The SQL NOT EXISTS Operator will act quite opposite to EXISTS Operator. It is used to restrict the number of rows returned by the SELECT Statement.
The NOT EXISTS in SQL Server will check the Subquery for rows existence, and if there are no rows then it will return TRUE, otherwise FALSE. Or we can simply say, SQL Server Not Exists operator will return the results exactly opposite to the result returned by the Subquery.
Before going into this example, I suggest you to refer the SQL Subquery article to understand the subquery designing and query parsing.
SQL NOT EXISTS Syntax
The basic syntax of the NOT EXISTS in SQL Server can be written as:
SELECT [Column Names] FROM [Source] WHERE NOT EXISTS (Write Subquery to Check)
- Columns: It allows us to choose the number of columns from the tables. It may be One or more.
- Source: One or more tables present in the Database. SQL JOINS are used to join multiple tables.
- Subquery: Here we have to provide the Subquery. If the subquery returns true then it will return the records otherwise, it doesn’t return any records.
In this article, we will show you, How to use the SQL Server NOT EXISTS Operator with examples. For this, We are going to use the below-shown data
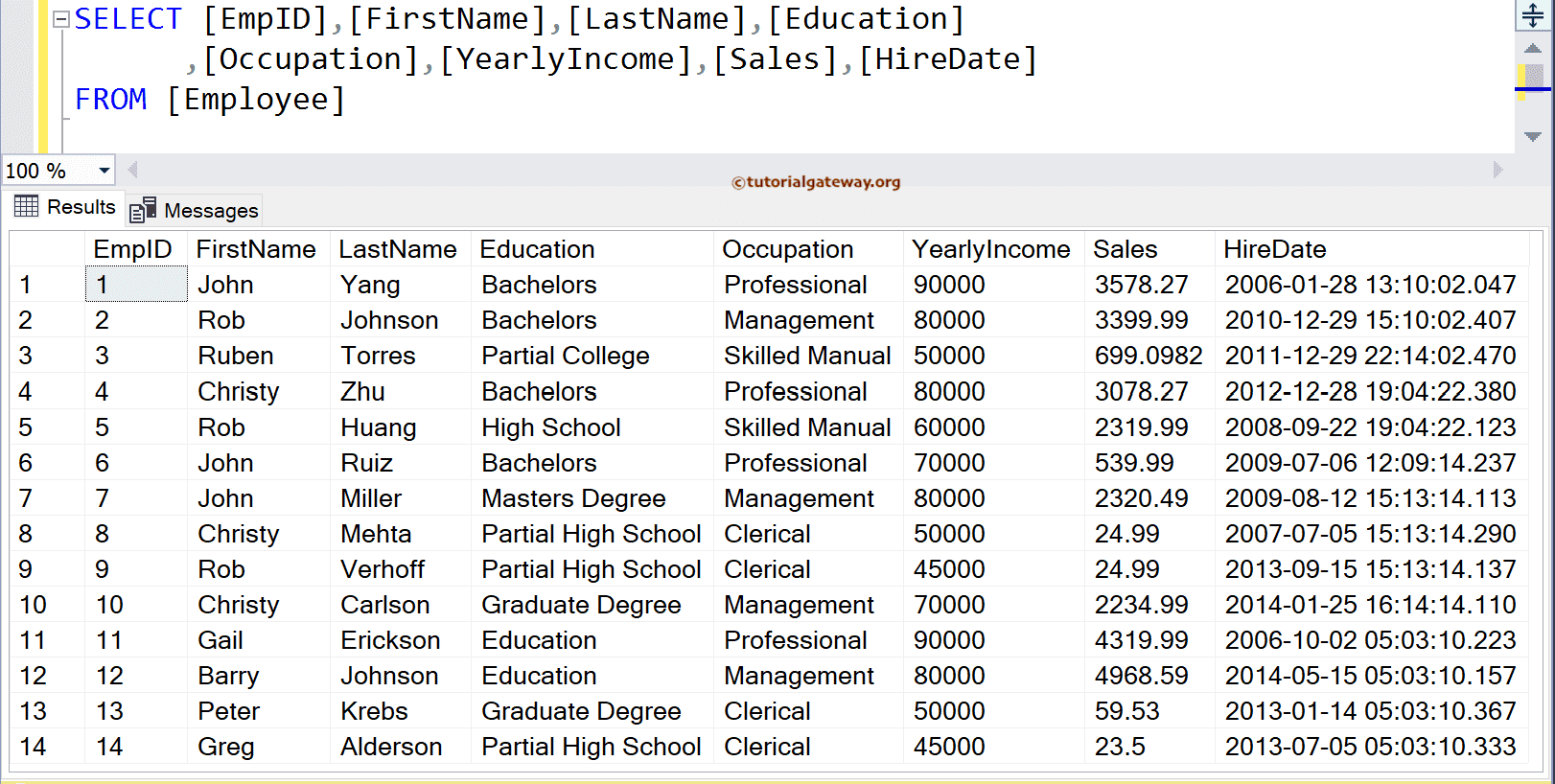
SQL NOT EXISTS Example 1
The following query will find all the Employees present in the Employees table whose [Sales] is less than 1000
-- SQL Server NOT EXISTS Example
USE [SQL Tutorial]
GO
SELECT Employ1.[EmpID]
,Employ1.[FirstName] + ' ' + Employ1.[LastName] AS [Full Name]
,Employ1.[Education]
,Employ1.[Occupation]
,Employ1.[YearlyIncome]
,Employ1.[Sales]
,Employ1.[HireDate]
FROM [Employee] AS Employ1
WHERE NOT EXISTS( SELECT * FROM [Employee] AS Employ2
WHERE Employ1.[EmpID] = Employ2.[EmpID]
AND [Sales] > 1000
)
OUTPUT
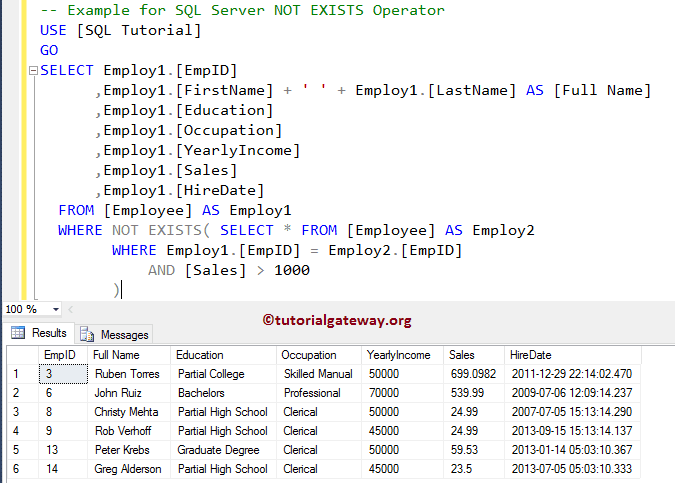
Let me change the Not Exists condition as Sales < 10000, it means subquery will return all the available rows. And the NOT EXISTS will return zero records because it will return the exact opposite result of the subquery.
-- SQL Server NOT EXISTS Example
USE [SQL Tutorial]
GO
SELECT Employ1.[EmpID]
,Employ1.[FirstName] + ' ' + Employ1.[LastName] AS [Full Name]
,Employ1.[Education]
,Employ1.[Occupation]
,Employ1.[YearlyIncome]
,Employ1.[Sales]
,Employ1.[HireDate]
FROM [Employee] AS Employ1
WHERE NOT EXISTS( SELECT * FROM [Employee] AS Employ2
WHERE Employ1.[EmpID] = Employ2.[EmpID]
AND [Sales] < 10000
)
OUTPUT
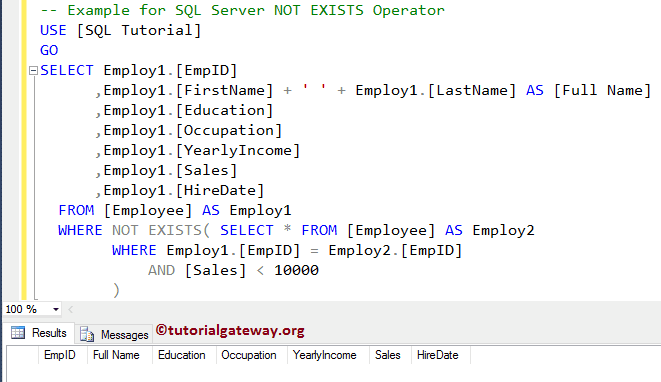
As you can see that the query is returning Empty records, because the subquery is returning TRUE, and Not exists will return false. Let us show you one more example for better understanding.
Let me change the condition to Sales > 10000, which is a false condition. So, SQL NOT EXISTS operator will return all the records.
-- SQL Server NOT EXISTS Example
USE [SQL Tutorial]
GO
SELECT Employ1.[EmpID]
,Employ1.[FirstName] + ' ' + Employ1.[LastName] AS [Full Name]
,Employ1.[Education]
,Employ1.[Occupation]
,Employ1.[YearlyIncome]
,Employ1.[Sales]
,Employ1.[HireDate]
FROM [Employee] AS Employ1
WHERE NOT EXISTS( SELECT * FROM [Employee] AS Employ2
WHERE Employ1.[EmpID] = Employ2.[EmpID]
AND [Sales] > 10000
)
OUTPUT
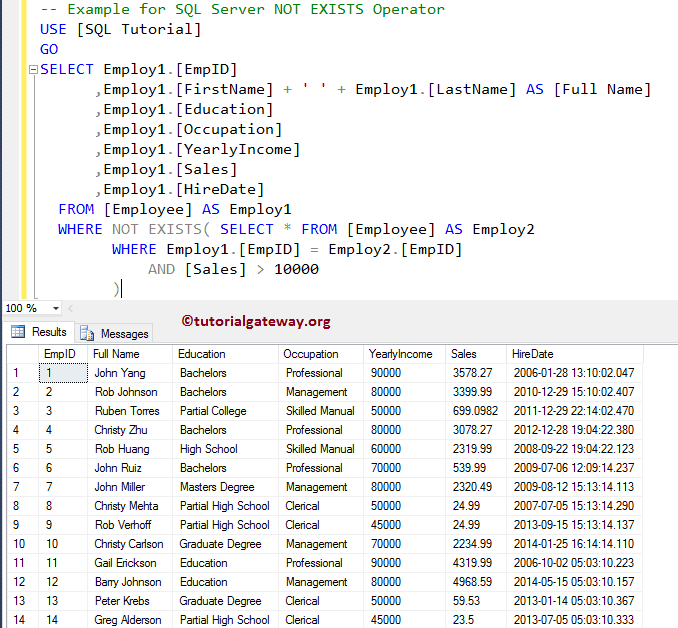
As you can see from the above screenshot, it is returning all the rows. Because the subquery returns FALSE, it means the Sql Server NOT EXISTS will return TRUE
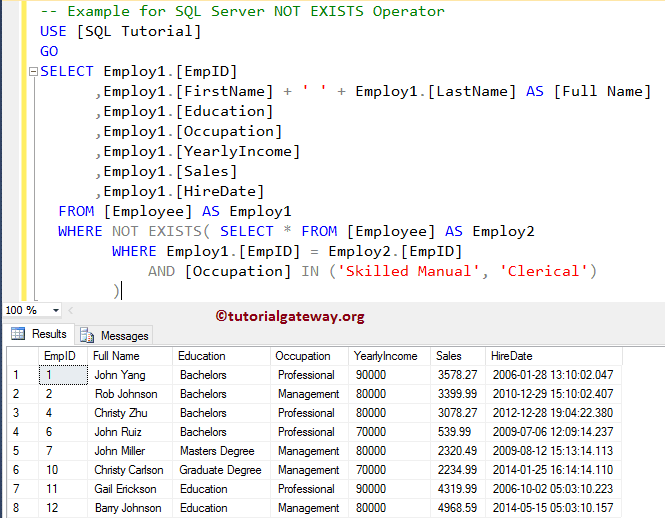
SQL Not Exists Example 2
The following SQL Server Not Exists query will find the Employees whose Occupation is neither Skilled Manual nor Clerical. Here we are going to use the SQL IN Operator inside the Subquery
-- Example for SQL Server NOT EXISTS Operator
USE [SQL Tutorial]
GO
SELECT Employ1.[EmpID]
,Employ1.[FirstName] + ' ' + Employ1.[LastName] AS [Full Name]
,Employ1.[Education]
,Employ1.[Occupation]
,Employ1.[YearlyIncome]
,Employ1.[Sales]
,Employ1.[HireDate]
FROM [Employee] AS Employ1
WHERE NOT EXISTS( SELECT * FROM [Employee] AS Employ2
WHERE Employ1.[EmpID] = Employ2.[EmpID]
AND [Occupation] IN ('Skilled Manual', 'Clerical')
)
OUTPUT
Thank You for Visiting Our Blog
