SQL DATEADD Function is used to add a specific interval to the existing date. For example, For every product order, we will save the Ordered Date, and we can use this SQL Server Dateadd function to generate the expected delivery date.
SQL DATEADD Syntax
DATEADD (Datepart, Number, Date)
Datepart: It is part of a given data to which we are going to add the Number argument of the SQL Server Dateadd function.
The following table will display the list of available datepart arguments in the SQL dateadd function.
| Datepart | Abbreviations | Description |
|---|---|---|
| year | yy,yyyy | This will add a specified number of years (in the second argument) |
| quarter | qq, q | Add the specified number of Quarters (in the second argument) |
| month | mm, m | Add Months |
| dayofyear | dy, y | This argument will add a day of the year |
| day | dd, d | This will add a specified number of days |
| week | wk, ww | Add the specified number of Weeks (in the second argument) |
| weekday | dw, w | Add Weekdays |
| hour | hh | It will add Hours |
| minute | mi, n | It adds the specified number of Minutes. |
| second | ss, s | Add Seconds |
| millisecond | ms | This dateadd argument will add Milliseconds |
| microsecond | mcs | Add Microseconds |
| nanosecond | ns | Add Nanoseconds |
Date: Please specify the valid SQL Server date as the third argument, and it can be a column, expression, or any variable.
Number: Please specify the number you want to add for this SQL Server dateadd function.
- If you specify the positive integer as the second argument (Number), it will add the specified number to the given date.
- If you specify the Negative integer, the function will subtract that.
- And, If you specify the Decimal number as the second argument (Number), this SQL Dateadd function will truncate the decimal values and add the specified number to the given datetime.
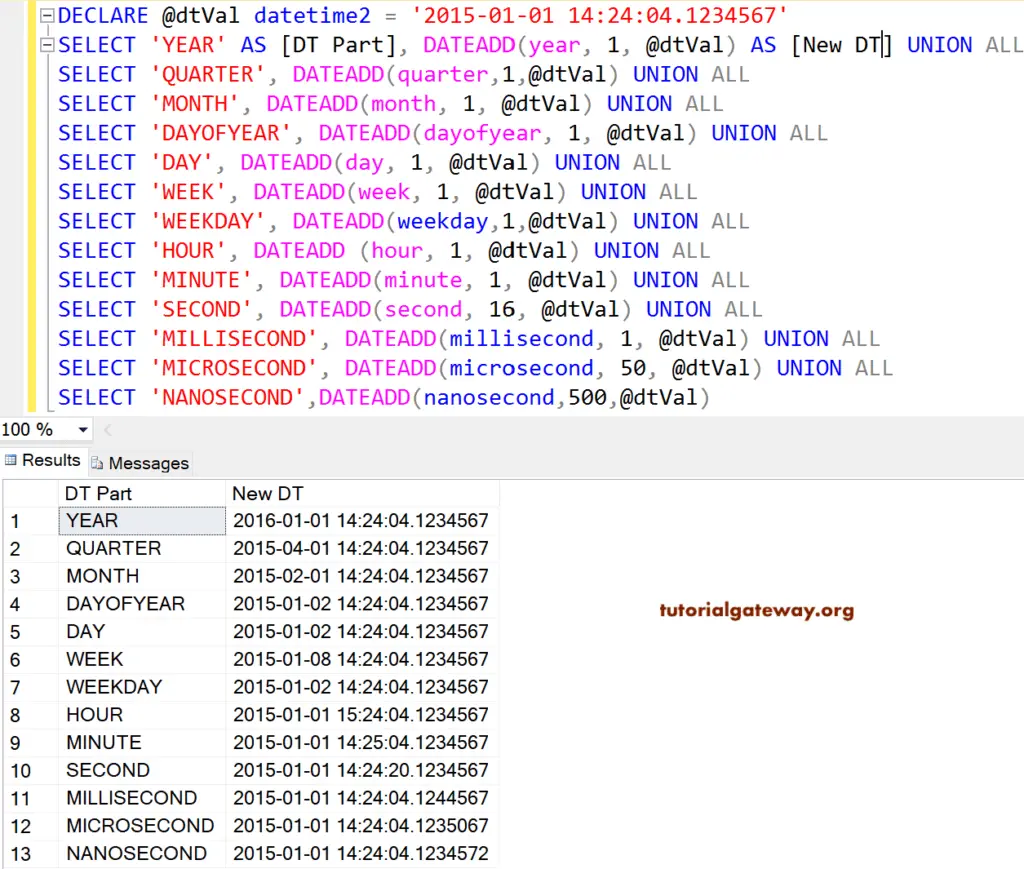
SQL DATEADD Positive integers
In this SQL Dateadd example, we are going to use the positive integer as a second argument. In this transact query, we declared one variable and assigned the date and time to that variable.
(year, 1, @dtVal) – this dateadd function will add 1 year to the given date. Next, (month, 1, @dtVal) add 1 month to the given date.
Negative Integer in SQL Server DATEADD
In this Dateadd example, we use the Negative integer as a second argument.
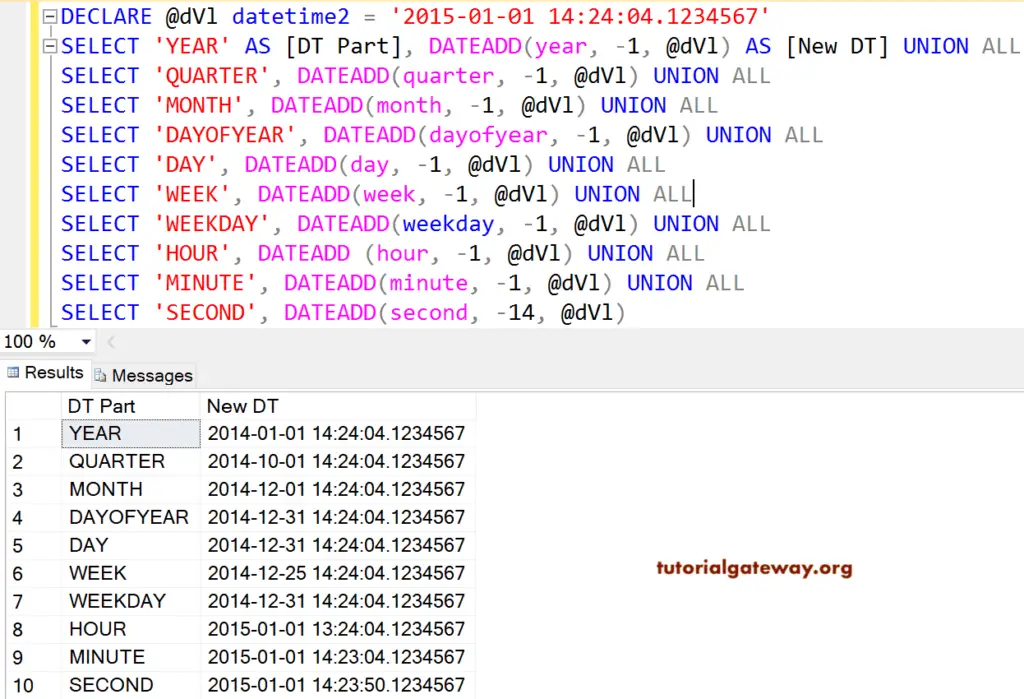
We asked to add 1 year to the given date, but the function subtracted 1 year from it. This is because the Negative value is used to subtract (year, -1, @dVl).
We asked the SQL Server Dateadd function to add 1 Month to the given date, but the function subtracted 1 Month from it. This is because the Negative value is used to subtract (month, -1, @dVl).
DATEADD Decimal Values
In this Date Function example, we are going to use the decimal value as a second argument.
DECLARE @dtValue datetime2 = '2015-01-01 14:24:04.1234567' SELECT 'YEAR' AS [D Part], DATEADD(year, 2.23, @dtValue) AS [New D T] UNION ALL SELECT 'QUARTER', DATEADD(quarter, 3.98, @dtValue) UNION ALL SELECT 'MONTH', DATEADD(month, -4.51, @dtValue)
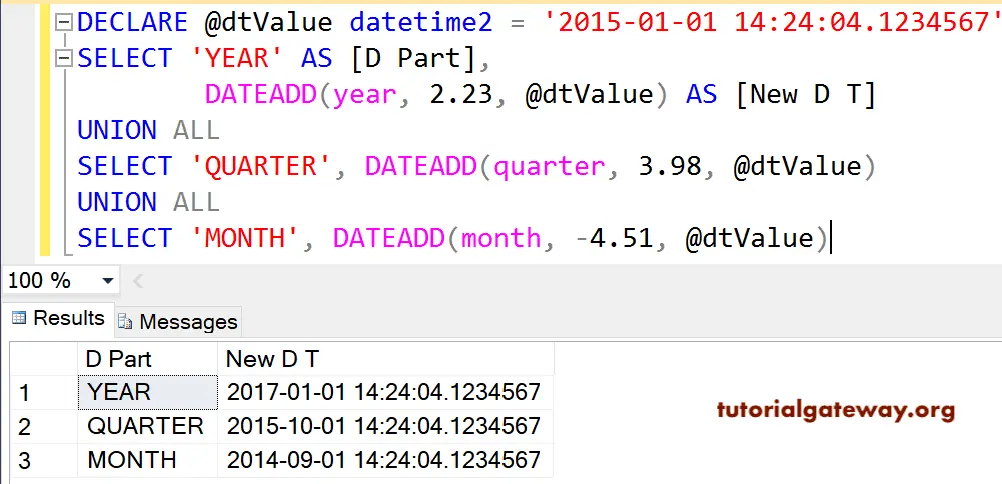
We asked the SQL Dateadd function to add 2.23 years to the given date, but the function added 2 years only. This is because .23 values are truncated.
We asked to add 4.51 months to the given date, but the function subtracted 4 months from a given date. This is because the Negative value is used to subtract, and the .51 value is truncated.
