The SQL WHERE Clause restricts the number of rows (or records) returned by the Select Statement. It means the SQL Server Select statement returns the records only If the condition specified after the Where keyword is TRUE.
SQL Where Clause example: For instance, we want to order shoes on the Amazon website. When we type shoes in the search bar, it will show thousands of shoes with different brand names and sizes. However, to select the required shoe, we have to use filters such as price range between 2000 to 2500, color = black, and brand name = Nike or Adidas.
Using the above filters will only display the shoes that match the above requirements, so we can select them easily. Let us see what happens internally (Query against the Amazon Database). It uses the SQL Where clause, and it will go something like this:
SELECT [Product Name], [Size], [Brand], [Price], [Discount]
FROM [Products_table]
WHERE ([Product Name] = 'Shoes') AND
(Brand = 'Nike' OR 'Adidas') AND
([Price] BETWEEN 2000 AND 2500)
SQL WHERE Clause Syntax
The Syntax of the SQL Server SELECT Statement and WHERE clause can be written as:
SELECT [Column Names] FROM [Source] WHERE [Conditions]
From the above syntax
- Columns: It allows us to choose the number of columns from the tables. It may be one or more.
- Source: One or more tables from the Database. JOINS are used to join multiple tables.
- Conditions: Here, we have to provide filters or conditions. If the condition is TRUE, then only the SELECT Statement returns the records.
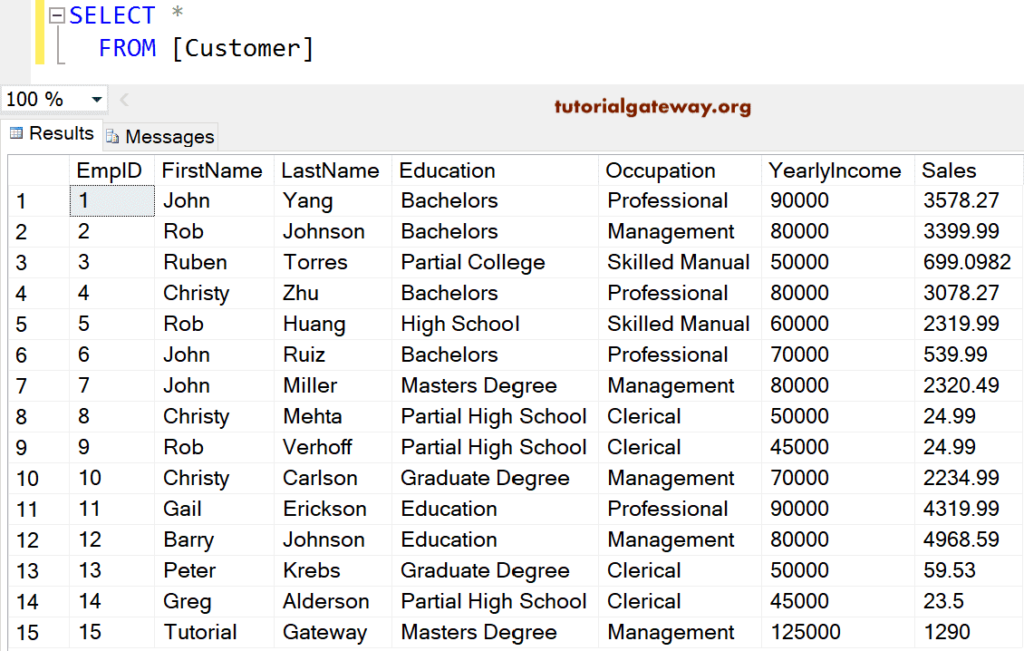
We use the below-shown data to explain the SQL Server WHERE Clause to filter the data before extracting it using the SELECT statement.
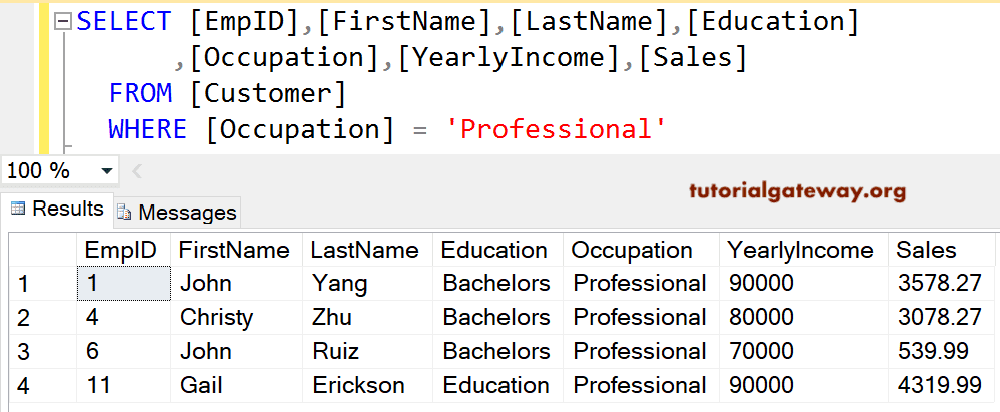
SQL WHERE Single Condition
Using a single condition inside the WHERE Clause.
SELECT [EmpID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Customer]
WHERE [Occupation] = 'Professional'
The above query will retrieve the mentioned records and return customers whose Occupation is exactly equal to Professional.
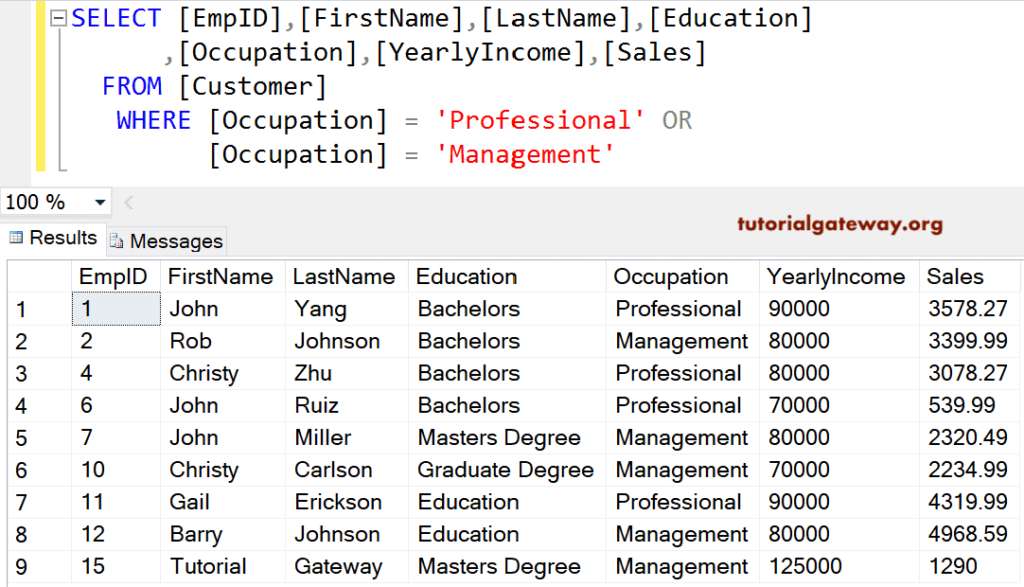
SQL Where Clause Multiple Conditions Example
This example uses Multiple Conditions in this SQL Where Clause. The below query returns all the Customer records whose occupation is equal to either Professional or Management.
SELECT [EmpID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Customer]
WHERE [Occupation] = 'Professional' OR
[Occupation] = 'Management'
General Expressions
Instead of testing conditions against Column Names, it allows us to test general conditions. For instance, the below condition checking 1 is exactly equal to 2, which is False. So the SELECT statement will not return any record in Server.
SELECT [EmpID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Customer]
WHERE 1 = 2
Let us change the SQL Where clause condition from (1 = 2) to (1 = 1) general expression. Here the condition is TRUE, so it is displaying all the records present in the Customers Table
SELECT [EmpID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Customer]
WHERE 1 = 1
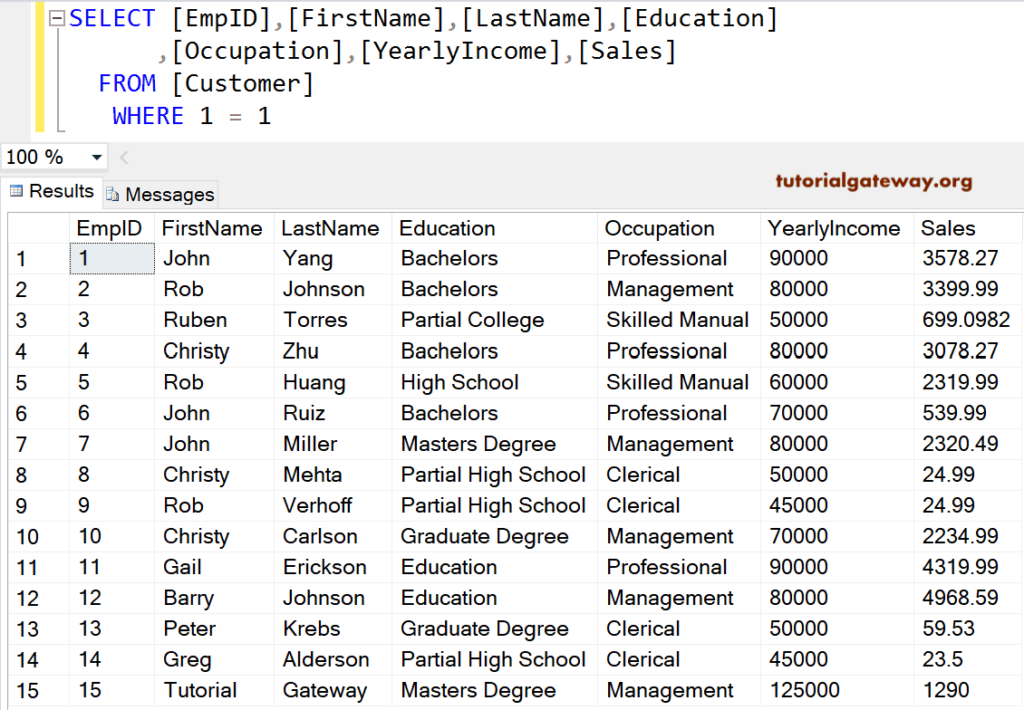
Do not use ALIAS Column Names in the condition. Because the condition will execute first, and then the SELECT statement will choose the Columns. So, the WHERE Clause does not understand the ALIAS Columns declared in the SELECT statement.
SQL Where Subquery condition
We can use Subqueries to check the column against the expression. Here, we use where and subquery to display the records whose yearly income is greater than or equal to Average Income. Here, we used AVG to find the average yearly income column.
SELECT [EmpID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Customer]
WHERE [YearlyIncome] >= (SELECT AVG([YearlyIncome])
FROM [Customer])
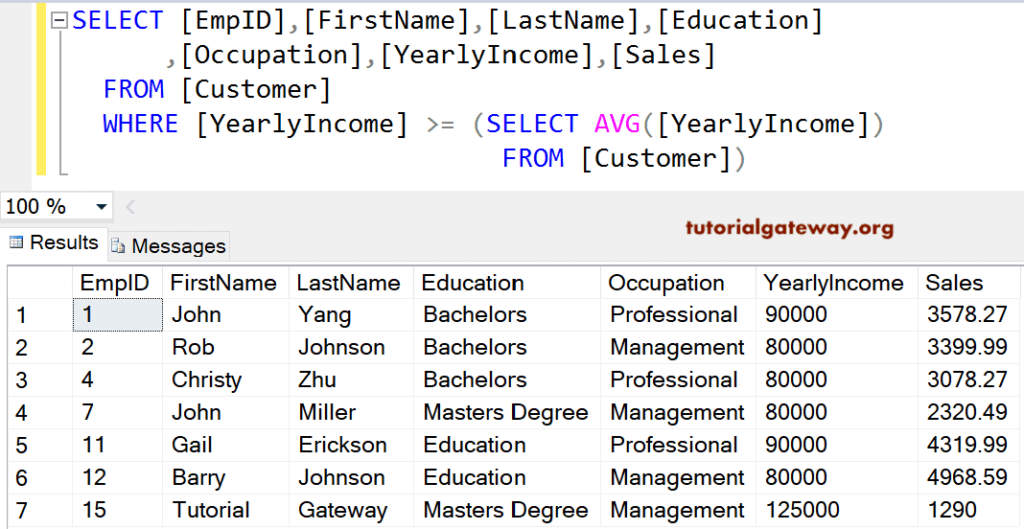
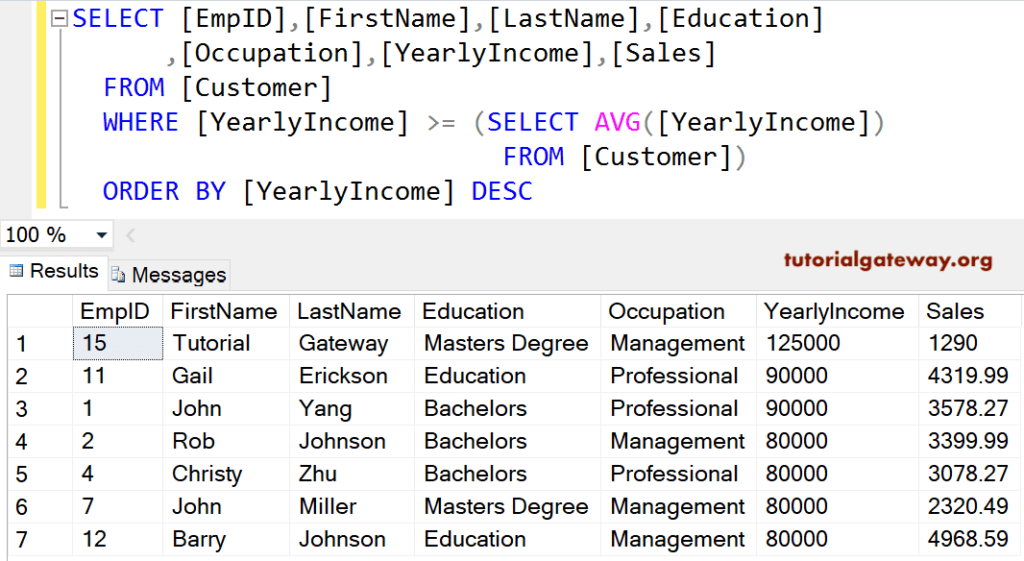
SQL Where Order By Clause
We can also use Where along with the Order By Clause. The Order By clause will sort those query results based on the income in descending order.
SELECT [EmpID]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Customer]
WHERE [YearlyIncome] >= (SELECT AVG([YearlyIncome])
FROM [Customer])
ORDER BY [YearlyIncome] DESC
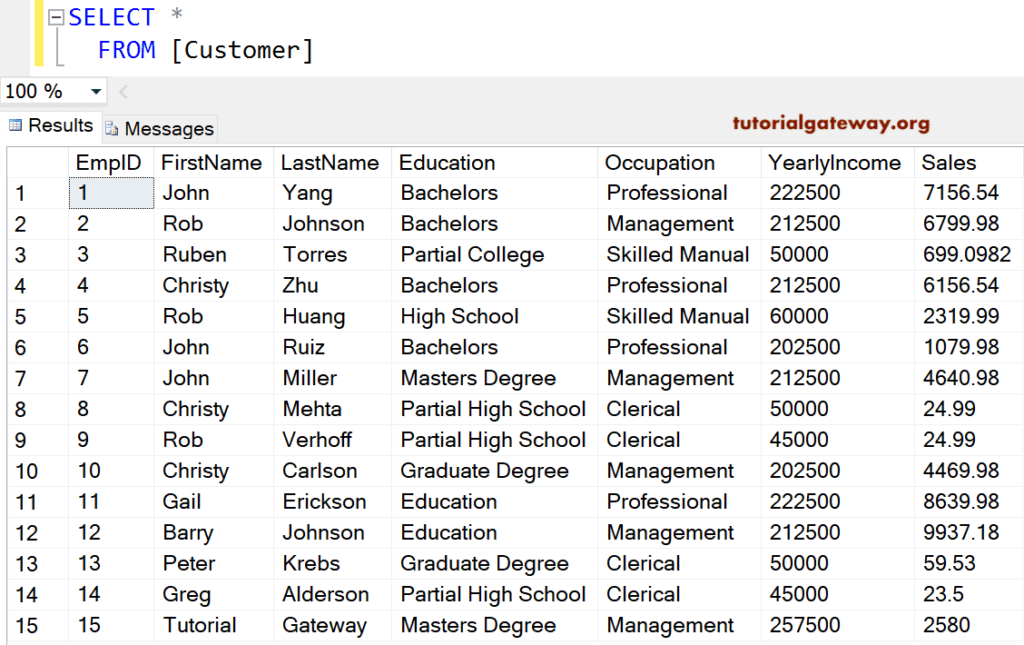
Update Example
This clause does not restrict the records selected by the Select Statement. It is useful, in fact, mandatory to use this inside an Update Statement.
The below SQL WHERE Update clause query adds 132500 to the Yearly income column and multiplies Sales by 2 for all the customers whose Occupation is either Management or professional
UPDATE [Customer]
SET [YearlyIncome] = [YearlyIncome] + 132500
,[Sales] = [Sales] * 2
FROM [Customer]
WHERE [Occupation] = 'Management' OR
[Occupation] = 'Professional'
Messages
--------
(9 row(s) affected)Now, let us see the Customer table to check whether we successfully updated the records or not.
Delete Example
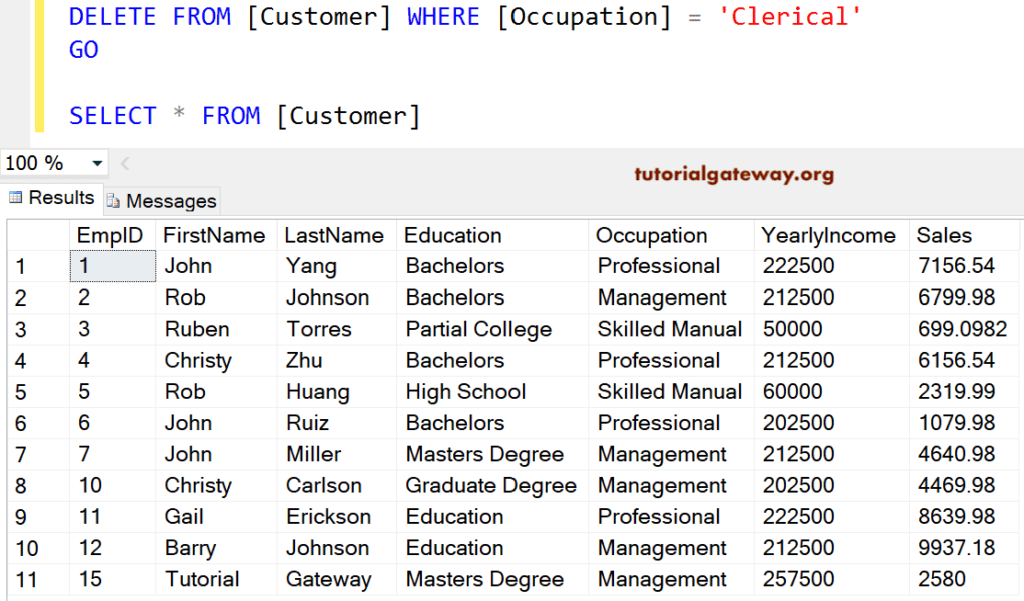
When we are deleting records, this will help us to restrict the number of records we want to delete. It is useful in Delete Statement.
The below SQL Where Delete query deletes all the customer records whose Occupation is Clerical
DELETE FROM [Customer] WHERE [Occupation] = 'Clerical' GO SELECT [EmpID], [FirstName], [LastName], [Education] ,[Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales] FROM [Customer]
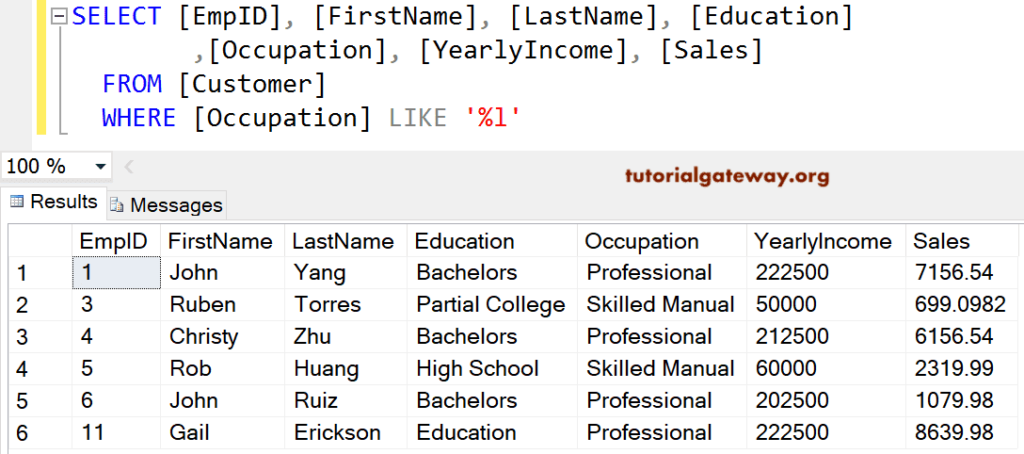
SQL Where Like Example
We can use Like Operator along with this to perform Wildcard searches against the Table. The below code writes all the records from the customer table whose Occupation ends with l.
SELECT [EmpID], [FirstName], [LastName], [Education] ,[Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales] FROM [Customer] WHERE [Occupation] LIKE '%l'