A database is a storage location where we can store our business data. The database uses tables to store our information in a normalized way. So by creating a database in SQL Server, We can easily Select, Update and Delete the business data.
Let us see how to Create a Database in SQL Server, Rename, and Delete DB with an example of each.
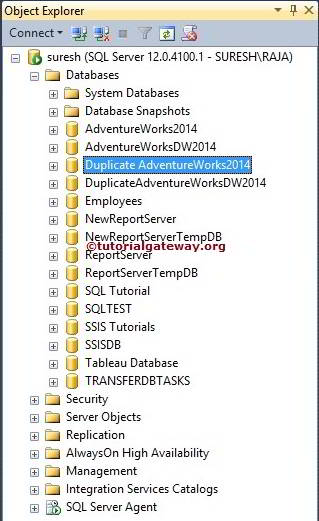
Before we start creating a new database, Let us see the list of available ones in our SQL Server. The list of available DBS in the current instance is.
SQL Create Database syntax
The syntax for creating a Database in SQL Server is shown below.
CREATE DATABASE DName
How to Create Database in SQL Server Example
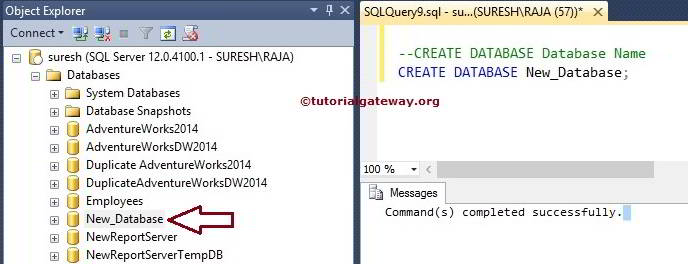
In this example, we create a new one called New_Database. So, Replace the DName with New_Database in the Server query window.
- Guide to Attach and Detach Database articles to copy the MDF and LDF files from one computer to another.
CREATE DATABASE New_Database;
Click on the Execute button to execute the command.
The Command is executed successfully, and you can see the New_Database in our object explorer. If you didn’t find the newly created database in SQL Server Object Explorer, Please click the refresh button.
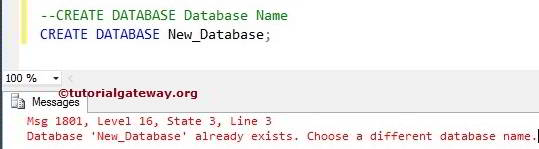
Let us see, what will happen when we execute the same Create Database command again. It is throwing an error saying: New_database already exists. Choose a different name.
How to Check Whether Database name exists or Not?
In an organization, we may or may not have the privilege of knowing the available databases. So, it is always advisable to check whether the name already exists or not. This can be done in two ways:
The following SQL Server statement will only execute Create Database Statement if the New_database is not available in the system.
IF NOT EXISTS
(
SELECT name FROM master.dbo.sysdatabases
WHERE name = N'New_Database'
)
CREATE DATABASE [New_Database]
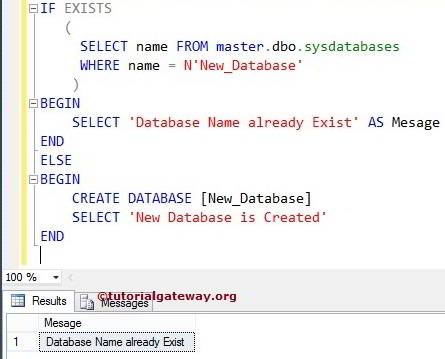
We just replaced the If Not Exists with If Exists and added a select statement to display the message. The steps involved in the Following statement are:
- The Select Statement will check for the DB name New_database in the system.
- If the New_database already exists, then the following query will display a message saying DB already exists.
- If the DB does not exist, then only the following else block code will be executed. It means the SQL Server Create database command only executes if the New_database is not available in a system DB
IF EXISTS
(
SELECT name FROM master.dbo.sysdatabases
WHERE name = N'New_Database'
)
BEGIN
SELECT 'Database Name already Exist' AS Message
END
ELSE
BEGIN
CREATE DATABASE [New_Database]
SELECT 'New DB is Stored'
END
How to Create Database in SQL Server Management Studio?
In order to create a new database, first, open the SQL Server Management Studio. Right-click on the below-shown folder and select the New .. option from the context menu.
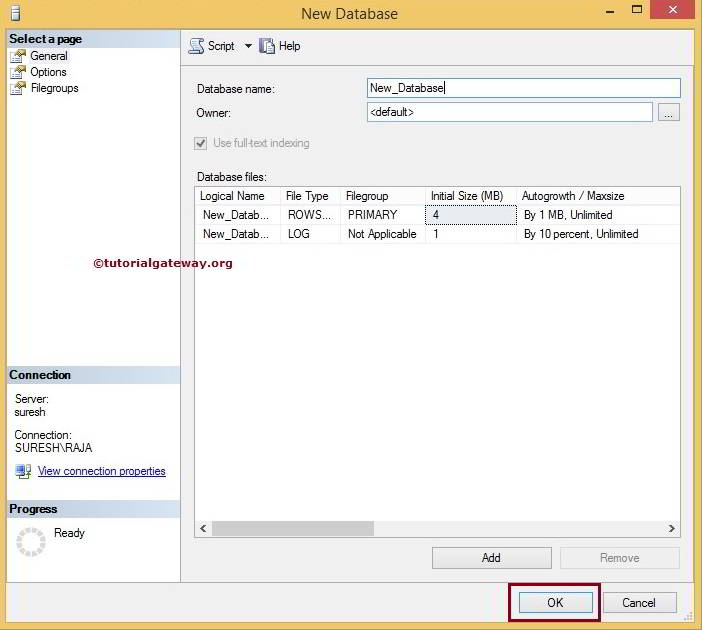
Once you select the option, the following window will be opened. Here we left Owner as default and DB name as New_database as shown below. Click OK to create a new database in SQL Server.
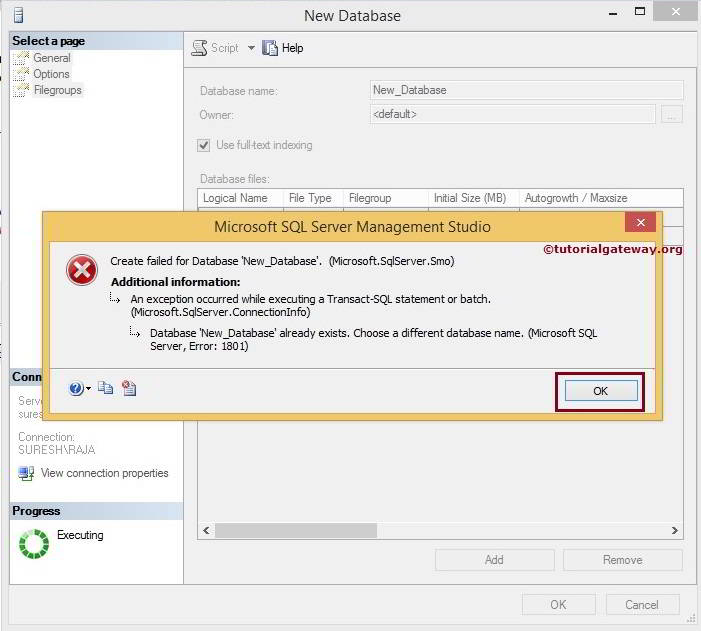
Let us see what will happen when we create a Database in SQL Server with an existing name. As you can observe that it is throwing an error
How to Delete Database in SQL Server?
To Delete a database, we can simply use the following SQL Server syntax, and the syntax for Drop is:
DROP DATABASE [DName]
In this example, we are going to delete New_Database. So, you have to replace the [DName] with the required name. Therefore, within the query window, Please write the following Drop Database query.
Let us see, What will happen when we execute the same Drop command once again:
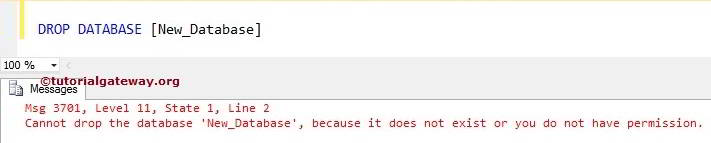
The above screenshot shows that it is throwing an error saying: It doesn’t exist.
A better approach is to check whether the name exists or not. Because sometimes, your colleagues or team leader may delete the DB you are trying to delete.
IF EXISTS
(
SELECT name FROM master.dbo.sysdatabases
WHERE name = N'New_Database'
)
DROP DATABASE [New_Database]
Messages
-------
Command(s) completed successfully.The select statement inside the If exists block will check whether the DB name New_database is in the system. If True (DB exists), then only the next DROP statement will execute. Otherwise, it will skip and will not perform the drop.
How to Rename Database in SQL Server?
To rename the database in the SQL server, we can simply use the system stored procedure sp_renamed, and the syntax is:
SP_RENAMEDB [Old Name],[New Name]
In this example, we rename New_Dt with New_Db. So, within the query window, Please write the following query.
SP_RENAMEDB [New_Dt],[New_Db]
Messages
-------
The name 'New_Db' has been set.Rename the Database along with the Files
This section shows you how to Rename the Database in Sql Server along with Files (MDF and LDF). For this SQL Server Rename Database demonstration, we created a database OldNameDB.
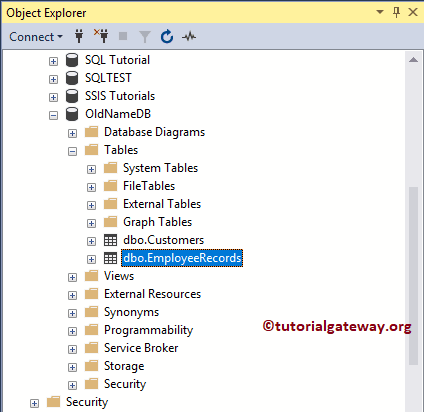
The below query will show you the Logical File names, and the Physical location of the database.
USE master GO SELECT name, physical_name, type_desc, state_desc, size FROM sys.master_files WHERE database_id = DB_ID(N'NewNameDB') GO
Rename Database using Query
Generally, we use a sp_renamedb stored procedure to rename the Database. However, this will only change the name that appears over here.
EXEC sp_renamedb 'NewNameDB', 'OldNameDB'
Messages
--------
The name 'NewNameDB' has been set.You can see the new name under the SQL Server Object Explorer
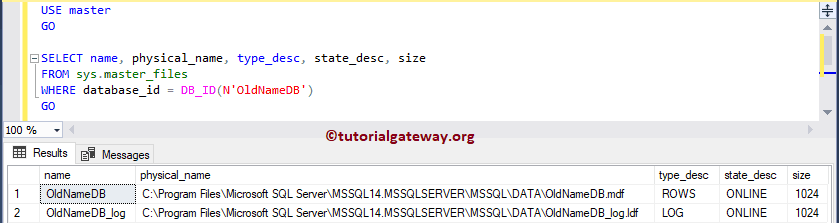
Let me execute the below database query
USE master GO SELECT name, physical_name, type_desc, state_desc, size FROM sys.master_files WHERE database_id = DB_ID(N'NewNameDB') GO
You can see from the Output sp_renamedb hasn’t changed the Logical database Name or the Files representing the Database.
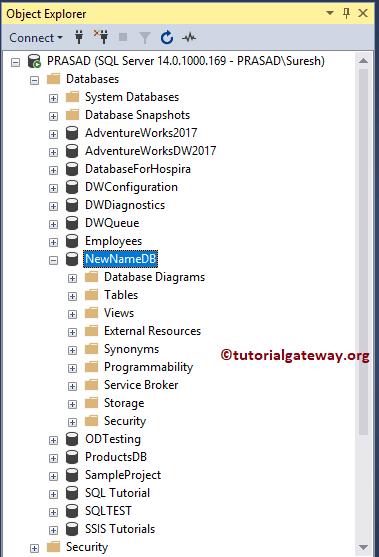
Let me rename the Database to OldNameDB and perform the following operations in a specified manner.
Rename the Database along with the Files
In SQL Server rename database along with files involves modifying the MDF and LDF file names. It will modify the Logical names of the Database.
-- Set the db to Single User ALTER DATABASE OldNameDB SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE ALTER DATABASE OldNameDB MODIFY FILE (NAME = N'OldNameDB', NEWNAME = N'NewNameDB') GO ALTER DATABASE OldNameDB MODIFY FILE (NAME = N'OldNameDB_log', NEWNAME = N'NewNameDB_log') GO
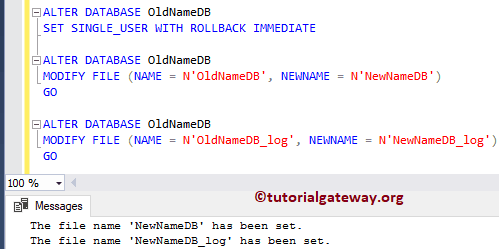
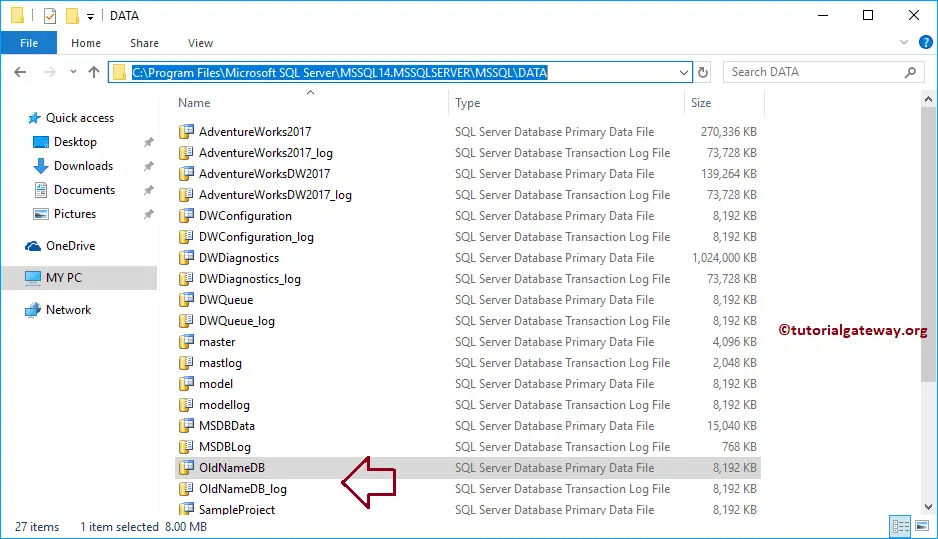
It will detach the OldNameDB Database. After detaching the database, you can modify the File names in the physical location.
USE master GO EXEC sp_detach_db @dbname = N'OldNameDB' GO
Messages
--------
Commands completed successfully.Navigate yourself to the location of the database
We renamed the MDF and LDF names
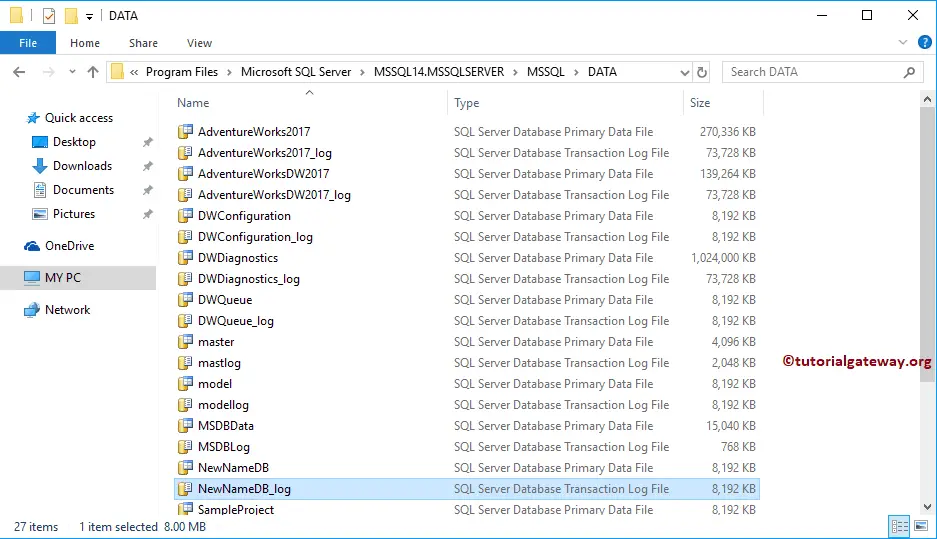
It will create a new Database called NewNameDB using the File names that we changed before.
USE master GO CREATE DATABASE NewNameDB ON (FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft ...\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\NewNameDB.mdf'), (FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft .....\MSSQL14.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\NewNameDB_log.ldf') FOR ATTACH GO
Messages
--------
Commands completed successfully.Now you can see the database with a new name
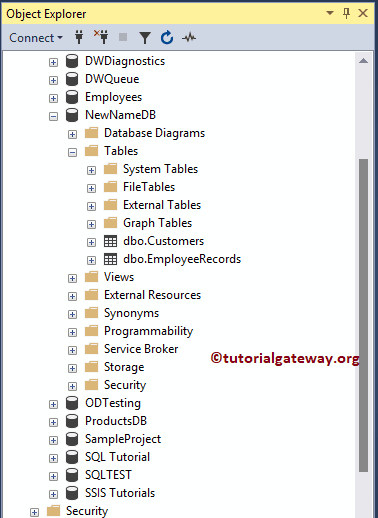
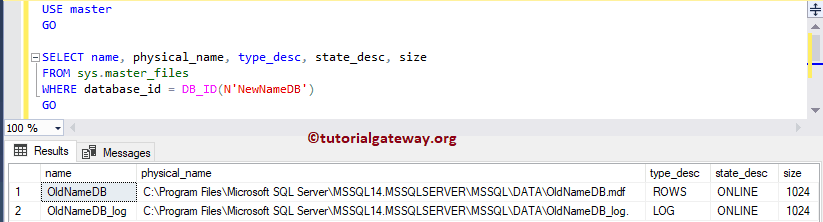
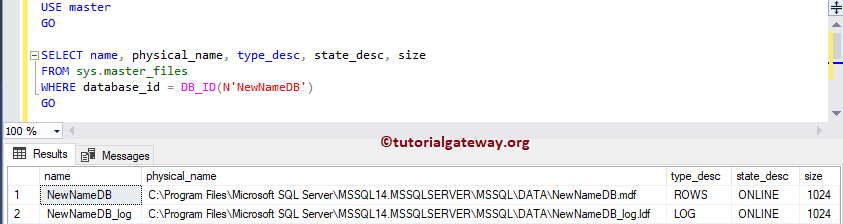
Let me see the Logical File name and the files
USE master GO SELECT name, physical_name, type_desc, state_desc, size FROM sys.master_files WHERE database_id = DB_ID(N'NewNameDB') GO
I think I forgot to set the database to Multi-user.
ALTER DATABASE NewNameDB SET MULTI_USER GO
Messages
--------
Commands completed successfully.