Tableau provides various Logical Functions to perform logical operations on our data. They are Tableau AND, NOT, OR, IF, ELSEIF, IF Else, CASE, ISNULL, IFNULL, ZN, IIF, etc. In this article, we will show you how to use Logical Functions with examples.
To demonstrate these Tableau Logical Functions, we are going to use the data present in the Global Super Store Excel Worksheet. So, Please refer to the Connecting to Excel Files and CASE article to understand the connection settings.
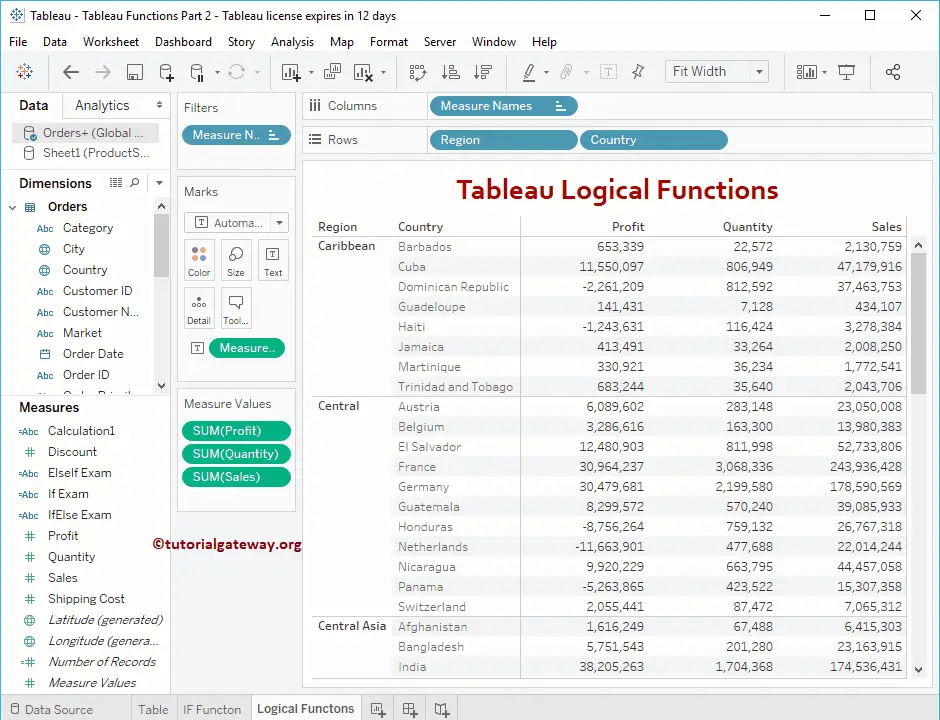
Tableau Logical Functions
The following examples will show you the list of Logical Functions.
Tableau Logical AND Function
The Tableau AND function is used to check multiple expressions, and the syntax of the AND is as shown below:
Expression_1 AND Expression_2
As you see from the above syntax, the AND function accepts two arguments. If both the conditions are True, it returns True. Otherwise, it returns False.
To demonstrate these Tableau logical AND functions, we have to use Calculated Fields. To create a calculated field, please navigate to the Analysis Tab and select the Create Calculated Field… option.
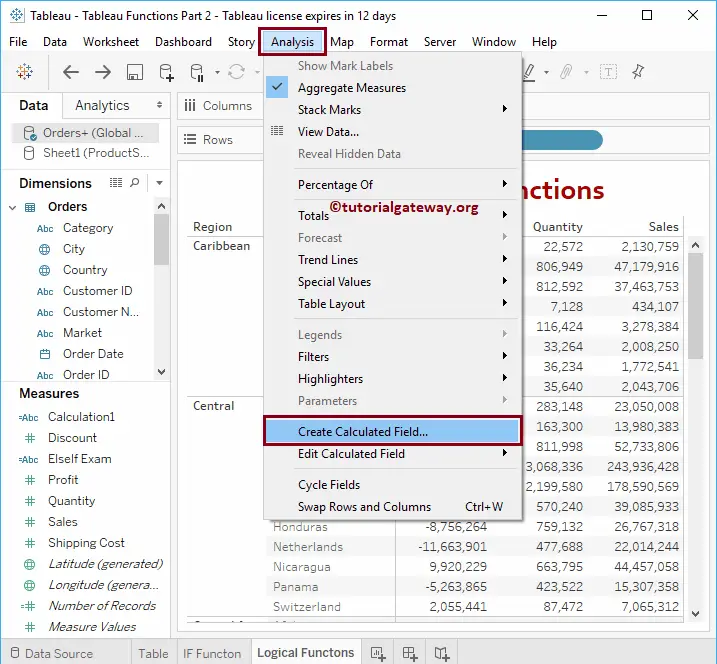
Once you click on the Create Calculated Field… option, the following window will be opened. Here, we renamed the default calculation name as AND Function. Please refer to the IF Statement and other articles on functions.
It will check whether the Profit is greater than 0 and the Quantity is greater than 25000. If both these conditions are true, the Tableau logical AND function will return Good; otherwise, it will return Bad.
IF(SUM([Profit]) > 0 AND SUM(Quantity) > 25000) THEN 'Good' ELSE 'Bad' END
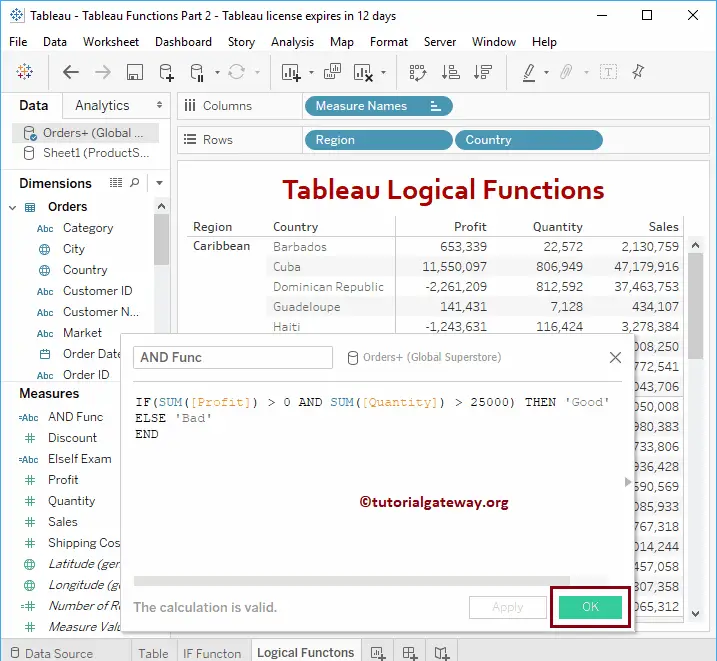
Let me add this AND calculated field to the table (by dragging a field to Rows Shelf). Please refer to the Create Table Report and formatting articles to understand the process of creating a table.
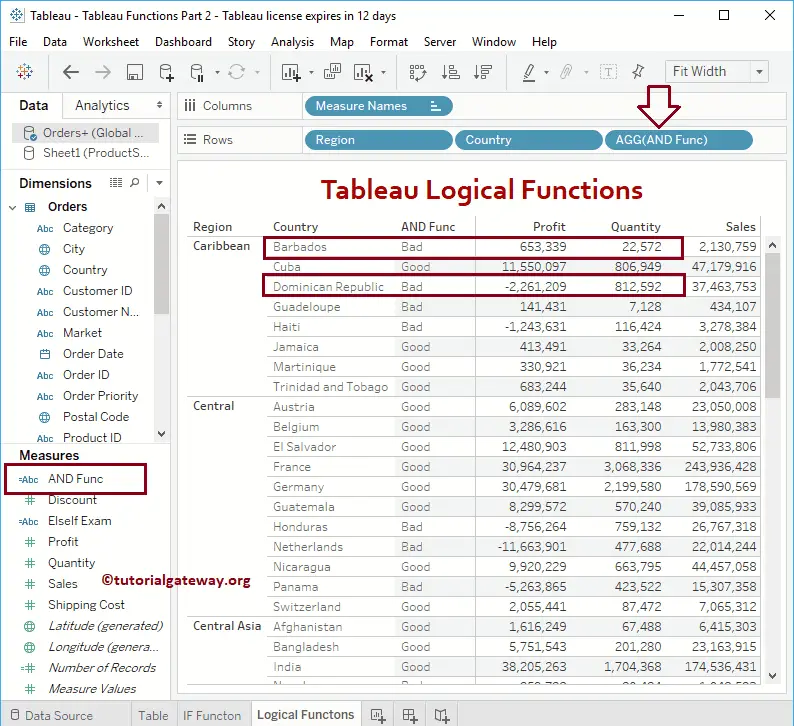
Tableau Logical OR Function
The Tableau OR function is like either or statement in English. If both the conditions are False, it will return False; otherwise, it will return True. The syntax of this OR is:
Expression_1 OR Expression_2
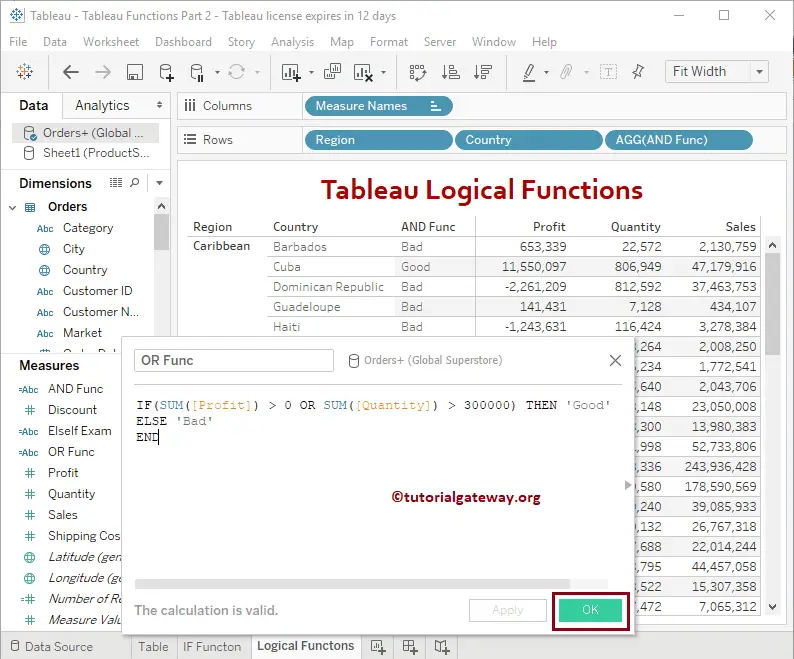
The below statement will return Good if either of these two statements is True
IF(SUM([Profit]) > 0 OR SUM(Quantity) > 300000) THEN 'Good' ELSE 'Bad' END
Let me add this field to the Rows shelf
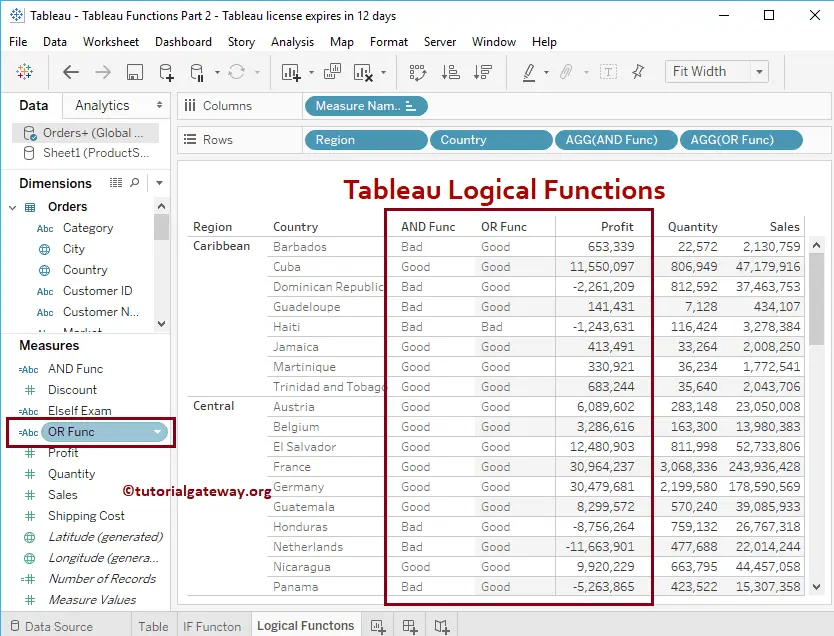
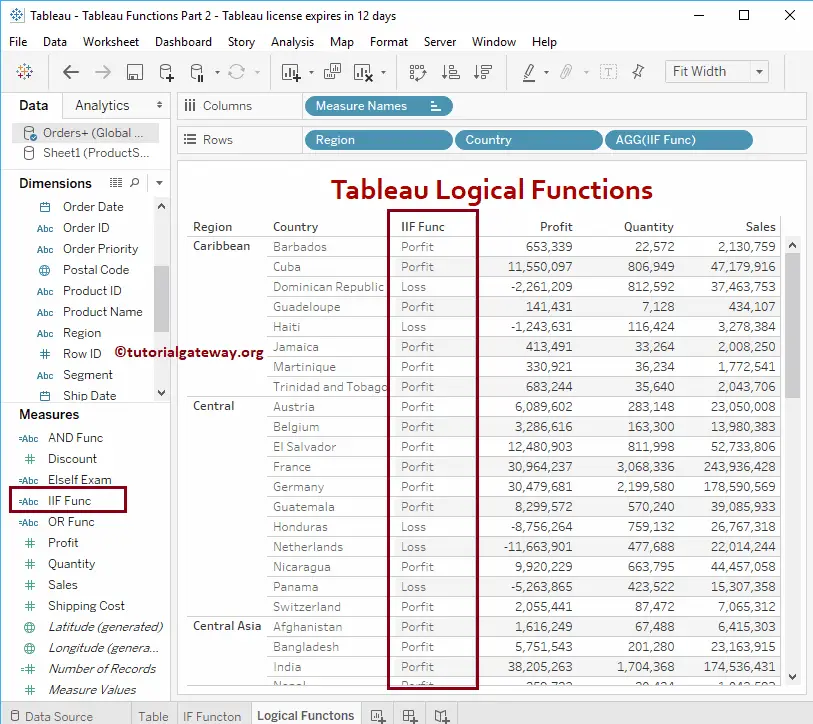
Tableau IIF Function
The IIF function is the simple version of the If Else Function. If both conditions are True, then it will return the First Statement; otherwise, the second statement. The syntax of this Tableau IIF Function is:
IIF(Expression, True_statement, False_Statement)
The following Tableau IIF function returns Profit if the condition is True. Otherwise, Loss will return.
IIF(SUM([Profit]) > 0, 'Profit', 'Loss')
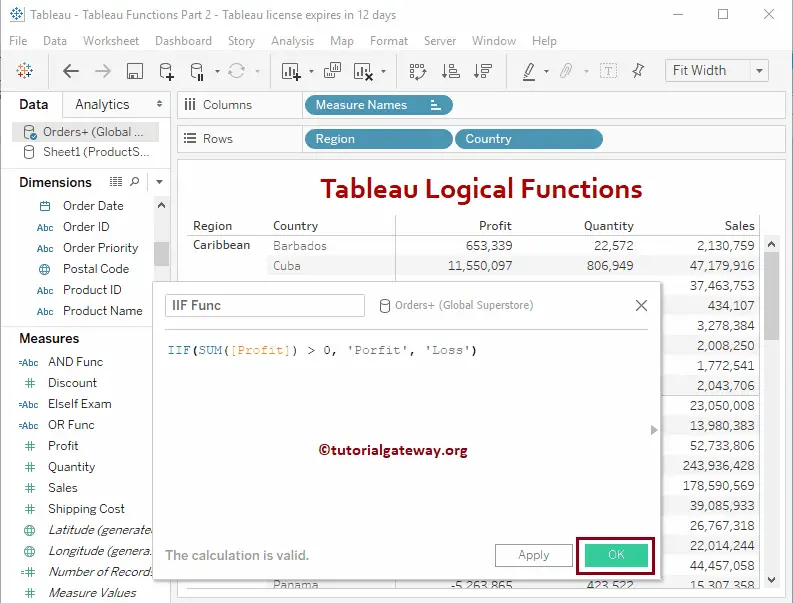
Now you can see the result of the Tableau IIF function
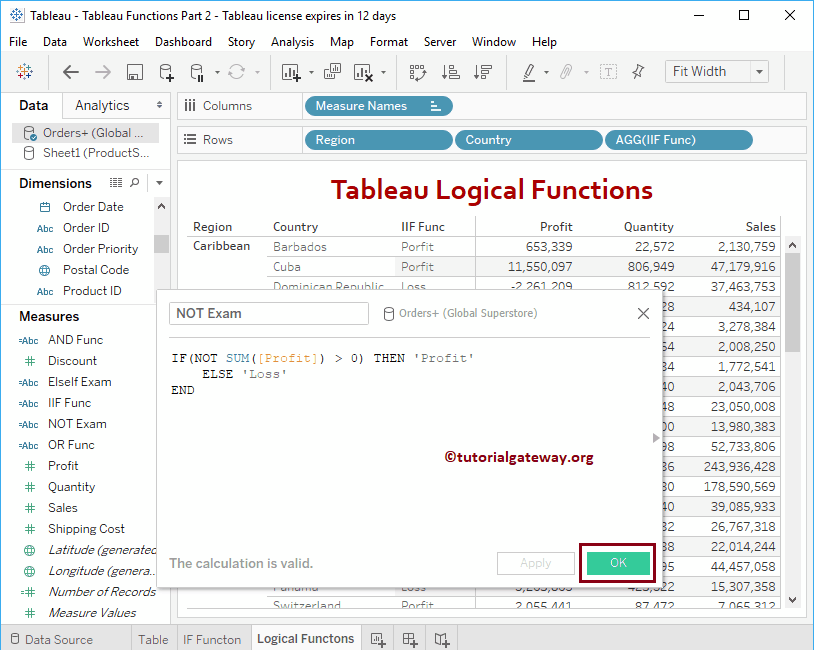
NOT
The Tableau NOT function returns the exact opposite, which means, True will become false, and vice versa, and the syntax of this NOT is:
NOT(Expression)
The below Not statement will return Loss if the condition is True. Otherwise, Profit will return.
IF(NOT SUM([Profit]) > 0) THEN 'Profit' ELSE 'Loss' END
You can see the NOT result by yourself
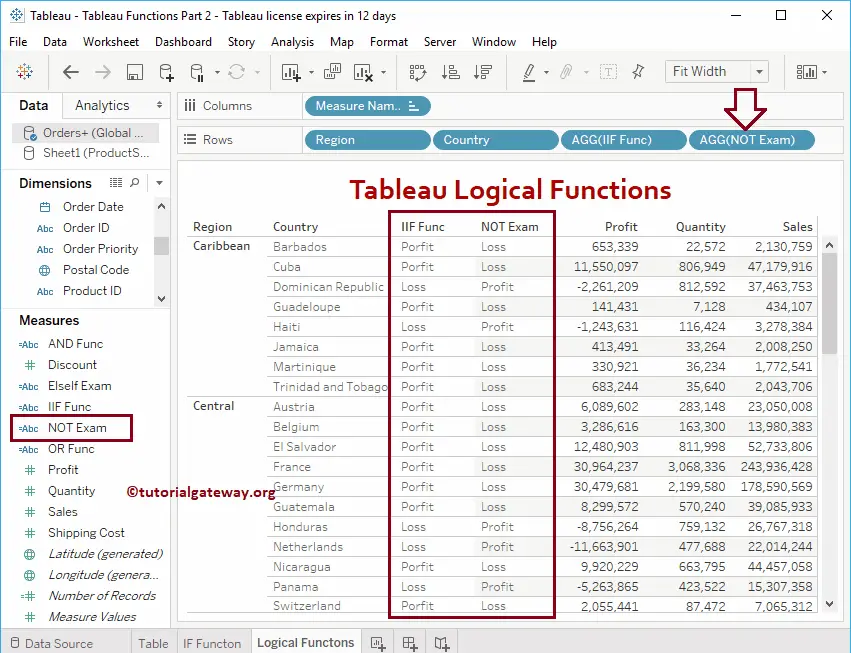
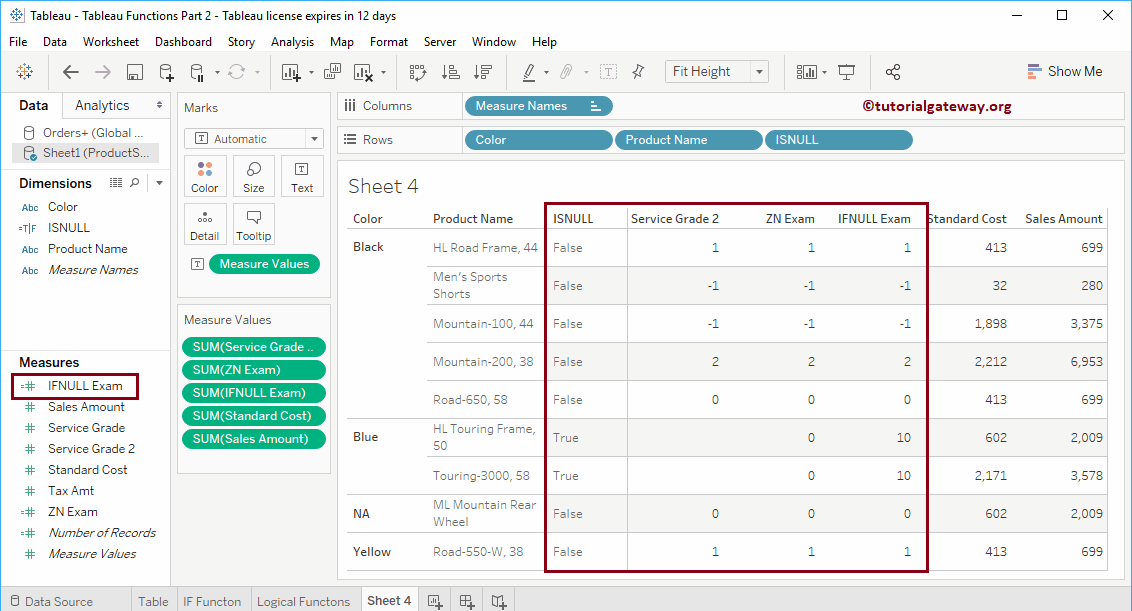
Tableau ISNULL Function
To demonstrate this Tableau ISNULL function, we will use the below-shown table.
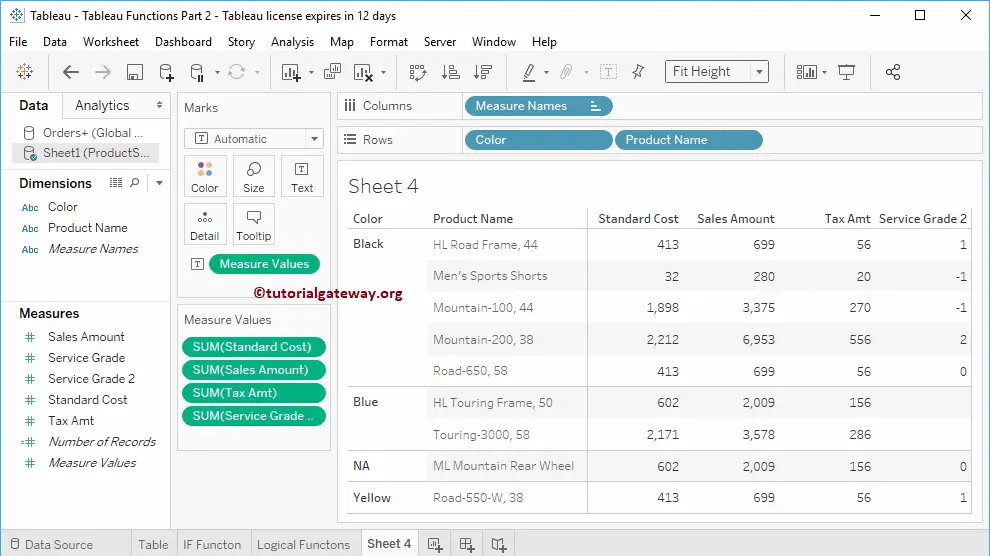
The ISNULL function will check whether it is NULL or Not. If it is NULL, then it returns TRUE; otherwise, False will return.
The syntax of the Tableau ISNULL Function is:
ISNULL(Expression)
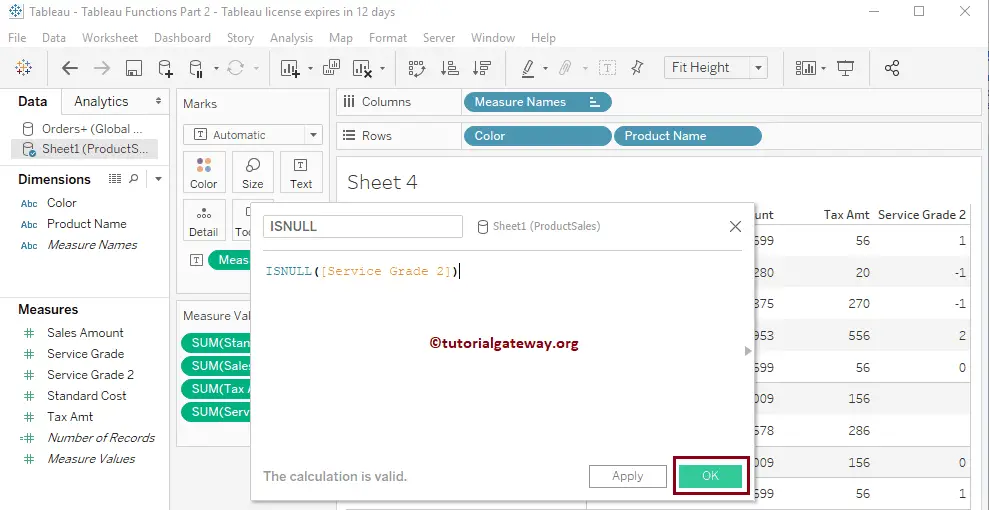
The following Tableau ISNUL statement will check nulls in the Service Grade 2 column.
ISNULL([Service Grader 2])
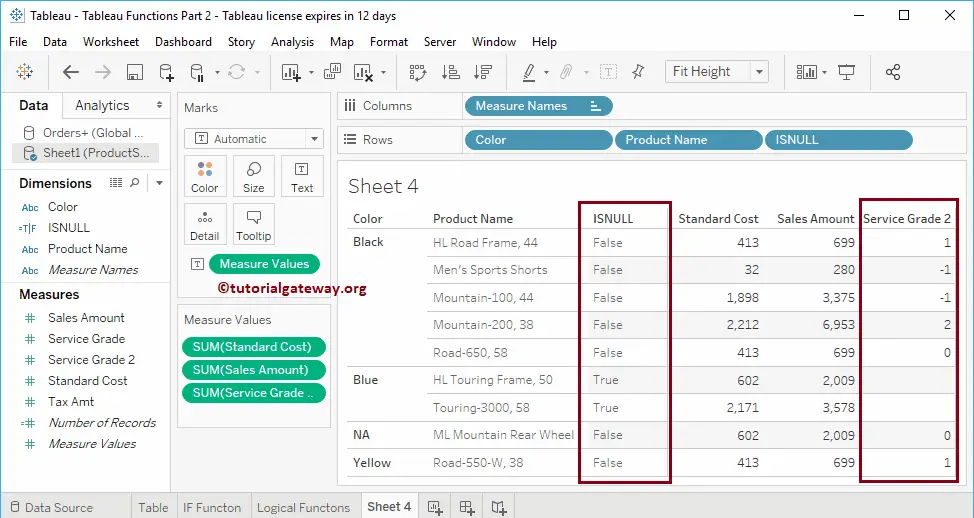
As you can see, this Tableau ISNULL function returned True for the products under Blue Color.
ZN
The ZN Function will return the original values of Not Null values and 0 for Null values. In simple English, ZN in Tableau replaces the NULL values with 0.
The syntax of the Tableau logical ZN Function is:
ZN(Expression)
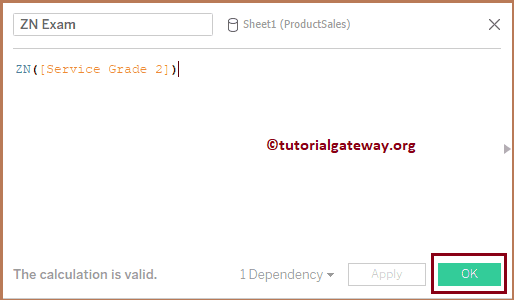
The below logical function statement will replace NULL with 0.
ZN([Service Grader 2])
From the below screenshot, you can see the result of a ZN function.
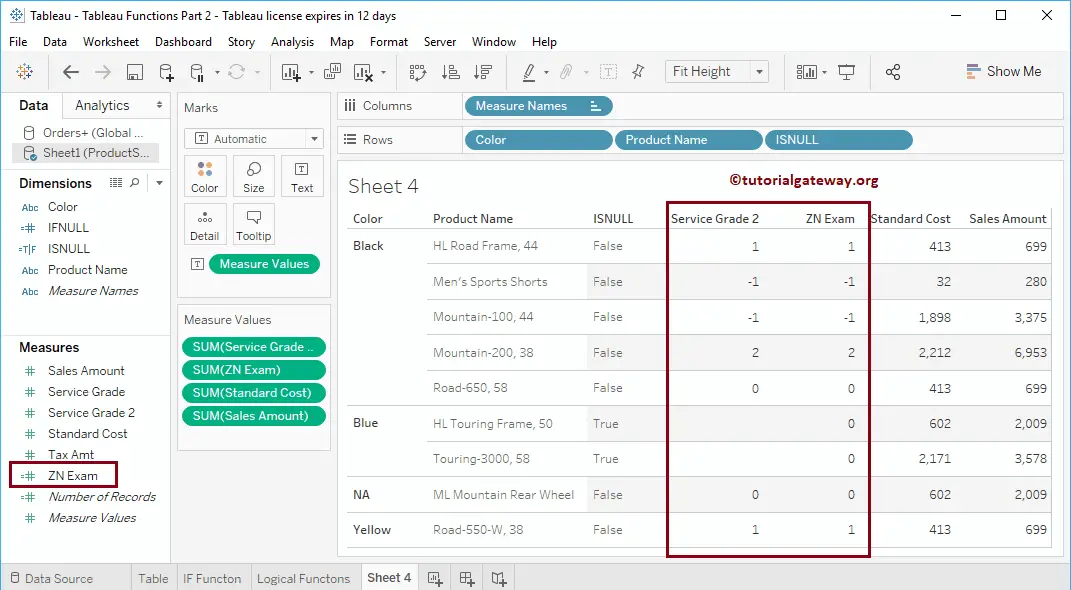
Tableau IFNULL Function
The IFNULL function is used to replace the NULL values with your own. The syntax of the Tableau IFNULL Function is:
IFNULL(Expression, Value)
The following IFNULL statement will replace NULLs with 10 if nulls are present.
IFNULL([Service Grader 2], 10)
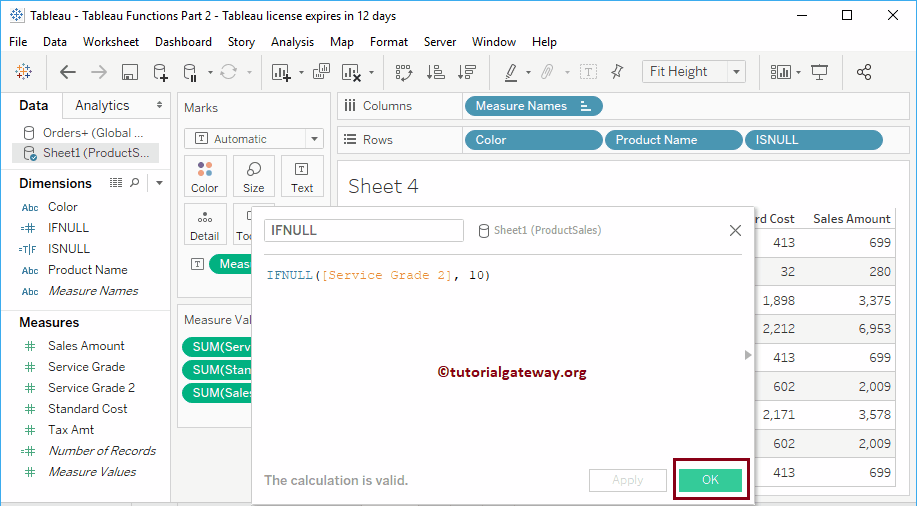
Let us see the result of the Tableau IFNULL logical function.