The Python factorial function is used to find the factorial of a specified expression or a specific number. The syntax of the Python factorial function is shown below
math.factorial(number);
- If the number argument is a positive integer, it returns the factorial of a given number.
- If it is Negative integer, Positive or Negative Decimals, it returns ValueError. And if it is not a number, it returns TypeError.
Python factorial Function Example
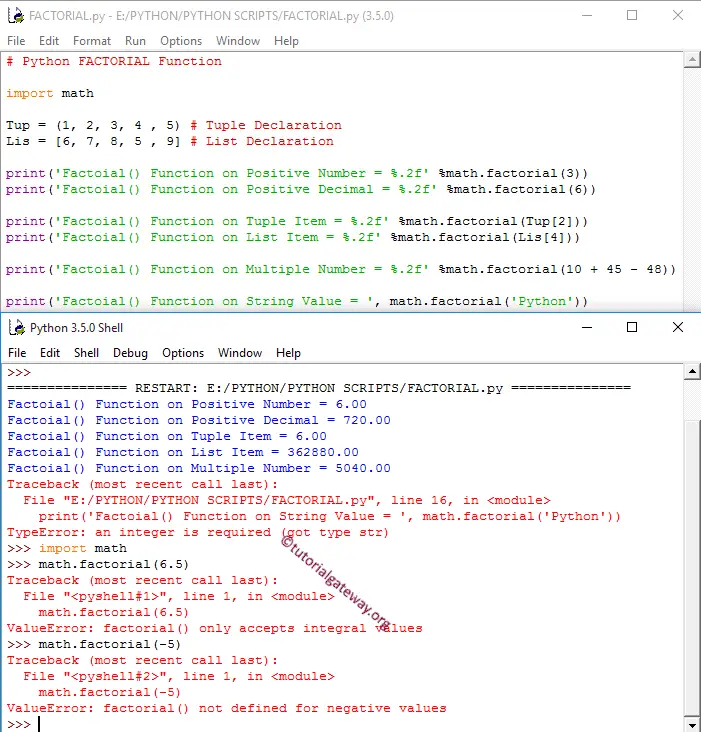
This math function finds the factorial of a given number. In this math example, we will find the same for different data types and display the output.
- First, we used the Python factorial Function directly on Positive integers.
- Next two statements, We used it on Tuple and List items. If you observe the above Python screenshot, this Math function is working perfectly on them.
- Next, we tried directly on multiple values.
- Here, we used the factorial on the String value, and it returns TypeError: an integer is required (got type str)
- Next, We used on Decimal value. It returns ValueError: it only accepts integral values
- Last, We tried it on Negative value. It is returning ValueError: it. not defined for negative values.
import math
Tup = (1, 2, 3, 4 , 5) # Tuple Declaration
Lis = [6, 7, 8, 5 , 9] # List Declaration
print('Factoial() Function on Positive Number = %.2f' %math.factorial(3))
print('Factoial() Function on Positive Decimal = %.2f' %math.factorial(6))
print('Factoial() Function on Tuple Item = %.2f' %math.factorial(Tup[2]))
print('Factoial() Function on List Item = %.2f' %math.factorial(Lis[4]))
print('Factoial() Function on Multiple Number = %.2f' %math.factorial(10 + 45 - 48))
print('Factoial() Function on String Value = ', math.factorial('Python'))