword must immediately follow the Name to define it.
- FName: It can be any name you wish to give other than the system reserved keywords.
- Parameters: Every Python function accepts 0 or more parameters. It completely depends upon the user’s requirements.
- Local Variable Declaration: Sometimes, we may need some temporary variable only for that particular method, then we can declare the local scope variables inside it. It is not compulsory, and it entirely depends upon user requirements. Remember, these variables are only available to this method, and we can’t access them outside.
- Logic: Any mathematical, code, or calculations you must implement in this Python function.
- Executable Statement: Any print statements to print some data from this particular def.
- return: This keyword is required to return something from the method. For example, returning the sum of two integers, etc.
User Defined Functions in Python implementation
To implement the user defined in a program, we have to follow a few rules, such as:
Python Function Declaration
It informs about the def name and number of arguments.
def Name (Parameters):
For example,
def Add(a, b):
How to call a Function?
Nothing but calling the original method with a valid number of arguments. For example, Add (2, 3). And remember, User defined name should exactly match the method call.
Definition
The Python function definition is where we will put all the logic, calculations, etc. Please don’t forget the return statement inside the method body; otherwise, the program not return anything. While calling it, always pass the required arguments for the block. For example,
def Adding(a, b):
Sum = a + b
return Sum
print("After Calling:", Adding(3, 4))
After Calling: 7
>>> Adding(8, 9)
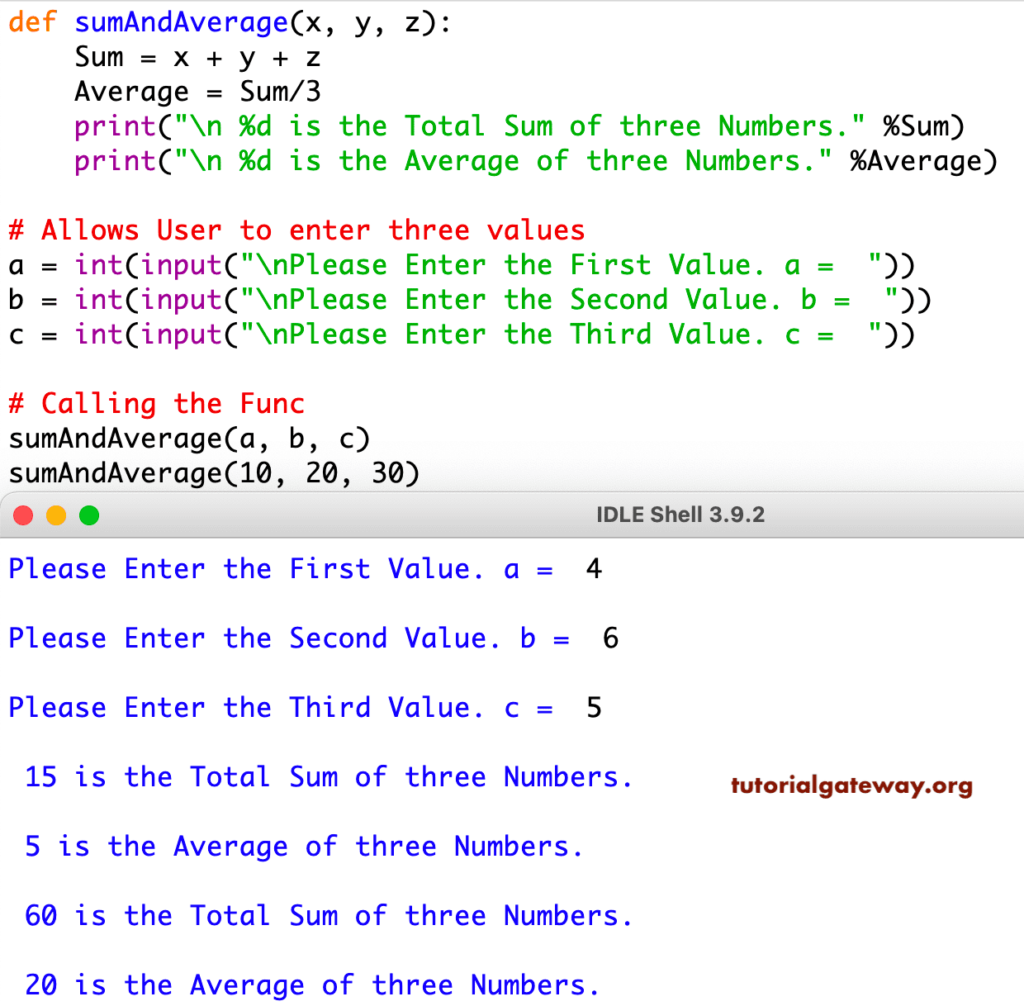
17Program to find the Sum and Average of 3 Numbers
The user is asked to enter three numbers in this Python functions program. Then by calling the method, we calculate the Sum and Average of that three numbers.
def sumAndAverage(x, y, z):
Sum = x + y + z
Average = Sum/3
print("\n %d is the Total Sum of three Numbers." %Sum)
print("\n %d is the Average of three Numbers.\n" %Average)
# Allows User to enter three values
a = int(input("\nPlease Enter the First Value. a = "))
b = int(input("\nPlease Enter the Second Value. b = "))
c = int(input("\nPlease Enter the Third Value. c = "))
# Calling the Func
sumAndAverage(a, b, c)
sumAndAverage(10, 20, 30)
It is called a Python function declaration. If you forget this declaration, then it throws an error.
def sumAndAverage(x, y, z):
The below statements ask the user to enter 3 numbers and store the user input values in a, b, and c variables.
a = int(input("\nPlease Enter the First Value. a = "))
b = int(input("\nPlease Enter the Second Value. b = "))
c = int(input("\nPlease Enter the Third Value. c = "))
In the next line, we call it multiple times, first with user-specified values, then static 10, 20, and 30.
sumAndAverage(a, b, c) sumAndAverage(10, 20, 30)
When it reaches this method, it traverses to check for the sumAndAverage(). If it fails to identify the func name, it throws an error.
Within the Python function definition,
def sumAndAverage(x, y, z):
Sum = x + y + z
Average = Sum/3
We declared 2 local variables, Sum and Average. In the next line, we calculated the sum and average of three numbers using Assignment Operators. Please refer to print(), factorial(), and round()
Sum = x + y + z
Sum = 10 + 20 + 30 = 60
Average = Sum / 3
Average = 60 / 3 = 20
Prints the sum and average to the output.
print("\n %d is the Total Sum of three Numbers." %Sum)
print("\n %d is the Average of three Numbers.\n" %Average)
In the next line, We called Average() one more time. This time, we passed local variables as method arguments. We called 2 times because it helps you to understand that we can call the func n number of times.
Types of Functions in Python
The following examples explain the list of available types of functions in Python programming.
Python Function with No argument and No Return value
In this type of function in Python, While defining, declaring, or calling them, We won’t pass any arguments to them. This type of function won’t return any value when we call them.
Whenever we are not expecting any return value, we might need some print statements as output. In such a scenario, we can use these types of functions in Python.
No argument and No Return value Example
In this Python type of function program, we are going to calculate the Sum of 2 integer values and print the output from the user-defined itself.
# With No Arguments, and No Return Value
def Adding():
a = 20
b = 30
Sum = a + b
print("After Calling :", Sum)
Adding()
No arguments and no Return value output
After Calling : 50
>>> Adding()
After Calling : 50If you observe the Addition(), We haven’t passed any arguments /parameters to the Addition()
We declared the integer variables a, and b, and assigned 20 to a and 30 to b. In the next line, we calculate the sum using the Arithmetic operator ( + )
a = 20
b = 30
Sum = a + b
The below Python print statement is to print the output. Whenever we call the Adding(), it prints the same output because a and b have fixed values inside the method.
print("After Calling :", Sum)
Python Function with no argument and with a Return value
In this type of function in Python, We won’t pass any arguments to it while defining, declaring, or calling it. When we call this type of function, it returns some value.
No arguments and with a Return value Example
In this Python type of function in the program, we are going to calculate the multiplication of 2 integer values using the user-defined without arguments and return keyword.
# With No Arguments, and with Return Value
def Multiplication():
a = 10
b = 25
Multi = a * b
return Multi
print("After Calling the Multiplication : ", Multiplication())
No arguments and with a Return value output
After Calling the Multiplication : 250
>>> Multiplication()
250Within the Multiplication (), We haven’t passed any arguments /parameters. Next, We declared the integer variables of Multi, a, b, and we assigned 10 to a, and 25 to b. In the next line, we Multiplied both a and b using an Arithmetic operator ( * ).
a = 10 b = 25 Multi = a * b
Lastly, the print statement is to print the output. Remember, we are using the print statement outside the defined method and the name inside the print statement. (nothing but calling the method)
print("After Calling the Multiplication : ", Multiplication())
Here also, Whenever we call the Multiplication(), it prints the same output because a and b have fixed values inside it.
Python Function with argument and No Return value
If you observe the above 2 types of functions, No matter how many times you executive, Python gives the same output. We don’t have any control over the variable values (a, b) because they are fixed values. In real-time, we mostly deal with dynamic data means we have to allow the user to enter his own values rather than fixed ones.
This Python type of function allows us to pass the arguments while calling it. But, This type won’t return any value when we call it.
With argument and No Return value Example
This program for the type of function in Python allows the user to enter 2 integer values, and then, We are going to pass those values to the user-defined method to Multiply them.
# With Arguments, and NO Return Value
def Multiplications(a, b):
Multi = a * b
print("After Calling the Function:", Multi)
Multiplications(10, 20)
We called the Multiplication method with different values, and it gives the output as per the values.
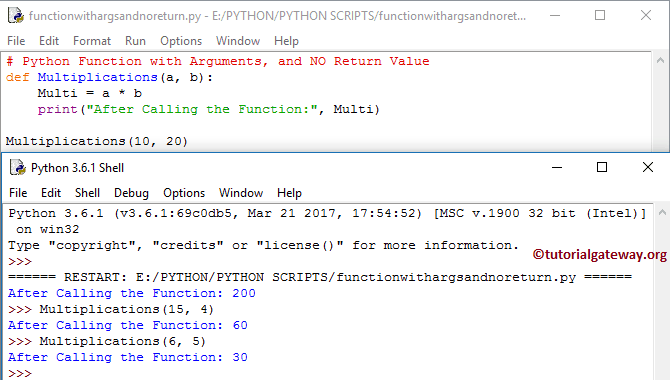
Within the Multiplication(a, b), We declared the variables of Multi, and also, we also had (a, b) arguments in it. It means this one allows the user to pass 2 values.
In the next line, we added both a and b using an Arithmetic operator ( * )
Multi = a * b
In the next line, the print statement is to print the output.
print("After Calling the Function:", Multi)
Python Function with argument and Return value
This type of Python function allows us to pass the arguments to it while calling it. This type of function returns some value when we call them. This type of user-defined method called a fully dynamic, means it provides maximum control to the end-user.
With arguments and Return value Example
This type of function in the Python program allows the user to enter 2 integer values. Then, we pass those values to the user-defined method to add those values and return the value using the return keyword.
# Wwith Arguments, and Return Value
def Addition(a, b):
Sum = a + b
return Sum
# We are calling it Outside the Definition
print("After Calling :", Addition(25, 45))
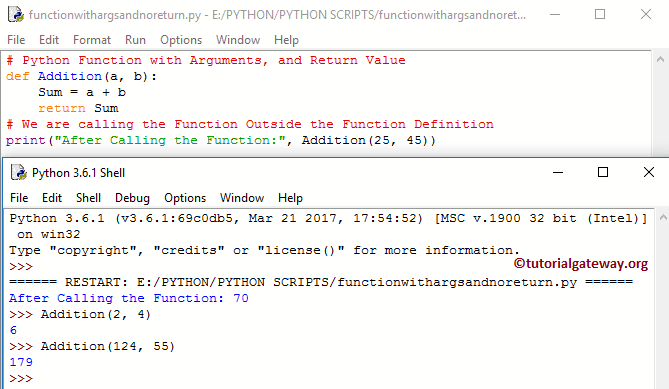
Within the Addition(a, b), We declared the variables of Sum, and also, we also had (a, b) arguments in it. It means this allows the user to pass two values. In the following line, we added both a and b using an Arithmetic operator ( * )
Multi = a * b
In the next line, the print statement is to print the multi-variable output.
print("After Calling :", Multi)
As you can see from the above output, we called the addition method with different values, and it gives the output as per the values.
Advantages of functions in Python
- It helps to divide the large programs into small groups so that we can read the code and debug the program faster and better.
- Python Functions stop us from writing the same logic at various times. We can bind the logic in one def and then call the same repeatedly.
- Many persons can work on the same program by assigning different methods to each.
- It encourages us to call the same method with different inputs multiple times.

Comments are closed.