The SQL Server Views are the virtual tables with columns and rows from the referenced table. This study explains how to create, modify, rename, and delete Views in SQL Server.
Unless we define indexed, a view in SQL Server does not store a set of values in a database. Therefore, when you use the SELECT Statement against a view, the records will come from the table we referenced while creating.
Create View in SQL Server
You can use SQL Server Transact query or Management Studio to create or replace views. Before we get into the example, You can use them for the following purposes:
- First, simplify the data as per the user’s needs.
- Restrict the Users not to access the entire database.
SQL Server Create View Statement
This example shows how to create a View in SQL Server using the Create Statement.
CREATE VIEW EmployeesViewbyQuery AS SELECT [FirstName] + ' ' + [LastName] AS Name ,[Occupation] ,[Education] ,dept.DepartmentName AS Department ,[YearlyIncome] AS Income ,[Sales] FROM [MyEmployees Table] INNER JOIN Department AS dept ON Dept.[id] = [MyEmployees Table].DeptID GO
Let us see the rows and columns result set
SELECT * FROM [dbo].[EmployeesViewbyQuery]
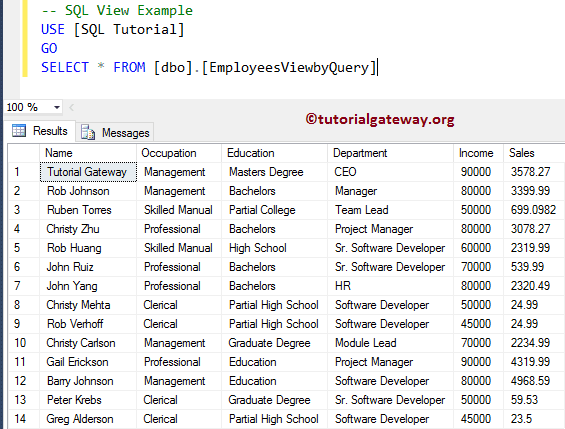
Create View in SQL Server Management Studio
This example shows the steps to create a View using the SQL Server Management Studio. The restrictions to remember while creating are
- It can be created only in the current database
- It allows us to have a maximum of 1024 columns
To see the existing Views, select the Database that has them. As you see, our database has none.
Right-click on the folder in Management Studio will open the context menu. To create it, Please select the shown option from it.
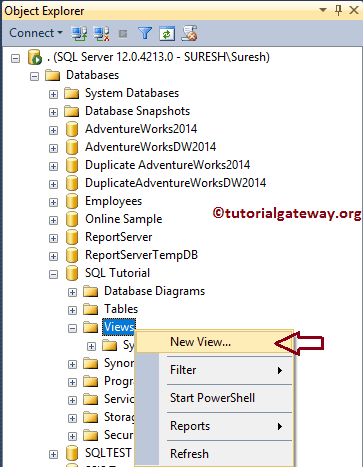
Once you click on the option, the Query Designer opens in a separate pop-up window to add the required tables.
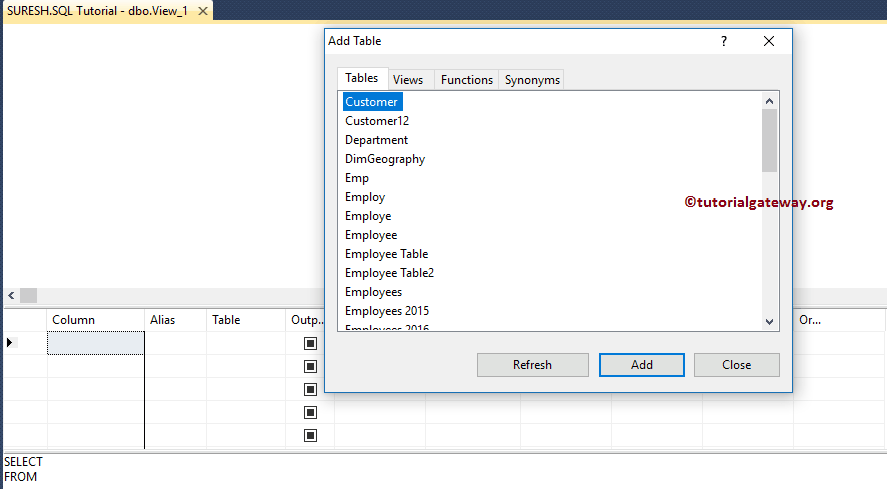
You can add functions, tables, or views. For example, from the below image, you can observe that we selected the MyEmployees table and Department table.
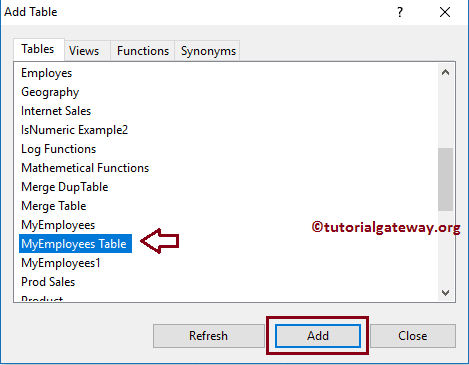
Once you select the required tables, it will show the Query Designer. Please choose the columns needed by check-marking the column names in the Diagram Pane.
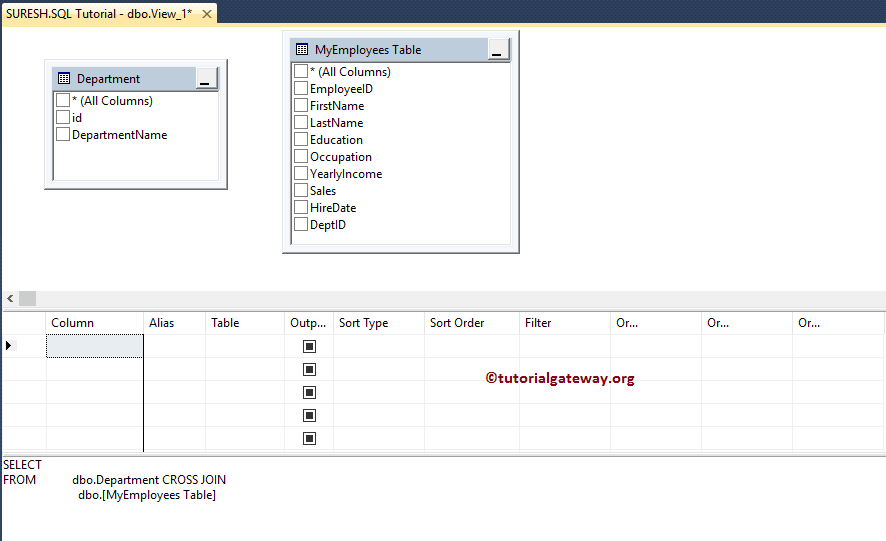
We chose the First Name, Last Name, Education, Occupation, Department, Yearly Income, Sales, and Hire Date from this SQL Server Views example from two tables. Remember, you can join two tables by dragging one column onto the other.
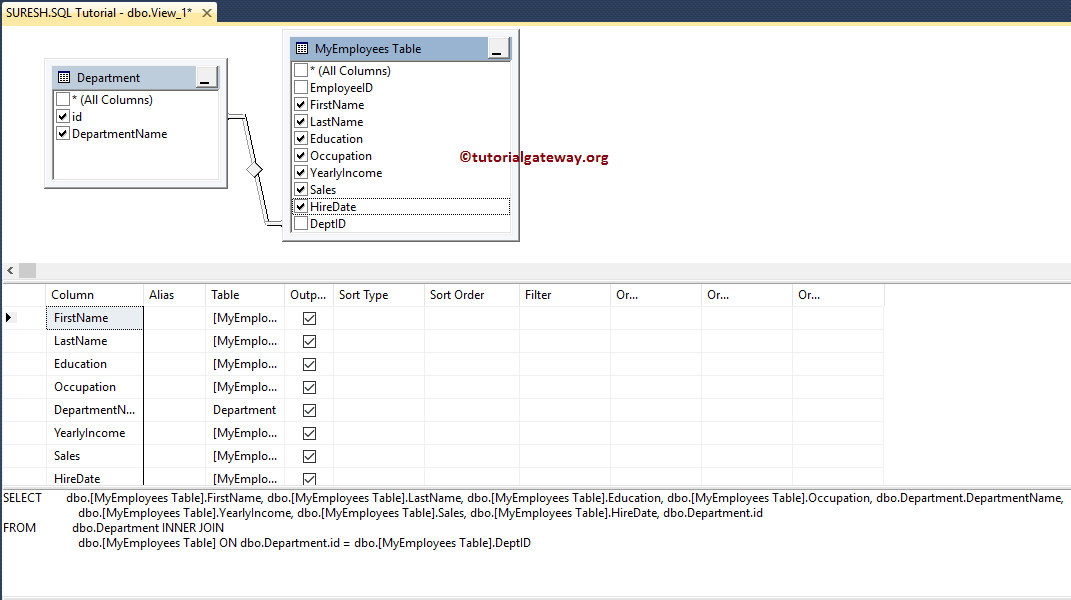
The sort Type property is to apply for ORDER BY functionality. Please change the Sort Type within the Grid Pane to Ascending or Descending. In this example, we are sorting Yearly Income in Descending Order.
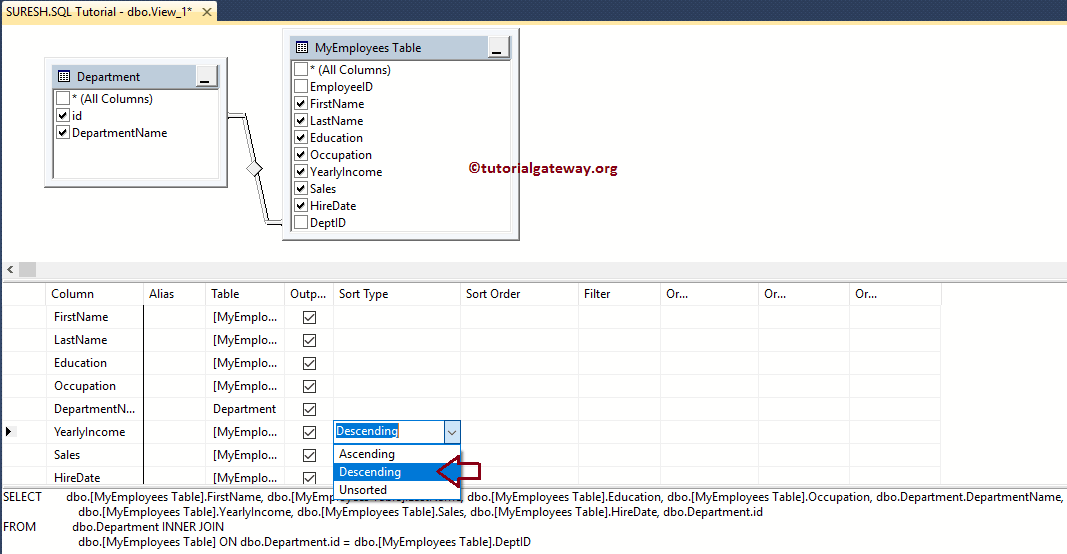
Once you select the Descending Operation, it will show you the sorting representation.
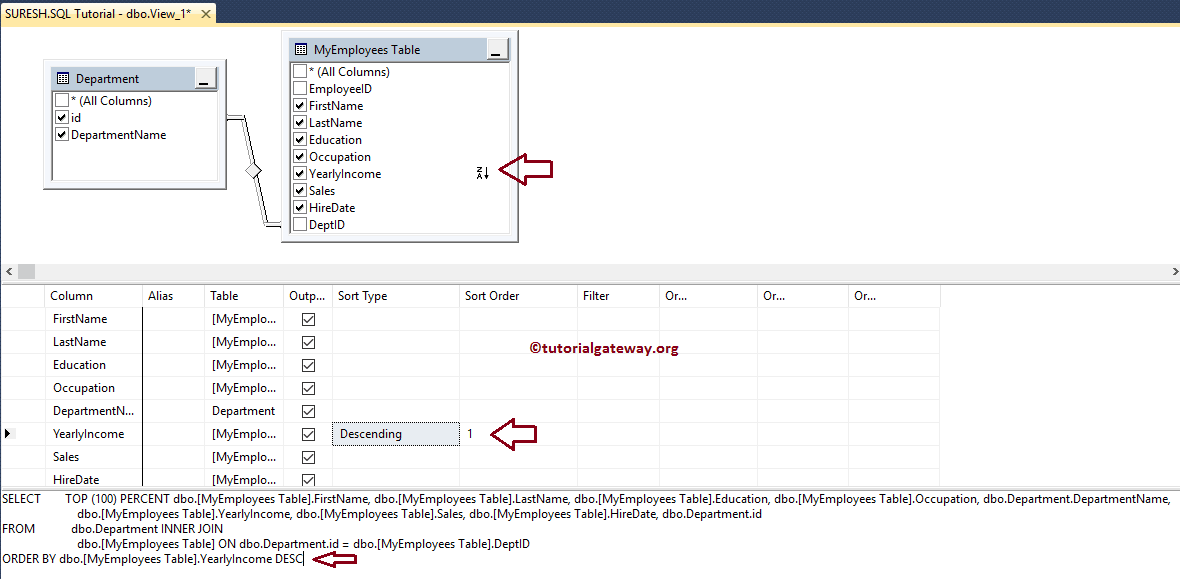
The final select query that we designed
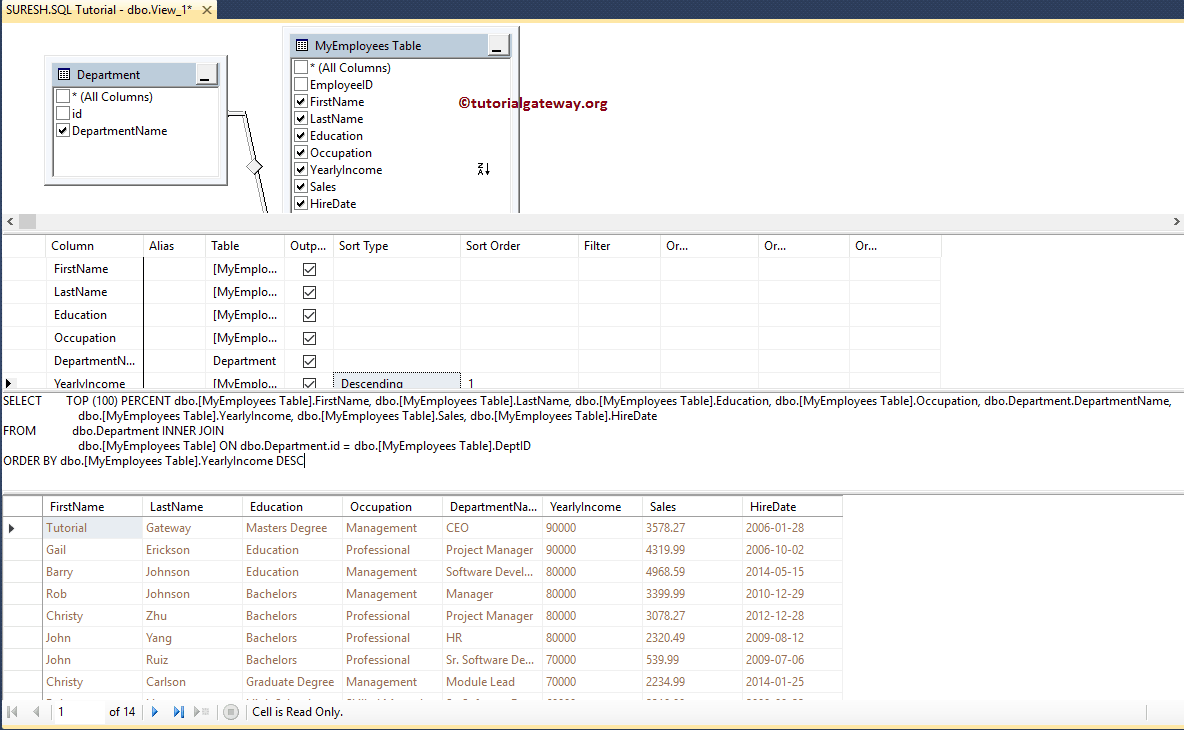
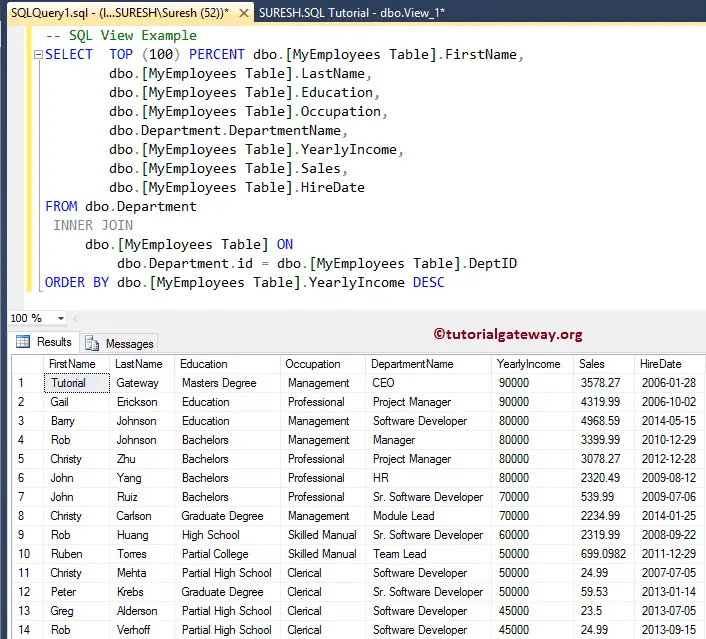
Let us execute this SQL Server views query we designed using the Management Studio and see the result.
SELECT TOP (100) PERCENT dbo.[MyEmployees Table].FirstName,
dbo.[MyEmployees Table].LastName,
dbo.[MyEmployees Table].Education,
dbo.[MyEmployees Table].Occupation,
dbo.Department.DepartmentName,
dbo.[MyEmployees Table].YearlyIncome,
dbo.[MyEmployees Table].Sales,
dbo.[MyEmployees Table].HireDate
FROM dbo.Department
INNER JOIN
dbo.[MyEmployees Table] ON
dbo.Department.id = dbo.[MyEmployees Table].DeptID
ORDER BY dbo.[MyEmployees Table].YearlyIncome DESC
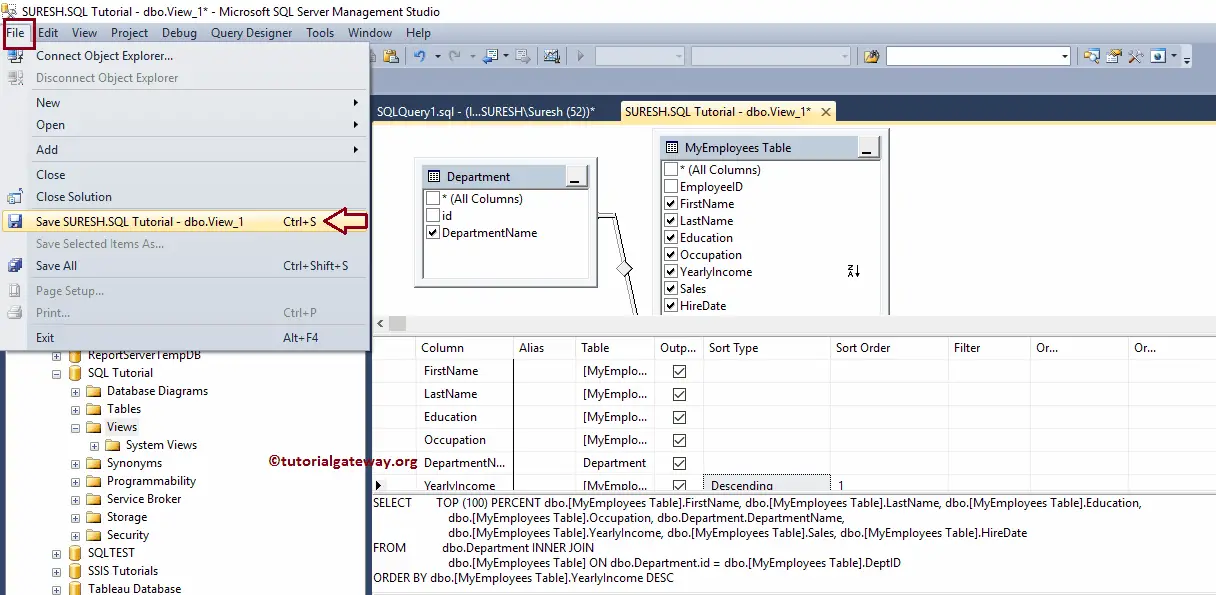
Next, go to File Menu and select the Save option to save the designed query.
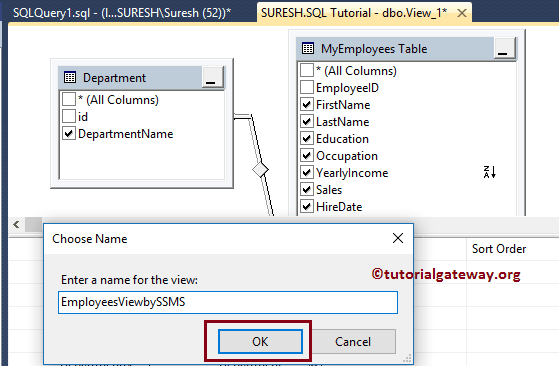
It will open the Choose name pop-up window to change the default name.
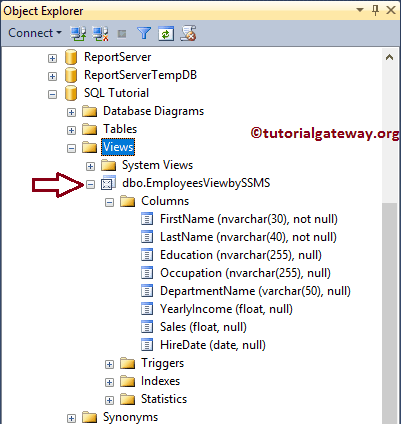
Expand the folder, see the created one, and expand it to see the Column names.
NOTE: Some clients only give access to Views and will not allow you to access their main database.
Rename Views in SQL Server
It allows you to use the built-in stored procedure sp_rename or the management studio to rename views.
Rename View using Management Studio
This example renames them using SSMS. And to rename it, Please navigate to the one you want to modify. And right-click on the name and select the Rename option.
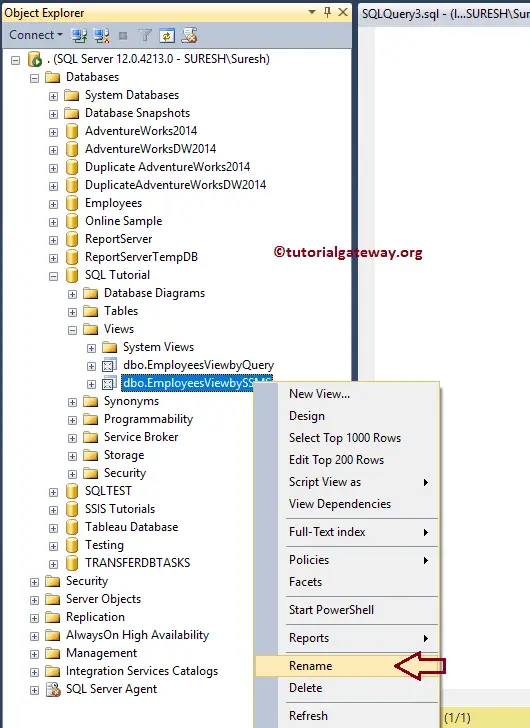
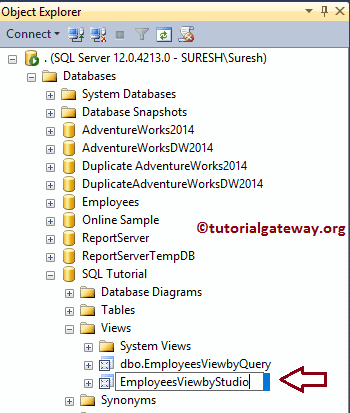
Once you click on the Rename option, SSMS allows us to rename them.
SQL Server Rename Views using SP_RENAME
We can use the SQL Server sp_rename stored procedure to rename views. The sp_rename syntax is:
SP_RENAME Old_Name, New_Name
Using the sp_rename stored procedure, you can rename the existing. To do so, click the New query and return the following query.
SP_RENAME EmployeesViewbyStudio, EmployeesVwName
Modify Views in SQL Server
The following examples help you understand the steps involved in modifying the Views. But first, let us see the limitations or restrictions to follow:
- Dependency Objects such as triggers or stored procedures will not affect by modification.
- You can use the ALTER statement on indexed ones because it will drop all indexes unconditionally.
Modify Views in SSMS
To modify in Management Studio, navigate to the one you want to change. Next, right-click on it and select the Design option.
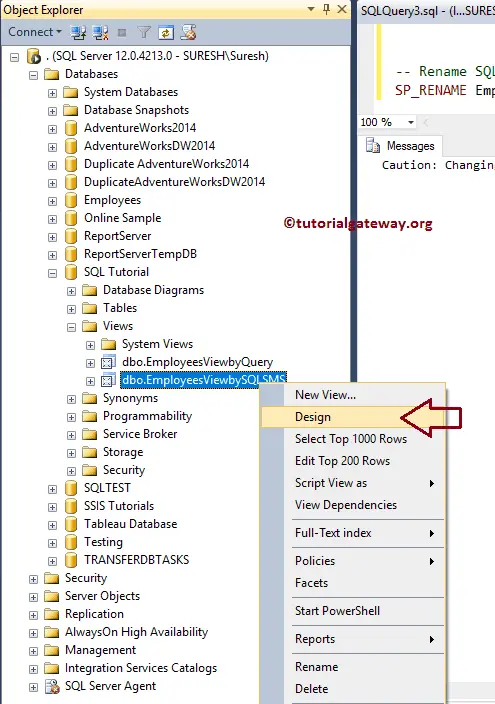
It opens a new design query window with existing tables and the relationship.
Here, we are using the Filter (WHERE Clause) to restrict the Employees whose Occupation = Professional, and we are using two columns in the ORDER BY Clause.
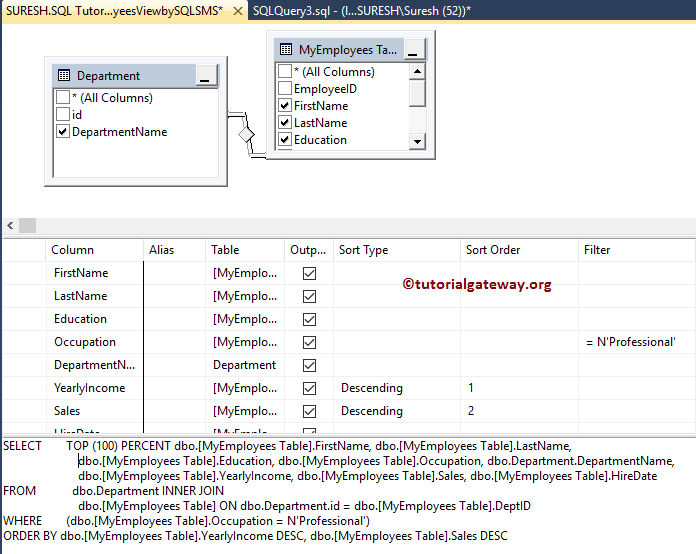
Let me select all the records from below to show the modified records.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[DepartmentName]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [dbo].[EmployeesViewbySQLSMS]
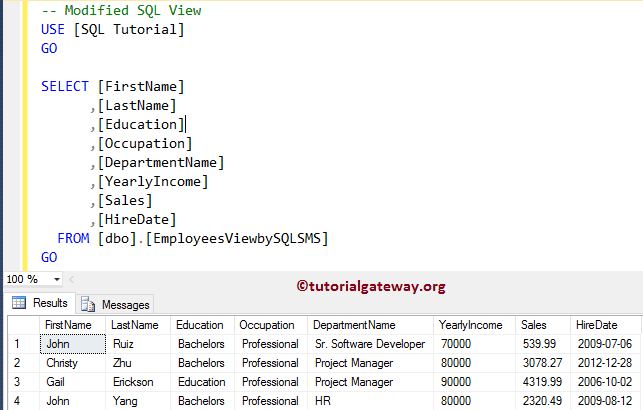
Alter View Statement to Modify
The SQL Server ALTER VIEW statement is an ideal way to modify existing views. To do so, click the new query and write the subsequent query.
ALTER VIEW [dbo].[EmployeesViewbySQLSMS]
AS
SELECT TOP 10 emp.FirstName,
emp.LastName,
emp.Education,
emp.Occupation,
Dept.DepartmentName,
emp.YearlyIncome,
emp.Sales
FROM dbo.Department AS Dept
INNER JOIN
dbo.[MyEmployees Table] AS emp ON
Dept.id = emp.DeptID
ORDER BY emp.YearlyIncome DESC,
emp.Sales DESC
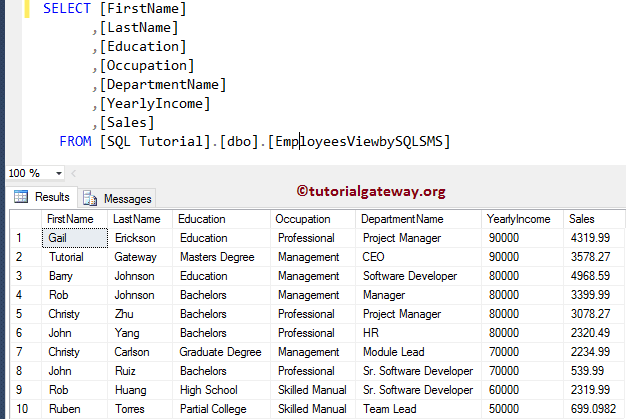
Let us see the Output.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[DepartmentName]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [EmployeesViewbySQLSMS]
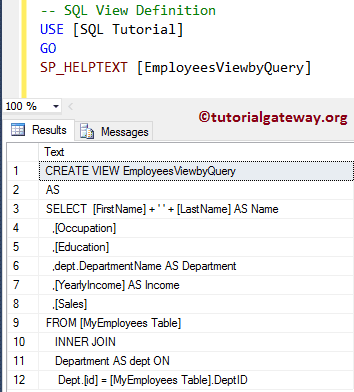
How to find the definition of a View?
Use the SQL Server sp_helptext stored procedure to get the definition of Views.
SP_HELPTEXT [EmployeesViewbyQuery]
Delete Views
The following examples show how to delete it.
- Deleting or Dropping a Table will not drop the dependent, so you have to explicitly use the SQL Server DROP VIEW statement to delete them.
- When you drop it, all the information (including the definition) will delete from the system catalog.
Delete Views using Management Studio
To delete using the Management Studio, right-click on the name and click the Delete option. For this demonstration, we want to delete the below one.
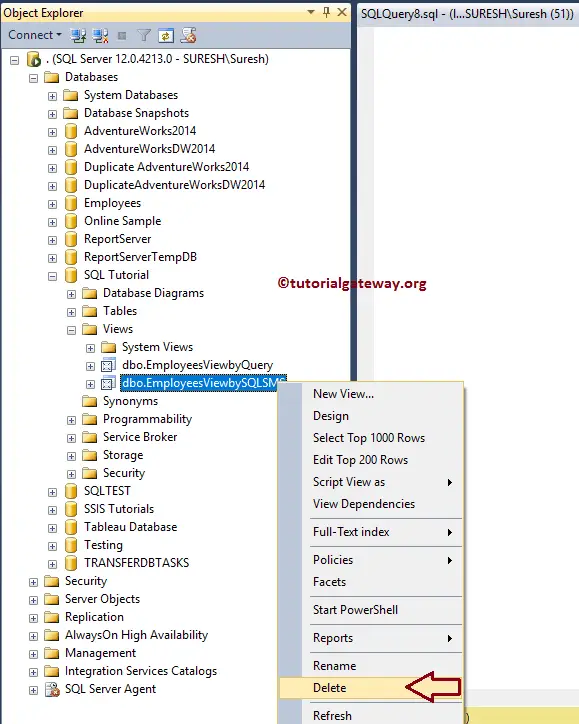
Selecting the delete option will open a Delete Object window. Next, click the Show Dependencies button to check the dependencies, then click OK to delete.
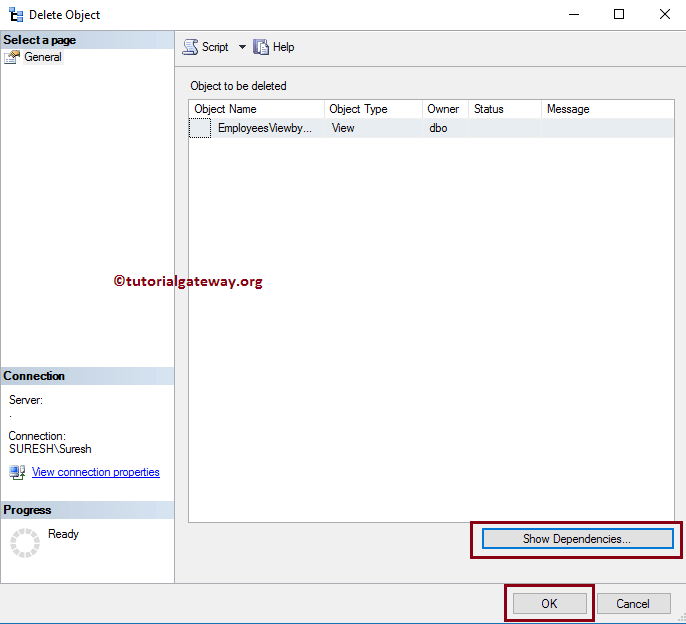
Delete or Drop Views using Query
Let me use the SQL Server DROP statement to delete Views.
DROP VIEW [dbo].[EmployeesVwbyQuery] GO
TIP: It is good practice to check whether it exists in the database or not using IF OBJECT_ID (N’VwName’, ‘V’) IS NOT NULL

Comments are closed.