This SQL Delete Statement deletes one or more existing records from a table or a view. The syntax of the SQL Server delete statement is
DELETE FROM [Table_Name] WHERE Condition
Condition: Provide the filters or conditions. If the condition is TRUE, then only the SQL Server Statement will delete the records. We use this table to perform the different operation types of delete is
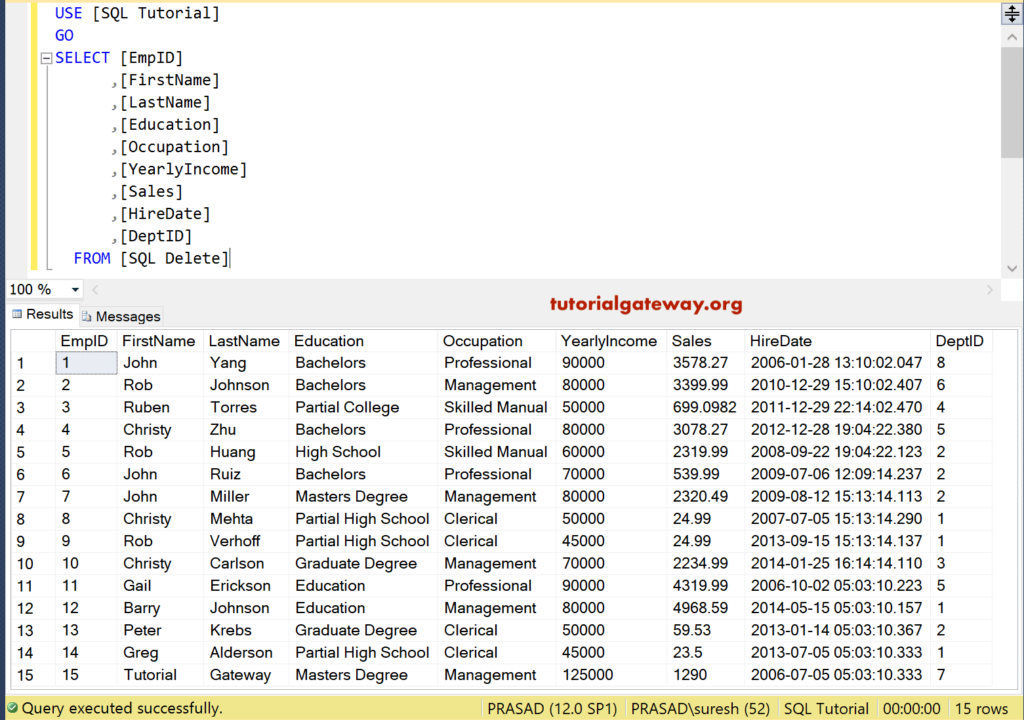
SQL Server Delete Single record
We are going to delete a single record from the Table. For this, we are using the Where Clause to restrict this SQL Server delete Statement to eliminate a single record. If you omit the where clause, it will delete all rows in a table.
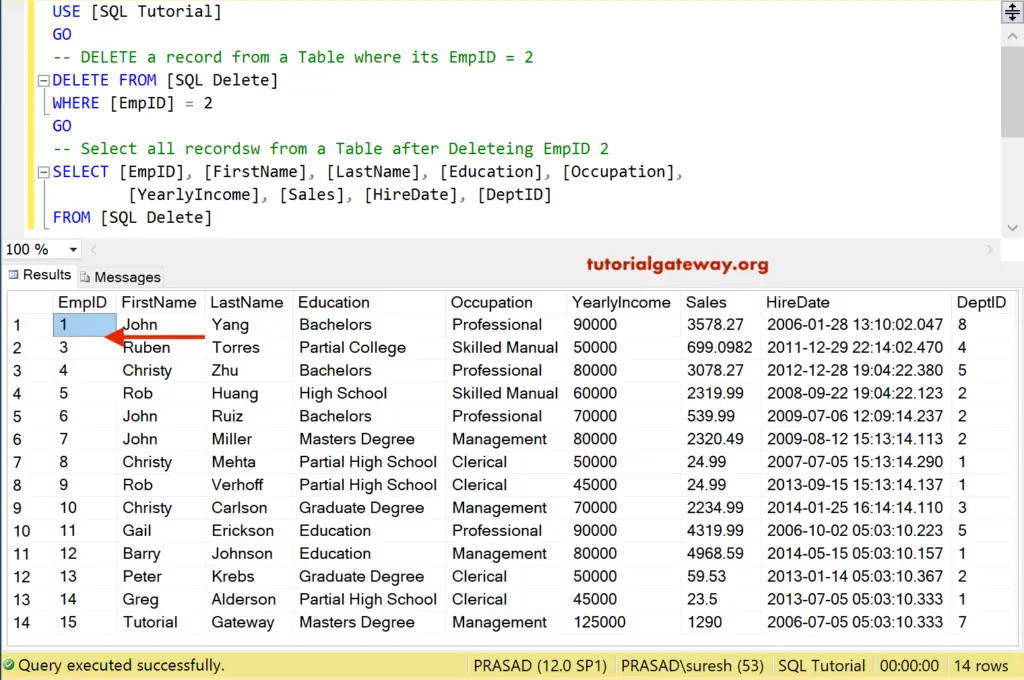
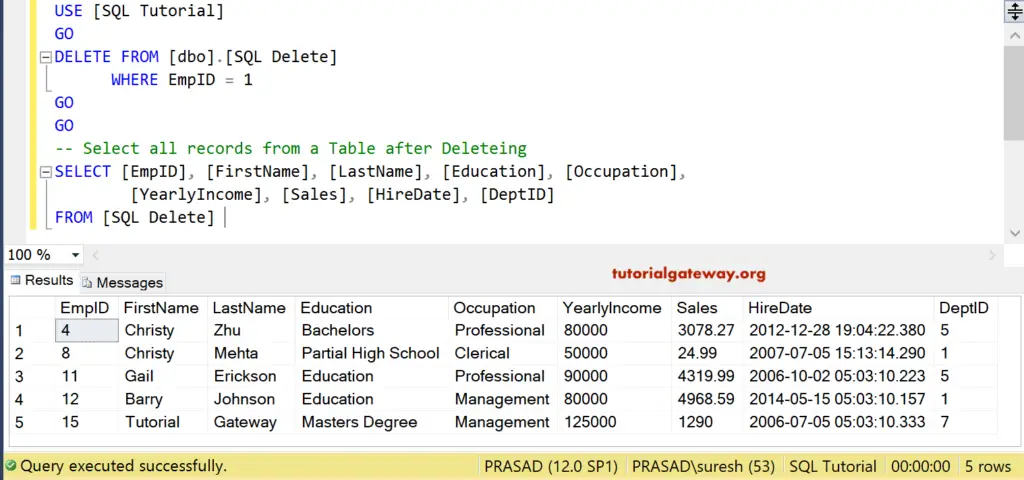
DELETE FROM [SQLDelete] WHERE [EmpID] = 2
It eliminated the employee record, whose ID value = 103
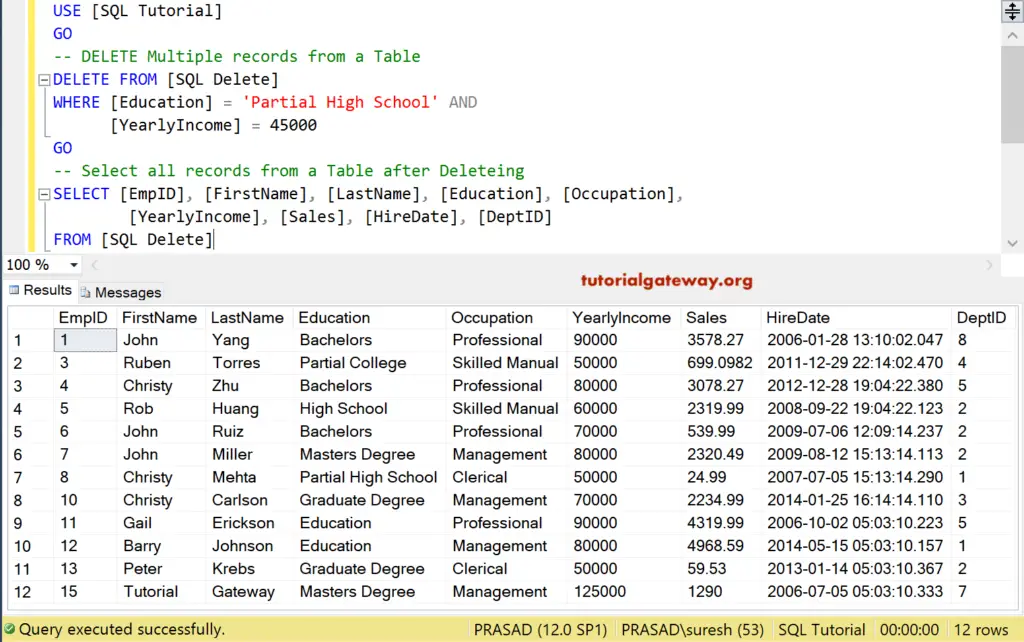
SQL Delete Multiple records
In this Multiple records example, We use AND Operator in the Where Clause to check multiple conditions before it starts removing a record.
DELETE FROM [SQLDelete]
WHERE [Education] = 'Partial High School' AND
[YearlyIncome] = 45000
Remove all the records whose Education is Partial High School and whose Yearly Income is 45000.
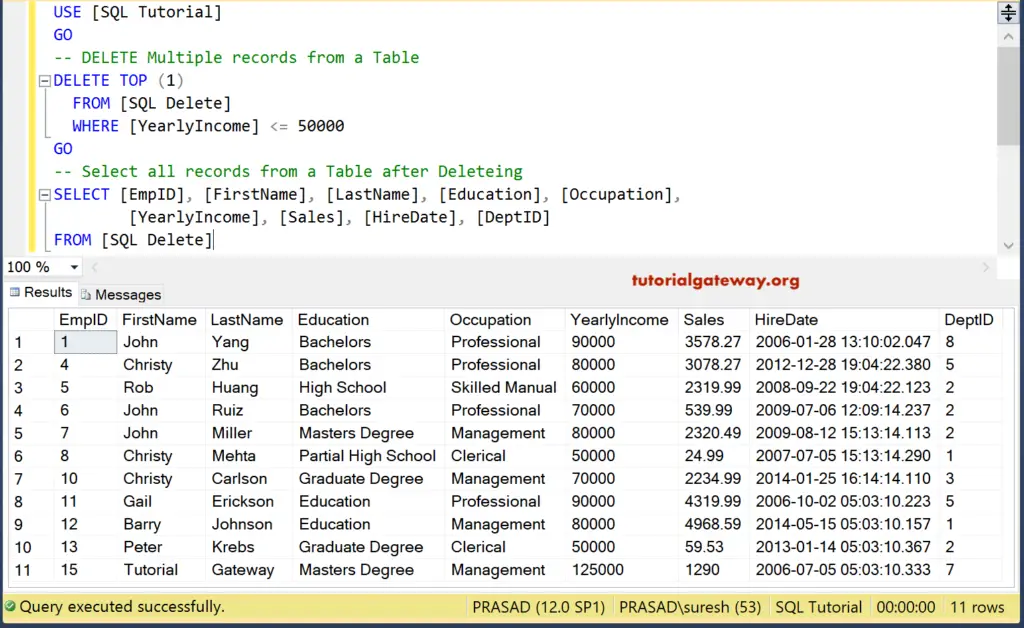
SQL Delete Top Clause
In this SQL Server delete statement example, we remove the first record from the table whose yearly income is less than or equal to 5000. For this Server example, we are using Select TOP.
DELETE TOP (1) FROM [SQLDelete] WHERE [YearlyIncome] <= 50000
It will check for the records whose yearly income is less than or equal to 5000, and then TOP Clause will select the First record.
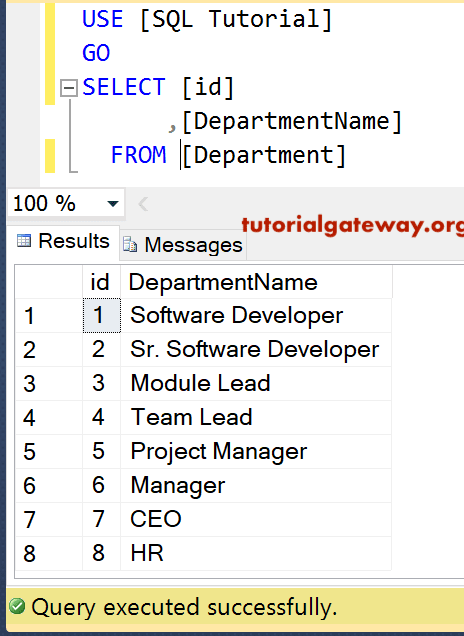
Let me remove the records from the Table based on the Department name in another table. For this, we are using Inner Join along with the delete statement to join two tables. The data inside the Department table.
CODE
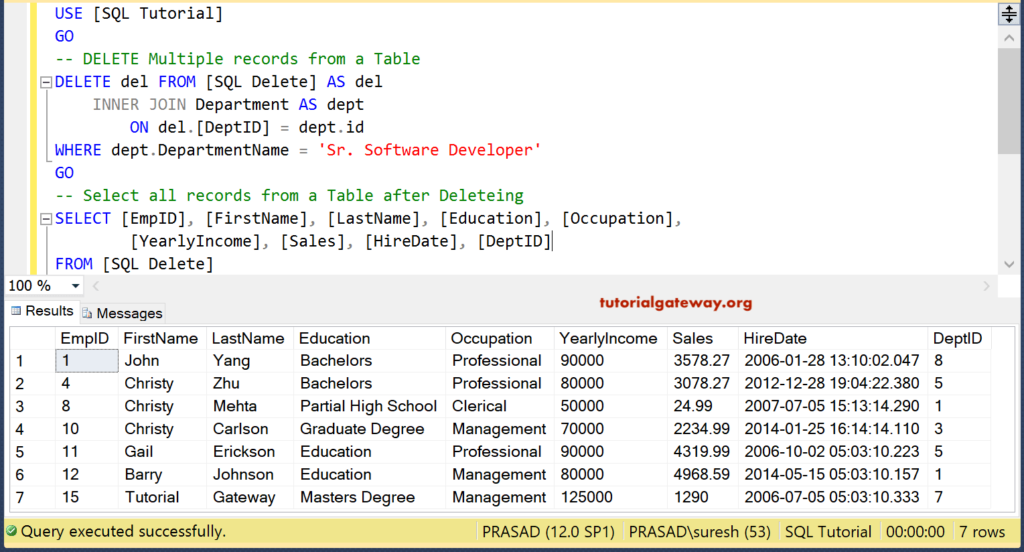
DELETE del
FROM [SQLDelete] AS del
INNER JOIN
Department AS dept ON
del.[DeptID] = dept.id
WHERE dept.DepartmentName = 'Sr. Software Developer'
It removed all the records whose department name is Sr. Software Developer. Remember, the Department name is coming from the Department Table.
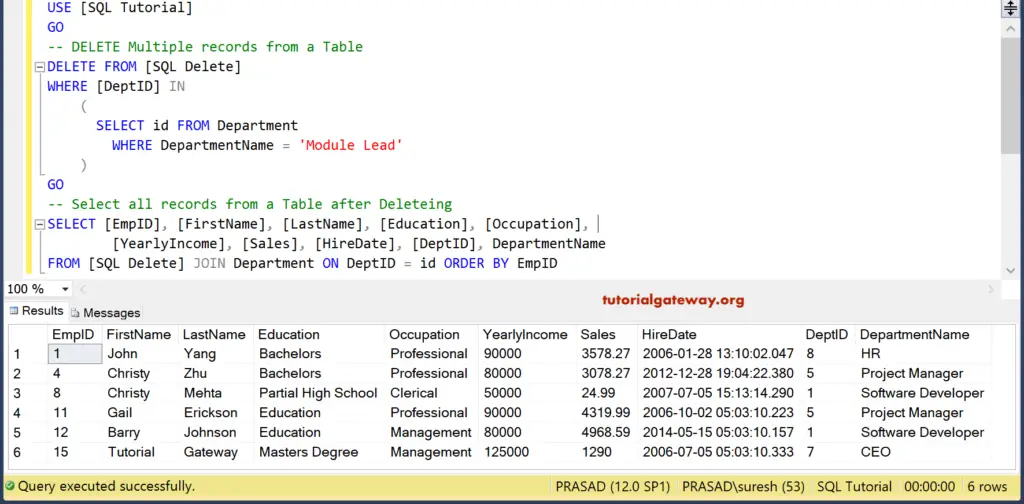
Delete Subquery
In this SQL Server delete statement with a subquery example, let us take out the rows from the Table based on the Department name in another table. For this, we are using Subquery.
DELETE FROM [SQLDelete]
WHERE [DeptID] IN
(
SELECT id FROM Department
WHERE DepartmentName = 'Module Lead'
)
Eliminating all the records from the table whose department name is Module Lead.
Removing All Columns
In this example, We are going to take out all the Columns.
DELETE FROM [SQLDelete]
NOTE: If you accidentally forgot the Where Clause, then you will end up removing all the records from Source.
SQL Server Delete Statement Using Management Studio
If you can access the Management Studio in SQL Server, use Intellisense to write this Statement. To do so, Right Click on the Table -> Select Script Table as -> DeleteTo -> New Query Editor Window
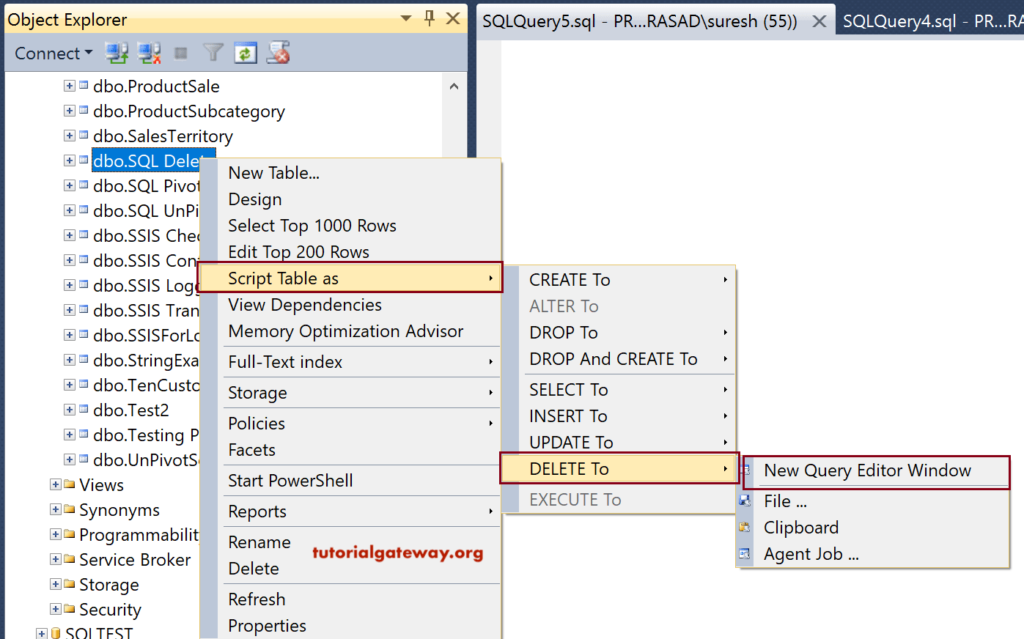
It will generate the statement for the selected table, and the Code is
Let us add the below-shown Search Condition
SQL Delete Stored Procedure
Let us see how to use this Statement inside a Stored procedure. Here, we are removing records whose Occupation equals Clerical or whose yearly income is less than or equal to 60000.
IF OBJECT_ID ( 'sp_DeleteEmpRecords', 'P' ) IS NOT NULL
DROP PROCEDURE sp_DeleteEmpRecords;
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_DeleteEmpRecords
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DELETE FROM [SQLDelete]
WHERE Occupation = 'Clerical' OR
YearlyIncome <= 60000
END
GO
Messages
-------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me use EXEC Command to execute the stored procedure
EXEC dbo.sp_DeleteEmpRecords GO
Messages
-------
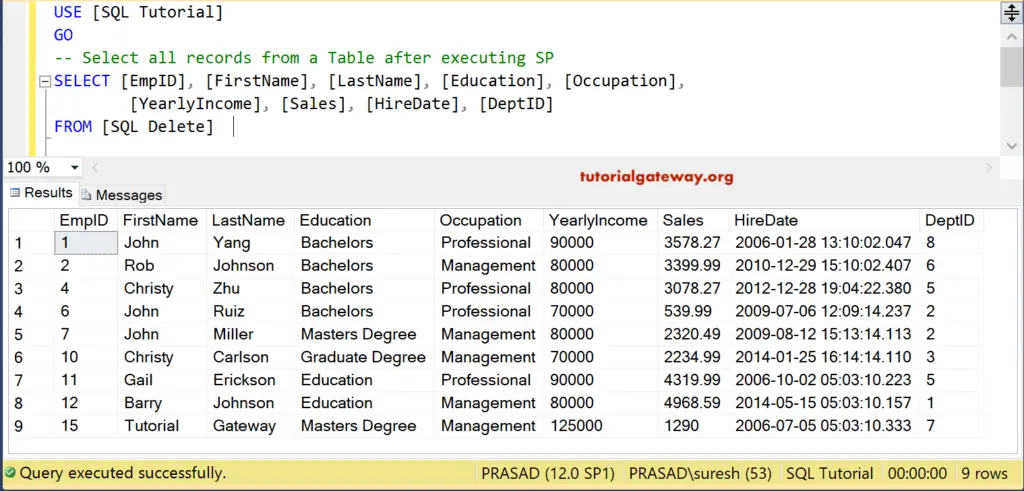
Command(s) completed successfully.Now, let us see whether the execution of the stored procedure cleared the rows in our table or not
-- Select all records from a Table after executing SP SELECT [EmpID], [FirstName], [LastName], [Education], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales], [HireDate], [DeptID] FROM [SQLDelete]
Between example
This SQL Delete Statement example uses the BETWEEN Operator to remove the records between two dates.
DELETE FROM [SQLDelete] WHERE [HireDate] BETWEEN '2016-01-27- AND '2007-01-28'
Messages
-------
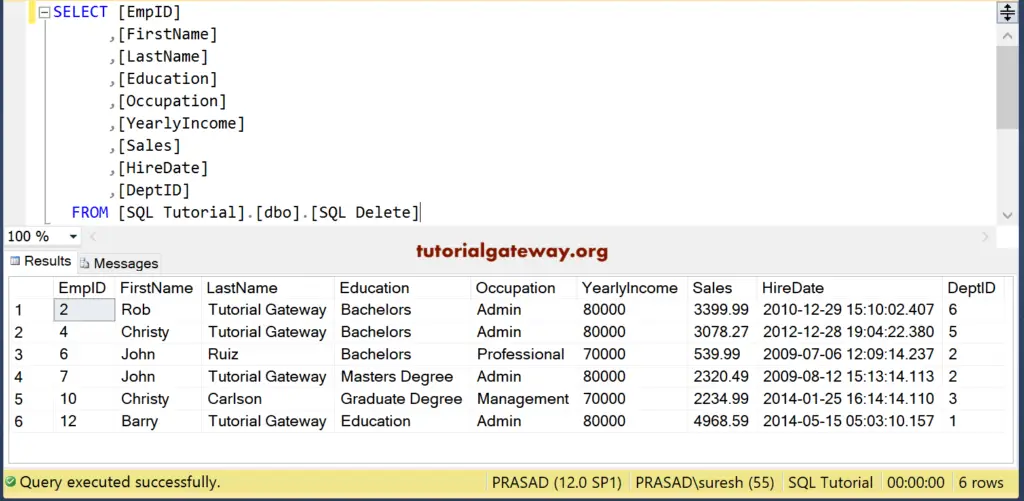
(3 row(s) affected)The above query will remove all the records whose Hire date is between 2006-01-27 and 2007-01-28
SQL Delete If Exists example
While removing a record from a table, it is always a good practice to check whether the records exist or not. Here, we are going to use the EXISTS Operator to check the records in the sd Table against the department table. If they exist and their last name is ‘Tutorial Gateway’, then remove that record.
DELETE FROM [SQLDelete] as sd
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT * FROM Department
WHERE sd.DeptID = Department.id
AND sd.LastName = 'Tutorial Gateway'
Messages
-------
(4 row(s) affected)and the remaining data view is
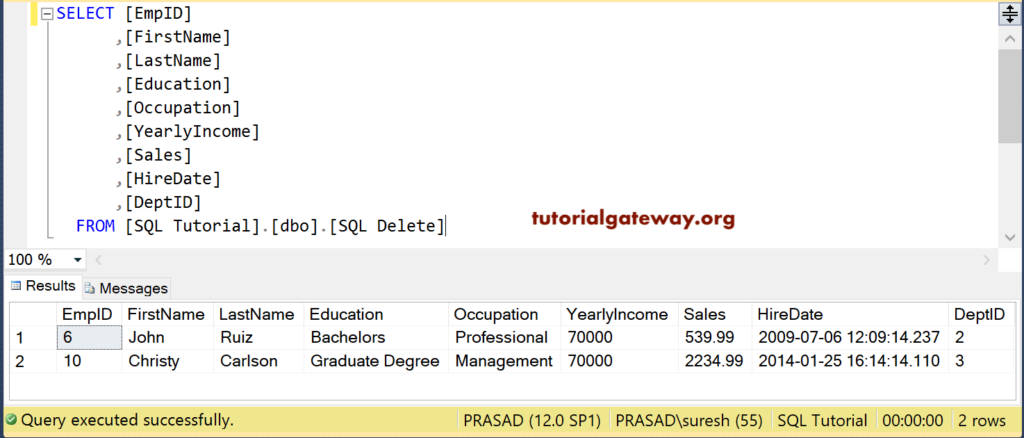
SQL Delete IS Null Statement example
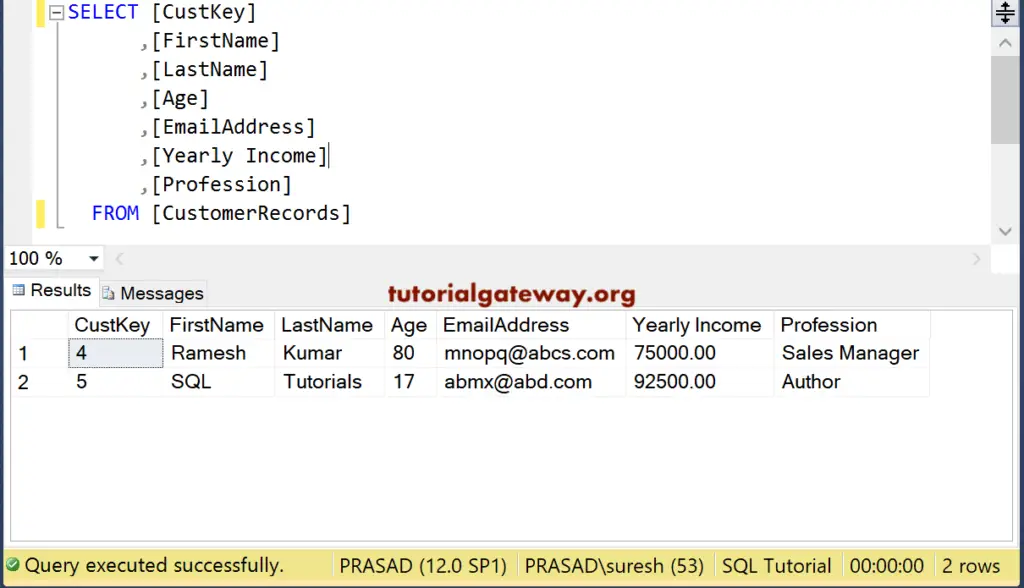
The data that we used for this Is Null demonstrating is
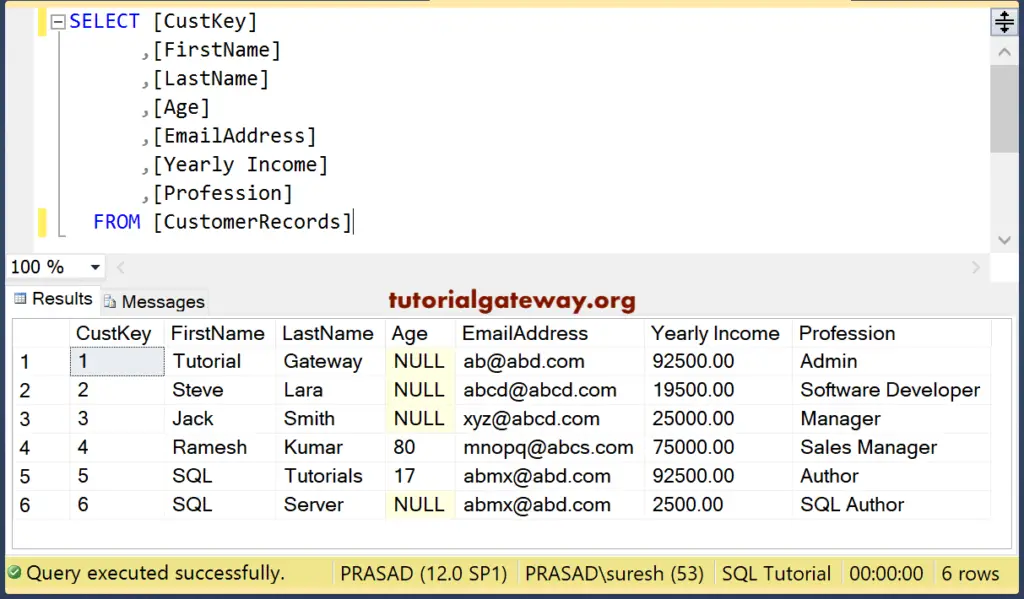
In this example, we are going to remove all the employees whose Age is NULL. For this, we used the IS NULL operator.
DELETE FROM [CustomerRecords] WHERE [Age] IS NULL
Messages
-------
(4 row(s) affected)and the remaining data is