The SQL INSERT statement adds new records into tables or loads data into tables. The syntax of this insert statement is
INSERT INTO [DestinationTable] ([Column1], [Column2],..., [ColumnN]) VALUES ([Column1_Value], [Column2_Value],..., [ColumnN_Value])
- DestinationTable: Fully qualifies Table name to put records
- Column1…..ColumnN: Choose the number of columns from the tables.
- Column1_Value…..ColumnN_Value: Values that you want to put. For example, Column1_Value loaded for Column1. If you omit the field names, you must specify the column_values (field values) in the order defined by the destination table structure.
We can write this SQL Server Insert Statement as,
INSERT INTO [DestinationTable] VALUES ([Column1_Value], [Column2_Value],..., [ColumnN_Value])
This table holds two records, and we will perform the insert operations on it.
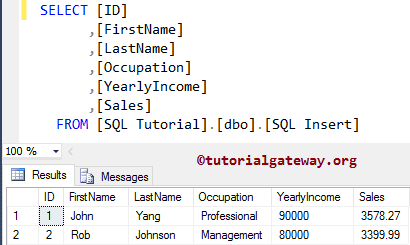
SQL Server INSERT Statement Example
This Insert Statement example put a new record into a Table in a more traditional way. Here, we haven’t loaded the ID value because it is an identity column, and it will be updated automatically.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[SQLInsert] (
[FirstName], [LastName], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales])
VALUES ('Tutorial', 'Gateway', 'Education', 10000, 200)
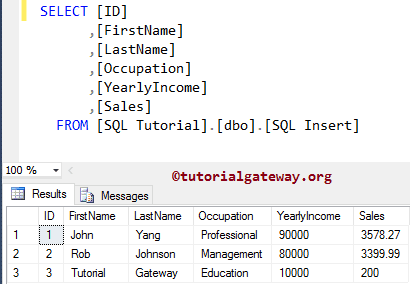
If we are loading data for all the Columns into the target, then we can ignore the column names of the destination (Syntax 2). It means the above SQL Insert Statement can also write as:
INSERT INTO [dbo].[SQLInsert]
VALUES ('SQL', 'Programming', 'Database', 50000, 1800)
TIP: It is not good practice to ignore the column names. So, always provide the column names in SQL Server.
Above query will place data into [FirstName], [LastName], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], and [Sales] columns. Whenever you omit the field names, you must specify the column_values (field values) in the order defined by the destination table structure. It means SQL value will put in [FirstName] column etc.
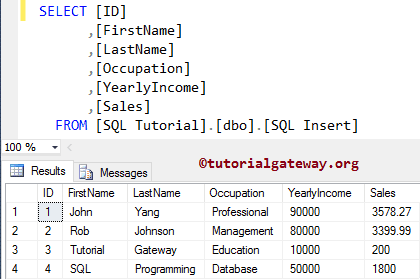
How to Insert Multiple Records into a Table?
This Sql Server Insert Statement example loads multiple records into a Table in a more traditional way.
INSERT INTO [SQLInsert]
VALUES ('Virat', 'Kohli', 'Cricket', 15700, 800)
INSERT INTO [dbo].[SQLInsert]
VALUES ('Rohit', 'Sharma', 'Cricket', 15000, 500)
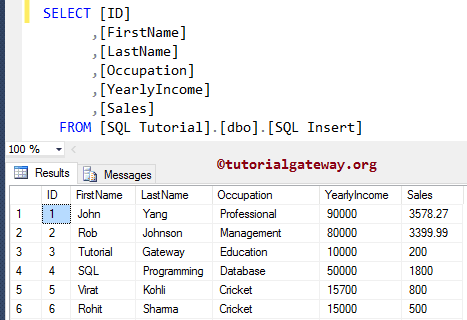
The oldest way to load multiple records.
INSERT INTO [SQLInsert] SELECT 'John', 'Levi', 'Professional', 75700, 1900 UNION ALL SELECT 'Doe', 'Martin', 'Management', 95000, 5600
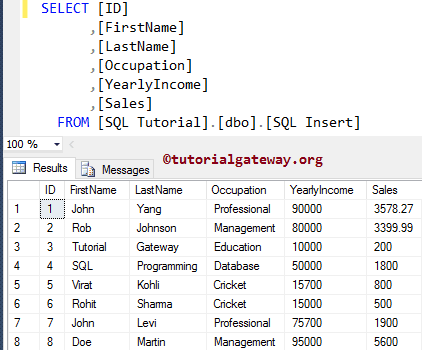
Here, we use the most popular way to put multiple records into the Table. it will work in 2008 and later versions.
INSERT INTO [SQLInsert]
VALUES ('Imran', 'Khan', 'Skilled Professional', 15900, 100)
,('Doe', 'Lara', 'Management', 15000, 60)
,('Ramesh', 'Kumar', 'Professional', 65000, 630)
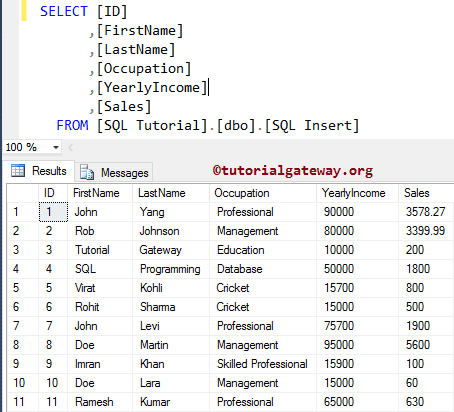
How to Insert a few records into a table?
In this SQL Server Insert Statement example, we put a few Records into a table. Remember, When you are loading a few records into the destination, you must specify the column names.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[SQLInsert] (
[FirstName], [Occupation], [Sales])
VALUES ('Insert', 'SQL Tutorials', 1225)
The above query will put data into [FirstName], [Occupation], and [Sales] columns. NULL values are added in the remaining columns.
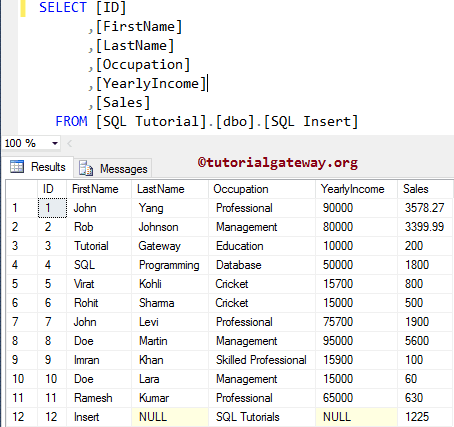
SQL Insert Into Select Statement
The Employ we use for the query
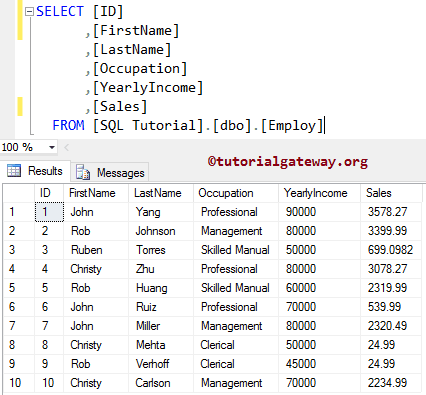
In this SQL Insert Statement example, we select rows from the Employ and load them into a destination. Here, we restrict the rows using the WHERE Clause.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[SQLInsert] SELECT [FirstName], [LastName], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales] FROM Employ WHERE ID > 2
Above query add [FirstName], [LastName], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], and [Sales] columns from the source where [ID] value is greater than 2 into the destination.
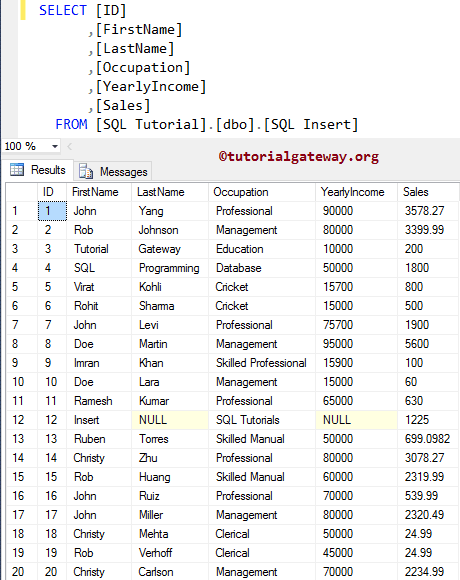
Please refer to the article. Let us see whether the selected data loaded into the destination or not.

Comments are closed.