The Python Arithmetic operators help accomplish mathematical operations on numeric data types, such as integers and floating-point numbers. This article will explain the arithmetic operators available in Python Programming language and how to use them in real-time scenarios.
Arithmetic operators are the fundamental concept in the programming world, and this page dives deeper into it. Python Arithmetic operators include +, -, *, /, //, **, and % to perform Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, Floor Division, Exponent (or Power), and Modulus. All these Python Arithmetic are binary operators, which means they operate on two operands.
You need these arithmetic operators to perform simple calculations, complex mathematical operations, scientific computations, financial analysis, etc. While working with the Python Arithmetic operators, you should be careful with the parentheses because parentheses control the order of the operator’s execution. So, understanding these operators is crucial for every programmer.
Python Arithmetic Operators
The below table shows all the Python Arithmetic Operators with examples.
| Python Arithmetic Operators | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition of two operands | 10 + 2 = 12 |
| – | Subtraction of one operand from another | 10 – 2 = 8 |
| * | Multiplication of two operands | 10 * 2 = 20 |
| / | Divide one operand by another. | 10 / 2 = 5.0 |
| % | Modulus – It returns the remainder after the division | 10 % 2 = 0 (Here remainder is zero). If it is 10 % 3, then it will be 1. |
| ** | Exponent – Raised a Number to the Power. It returns the Power of One variable against the other. | 10 ** 2 = 100 (10 Power 2 or 10²). |
| // | Floor Division – Same as Division, but it will return the integer value by flooring the extra decimals | 17 // 3 = 5. If you divide 17 by 3, you get 5.667. The floor division operator will trim the decimal values and outputs the integer. |
Python Arithmetic Operators Example
For this example, we use two variables, a and b, and their values are 12 and 3. We will use these two variables to perform various arithmetic operations with the help of Python operators.
a = 12
b = 3
addition = a+b
subtraction = a-b
multiplication = a*b
division = a / b
modulus = a % b
exponent = a**b
Floor_Division = a // b
print("Addition of two numbers 12 and 3 is : ", addition)
print("Subtracting Number 3 from 12 is : ", subtraction)
print("Multiplication of two numbers 12 and 3 is : ", multiplication)
print("Division of two numbers 12 and 3 is : ", division)
print("Modulus of two numbers 12 and 3 is : ", modulus)
print("Exponent of two numbers 12 and 3 is : ", exponent)
print("Floor Division of two numbers 12 and 3 is : ", Floor_Division)
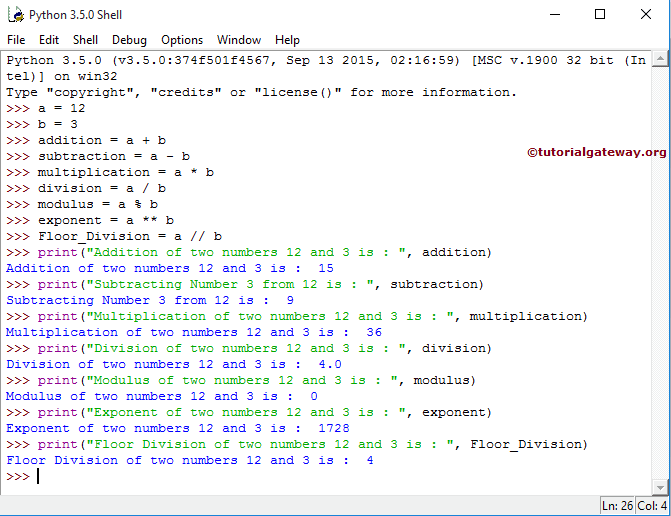
The following Python statement will find the exponent. It means 12 power 3 = 12 * 12 * 12 = 1728
exponent = a ** b
When we use the division ( / ) operator, the result will be a float or decimal value. If you want to display the output as an integer value by rounding the value, then use Floor Division ( // ).
Python Arithmetic Operators Precedence and Parentheses Example
Operator precedence refers to the rules that decide in which order the expression has to evaluate. If you use multiple arithmetic operators in a single statement, Python follows a specific order of precedence while evaluating expressions. While working with complex expressions, we must have to use multiple operators. So, the good thing is you can control the order of the operator execution, and the bad thing is if you misplace the parentheses, the result becomes inaccurate.
The order of the Python arithmetic operators precedence is as follows:
- Parentheses () evaluate first.
- Addition (+) and Subtraction (-) evaluate from left to right.
- Multiplication (*), Division (/), and Floor Division (//) evaluate from left to right.
- Exponentiation (**) has the highest precedence.
The below Python Arithmetic Operators example explains how parentheses can influence the order of operations.
When there is a combination of + and – in a single statement, they execute from left to right.
- 10 + 5 – 3 = First 10+5 = 15, and then 15 -3 = 12
- 10 – 5 + 3 = First 10 -5 = 5, and then 5 + 3 = 8
# + and - from left to right print(10 + 5 - 3) print(10 - 5 + 3)
12
8Similarly, when there is a combination of any two or three *, /, and // Python Arithmetic Operators, they execute from left to right. However, if we combine them with addition and subtraction, *, /, and // execute first and then + and -.
- 10 * 5 / 2 = First 10 * 5 = 50, and then 50 / 2 = 25.0
- 10 + 5 * 4 = First 5 * 4 = 20, and then 10 + 20 = 30
- 2 + 10 * 5 // 3 = First 10 * 5 = 50, second 50 // 3 = 16, and then 2 + 16 = 18
print(10 * 5 / 2) print(10 + 5 * 4) print(2 + 10 * 5 // 3)
25.0
30
18Parentheses () evaluate first. So, they alter the complete execution process. For instance,
- 10 – (5 + 3) = First 5 + 3 = 8, and then 10 – 8 = 2. If we remove the parenthesis, the result will become 8.
- 2 + (10 – 5) * 6 = First, 10 – 5 = 5, second 5 * 6 = 30, and then 2 + 30 = 32.
print(10 - (5 + 3)) print(2 + (10 - 5) * 6)
2
32Arithmetic Operations on Strings
In this Python Arithmetic operators example, we use two variables, a and b, of string data type. Next, we use these two variables to show the problems we generally face while performing arithmetic operations on String Data type.
a = "Tutorial" b = "Gateway" print(a + b) print(a + " " + b) print(a * 3) print((a + " ")* 3) print(a + 3) print(a + str(3))
TIP: Please be careful with brackets. If you misplace it, you will end up with the wrong results.
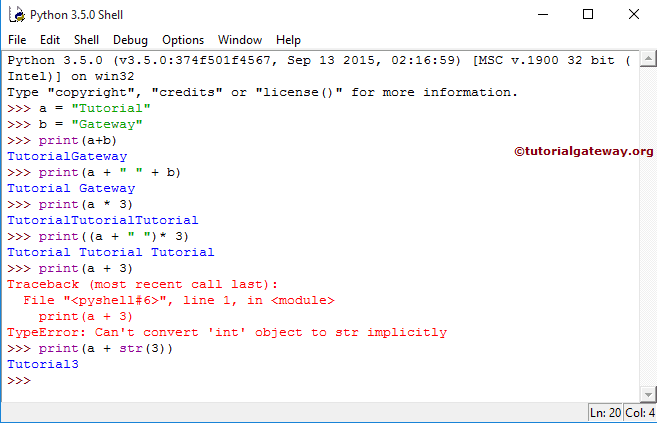
In this program for Arithmetic operators in Python, First, We declared two variables, a and b, of string data type, and their values are “Tutorial” and “Gateway”.
a = "Tutorial" b = "Gateway"
It displays the output as “TutorialGateway” because when we use the ‘+’ operator between string variables, the controller concat the two strings.
print(a+b)
Inserts the empty space between “Tutorial” and “Gateway”. It means the output will be “Tutorial Gateway”.
print(a+ " " +b)
Displays Tutorial three times using one of the Python Arithmetic Operators *
print(a * 3)
Insert space in between each iteration.
print((a + " ")* 3)
It is interesting because we use the ‘+’ symbol between string and integer.
print(a + 3)
It will throw an error because it will not implicitly convert integer objects to string objects. To resolve this, we have to convert three explicitly. Be careful while Concating the String and Integers.
Type casting plays a major role in these Python arithmetic operators.
print(a + str(3))
