How to insert values into Identity Column in SQL Server with an example. For this, we will use the below-shown Customer table inside the Database.
From the below code snippet, you can observe that the [Customer Key] column is an Identity column. And our job is to insert values into this SQL identity column [Customer Key], i.e., identity insert.
CREATE TABLE [Customer] ( [CustomerKey] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [FirstName] [varchar](50) NULL, [LastName] [varchar](50) NULL, [BirthDate] [date] NULL, [EmailAddress] [nvarchar](50) NULL, [Yearly Income] [money] NULL, [Profession] [nvarchar](100) NULL )
Insert values into the Identity Column in SQL
Before we start using the SQL Command, Let us see what will happen when we insert values into the Identity Column (Customer Key) using the following statement.
INSERT INTO [Customer]
([CustomerKey], [FirstName],[LastName],[BirthDate],[EmailAddress],[Yearly Income],[Profession])
VALUES (1, 'John', 'Miller', '2006-01-28',
'sql@tutorialgateway.org', 20000, 'Developer')
Run the above query to insert the value into an identity column
Messages
--------
Msg 544, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
Cannot insert explicit value for identity column in table 'Customer' when it is set to OFF.From the above screenshot, you can observe that it is throwing an error saying: Cannot insert explicit value for identity column in table ‘Customer’ when SQL IDENTITY_INSERT is set OFF. It is because any Column using an IDENTITY property will start based on the starting position and automatically increment based on the increment value for each row inserted into the table.
Let us see, What will happen when we insert the remaining values apart from the identity column (customer key) in Server.
-- Example
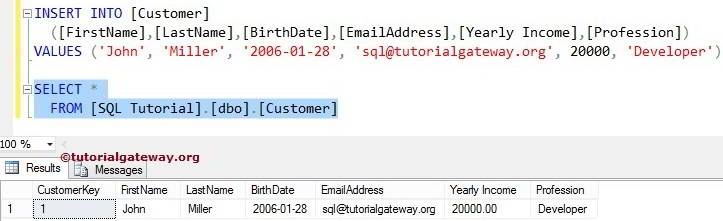
INSERT INTO [Customer]
([FirstName],[LastName],[BirthDate],
[EmailAddress],[Yearly Income],[Profession])
VALUES ('John', 'Miller', '2006-01-28',
'sql@tutorialgateway.org', 20000, 'Developer')
Messages
--------
(1 row(s) affected)From the above screenshot, you can observe that 1 row was affected. Now, let us see whether the above statement inserted the values into the Customer table or not by using the following Query.
SELECT * FROM [Customer]
From the below, you can observe that Customer Key value 1 is automatically inserted because of the IDENTITY.
SET IDENTITY_INSERT ON / OFF
In this insert example, We will use the SQL SET IDENTITY_INSERT property to set the IDENTITY of a column to ON and OFF.
-- Example
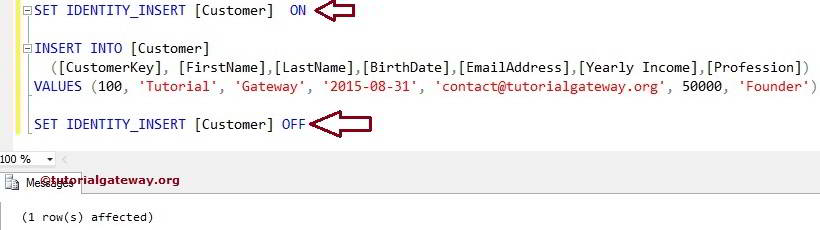
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [Customer] ON
INSERT INTO [Customer]
([CustomerKey], [FirstName],[LastName],[BirthDate],
[EmailAddress],[Yearly Income],[Profession])
VALUES (100, 'Tutorial', 'Gateway', '2015-08-31',
'contact@tutorialgateway.org', 50000, 'Founder')
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [Customer] OFF
The following statement will set the SQL Identity Insert ON on the Customers table.
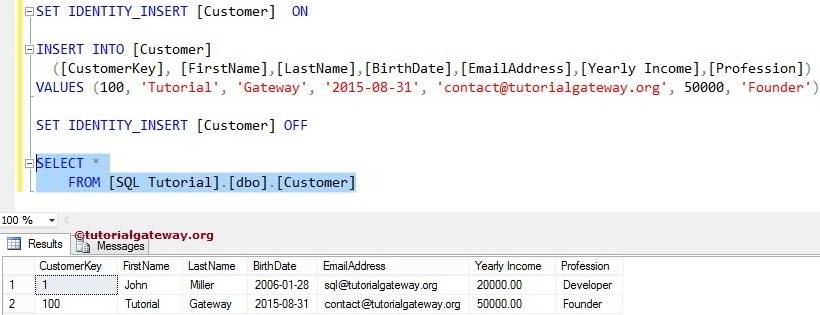
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [Customer] ON
The below statement will insert the explicit values into the Customer table. It includes the IDENTITY Column [Customer Key]
INSERT INTO [Customer]
([CustomerKey], [FirstName],[LastName],[BirthDate],
[EmailAddress],[Yearly Income],[Profession])
VALUES (100, 'Tutorial', 'Gateway', '2015-08-31',
'contact@tutorialgateway.org', 50000, 'Founder')
The following statement will set the Identity_Insert OFF on the Customers table. Remember, after this statement, you can’t insert values into the Identity column (Here, [Customer Key]).
SET IDENTITY_INSERT [Customer] OFF
Use the below query to check whether the above statement inserted the values into the Identity Column or not.
SELECT * FROM [Customer]
You can see that we successfully inserted the values into the identity column.
A session allows only one table to set its IDENTITY_INSERT property ON. SSMS returns an error message if you try to issue a SET IDENTITY_INSERT ON statement on multiple tables.

Comments are closed.