The SQL If Else statement is one of the most useful decision-making queries. The If statement will test the condition first, and depending upon the result, it will execute the statements.
When the test condition in the If statement is true, the query inside the if block will execute. Otherwise, the lines inside the Else block are executed. Let us see the syntax of the SQL Server If Else condition:
SQL If Else Statement Syntax
The syntax of the If Else statement in SQL Server is
IF (Test condition or Expression) BEGIN -- The condition is TRUE then these will be executed True statements; END ELSE BEGIN -- The condition is FALSE then these will be executed False statements; END
This SQL if else statement accepts any test condition as the argument. When the test condition or expression in the above structure is true, then True statements will execute. When the condition is false, then the False code will run.
SQL If Else Statement Flow chart
Let us see the flow chart of the SQL Server If Else statement for a better understanding.
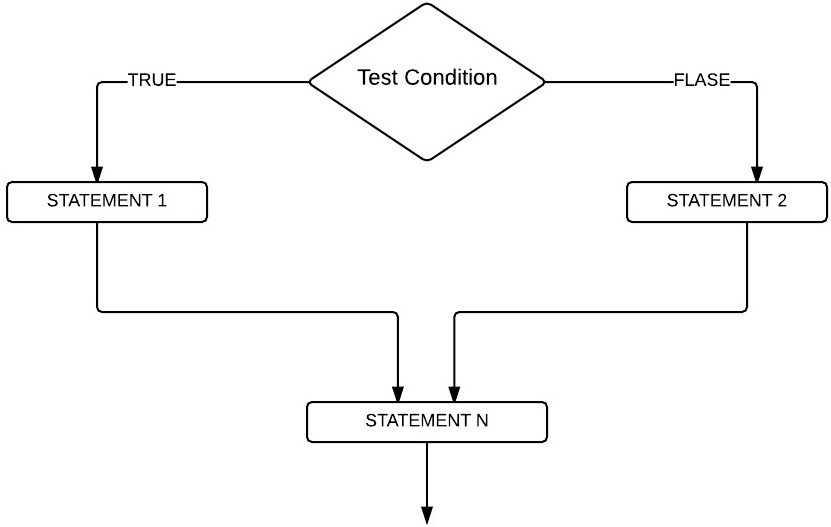
When the test condition is true, then STATEMENT1 will run, followed by STATEMENTN. And the condition is False, then STATEMENT2 will run, followed by STATEMENTN. Because it is out of the if else condition, and it has nothing to do with the Server condition result.
SQL Server If Else Statement Example
In this example, we are going to place four different Print lines. We will display two different messages when the expression is considered true. If the expression result is false, we will print another two messages.
--Declaring Number and Total Variables DECLARE @Marks INT = 72 ; IF @marks > = 50 BEGIN PRINT ' Congratulations '; PRINT ' You pass the Examination '; END ELSE BEGIN PRINT ' You Failed '; PRINT ' Better Luck Next Time '; END
OUTPUT 1: Here marks = 72. Here, the expression 72 >= 50 is TRUE. That’s why print inside the If Statement display’s the Message output.
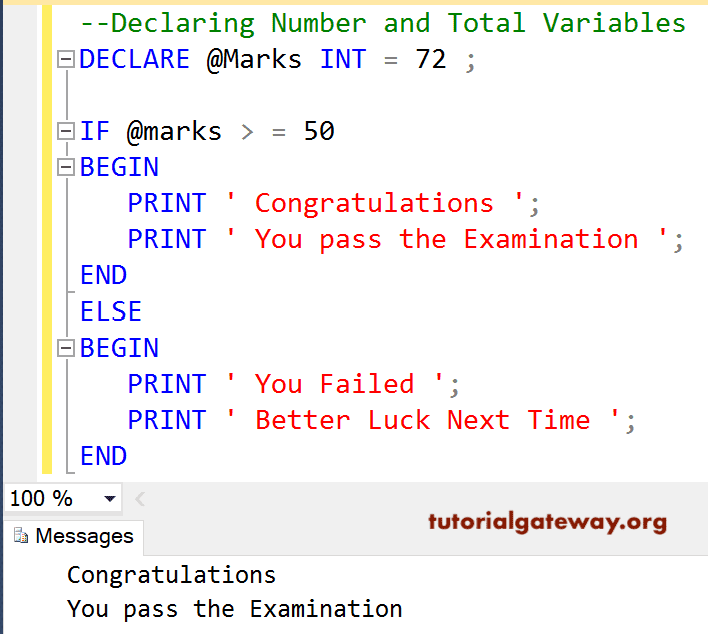
OUTPUT 2: Here, we changed the marks variable to 42, and the expression evaluated to FALSE. That’s why messages inside the Else block are displayed as Message output.
You Failed
Better Luck Next Time If Else Statement Example 2
In this SQL Server program, we are going to check whether the Employee Sales are greater than or equal to 2000 or not using our If Else Statement.
- If the condition inside the if clause is TRUE, We are going to display the Employee records Whose Sales are Greater than or Equal to 2000
- If the expression result is FALSE, the query returns the Employee records Whose Sales is Less than 2000
Before we start writing our query, Let us see if the data that we are going to use for this demonstration is
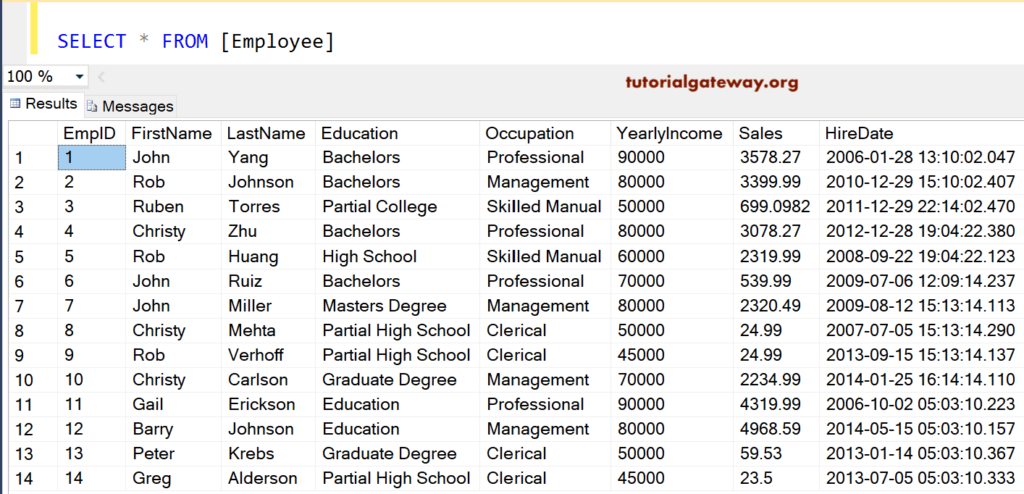
Let us see the code behind this SQL Server If Else Statement Example.
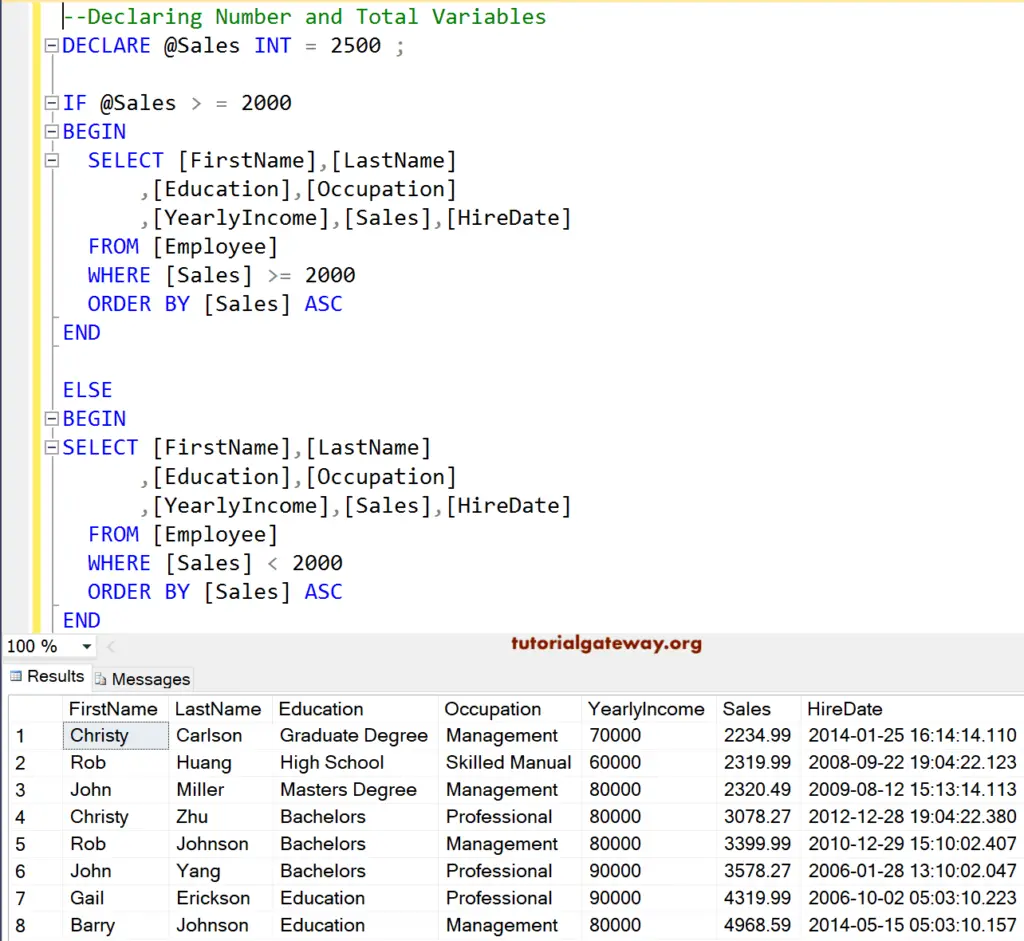
--Declaring Number and Total Variables
DECLARE @Sales INT = 2500 ;
IF @Sales > = 2000
BEGIN
SELECT [FirstName],[LastName]
,[Education],[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome],[Sales],[HireDate]
FROM [Employee]
WHERE [Sales] >= 2000
ORDER BY [Sales] ASC
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SELECT [FirstName],[LastName]
,[Education],[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome],[Sales],[HireDate]
FROM [Employee]
WHERE [Sales] < 2000
ORDER BY [Sales] ASC
END
OUTPUT 1: Here, we specified the Sales as 500. The expression in this If Statement is 500 >= 2000, which is FALSE. That’s why Output is displaying 6 out of 14 records whose sales are less than 2000
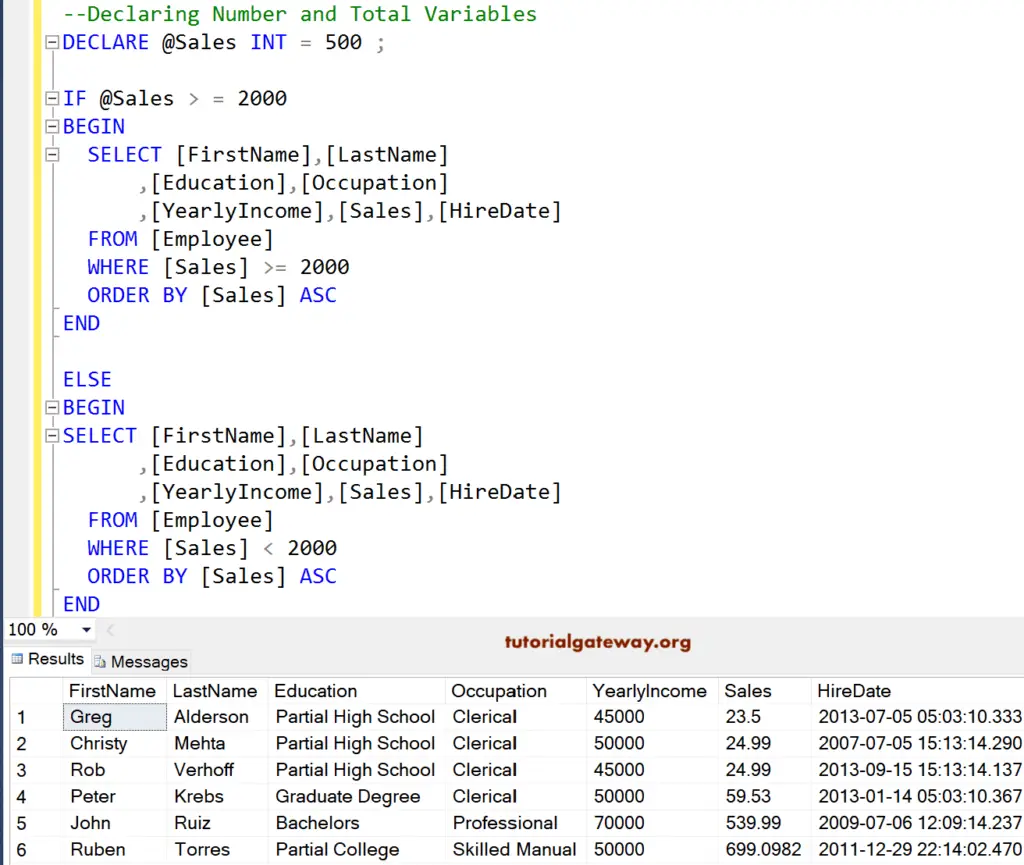
Here, we changed the Sales variable to 2500. The expression 2500 >= 2000 is TRUE. That’s why Output is displaying 8 out of 14 records whose sales are greater than or equal to 2000

Comments are closed.