SQL Server Check Constraint will limit the data inserted into the table columns. So, for example, if we want to restrict the number of digits in a phone number or limit the customer’s age between 18 to 60, then we can assign Check Constraint to that column.
Let us see how to assign SQL Server Check Constraint using transact query and Management Studio with examples. For this demonstration, we use the Customer Records table.
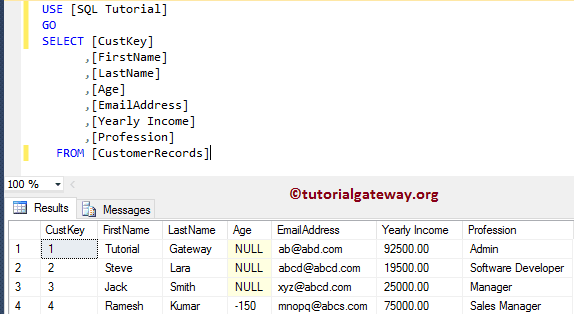
Let me update the Age for Custkey = 4. Please refer UPDATE Statement to understand the below SQL Server statement.
UPDATE [dbo].[CustomerRecords] SET [Age] = -150 WHERE [CustKey] = 4 GO
Although the age of any person is between 0 and 100 in most cases or 0 to 150 in rare cases. Our Age column accepts negative values which are not correct in real-time. We have to use the SQL Check Constraint to deal with this situation.
Messages
--------
(1 row(s) affected)Create SQL Server Check Constraint using Management Studio
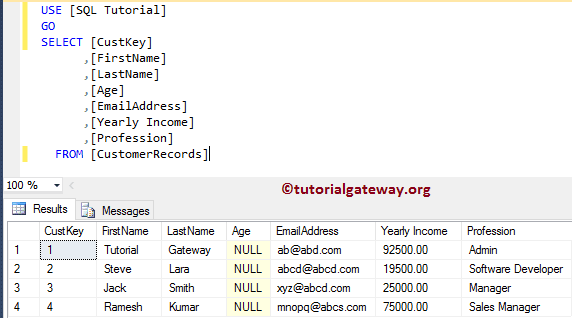
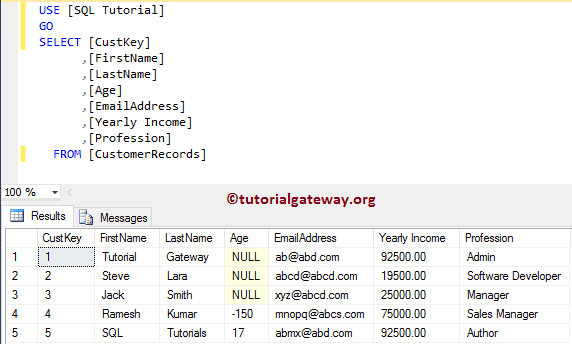
Before we start working on this, let me show you the final data inside our table:
In this example, we show you how to create the check using the Management Studio.
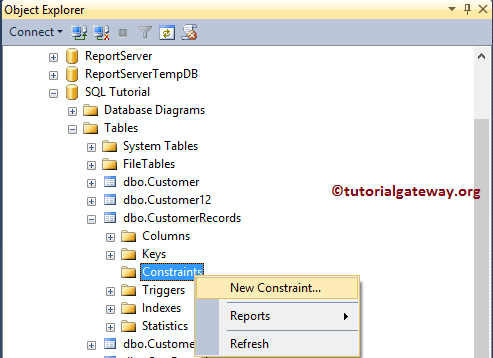
Within the object explorer, Expand the Database folder in which our table is located. Please select the table to create a SQL Check Constraint (here it is CustomerRecords). Next, go to the Constraints folder, and right-click on it will open the context menu. Please select New Constraint… option.
Once you select the New option, the management studio will open the corresponding table in design mode. And it will display a Check pop-up window.
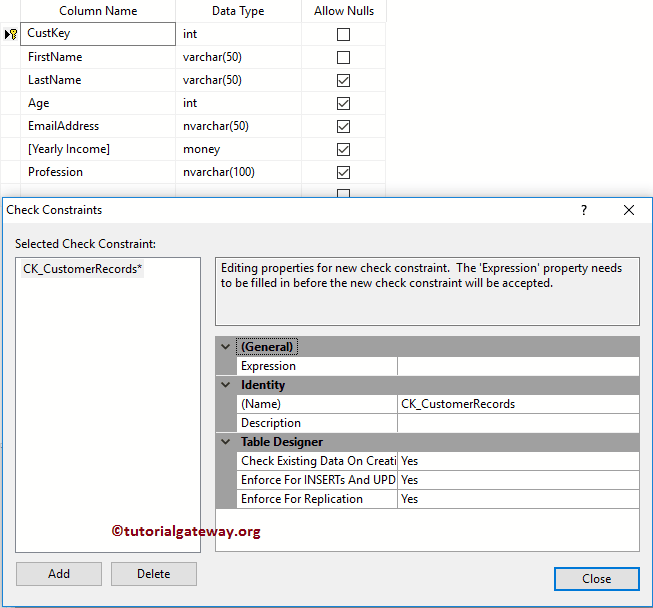
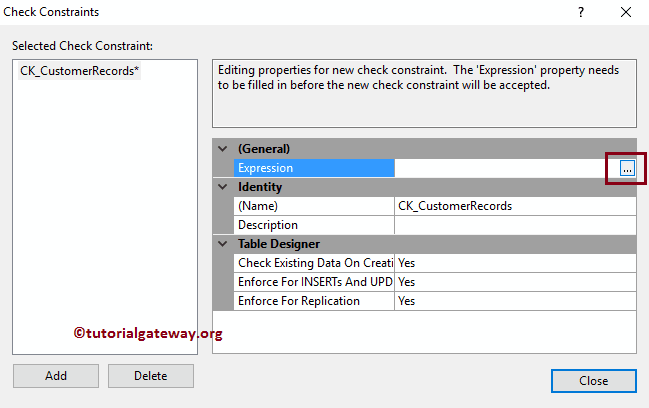
To enable the SQL Check Constraint, we have to provide a Boolean expression inside the Expression property. So, let me click on the … button beside the Expression.
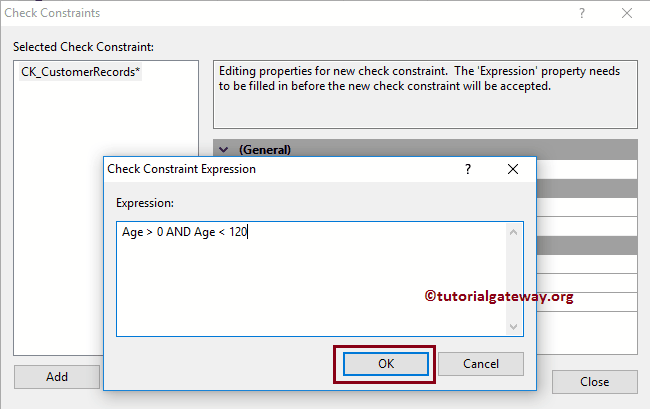
As you can see, we are writing a simple expression Age > 0 AND Age < 120. It means the Age should be between 0 and 120.
Next, we renamed the SQL Server Check constraint name as CK_CustomerRecords_Age. Please change the Name as per your requirements, and provide a valid description. Apart from these three, there is one more important property:
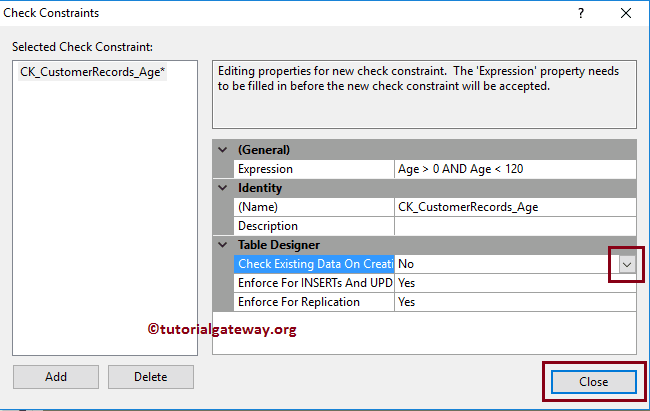
- Check Existing Data On Creation or Re-Enabling: This property has Boolean Yes or No options. If you set it as Yes, the check constraint will test the expression against the existing records. Otherwise, it will inspect for new records only. Therefore, let me keep it as Default Yes.
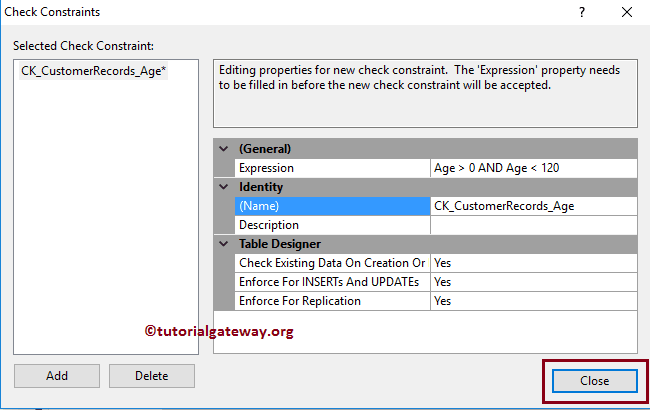
Let me save the table design.
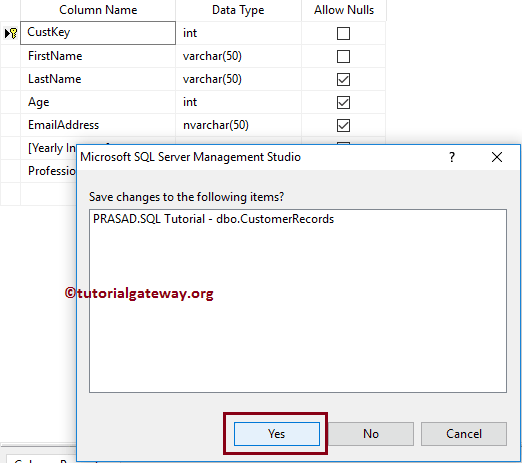
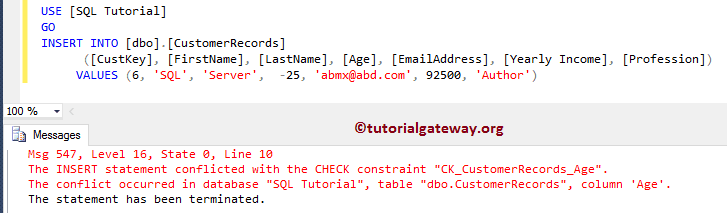
It is throwing an error. Because the Customer Records table had one value that is not satisfying the expression (-150 is not between 0 and 120)
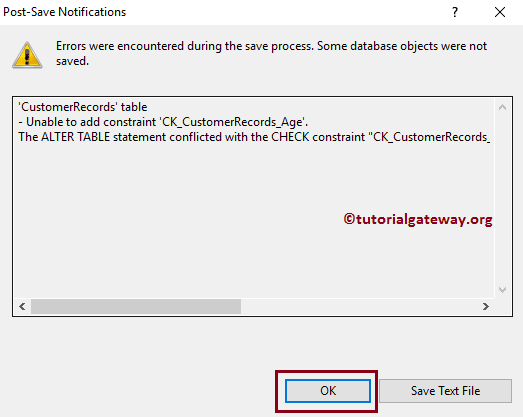
Let me change the SQL Check Constraint Existing Data On Creation or Re-Enabling property to No. It means it will not care about existing records. The check constraint will only test the expression for new records. OR, you can Delete or Update the record containing the -150 value.
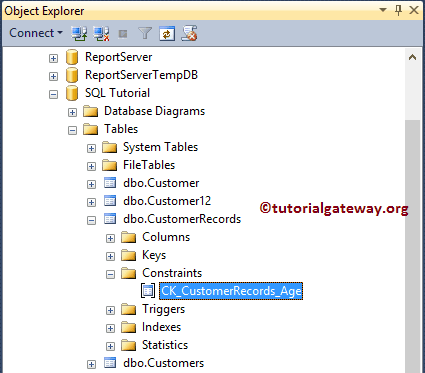
Now you can see our newly created Check constraint. For this, Go to the object explorer -> Database – > Table Name -> Expand Constraints Folder
Insert Values into SQL Server Check Constraint Column
Let me insert a value into the table using the INSERT Statement.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[CustomerRecords]
([CustKey], [FirstName], [LastName], [Age], [EmailAddress], [Yearly Income], [Profession])
VALUES (5, 'SQL', 'Tutorials', 175, 'abmx@abd.com', 92500, 'Author')
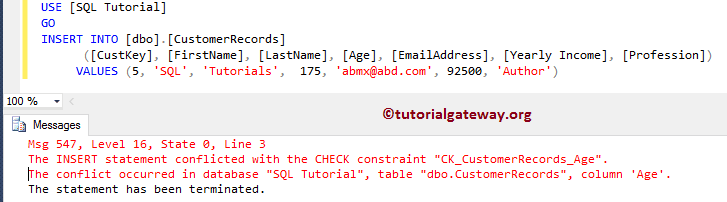
It is returning an Error. It is because we are inserting the Age value as 175, and 175 is not between 0 and 120.
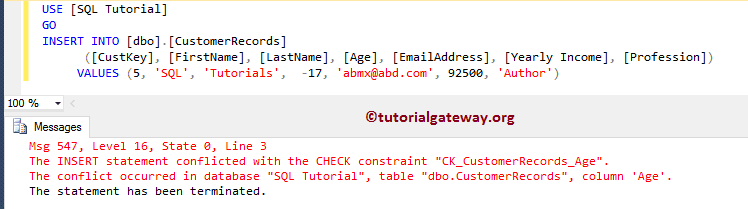
Let us try with a negative value. As you can see, it is also throwing the same error.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[CustomerRecords]
([CustKey], [FirstName], [LastName], [Age], [EmailAddress], [Yearly Income], [Profession])
VALUES (5, 'SQL', 'Tutorials', -17, 'abmx@abd.com', 92500, 'Author')
This time we will try with the correct value, and you can see our insertion is successful.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[CustomerRecords]
([CustKey], [FirstName], [LastName], [Age], [EmailAddress], [Yearly Income], [Profession])
VALUES (5, 'SQL', 'Tutorials', 17, 'abmx@abd.com', 92500, 'Author')
Messages
--------
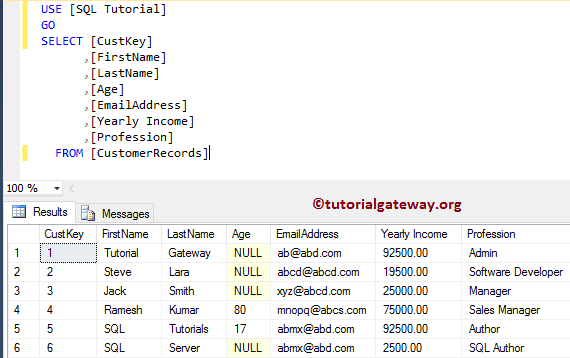
(1 row(s) affected)Let us see the total records in our table.
SELECT [CustKey]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Age]
,[EmailAddress]
,[Yearly Income]
,[Profession]
FROM [CustomerRecords]
SQL Check Constraint on an Existing table using Query
Before working with this, let me show you the final data inside our table:
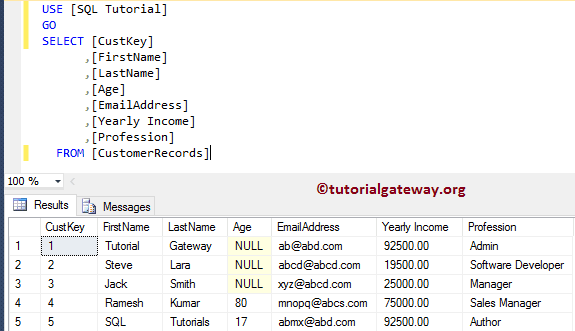
In this SQL example, we show how to add check constraints to the existing table.
To add this, we are using the Alter Table Statement to alter the table content. Then we used the ADD CONSTRAINT statement to add.
ALTER TABLE[CustomerRecords] ADD CONSTRAINT CK_CustomerRecords_Age CHECK([Age] > 0 AND [Age] < 120) GO
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me insert a negative value.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[CustomerRecords]
([CustKey], [FirstName], [LastName], [Age], [EmailAddress], [Yearly Income], [Profession])
VALUES (6, 'SQL', 'Server', -25, 'abmx@abd.com', 92500, 'Author')
Insert NULLS in SQL Check Constraint
What happens when we insert the NULL values into the Check constraint column? First, let me insert the NULL value into the Age Address Column.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[CustomerRecords]
([CustKey], [FirstName], [LastName], [Age], [EmailAddress], [Yearly Income], [Profession])
VALUES (6, 'SQL', 'Server', NULL, 'abmx@abd.com', 2500, 'SQL Author')
Messages
--------
(1 row(s) affected)It has inserted the NULL value into the check constraint. Because the expression results for NULL value returns undefined (Neither TRUE Nor FALSE), it allows the record.
Create Check on Multiple Columns
This SQL example creates a check constraint on multiple columns. The below code will restrict the user not is enter Age less than 18, and Yearly income greater than 100000
ALTER TABLE[CustomerRecords] ADD CONSTRAINT CK_CustomerRecords_AgeAndIncome CHECK([Age] >= 18 AND [YearlyIncome] <= 100000) GO
Create SQL Check Constraint on table creation
Here, we show you how to create a check constraint in the SQL server at the time of table creation. Refer to Create Table article.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[CustomerRecords2]( [CustKey] [int] NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, [FirstName] [varchar](50) NOT NULL, [LastName] [varchar](50) NULL, [Age] [int] NULL, [EmailAddress] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Yearly Income] [money] NULL, [Profession] [nvarchar](100) NULL, CONSTRAINT CK_CustomerRecords_AgeColumn CHECK([Age] > 0 AND [Age] < 120) ) GO
Messages
-------
Command(s) completed successfully.Delete SQL Check Constraint using transact query
If you know the name you want to delete, write the DROP Constraint statement along with the ALTER TABLE Statement transact query.
ALTER TABLE [dbo].[CustomerRecords] DROP CONSTRAINT CK_CustomerRecords_Age; GO
Messages
-------
Command(s) completed successfully.If you don’t know the name, use the following SELECT Statement to get the name.
SELECT name, create_date FROM sys.check_constraints WHERE OBJECT_NAME(parent_object_id) = N'CustomerRecords'; GO
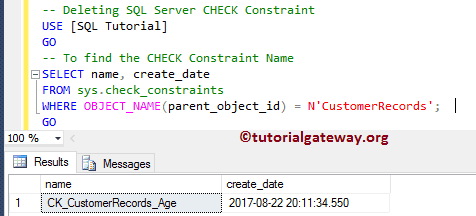
Once you get the name, you can use the ALTER TABLE Statement to Drop it.
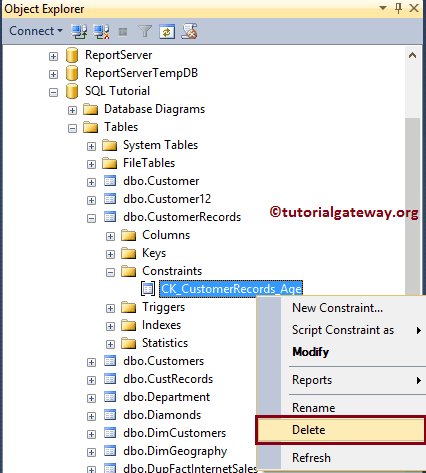
Delete Check using SSMS
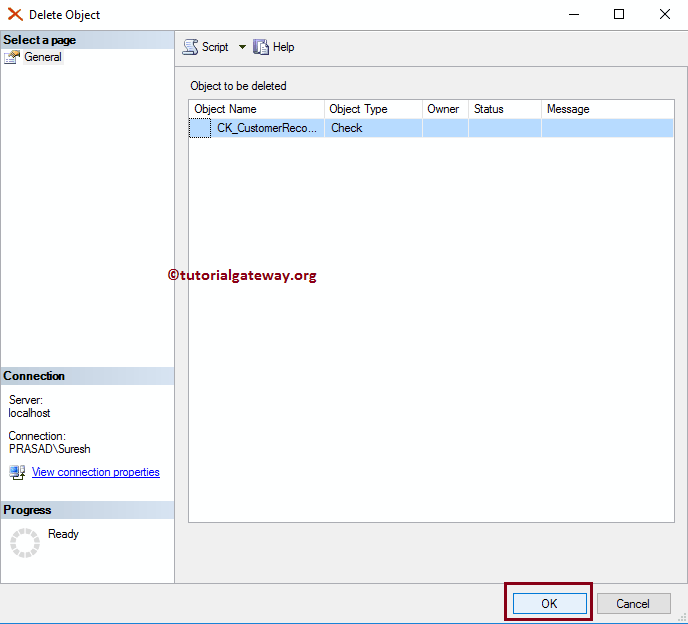
Within the object explorer, Expand the Database folder and the CustomerRecords table to find and delete the SQL Check Constraints folder. Right-click on the folder and select the Delete option.
Once you select the Delete option, a new Delete Object window will open. Click OK to delete it.