As we all know, Tables are useful for storing and Managing Data, and it is a combination of Rows and Columns. For this, we have to use SQL Server Create Table Statement, and the basic syntax is
CREATE TABLE [TableName]
(
Column_Name1 Data_Type(Size) [NULL | NOT NULL],
Column_Name2 Data_Type(Size) [NULL | NOT NULL],
…
Column_NameN Data_Type(Size) [NULL | NOT NULL]
);
The Sql Server create table syntax items.
- TableName: If you write the already existing name, it will throw an error
- Column_Name: Unique Column in the table of null or not nulls.
- Data Type: A valid Data type that the column will hold. For example, Int, Money, Varchar, Nvarchar, and Date.
- Size: Data types like Varchar, nvarchar, and Char expect the size. So, Please provide a valid number here.
- NULL or NOT NULL: If you select the NULL option, then the column will accept both normal values and NULL values. Otherwise, it will throw an error saying Column should not be empty.
SQL Create Table Example
In this SQL Server example, we create a new Customer table inside the Database.
CREATE TABLE [Customer] ( [CustomerKey] [int] NOT NULL, [Name] [varchar](150) NULL, [DateOfBirth] [date] NULL, [EmailAddress] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Profession] [nvarchar](100) NULL ) GO
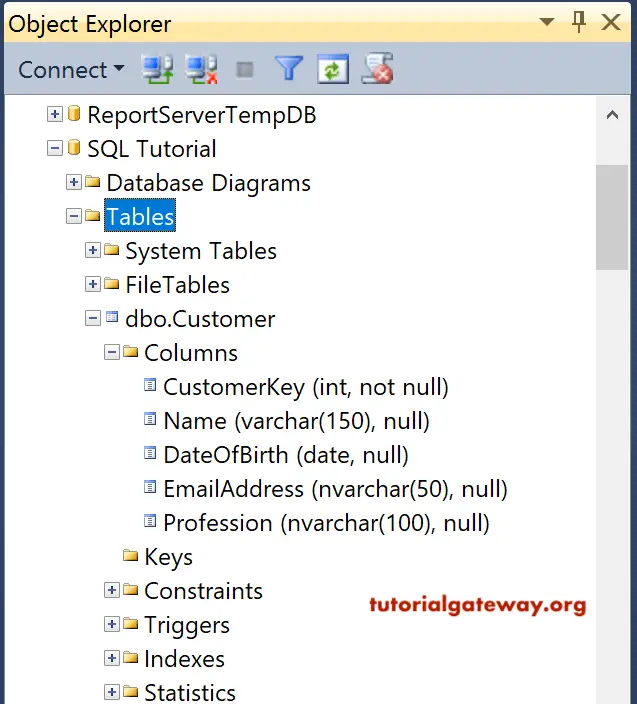
The command is executed successfully, and you can see the Newly created table in the object explorer.
Messages
-------
Command(s) completed successfully.From the above SQL Create Table code, you can observe that We declared 5 Columns:
- Our first column is CustomerKey of Integer data type, and it will not allow NULL values.
- The name column belongs to the Varchar data type, allowing NULL values. We also assigned the size to 150, which means both columns will accept up to 150 characters.
- The third column is the DateOfBirth of Date data type and allows NULLs. This will allow us to enter Date values only.
- EmailAddress and Profession columns belong to the NVarchar data type, and it will allow NULL values.
NOTE: Before you start creating a table in SQL Server, It is always advisable to check if it exists or not.
Let me show you the new one in Object Explorer. Please expand the Columns folder to see the available columns. If you didn’t find it, please click on the refresh button in object explorer.
SQL Create Table with Identity Column
In this example, we create a table with an identity column. For this, we defined the Customer Key column as an Identity column. This will auto-generate numbers starting with 1 and incremented by 1. (This is optional If you want, You can remove the IDENTITY (1, 1) portion completely)
CREATE TABLE [Customer11] ( [CustomerKey] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [FirstName] [varchar](50) NULL, [LastName] [varchar](50) NULL, [BirthDate] [date] NULL, [EmailAddress] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Yearly Income] [money] NULL, [Profession] [nvarchar](100) NULL ) GO
Messages
-------
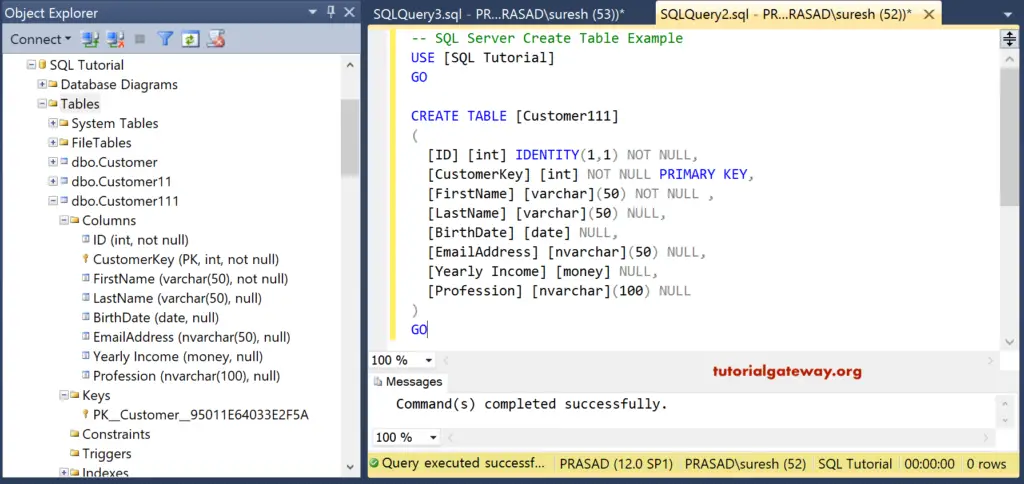
Command(s) completed successfully.See the newly created one

SQL Create Table Primary Key
How to create a Table with a Primary Key column. We just added the PRIMARY KEY word to the Customer key. This will create a primary key on the Customer key column.
CREATE TABLE [Customer111] ( [ID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [CustomerKey] [int] NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, [FirstName] [varchar](50) NOT NULL , [LastName] [varchar](50) NULL, [BirthDate] [date] NULL, [EmailAddress] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Yearly Income] [money] NULL, [Profession] [nvarchar](100) NULL ) GO
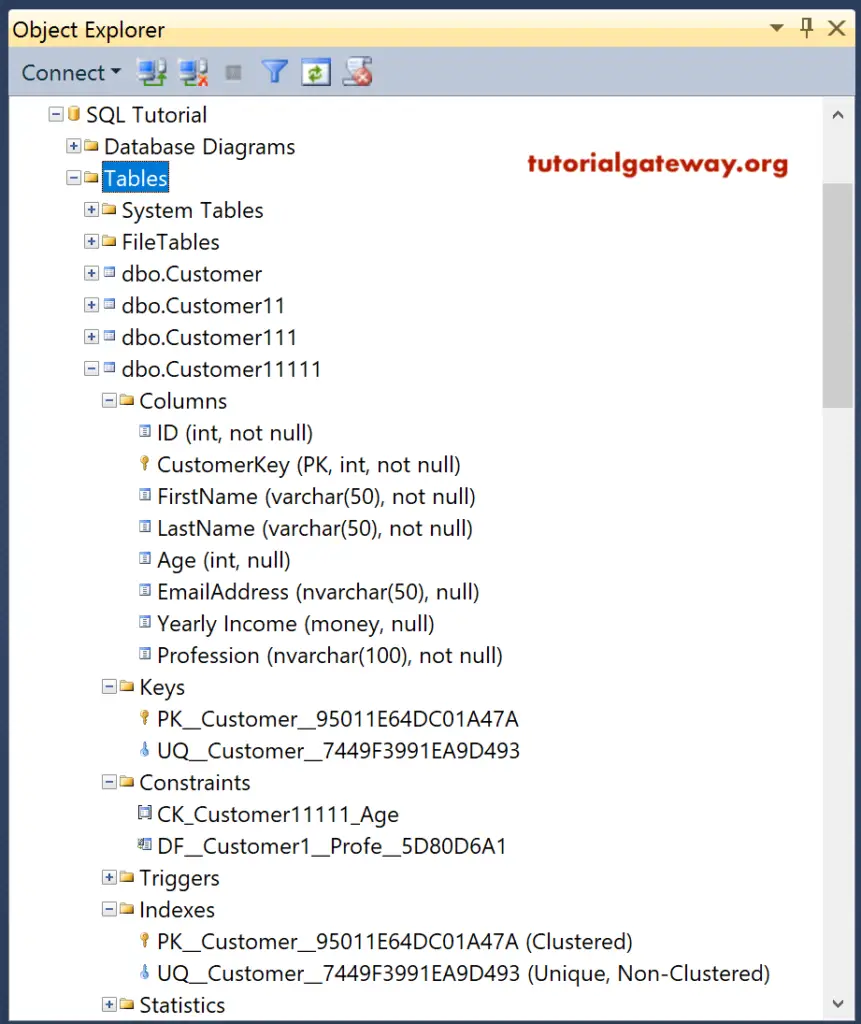
SQL Create Table with Identity, Primary, Unique, and Check Constraints
SQL create Table statement to create with Identity Column, Primary Key constraint, Unique Key, and Check Constraint columns.
I suggest you refer to the Primary Key, Unique Key, Default Constraint, and Check Constraint articles. As you can see,
- The Last Name will accept Unique values.
- If the user doesn’t provide a value to the Profession column, then it writes Software Developer as the default value.
- Check constraint check whether the Age value is between 0 and 100
CREATE TABLE [Customer11111]
(
[ID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[CustomerKey] [int] NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
[FirstName] [varchar](50) NOT NULL ,
[LastName] [varchar](50) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
[Age] [int] NULL,
[EmailAddress] [nvarchar](50) NULL,
[Yearly Income] [money] NULL,
[Profession] [nvarchar](100) NOT NULL DEFAULT ('Software Developer'),
CONSTRAINT CK_Customer11111_Age CHECK([Age] > 0 AND [Age] <= 100)
)
GO
Messages
-------
Command(s) completed successfully.If you expand the definition in Object Explorer, you can see all these constraints
Sql Server Create Table from Another
It provides Select into Statement to create a table using an existing one along with data (if any).. Data that we are going to use
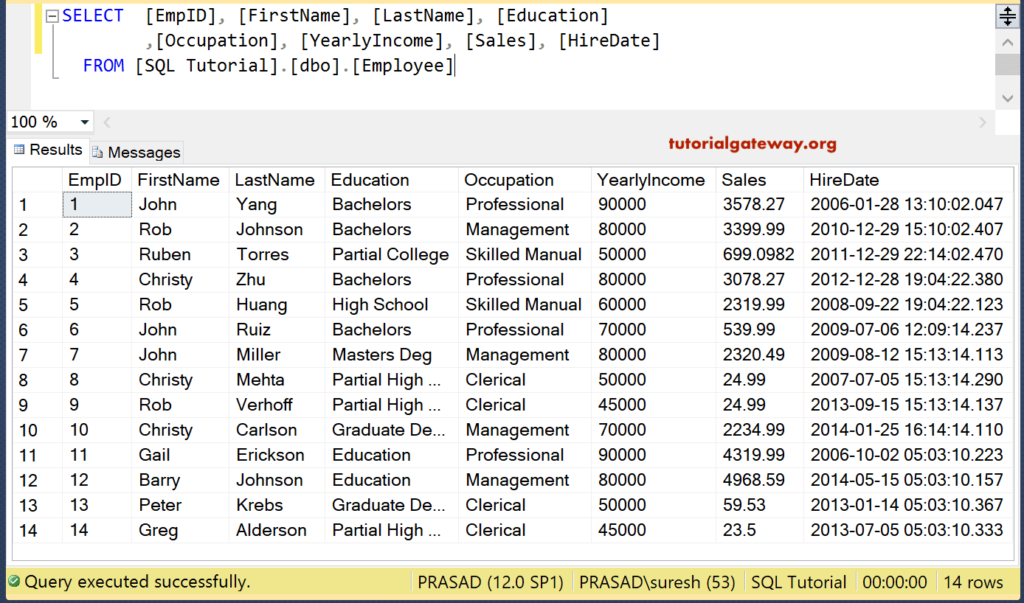
Below query produces Customer1111111 using the Employee definition, and inserts all the records present in the Employee.
SELECT [EmpID], [FirstName], [LastName], [Education] ,[Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales], [HireDate] INTO [dbo].[Customer1111111] FROM [dbo].[Employee]
Messages
-------
(14 row(s) affected)Data inside this
SELECT [EmpID], [FirstName], [LastName], [Education] ,[Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales], [HireDate] FROM [dbo].[Customer1111111]
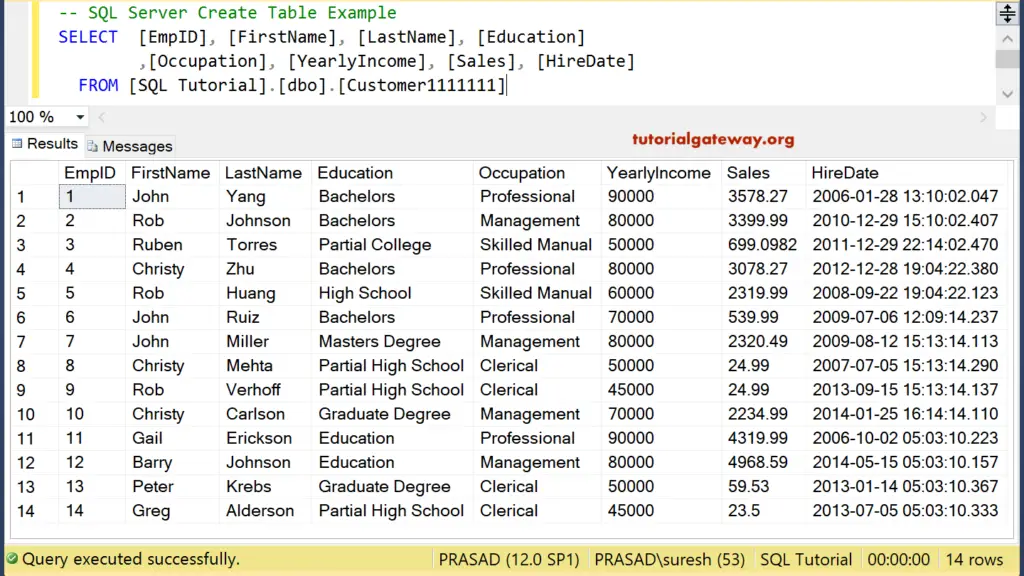
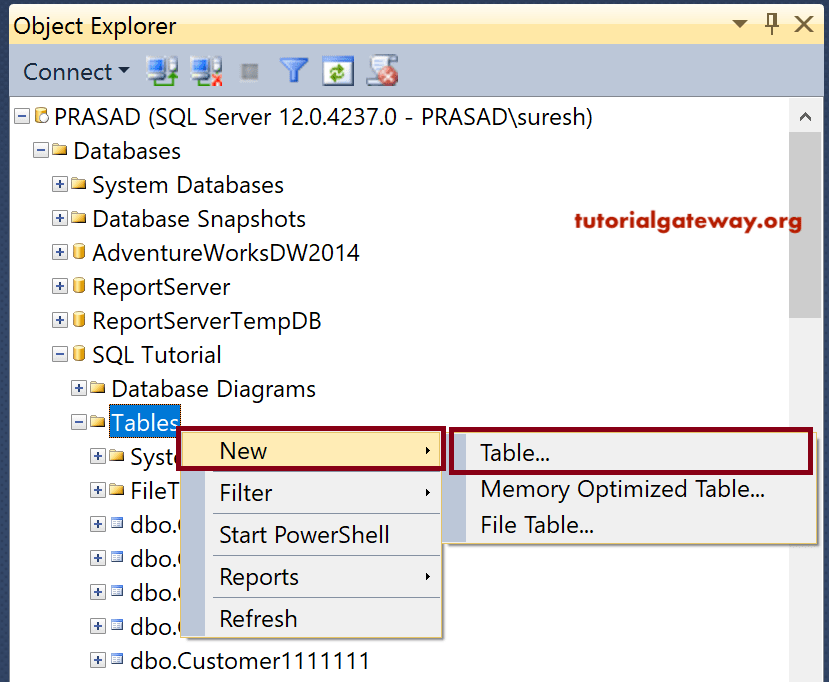
SQL Create Table in Management Studio
Within the Management Studio object explorer, Expand the Database folder in which you want to create a table. Please select the folder, and Right click on it will open the context menu. Select the New option and then select the below-shown option.
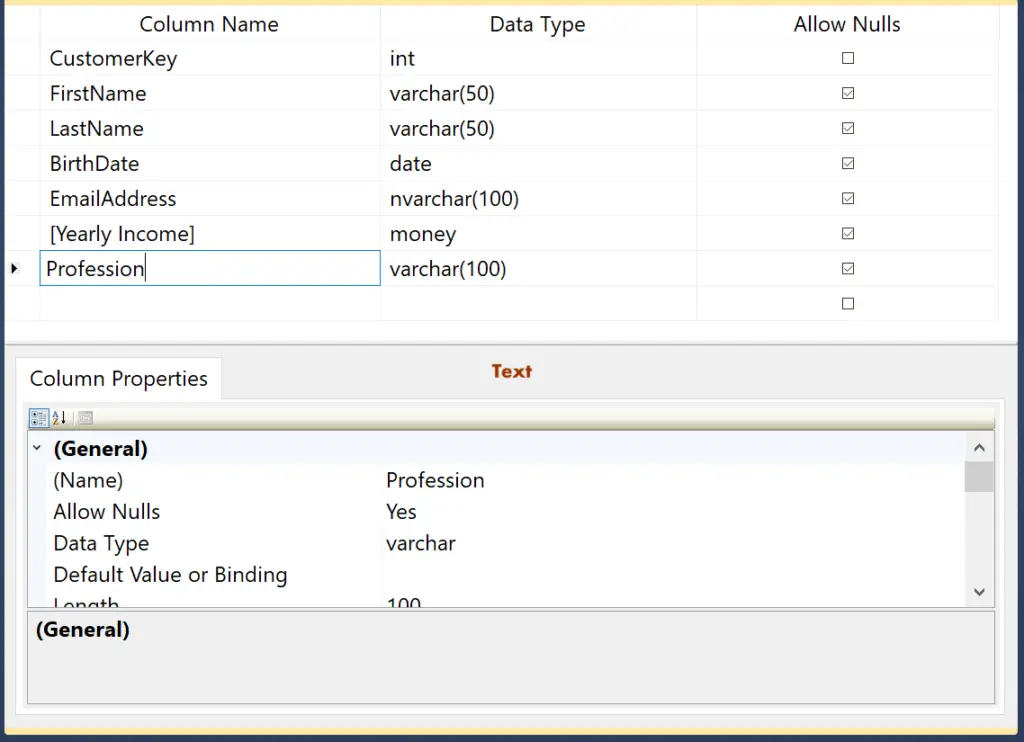
It will open the following window to type the Column Name, Data Type, and Checkbox to decide whether it allows any NULL values or Not. As you see, we added 7 columns of different data types.
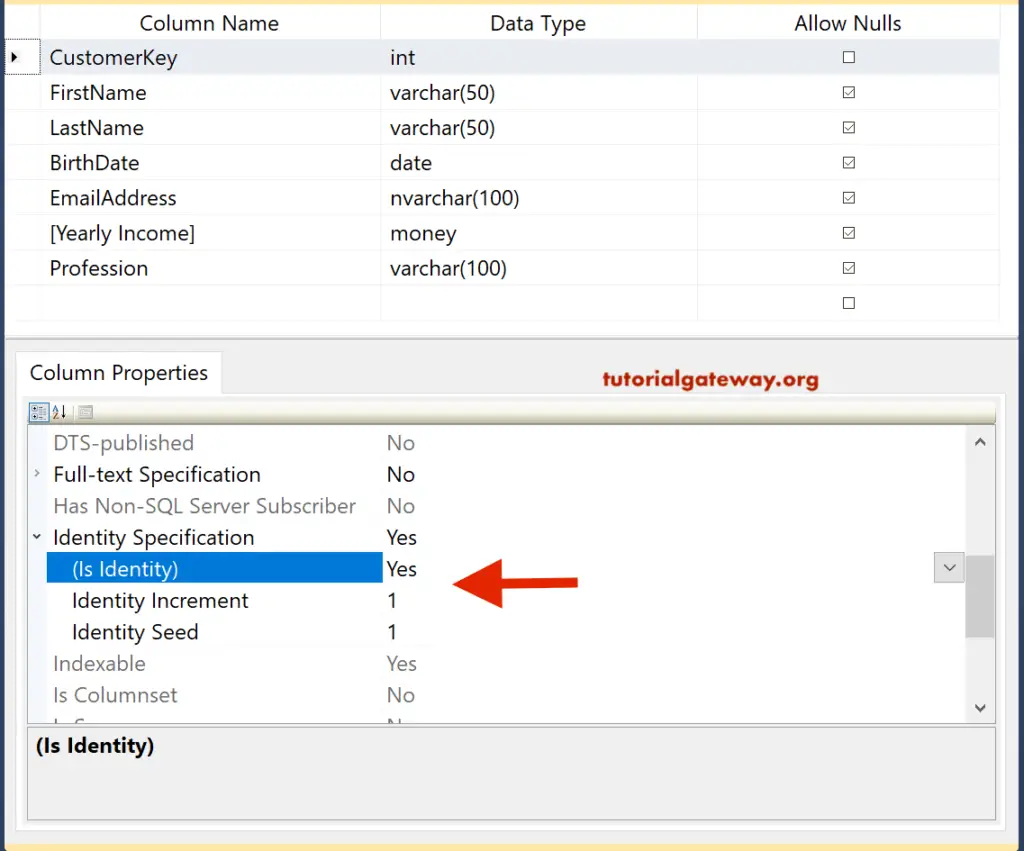
Add Identity Column using Management Studio.
Let me show you how to add an identity column to the already created table using SQL Server Management Studio. First, select the column and Go to the Column Properties tab. Please change the IsIdentity option from default No to Yes in the Identity Specification property.
Once you finish it, please click on the save button and rename the table name.
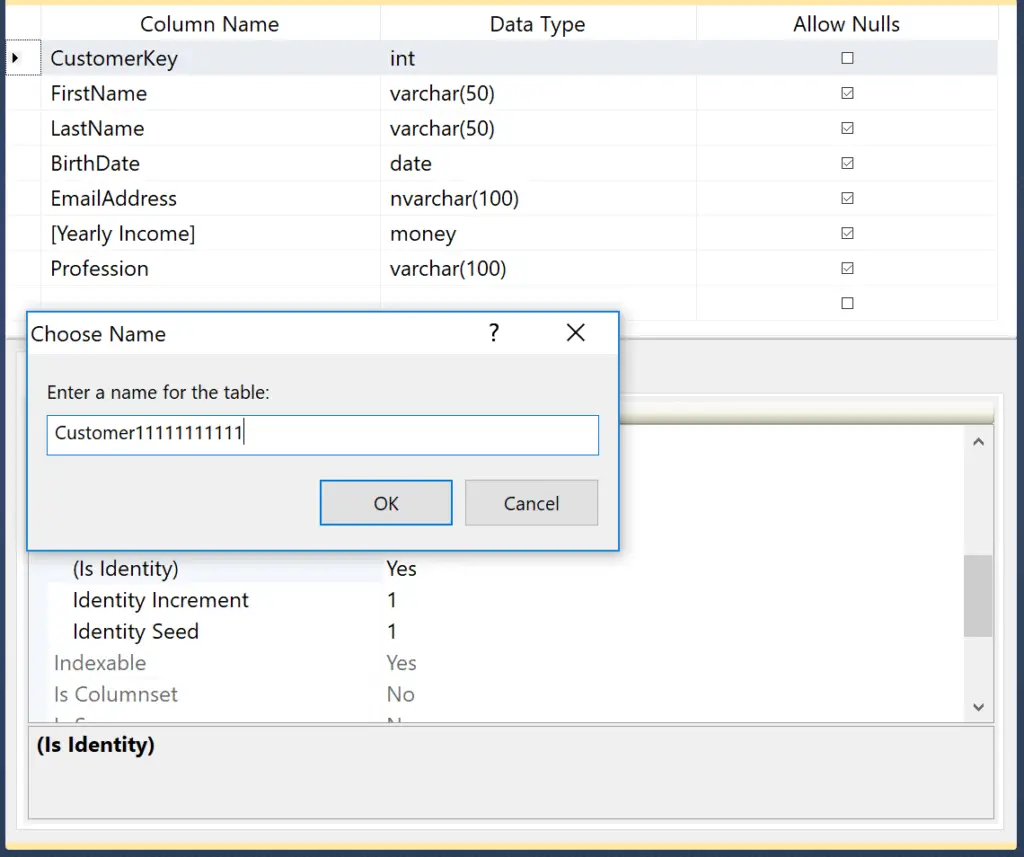
Click OK to finish saving. Write the following Select statement to check whether the table holds all the column names or not.
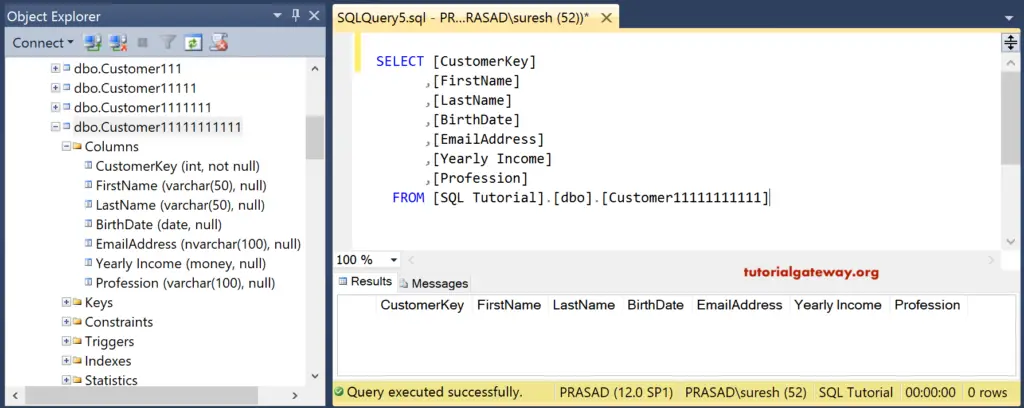
TIP: You can use the INSERT Statement or insert into to insert data into this newly generated one.
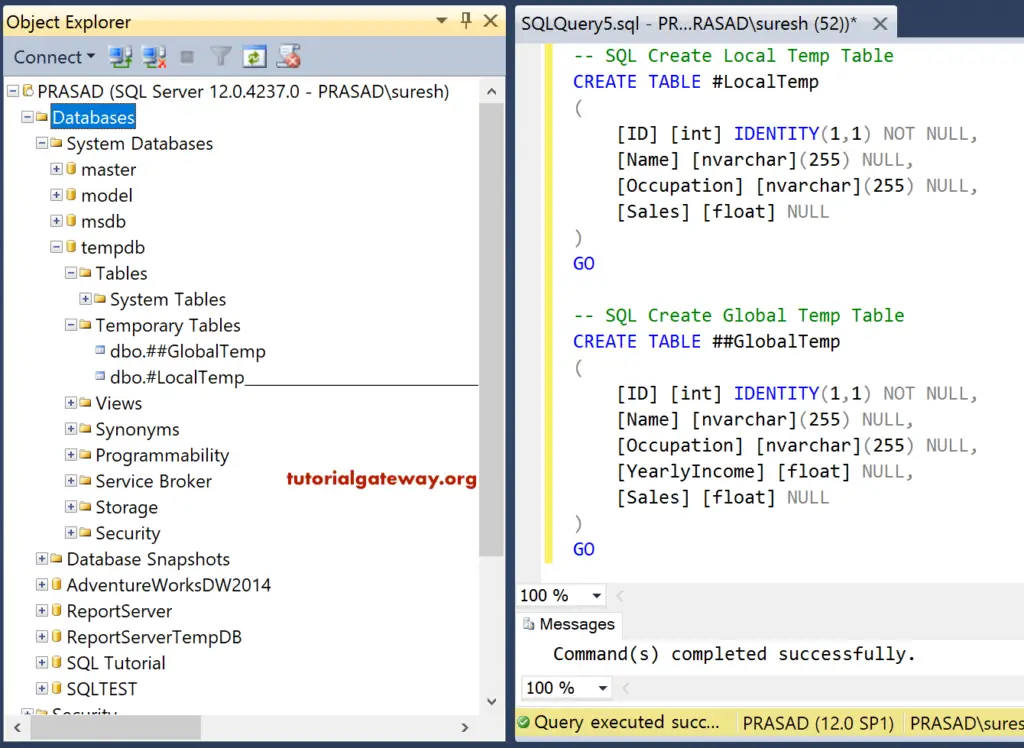
Local and Global Temp Tables
Here, we create SQL Server local and global temporary or temp tables. Please refer Temporary article.
-- Local Temp CREATE TABLE #LocalTemp ( [ID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [Name] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [Occupation] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [Sales] [float] NULL ) GO -- Global Temp CREATE TABLE ##GlobalTemp ( [ID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [Name] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [Occupation] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [YearlyIncome] [float] NULL, [Sales] [float] NULL ) GO

Comments are closed.