In this section, we discuss how to write a Python Program to Find the Sum of Digits of a Number using a While Loop, for loop, Functions, and Recursion.
Python Program to Find Sum of Digits of a Number using While Loop
This program allows the user to enter any positive integer. Then, Python divides the given number into individuals and adds those individual (Sum) digits using the While Loop.
Number = int(input("Please Enter any Number: "))
Sum = 0
while(Number > 0):
Reminder = Number % 10
Sum = Sum + Reminder
Number = Number //10
print("\n Sum of the digits of Given Number = %d" %Sum)

This program allows the user to enter any positive integer, and then that value is assigned to a variable Number. Next, Condition in the Python While Loop makes sure that the given number is greater than 0 (Means Positive integer and greater than 0).
The user Entered the value for this Python program to find the Sum of Digits: Number = 4567 and Sum = 0
First Iteration
Reminder = Number%10
Reminder = 4567 % 10 = 7
Sum= Sum+ Reminder
Sum= 0 + 7 = 7
Number = Number/10
Number= 4567 / 10 = 456
Python Program to Find Sum of Digits of a Number Second Iteration:
From the first Python Iteration, Number= 456 and Sum= 7
Reminder = 456 % 10 = 6
Sum= 7 + 6 = 13
Number= 456 / 10 = 45
Third Iteration: For the Third Iteration, the values of Number= 45 and Sum= 13
Reminder = 45 % 10 = 5
Sum= 13 + 5 = 18
Number= 45 / 10 = 4
Fourth Iteration: For the Fourth Iteration, Number= 4 and Sum= 18
Reminder= 4 % 10 = 4
Sum= 18 + 4 = 22
Number= 4 / 10 = 0
Here Number= 0. So, the while loop condition fails.
The last print statement prints the variable as the output. So, the output of the given variable 4567 is:
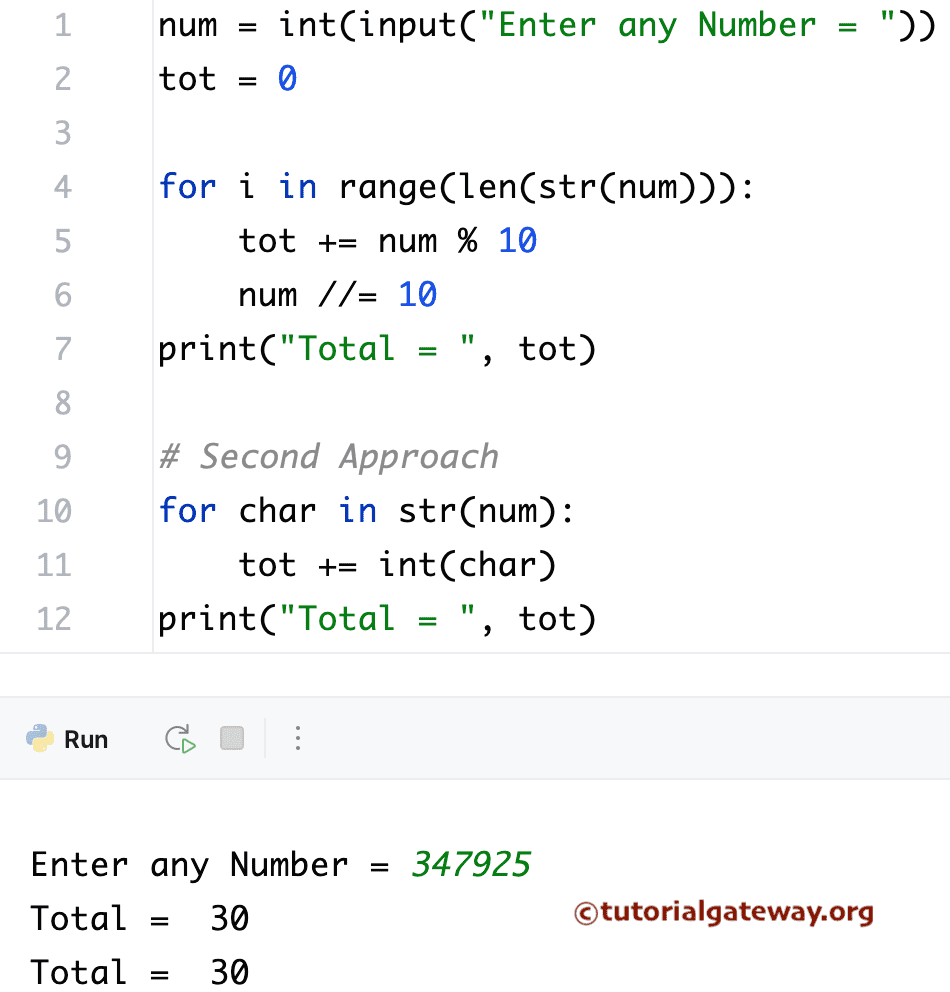
Python Program to find the Sum Of Digits using for loop
This program uses the for loop range. The str() function converts the number to a string, and the len() method returns the total digits. It means the for loop starts from the first digit and traverses up to the last digit.
num = int(input("Enter any Number = "))
tot = 0
for i in range(len(str(num))):
tot += num % 10
num //= 10
print("Total = ", tot)
You can also try the below shown for loop approach to calculate the sum of digits.
num = int(input("Enter any Number = "))
tot = 0
for char in str(num):
tot += int(char)
print("Total = ", tot)
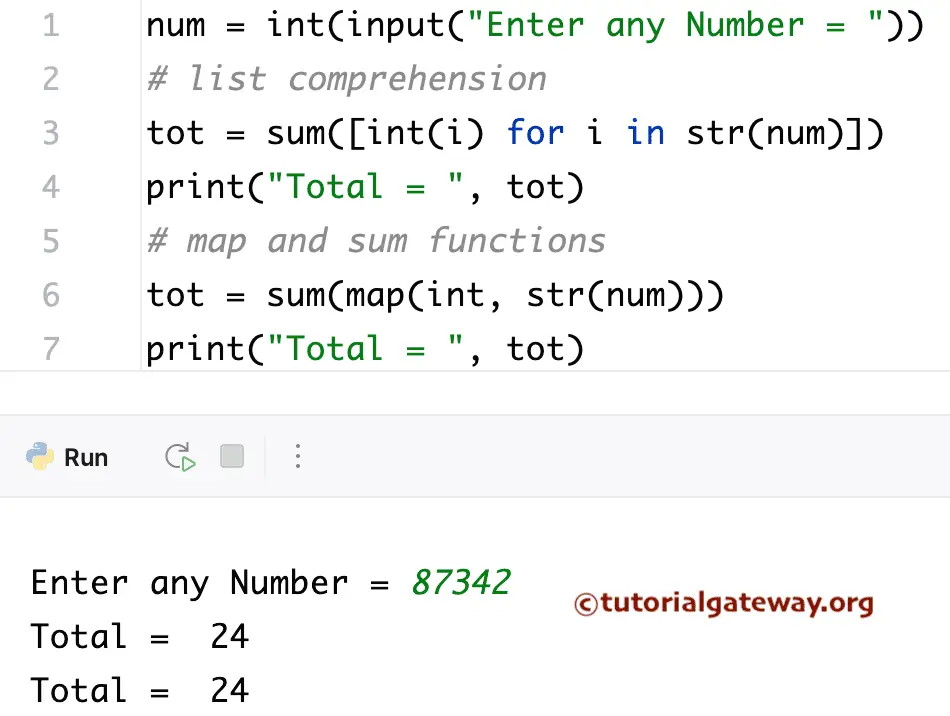
Python Program for Sum Of Digits using list comprehension
Please refer to the list comprehension and map function articles.
num = int(input("Enter any Number = "))
tot = sum([int(i) for i in str(num)])
print("Total = ", tot)
Using map and sum functions
num = int(input("Enter any Number = "))
tot = sum(map(int, str(num)))
print("Total = ", tot)
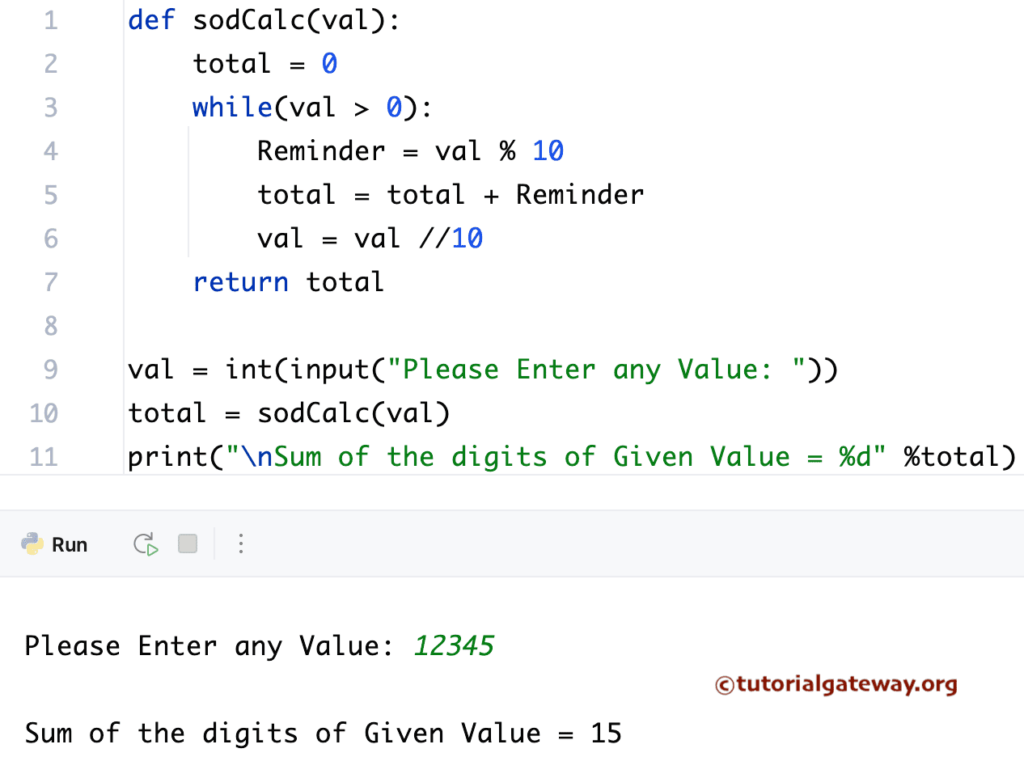
Python Program to Find Sum of Digits of a Number Using Functions
This sum of digits in the program allows the user to enter any positive integer. Then, the program divides the given number into individual digits and adds those individual (Sum) digits using Functions.
# using Functions
def sodCalc(val):
total = 0
while(val > 0):
Reminder = val % 10
total = total + Reminder
val = val //10
return total
val = int(input("Please Enter any Value: "))
total = sodCalc(val)
print("\n Sum of the digits of Given Value = %d" %total)
In this program, When the compiler reaches the sodCalc(val) line, the compiler immediately jumps to the below function:
def sodCalc(val):
Python Program to Find Sum of Digits of a Number using Recursion
This program to find the sum of digits allows the user to enter any positive integer. Then, Python divides the given integer into individual digits and adds those individual (Sum) digits by calling the function recursively.
tot = 0
def calcSOD(Num):
global tot
if(Num > 0):
Reminder = Num % 10
tot = tot + Reminder
calcSOD(Num //10)
return tot
Num = int(input("Please Enter any Value: "))
tot = calcSOD(Num)
print("\n Sum of the digits = %d" %tot)
Please Enter any Value: 456
Sum of the digits = 15Within this program, When the compiler reaches the Sum= calcSOD(Num) line, it immediately jumps to the below function:
calcSOD(Num):
In this function, the below statement helps to call the function Recursively with the updated value. If you miss this statement, it terminates after completing the first line.
calcSOD(Num //10)
For this Python Program to Find the Sum of Digits of a Number example, Number= 4567 returns the output as 7.
Let’s see the If Statement,
if (Num > 0), check whether the num is greater than 0 or not. For Recursive functions, placing a condition before using the function recursively is very important. Otherwise, we end up in infinite execution (Same as an infinite Loop).
Using recursion Example 2
It is another approach to finding the sum of digits using recursion.
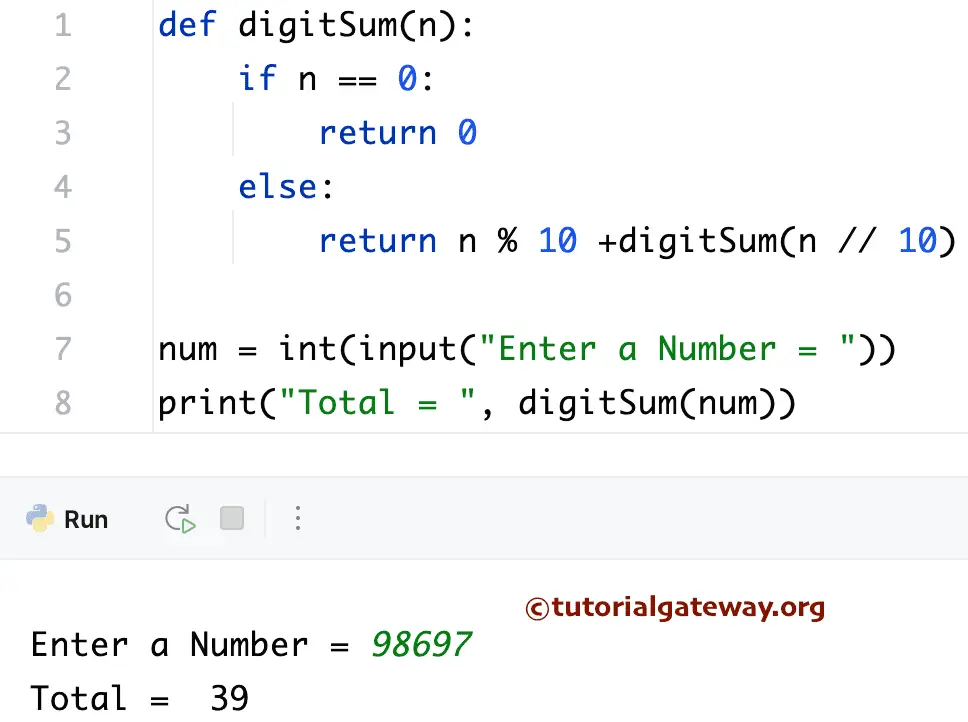
def digitSum(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
else:
return n % 10 +digitSum(n // 10)
num = int(input("Enter a Number = "))
print("Total = ", digitSum(num))