The SQL Server SELECT statement retrieves data from one or more database tables. In this article, we will show how to write a SQL SELECT with an example, and the syntax of the statement is:
SELECT [Column Names] FROM Source
Columns: Choose one or more numbers from the tables.
The SQL SELECT Statement returns all the records present in the table. If you want to restrict the Rows, please use the WHERE or TOP Clause. And to pick data from multiple database tables, you can use Joins.
We use this data to explain the Select Statement.
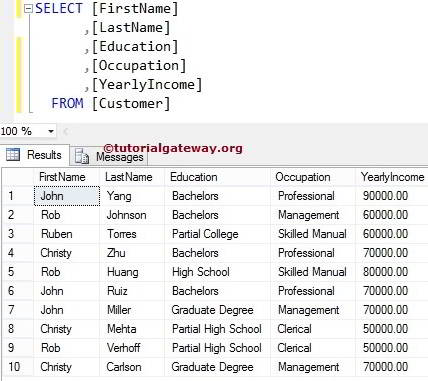
SQL Server Select All Columns Example
In this SQL select statement example, we choose all the Columns present in the customer’s table using an asterisk (*). In this statement, * is the shortcut to represent all the available columns in the source tables.
SELECT * FROM [Customer]
Problems with SQL SELECT * FROM Statement
- The Select * from statement will retrieve all the columns from the Table. Most of the time, we do not require all the columns in a table. So, Please avoid using * for choosing all the column names.
- The select * from will pick the columns in the default order. Sometimes we may need to change the order of the cols while displaying them.
- If there are any changes made in the underlying table (Reordering Columns, Removing or Adding them) will not reflect the Views created using SELECT *.
Please don’t use the SQL SELECT * FROM statement in real-time even to retrieve all the cols present in a table. The second approach, Placing all the column names after the SELECT keyword. For instance, the above query is the same as:
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
FROM [Customer]
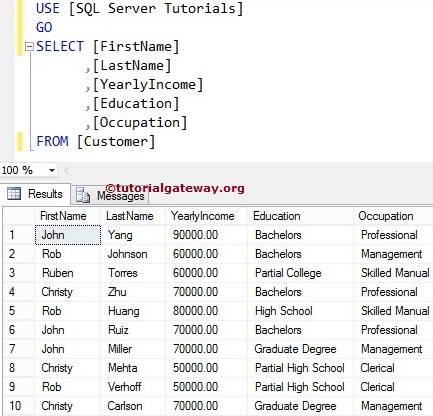
SQL SELECT few Columns statement
In real-time, placing all the columns in a table is not the case. So, you can restrict them in this statement. Because there will be some columns such as Barcodes, rowguid, Photos, etc., which may not require.
For this, this SQL statement allows us to choose a few or any specific columns from the tables by placing the required Column Names followed by a SELECT keyword.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
FROM [Customer]
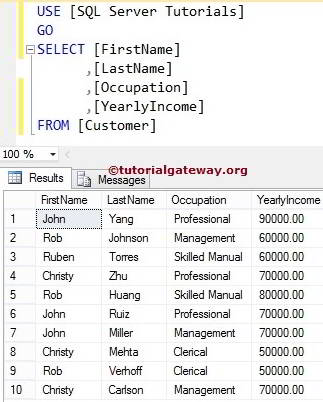
NOTE: If we forget the comma between the columns, then SQL Server assumes the second column as the Alias name for the first one. So, Please be careful.
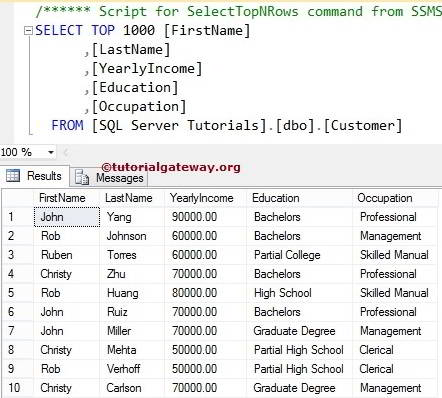
Select from Management Studio Example
Within the Management Studio, Navigate to the required Database and then pick the required Table. Right Click on the Table will open the Context Menu with different options.
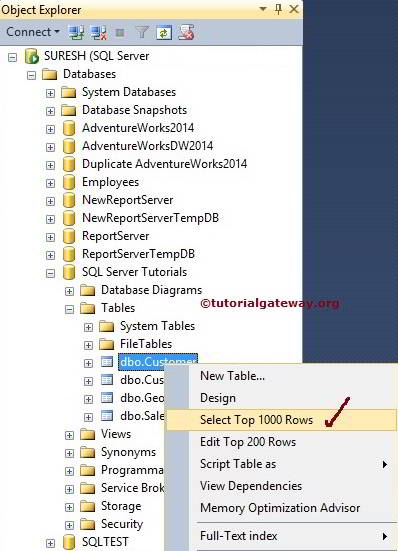
From the above context menu, We have to choose the Top 1000 Rows Option. This option generates the SQL SELECT Statement for us. To see all the records, remove the TOP Clause (Top 1000) from the above statement.