The SQL Server SELECT INTO statement is useful to insert the data into tables, but before that, first, it creates a new table. Then this SQL SELECT INTO inserts the chosen rows by the Select Statement into that new table.
If we haven’t created the destination table, then the SQL Server Select Into statement can be handy to insert the data into the destination table. If you have an existing table, then use Insert Into.
SQL Select Into Syntax
The Syntax of the SQL Server SELECT INTO Statement is as shown below:
SELECT [Column Names] INTO [New_Table] FROM Source WHERE Condition --This is optional
- Columns: It allows us to choose the number of columns to Select from the tables. It may be one or more.
- New_Table: Please specify the fully qualified Unique name for SQL Server.
- Source: One or more tables are present in the Database. Use JOINS to join multiple.
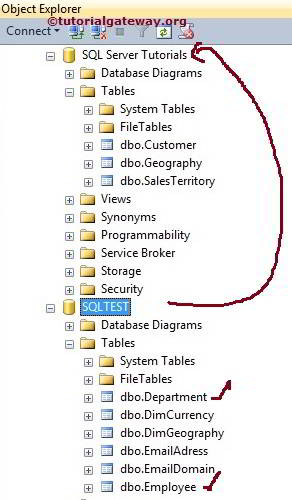
The screenshot below shows that We don’t have any Department or Employee table in the tutorials database. So our task is to Select the Data present in that table from the TEST Database and insert it into Tutorials Database using SQL SELECT INTO Statement.
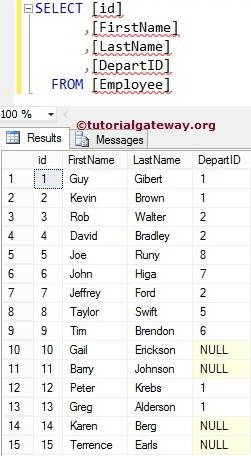
Data inside the Employee is
Data inside the Department Table is
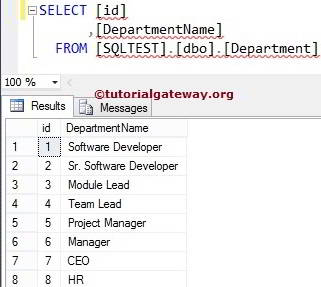
SQL SELECT INTO Insert All Columns
Here, we have chosen all the Columns present in the Department and inserted them into the Database.
SELECT [id]
,[DepartmentName]
INTO [SQLServer Tutorials].[dbo].[Department]
FROM [SQLTEST].[dbo].[Department]
OR We can also use the asterisk (*), and the sql select * into statement as well. But it is not good practice to use an asterisk, so always provide the column names.
SELECT * INTO [SQLServer Tutorials].[dbo].[Department] FROM [SQLTEST].[dbo].[Department]
The above query creates a new [Department] and inserts all the records from the source data. The Execution Message:
Messages
-------
(8 rows(s) affected)Let us see whether the table creates data in the destination database or not.
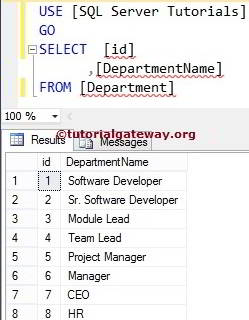
In this SQL Server Select Into example, We select a few Columns present in the Employee and insert them into Tutorials Database. Here, we restrict the rows as well using the WHERE Clause.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[DepartID]
INTO [SQLServer Tutorials].[dbo].[Employee]
FROM [SQLTEST].[dbo].[Employee]
WHERE [DepartID] = 1
The above query creates a new table called [Employee] and inserts [FirstName], [LastName], and [DepartID] columns from the source data, where the [DepartID] value is equal to 1.
Messages
-------
(4 rows(s) affected)Let’s see whether the table was created with data in the target database or not.
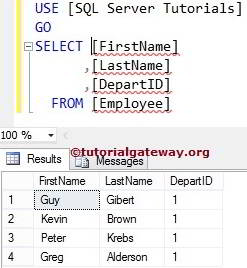
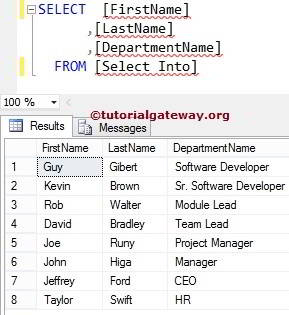
SQL SELECT INTO Insert Data from Multiple Tables
This example uses Columns present in both the Employee and Department. Next, insert them into Tutorials Database.
Here, we use the INNER JOIN for joining the two tables using the id column.
SELECT EMP.[FirstName]
,EMP.[LastName]
,DEPT.[DepartmentName]
INTO [SQLServer Tutorials].[dbo].[Select Into]
FROM [SQLTEST].[dbo].[Employee] EMP
INNER JOIN
[SQLTEST].[dbo].[Department] DEPT ON
EMP.id = DEPT.id
Messages
-------
(8 rows(s) affected)Let us see whether the data in the destination database is created or not.