Let me show you how to use Power BI DAX String Functions with examples. Microsoft Power BI DAX provides various String Functions such as LEN, LEFT, RIGHT, LOWER, UPPER, MID, SUBSTITUTE, FORMAT, CONCATENATE, CONCATENATEX, REPT, UNICHAR, VALUES, etc.
To demonstrate these Power BI DAX String functions, we are going to use the below shown data. As you can see, there are 15 records on this table.
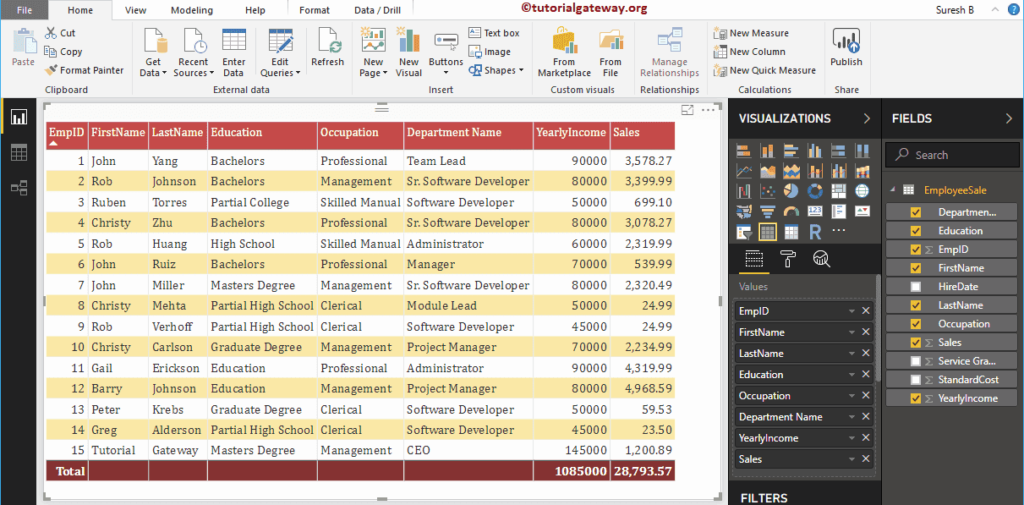
Power BI DAX String Functions
The following series of examples show you the list of DAX String Functions.
DAX LEN Function
The DAX Now function returns the length of a given string. The syntax of this Power BI DAX LEN is
LEN(string)
To demonstrate these DAX String functions in Power BI, we have to use the calculated column. To create a column, please click on the New Column option under the Home tab, or Modeling tab.
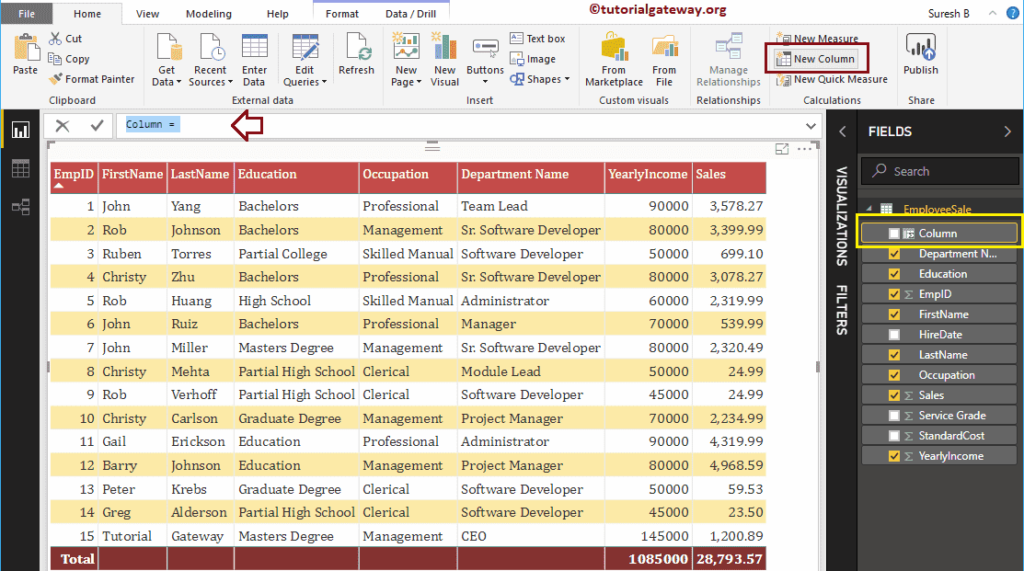
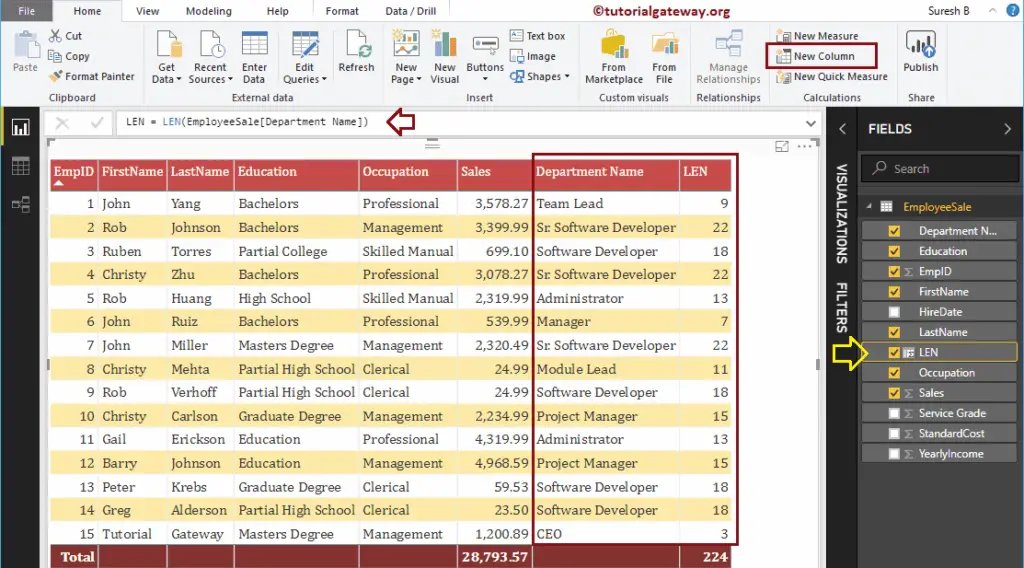
As you can see from the screenshot below, we renamed the default column name as LEN. The below statement finds the length of a character string in the Department name column.
LEN = LEN(EmployeeSales[Department Name])
Let me add this DAX LEN column to the table that we created earlier. Please refer to Create Table Report article to understand the steps involved in creating a table
DAX LEFT Function
The Power BI DAX LEFT function returns the leftmost characters from a string up to a specified index position. The DAX LEFT Function syntax is
LEFT(string, position)
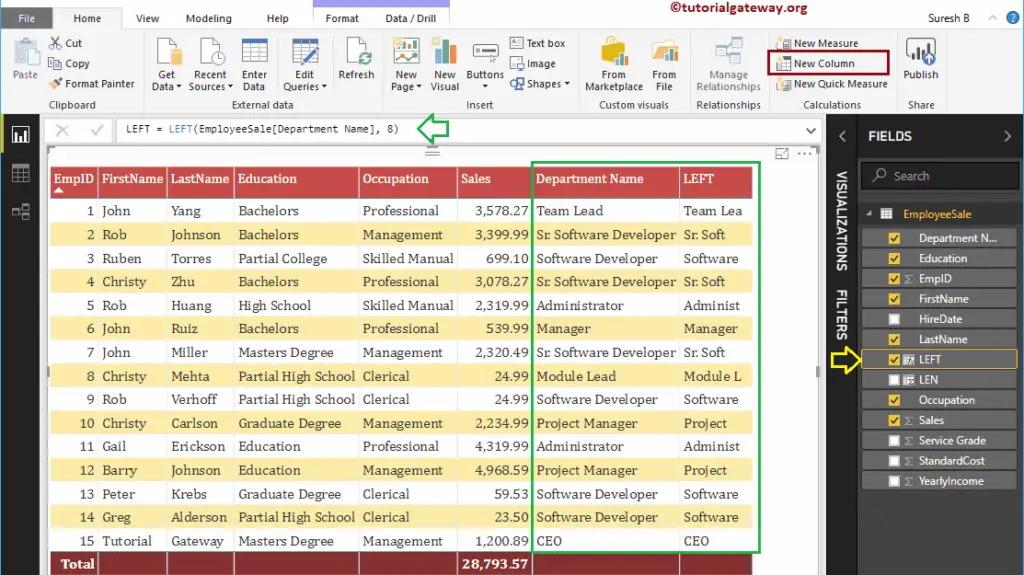
The below statement returns leftmost 8 characters from the Department name column
LEFT = LEFT(EmployeeSales[Department Name], 8)
DAX RIGHT Function
The Power BI DAX RIGHT function returns the rightmost characters from a string up to a specified index position. The syntax of DAX RIGHT Function is
RIGHT(string, position)
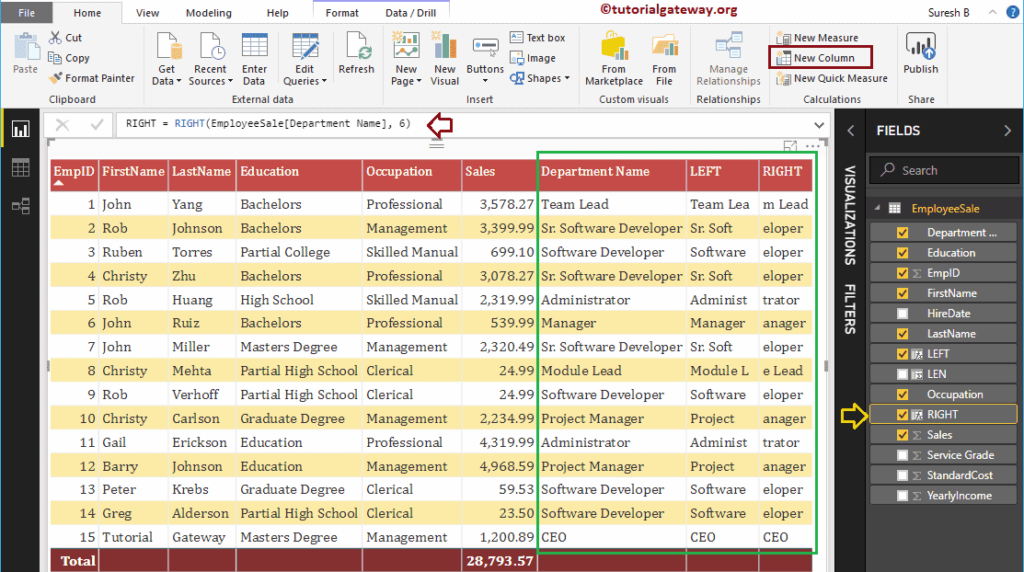
It returns rightmost 6 characters from the Department name column
RIGHT = RIGHT(EmployeeSales[Department Name], 6)
Power BI DAX LOWER Function
The DAX LOWER function converts the given string of characters to lower case. The syntax of DAX LOWER Function is
LOWER(string)
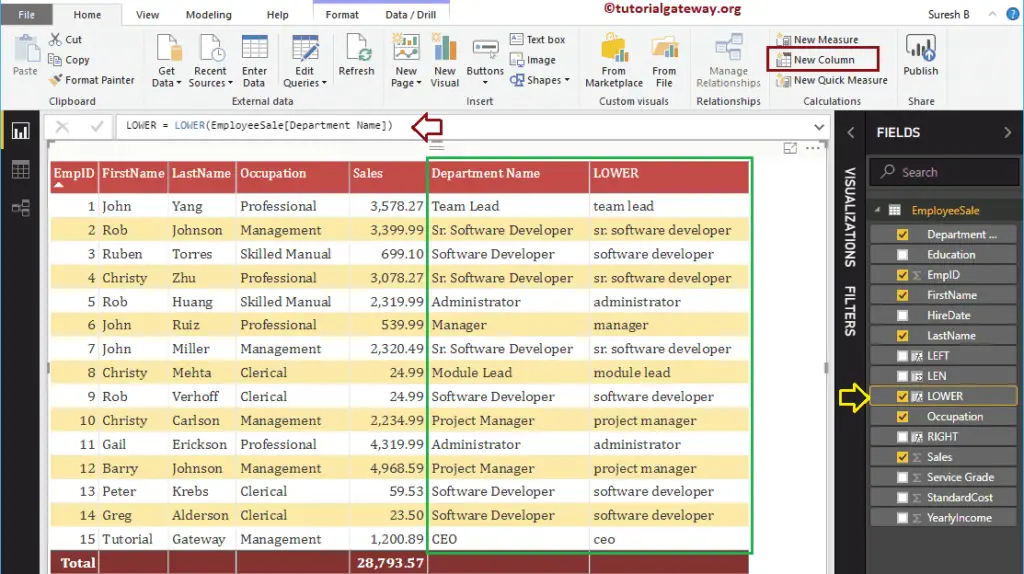
The following DAX lower function converts the Department name column into lowercase
LOWER = LOWER(EmployeeSales[Department Name])
DAX UPPER Function
The Power BI DAX UPPER function converts the given string into uppercase. The DAX UPPER Function syntax is
UPPER(string)
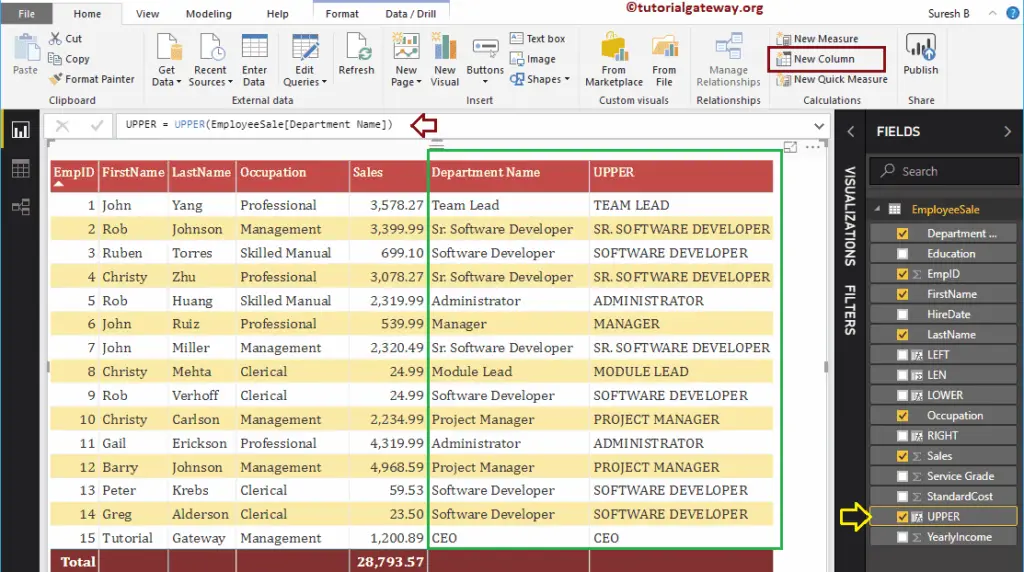
The below DAX upper function convert Department name column string into uppercase
UPPER = UPPER(EmployeeSales[Department Name])
DAX MID Function
The Power BI DAX MID function returns a substring from the original string. The syntax of DAX MID Function is
MID(string, starting_position, length)
This DAX MID function accepts three arguments:
- Starting position – Substring start from this position
- Length – Total length of a substring.
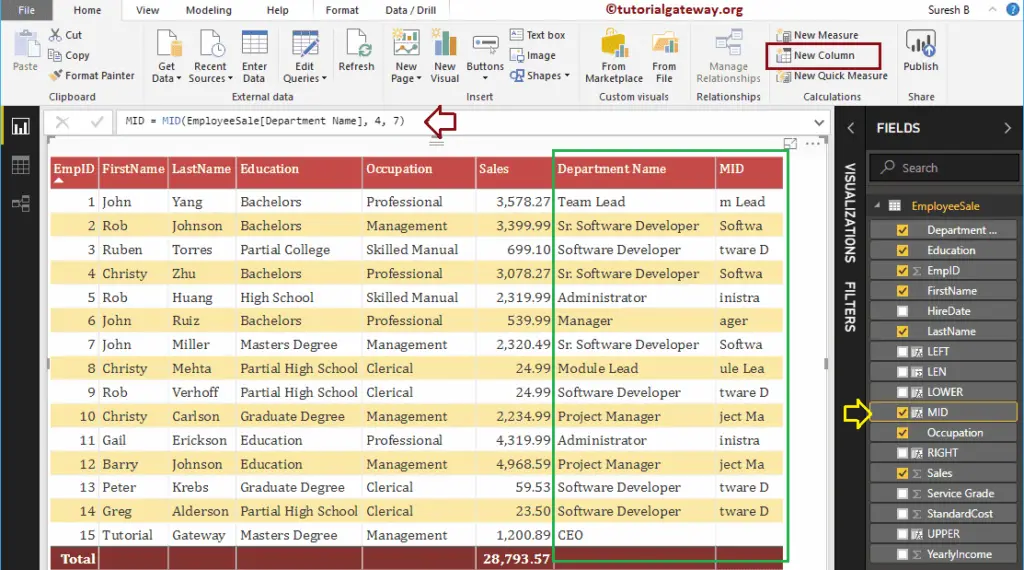
It returns a substring from the Department Name column. Substring starts at position no 4 and ends when string length reaches to 7.
MID = MID(EmployeeSales[Department Name], 4, 7)
Power BI DAX REPT Function
The Power BI DAX REPT function repeats a string for the user-specified number of times. The syntax of the DAX REPT Function is:
REPT(string, no_of_times)
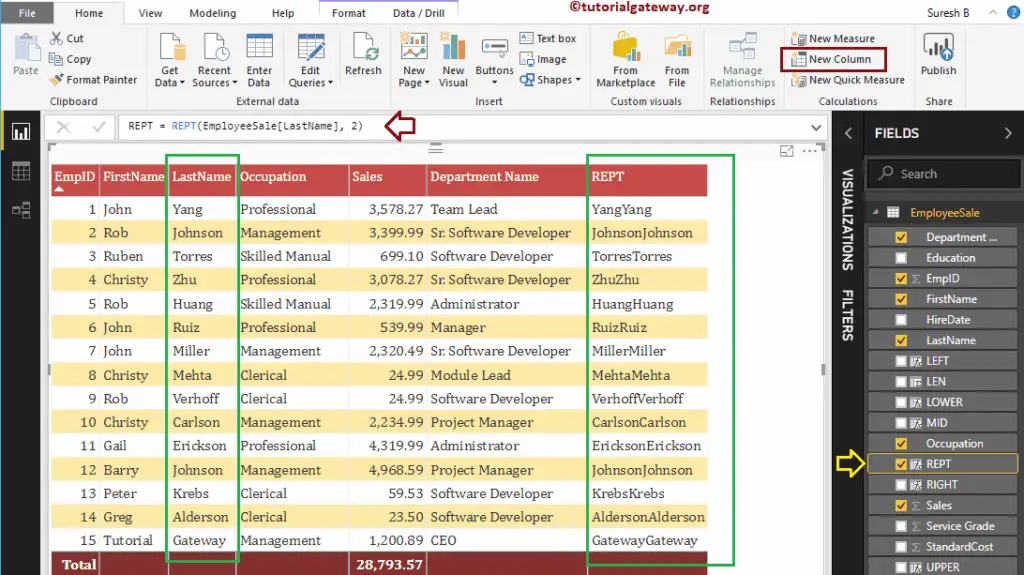
It repeats the data in the LastName column for 2 times.
REPT = REPT(EmployeeSales[LastName], 2)
DAX SUBSTITUTE Function
The Power BI DAX SUBSTITUTE function replaces the string with the user-specified value or substring. The syntax of this DAX SUBSTITUTE Function is:
SUBSTITUTE(string, old_string, new_string)
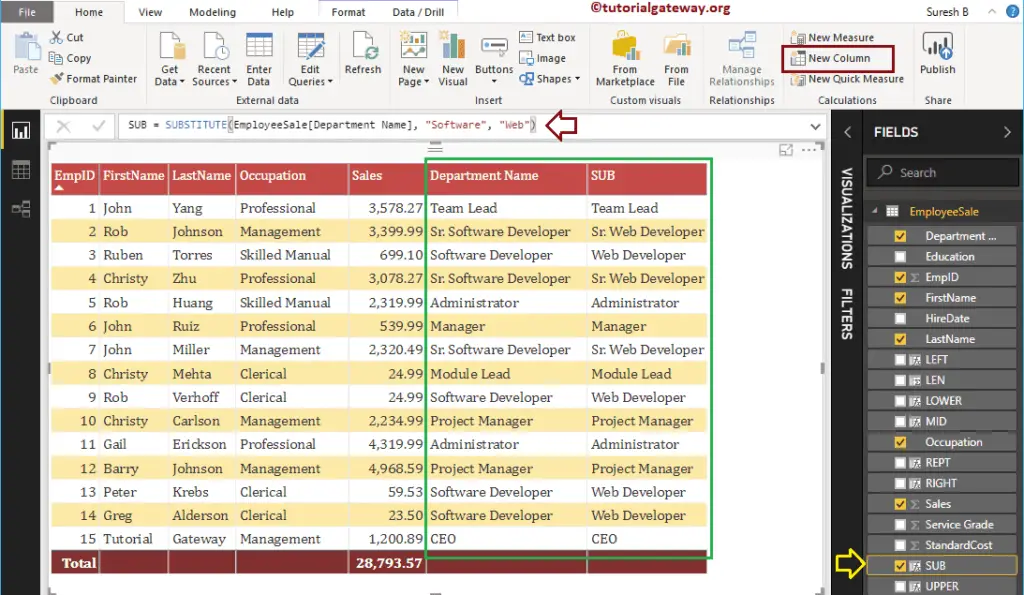
It replaces the Software word with Web inside the Department Name column values
SUBSTITUTE = SUBSTITUTE(EmployeeSales[Department Name], "Software", "Web")
DAX UNICHAR Function
The Power BI DAX UNICHAR function returns the Unicode character for the given ASCII value. The DAX UNICHAR Function syntax is:
UNICHAR(number)
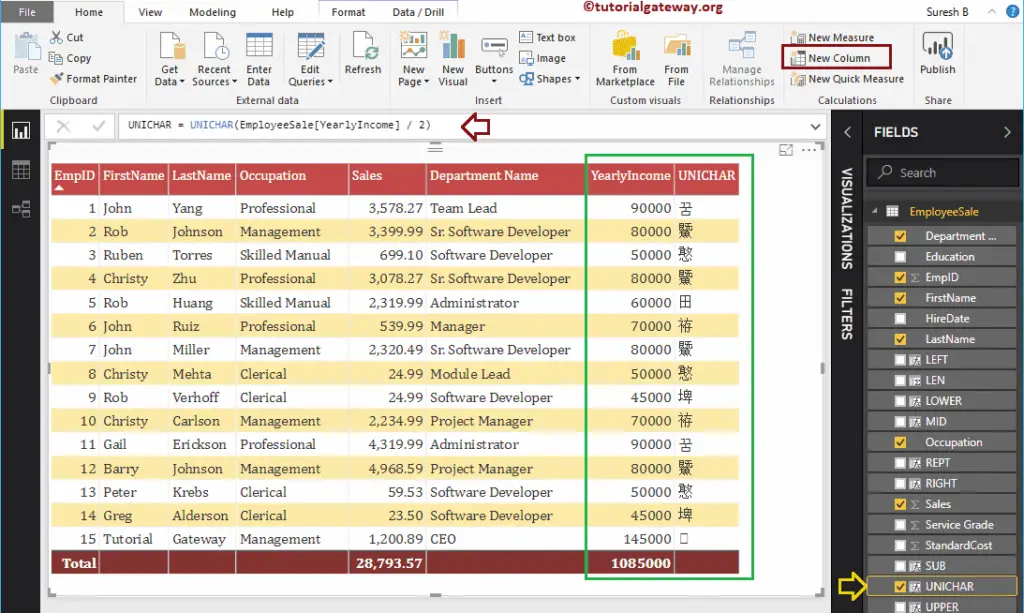
It returns the Unicode characters of Yearly income divide by 2
UNICHAR = UNICHAR(EmployeeSales[Yearly Income] / 2)
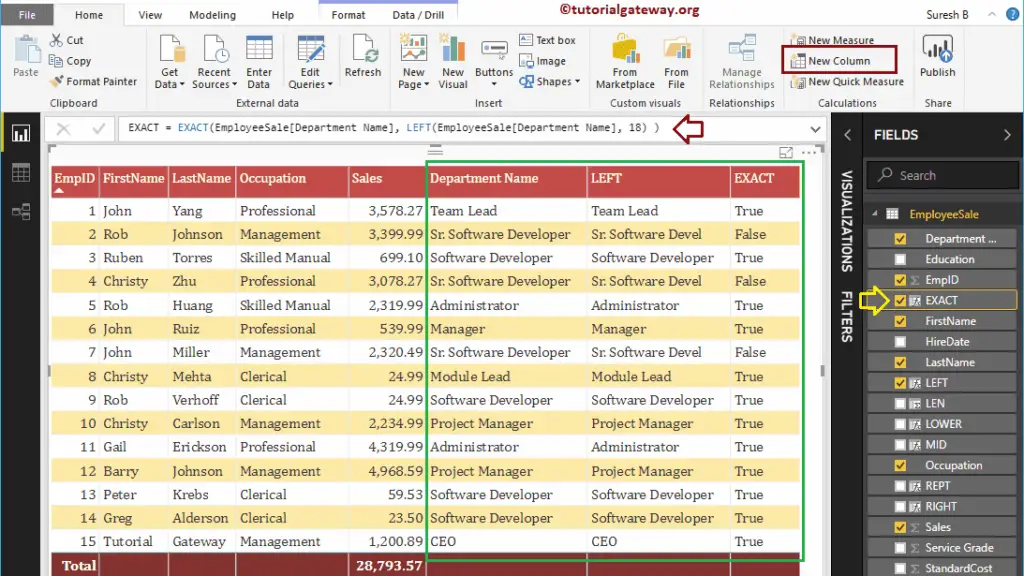
Power BI DAX EXACT Function
The DAX EXACT function compares two strings and returns true if they are exactly equal; otherwise, it returns false. The syntax of this DAX EXACT Function is:
EXACT(string1, string2)
Below DAX Exact statement compare Department Name with Leftmost 18 characters of Department Name
EXACT = EXACT(EmployeeSales[Department Name], LEFT(EmployeeSales[Department Name], 18))
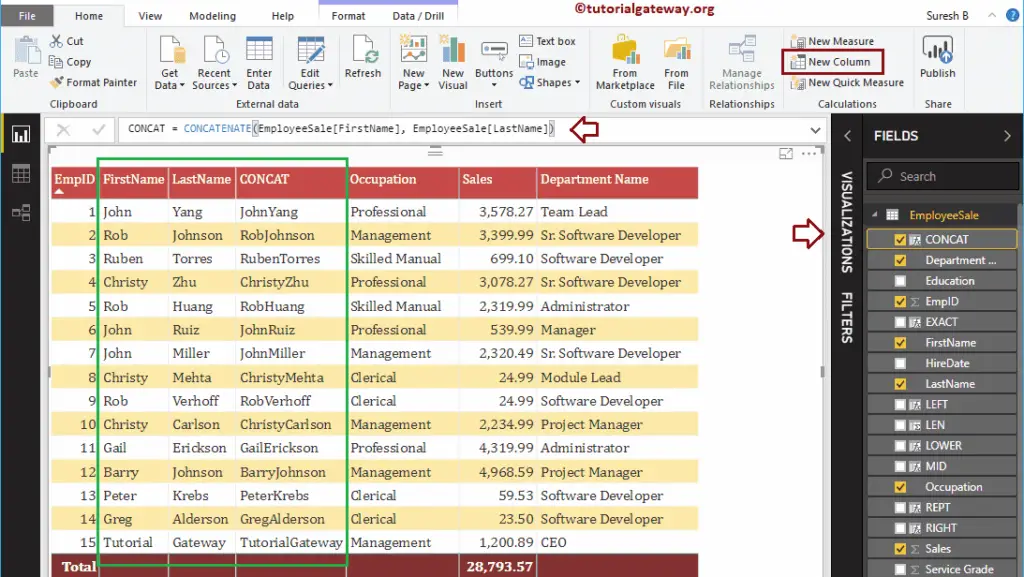
DAX CONCATENATE Function
The Power BI DAX CONCATENATE function is useful to concatenate two strings. The syntax of this DAX CONCATENATE Function is:
CONCATENATE(string1, string2)
The following DAX CONCATENATE function concatenate the first name and last name
CONCAT = CONCATENATE(EmployeeSales[FirstName], EmployeeSales[LastName])
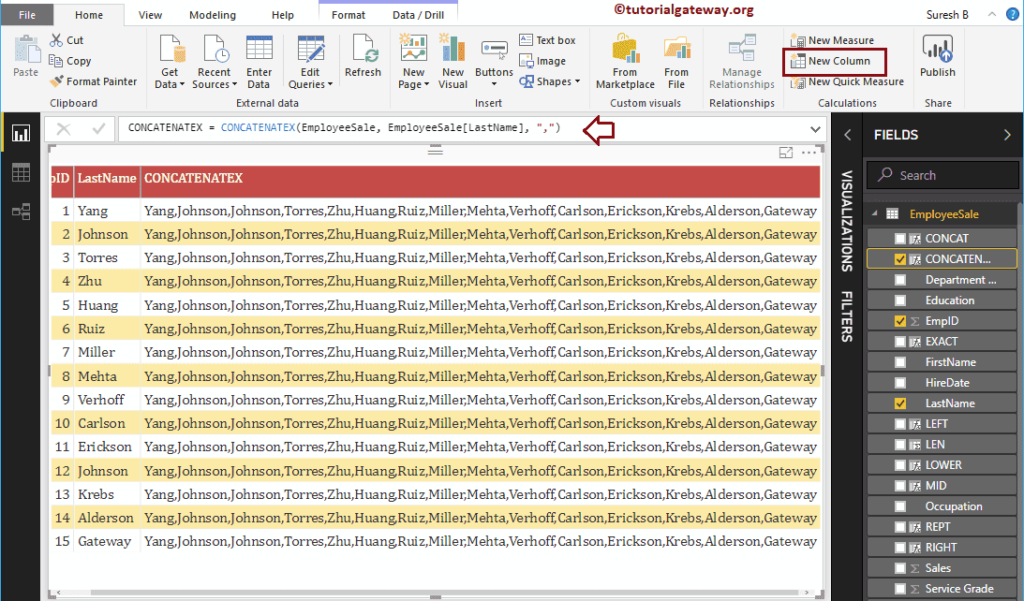
Power BI DAX CONCATENATEX Function
The DAX CONCATENATEX function is to concatenate all the rows in a column using the specified delimiter. The syntax of this DAX CONCATENATEX Function is:
CONCATENATEX(tableName, ColumnName, Delimiter)
The below statement concatenate all the rows in the last name column using a comma delimiter.
CONCATENATEX = CONCATENATEX(EmployeeSales, EmployeeSales[LastName], ",")
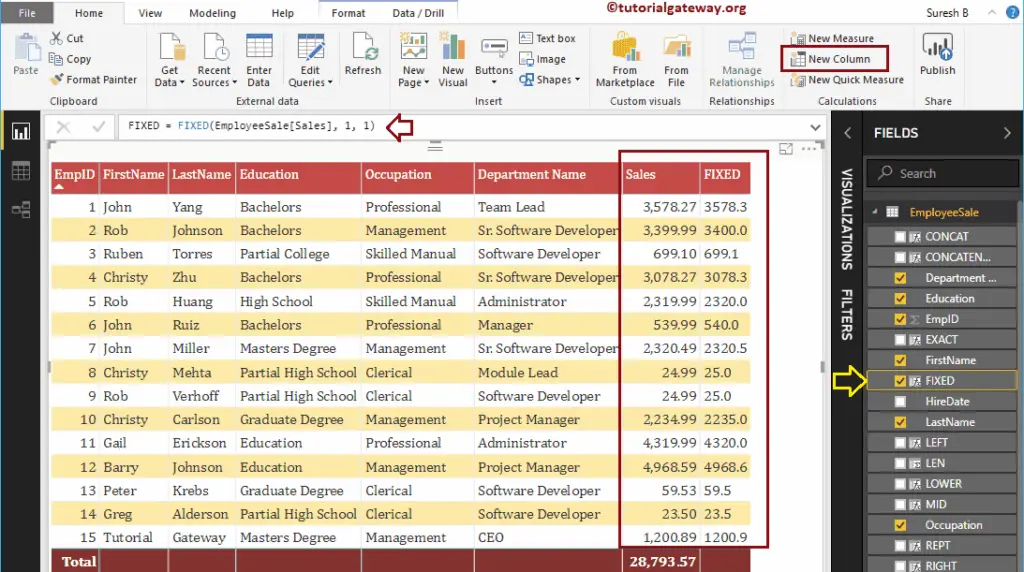
DAX FIXED Function
The Power BI DAX FIXED function is useful to round the given number to a specified number of digits and returns in text data type. The syntax of the DAX FIXED Function is:
FIXED(number, decimals, comma)
The below DAX FIXED function rounds sales decimals to a single digit, and it won’t allow comma
FIXED = FIXED(EmployeeSales[Sales], 1, 1)
DAX BLANK Function
The Power BI DAX BLANK function is useful to return a blank. You can also use this to check whether the crows have any blanks or not. The syntax of this DAX BLANK Function is:
BLANK()
Below If statement checks whether there are any blanks while dividing Sales by Service Grade, if true, Blank is replaced by 100. Otherwise, it returns the result.
BLACNK = IF(DIVIDE(EmployeeSales[Sales], EmployeeSales[Service Grade]) = BLANK(),
100, DIVIDE(EmployeeSales[Sales], EmployeeSales[Service Grade]))
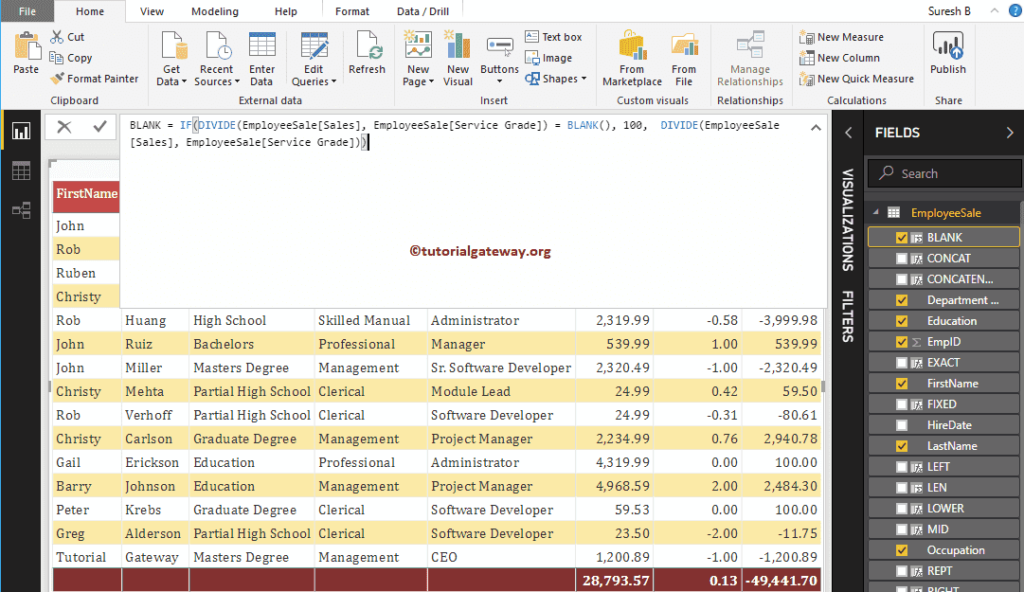
From the screenshot below, you can see the result.
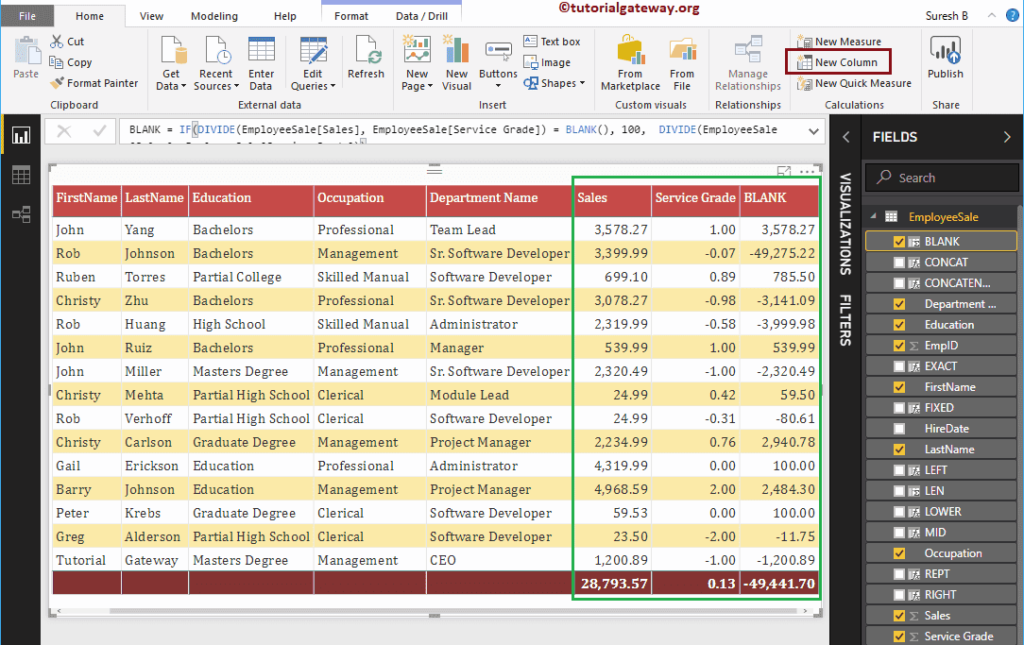
Power BI DAX UNICODE Function
The DAX UNICODE function returns the ASCII value of the first character in a string. The syntax of this DAX UNICODE Function is:
UNICODE(string)
It returns the ASCII value of the first character in the last name column
CODE = UNICODE(EmployeeSales[LastName])
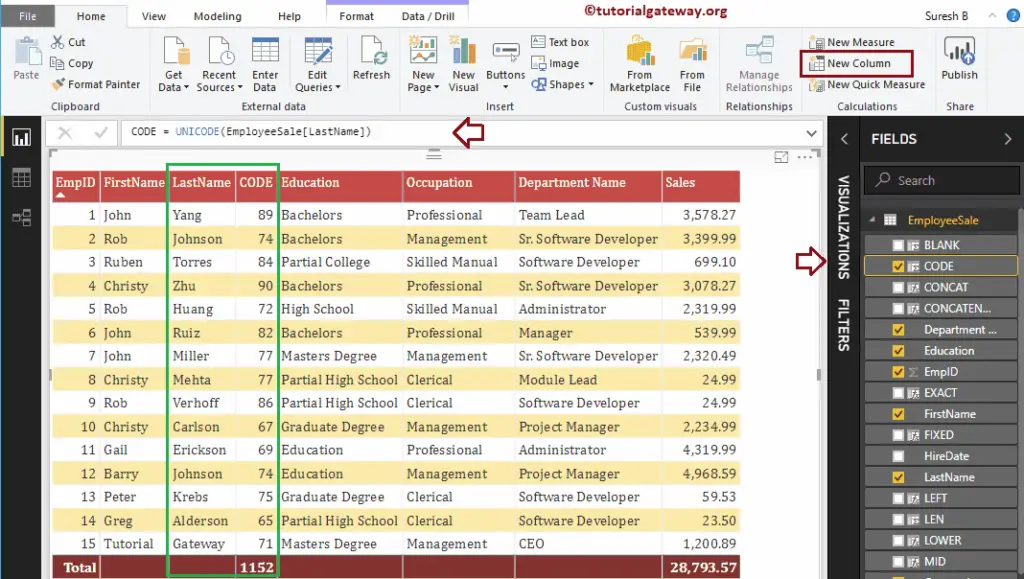
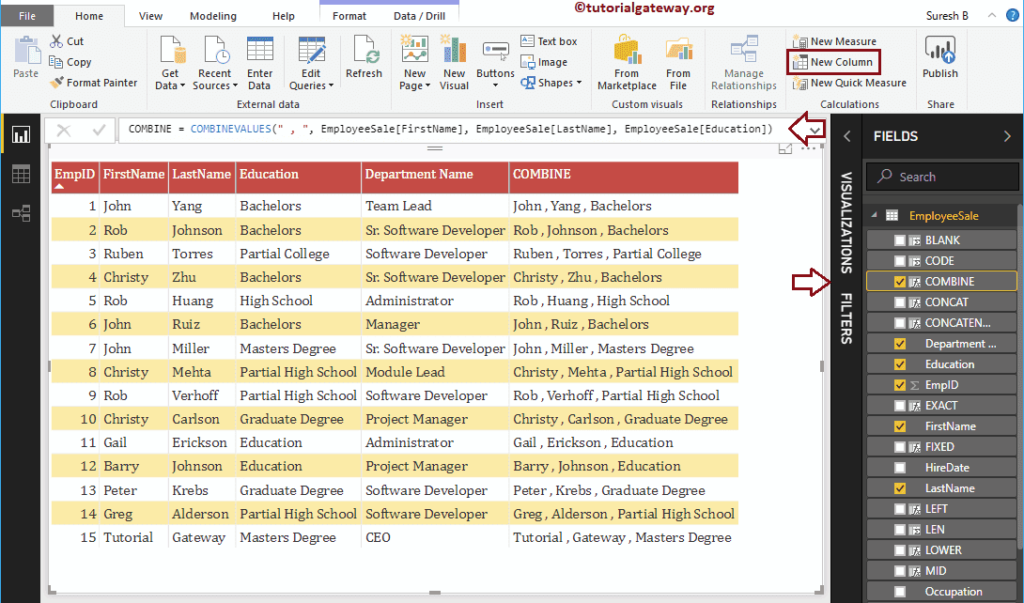
Power BI DAX COMBINEVALUES Function
The DAX COMBINEVALUES function combines two or more strings using the specified delimiter. The syntax of this DAX COMBINEVALUES Function is:
COMBINEVALUES(Delimiter, string1, string2,..)
The below statement combines First Name, Last Name, Education columns using a comma delimiter.
CONCATENATEX = CONCATENATEX(EmployeeSales, EmployeeSales[LastName], ",")
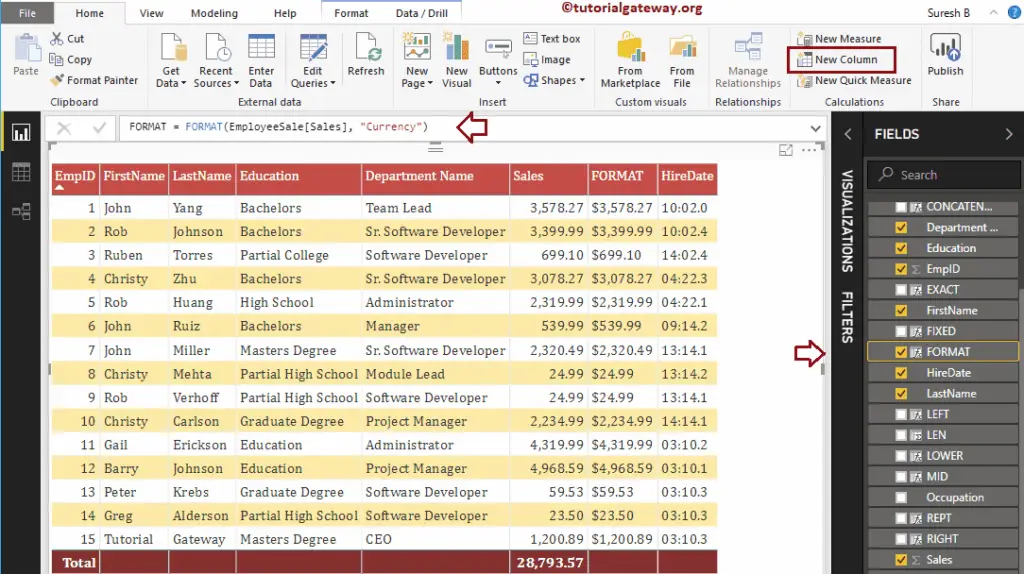
Power BI DAX FORMAT Function
The DAX FORMAT function format numbers and dates to predefined formats. The syntax of the DAX FORMAT Function is:
FORMAT(expression, format_type)
The below DAX FORMAT function formats the Sales amount into currency type
FORMAT = FORMAT(EmployeeSales[Sales], "Currency")
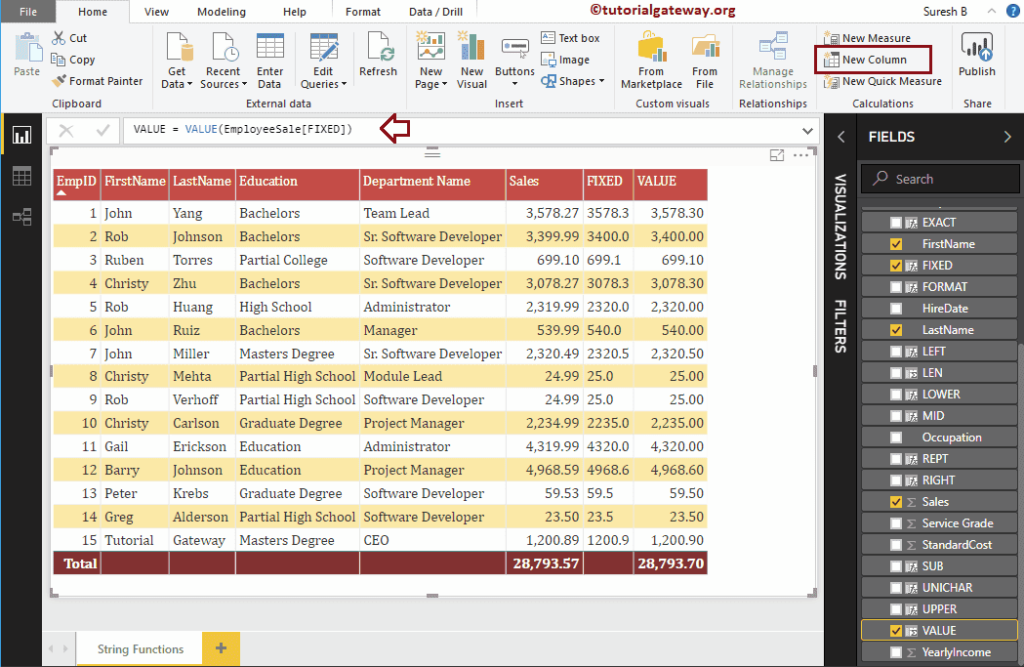
Power BI DAX VALUE Function
The DAX VALUE function converts the string numbers into a number. The syntax of the DAX VALUE Function is:
VALUE(string)
The below statement converts the string numbers in Fixed function result to a number
VALUE = VALUE(EmployeeSales[FIXED])