In SQL Server, there are two types of table partitions they are Horizontal and vertical. This article will show you what Horizontal Table Partitioning is and how to create it with an example.
SQL Server Horizontal Table Partition: Dividing a table into multiple tables is called Horizontal. It is helpful to organize data for quick access. For this example, dividing the Sales into Monthly or Quarterly partitions will help the end user select records quickly.
Remember, all the partition tables contain the same number of columns. Before we start creating Table Partitioning in SQL Server, let me show you the list of databases available in our local file system.
See the available databases on our server. For this SQL demonstration, we created a new database called PartSample.
Now you can see our newly created database PartSample in our file system.
How to create Table Partitioning in SQL Server?
In this SQL Server example, we will create a table partition to store data month-wise. I mean, orders or sales in each month will store in separate filegroups (files with ndf extension).
To achieve the same, we must create 12 separate file groups for 12 months, from January to December. To create a filegroup, we have to use Alter Database command.
ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP January GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP February GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP March GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP April GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP May GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP June GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP July GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP August GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP September GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP October GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP November GO ALTER DATABASE PartSample ADD FILEGROUP December GO
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Get System File Groups
Use the below query to check or see the list of file groups available in this table partitioning in the sql server database.
USE PartSample GO SELECT * FROM Sys.filegroups
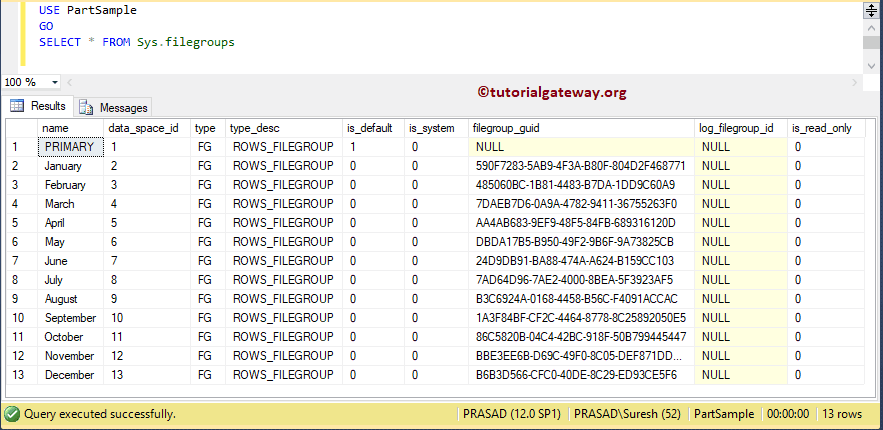
The below Table partitioning query returns the file group names
USE PartSample GO SELECT name AS [File Group Name] FROM Sys.filegroups WHERE type = 'FG'
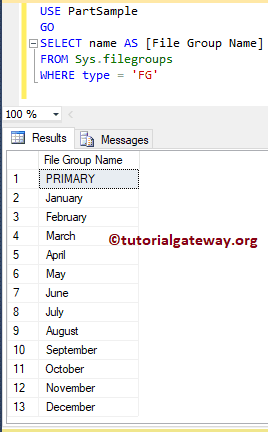
Add ndf files to File Groups to Table Partitioning in Sql Server
Once you create the filegroups, you have to add or assign or create ndf files. The below query will add ndf file to the January File group. Remember, we are not given the actual path, so please replace …. with the actual database path.
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartJan],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\..........\DATA\PartJan.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [January]
Execute the SQL Table partition query
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Use the below query to add ndf files for the remaining 11 months. Remember, this is the physical location where monthly data is going to store.
-- Adding ndf for February File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartFeb],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartFeb.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [February]
-- Adding ndf for March File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartMarch],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartMarch.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [March]
-- Adding ndf for April File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartApril],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartApril.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [April]
/-- Adding ndf for May File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartMay],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartMay.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [May]
-- Adding ndf for June File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartJune],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartJune.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [June]
-- Adding ndf for July File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartJuly],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartJuly.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [July]
-- Adding ndf for August File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartAug],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartAug.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [August]
-- Adding ndf for September File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartSept],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartSept.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [September]
-- Adding ndf for October File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartOct],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartOct.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [October]
-- Adding ndf for November File Group
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartNov],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartNov.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [November]
-- File Group for December
ALTER DATABASE [PartSample]
ADD FILE
(
NAME = [PartDec],
FILENAME = 'C:\Program Files\...............\DATA\PartDec.ndf',
SIZE = 5080 KB,
MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED,
FILEGROWTH = 2040 KB
) TO FILEGROUP [December]
Once you execute the query, the message will be
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.From the below screenshot you can see, ndf files have been created for each file group.
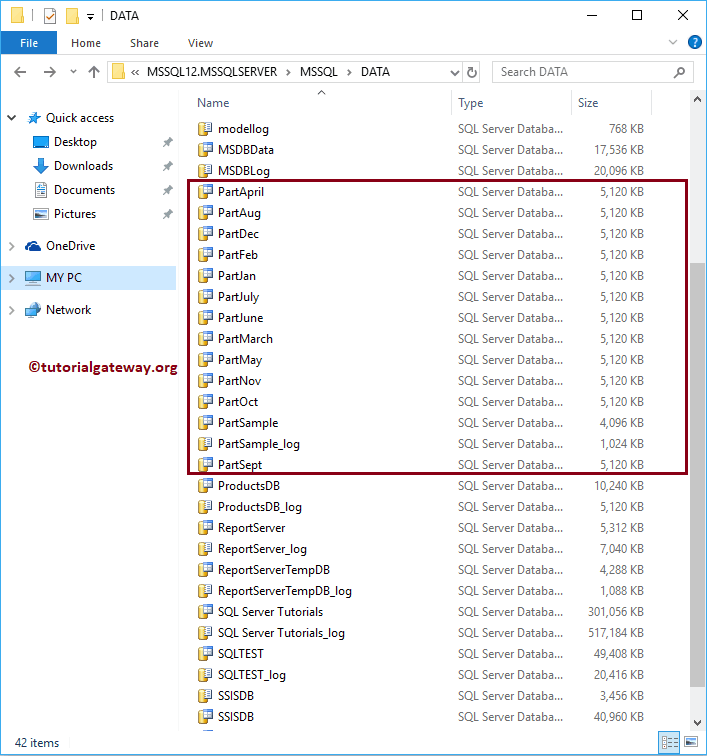
View File groups and respective ndf files of SQL Table partition
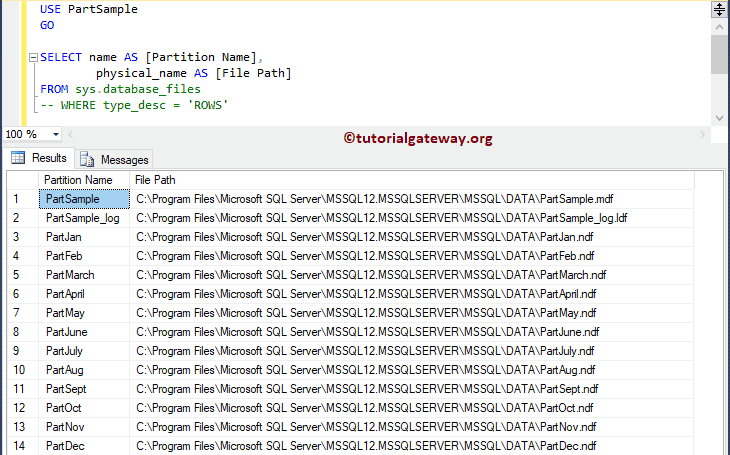
Use sys.database_files to get information about file groups and their physical locations.
USE PartSample GO SELECT * FROM sys.database_files
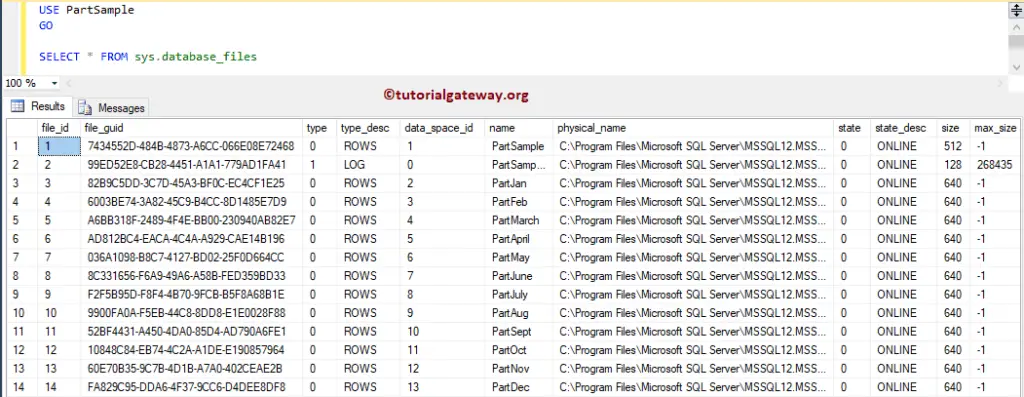
You can also use more specific columns in the select statement
USE PartSample GO SELECT name AS [Partition Name], physical_name AS [File Path] FROM sys.database_files -- WHERE type_desc = 'ROWS'
Create Partition Function for Table in Sql Server
This function will map the rows from the original to the partition tables. For this, the SQL partition function will use one column to identify the filegroup.
The below function will map the original table to file groups based on each month. This function compares the insert date value and map to one of the partitions based on the values we specified within the brackets ().
USE PartSample
GO
CREATE PARTITION FUNCTION [MonthlyPartition] (datetime)
AS RANGE RIGHT FOR VALUES ('20180201', '20180301', '20180401',
'20180501', '20180601', '20180701', '20180801',
'20180901', '20181001', '20181101', '20181201');
Execute the above query
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Create a Partition Scheme
This will map the partition tables with the file groups. The below scheme will map 20180201 to February etc.
USE PartSample GO CREATE PARTITION SCHEME MonthWisePartition AS PARTITION MonthlyPartition TO (January, February, March, April, May, June, July, August, September, October, November, December );
Execute the above query.
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Create a Table with Partitioning
Let me create a table using the newly created SQL Server Table partitioning schema. I suggest you refer Create table and Identity Column to understand the below code.
USE [PartSample] GO CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Insert]( [EmpID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [FirstName] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [LastName] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [Occupation] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [YearlyIncome] [float] NULL, [Sales] [float] NULL, [InsertDate] [datetime] NULL ) ON MonthWisePartition (InsertDate);
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me insert a few records into the newly created table. Please refer Insert Statement article to understand the insert operations.
USE [PartSample]
GO
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Insert]
VALUES ('Imran', 'Khan', 'Skilled Professional', 15900, 100, GETDATE())
,('Doe', 'Lara', 'Management', 15000, 60, GETDATE())
,('Ramesh', 'Kumar', 'Professional', 65000, 630, DATEADD(month, 1, GETDATE()))
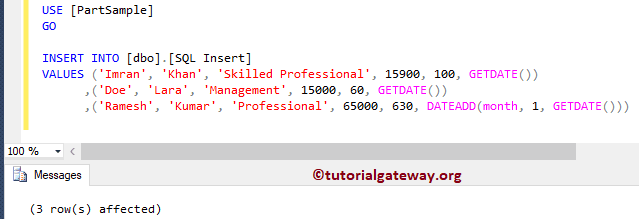
From the below, you can see those records.
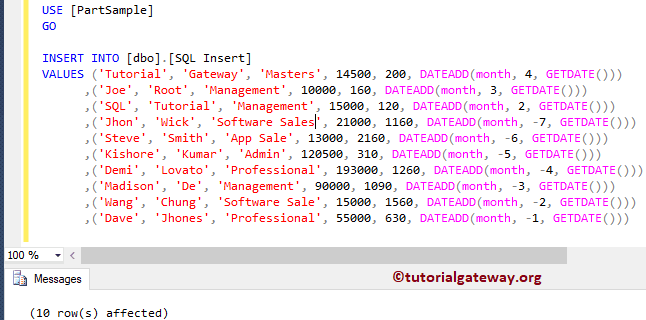
Next, we inserted a few more records with different dates. Notice, that we used the DATEADD function to add or delete months from the current date.
USE [PartSample]
GO
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Insert]
VALUES ('Tutorial', 'Gateway', 'Masters', 14500, 200, DATEADD(month, 4, GETDATE()))
,('Joe', 'Root', 'Management', 10000, 160, DATEADD(month, 3, GETDATE()))
,('SQL', 'Tutorial', 'Management', 15000, 120, DATEADD(month, 2, GETDATE()))
,('Jhon', 'Wick', 'Software Sales', 21000, 1160, DATEADD(month, -7, GETDATE()))
,('Steve', 'Smith', 'App Sale', 13000, 2160, DATEADD(month, -6, GETDATE()))
,('Kishore', 'Kumar', 'Admin', 120500, 310, DATEADD(month, -5, GETDATE()))
,('Demi', 'Lovato', 'Professional', 193000, 1260, DATEADD(month, -4, GETDATE()))
,('Madison', 'De', 'Management', 90000, 1090, DATEADD(month, -3, GETDATE()))
,('Wang', 'Chung', 'Software Sale', 15000, 1560, DATEADD(month, -2, GETDATE()))
,('Dave', 'Jhones', 'Professional', 55000, 630, DATEADD(month, -1, GETDATE()))
From the below screenshot, you can see all the records. If you observe the insert dates, each month had one record, and August had 2 records.
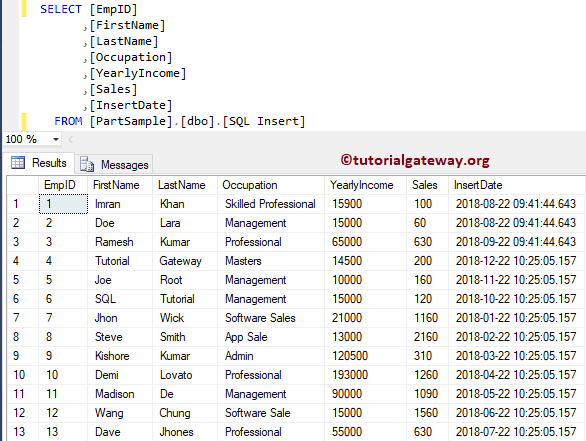
View Records in SQL Table Partitioning
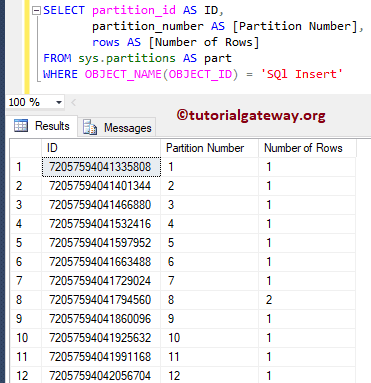
Use the below query to see the total number of rows per file group.
SELECT partition_id AS ID,
partition_number AS [Partition Number],
rows AS [Number of Rows]
FROM sys.partitions AS part
WHERE OBJECT_NAME(OBJECT_ID) = 'Insert'
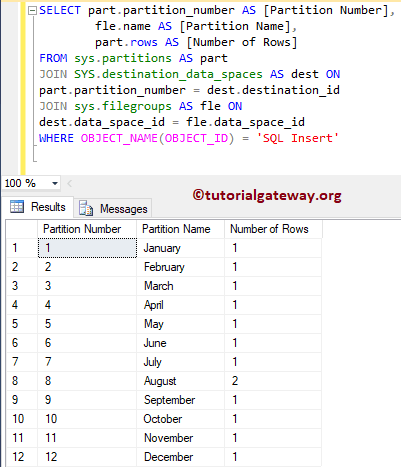
You can use the below query to see the File Group name along with the total number of rows in the SQL table partitioning.
USE PartSample SELECT part.partition_number AS [Partition Number], fle.name AS [Partition Name], part.rows AS [Number of Rows] FROM sys.partitions AS part JOIN SYS.destination_data_spaces AS dest ON part.partition_number = dest.destination_id JOIN sys.filegroups AS fle ON dest.data_space_id = fle.data_space_id WHERE OBJECT_NAME(OBJECT_ID) = 'Insert'
SQL Table Partitioning using SSMS
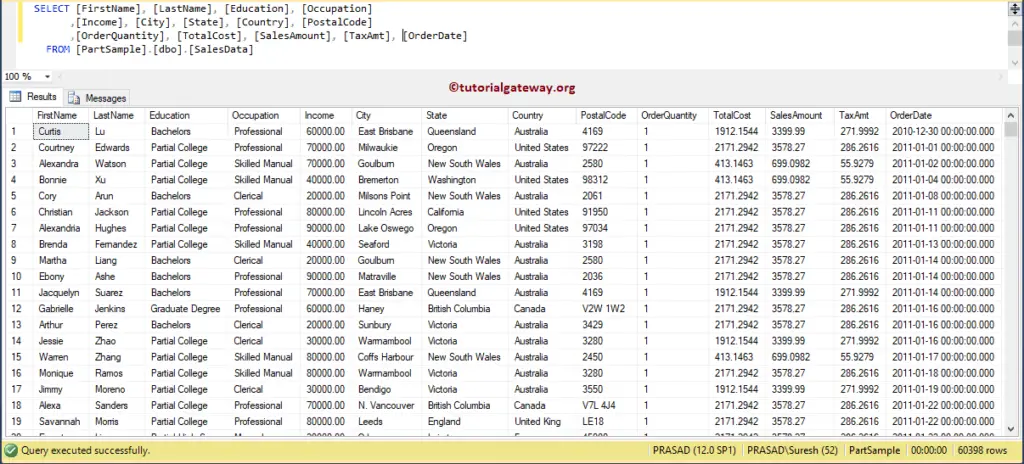
This section will show you how to create SQL Table Partitioning using SSMS or Management Studio. For this SQL Table partitioning demonstration, we will use the below-shown table. This table was created from the Adventure Works DW database. You can use the below query to get the same data.
-- SQL Server Table Partitioning using SSMS
USE [AdventureWorksDW2014]
GO
SELECT CUST.[FirstName]
,CUST.[LastName]
,CUST.[EnglishEducation] AS Education
,CUST.[EnglishOccupation] AS Occupation
,CUST.[YearlyIncome] AS Income
,GEO.[City]
,GEO.[StateProvinceName] AS State
,GEO.[EnglishCountryRegionName] AS Country
,GEO.[PostalCode]
,FACT.[OrderQuantity]
,FACT.[TotalProductCost] AS TotalCost
,FACT.[SalesAmount]
,FACT.[TaxAmt]
,FACT.OrderDate
FROM [DimGeography] AS GEO
INNER JOIN [DimCustomer] AS CUST
ON GEO.[GeographyKey] = CUST.[GeographyKey]
INNER JOIN [FactInternetSales] AS FACT
ON CUST.CustomerKey = FACT.CustomerKey
SQL Server Table Partitioning using Management Studio
To create a SQL Table Partitioning in SSMS, please navigate to the table you want to create a partition. Next, right-click on it, select Storage, and then Create Partition option from the context menu.
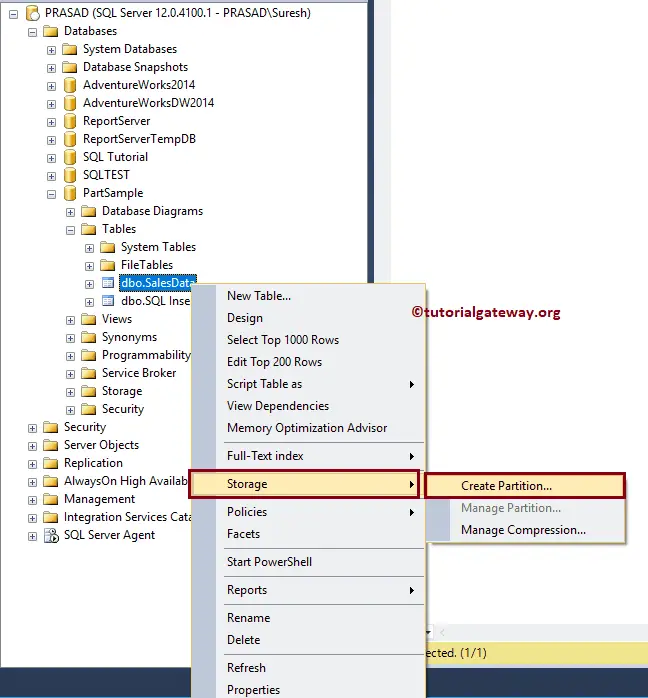
Selecting the Create Partition option will open a wizard. The first page is a welcome page.
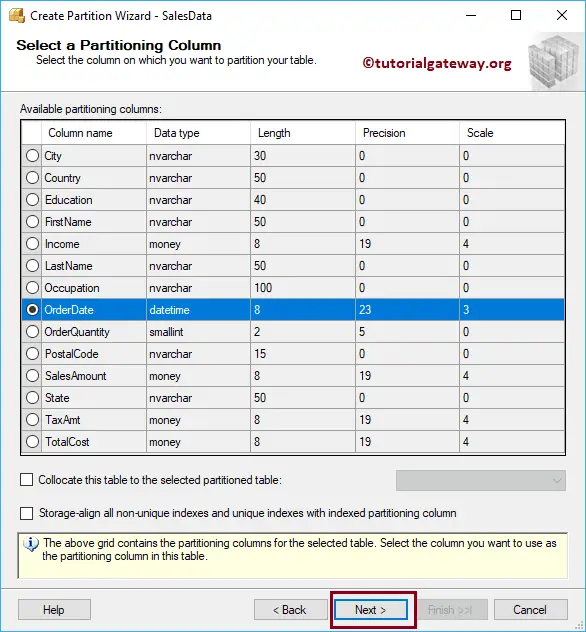
Sql Table Partition – Select a Partition Column
On this SQL page, you have to select the column that you want to use as a partition column. In this example, we are using the Order Date column.
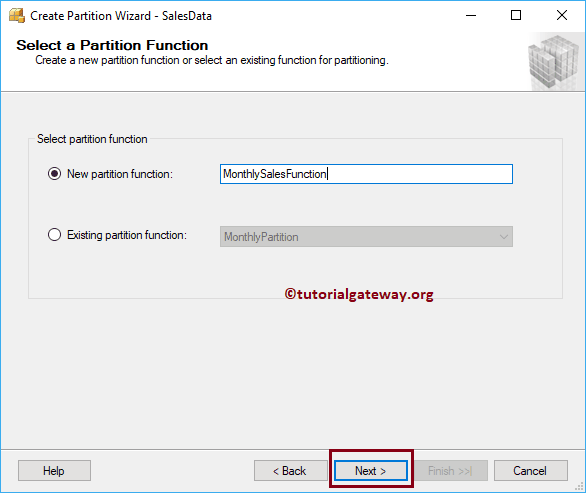
Select a Partition Function
Use this page to select the existing partition function or create a new partition function. Let me create a new one by assigning a name called Monthly Sales Function.
Select a Partition Scheme
On this page, you can select the existing partition scheme or create a new one. If you create a theme for a new function, the existing partition scheme selection is greyed out. Let me create a new by assigning a name called Monthly Sales Scheme.
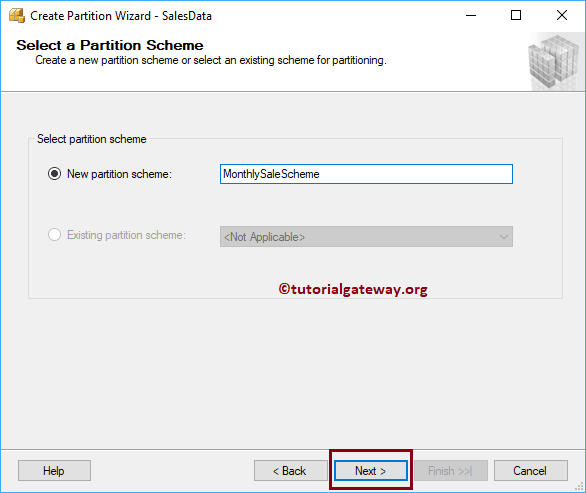
Let me show you what will happen if you select the Existing partition function called Monthly partition. This partition was previously created using Query.
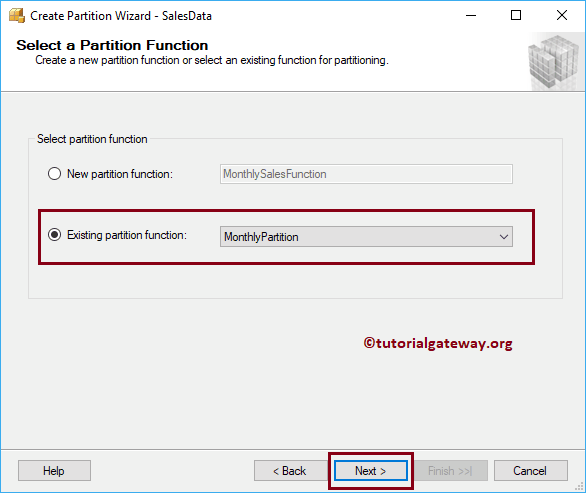
Now you can see it is allowing you to select the existing scheme. Or you can create a new scheme.
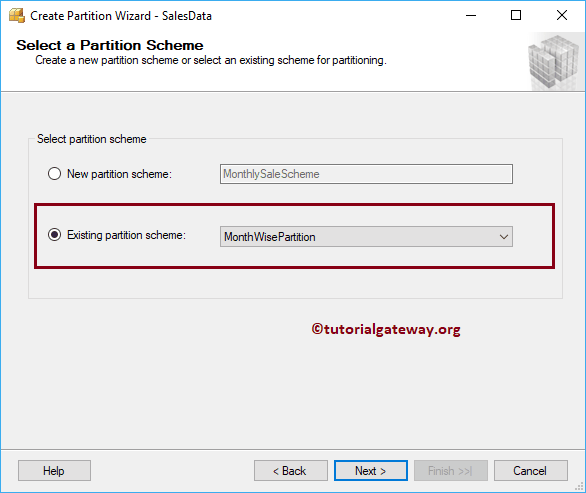
Let me undo those two steps and select New function and New Scheme.
SQL Table Partition – Map Partition
You can use either the Left boundary or right boundary.
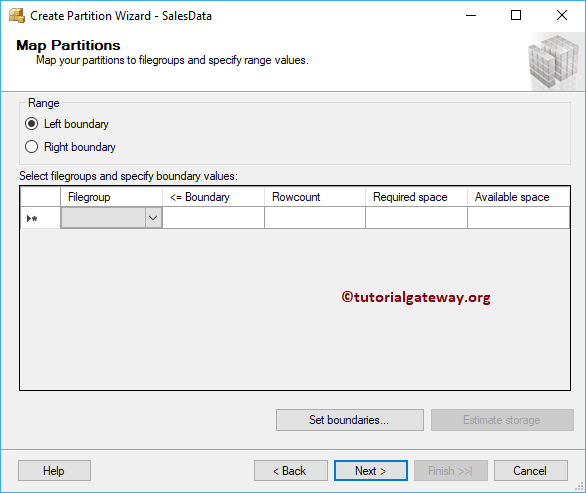
Use the drop-down box to select the Month names. Please use the Set boundaries button to choose the from date and to date, and Estimate Storage to estimate the required disk space.
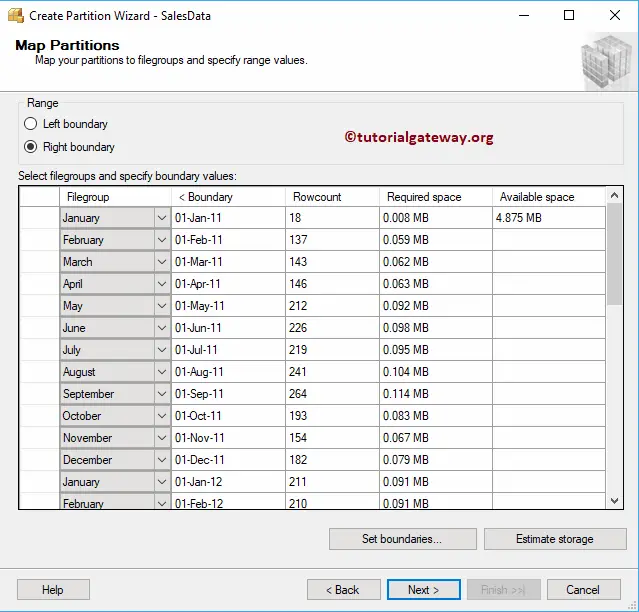
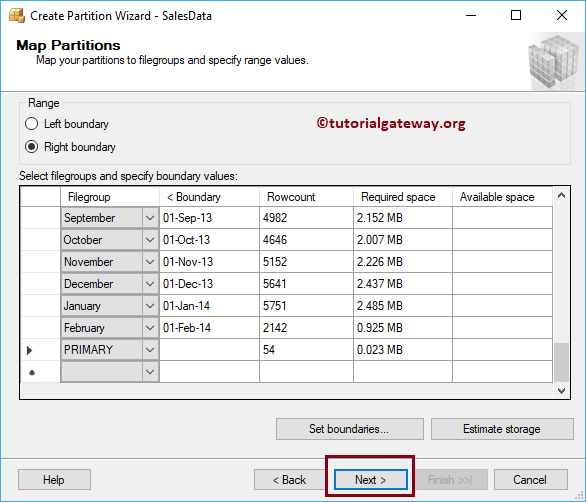
Don’t forget to select the PRIMARY filegroup (default one). Otherwise, it will throw an error.
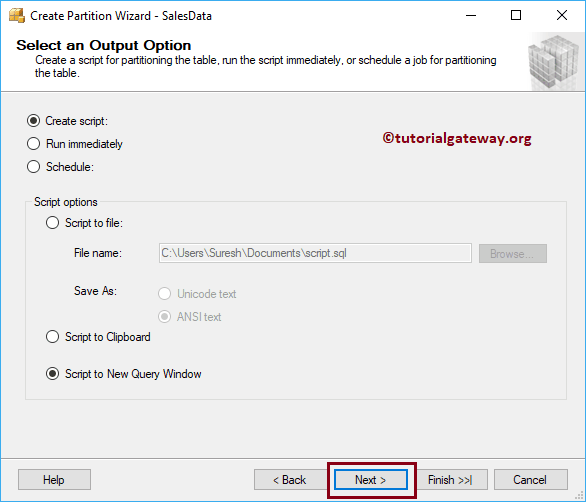
SQL Table Partition – Select an Output Option
Either you can
- Create a Script and run it later.
- Run immediately- This will run this table partition script straight away
- Schedule: You can use this script to run.
Select the Run Immediately option.
Click the Finish button to create a partition.
We have successfully created a table partition using a wizard.