Power BI Heat Map is useful for displaying the data along with the colors. By seeing the color, one can understand the profits easily. Let me show you how to create a HeatMap in Power BI with an example.
For this Power BI Heatmap demonstration, we will use the SQL Data Source we created in our previous article. So, Please refer to. the Connect to SQL Server and the List of Charts articles to understand the Power BI Data Source.
Create a Heat Map in Power BI
You won’t find a heat map under Power BI Visualization by default. However, you have multiple options to create a heat map.
- Sign in using the official domain-specific email ID to get map specific and table specific heat maps from the marketplace.
- Use any third-party file that you downloaded in the system.
- Convert a Table or Matrix to a heat map using the conditional formatting of background colors.
To create a heatmap, first, click on the Matrix under the Visualization section. It automatically creates a Matrix with dummy data.
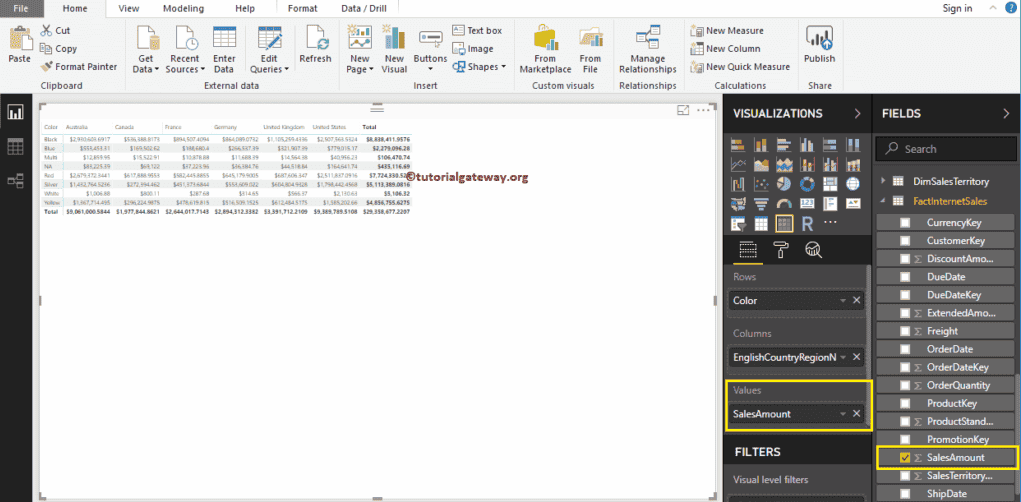
Next, drag and drop the English Country Region Name to the Column Group and the product Color to the Row Group. Now, you can see a Matrix without values.
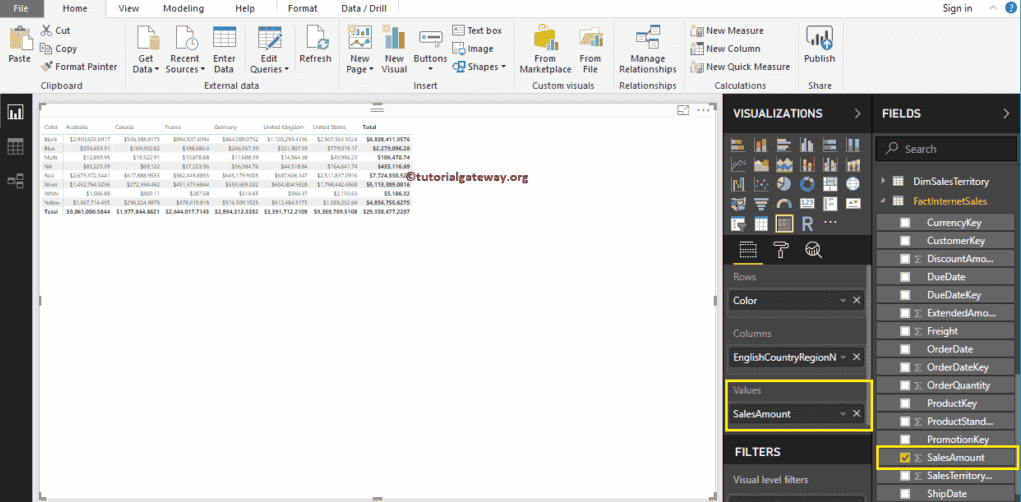
Next, let me drag the Sales Amount to the Values section. It automatically enables the Row totals and grand totals.
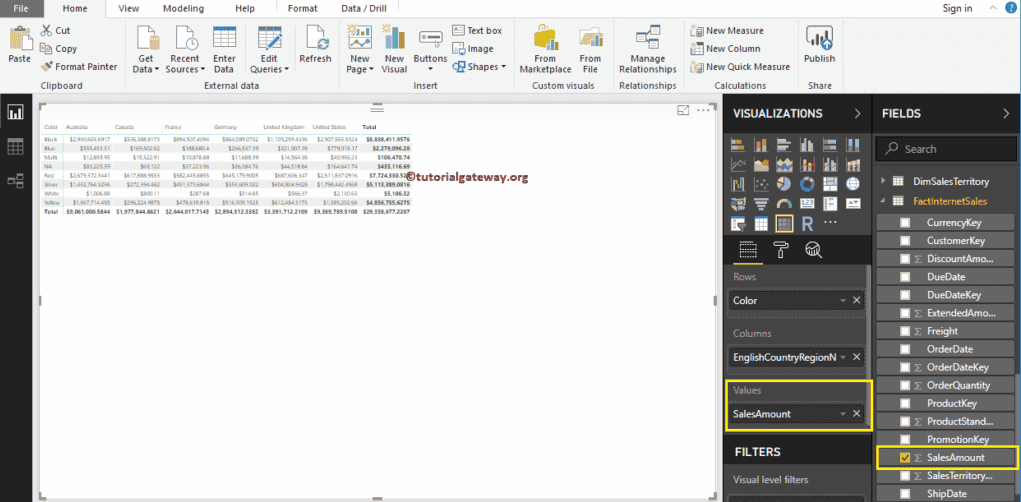
Please click on the Format button to convert this Matrix into a Heatmap in Power BI. I suggest you refer to Format a Matrix article to understand the formatting options.
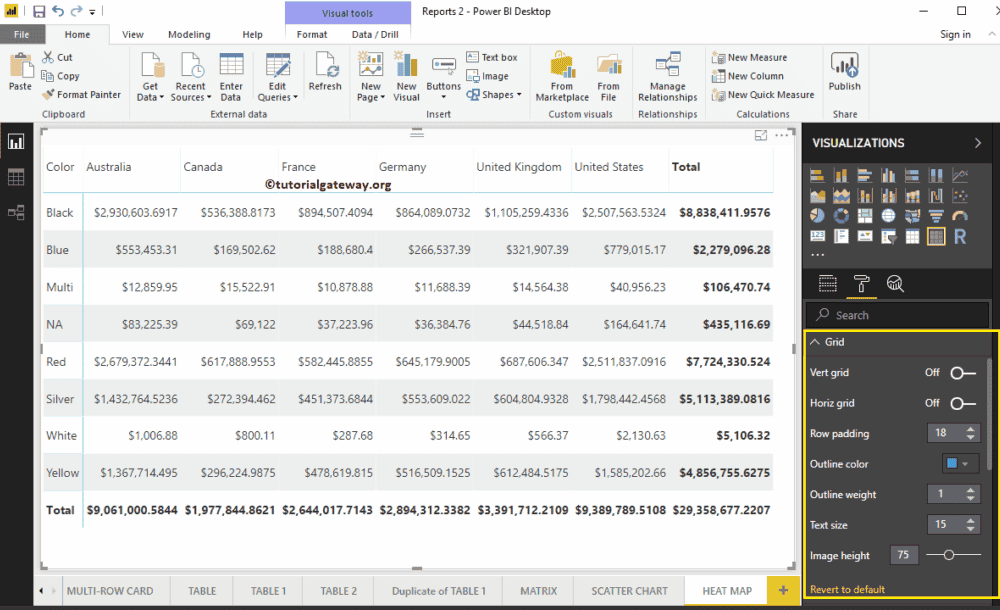
First, go to the Grid Section. As you can see from the below screenshot, we changed the row padding to 18 and the text size to 15
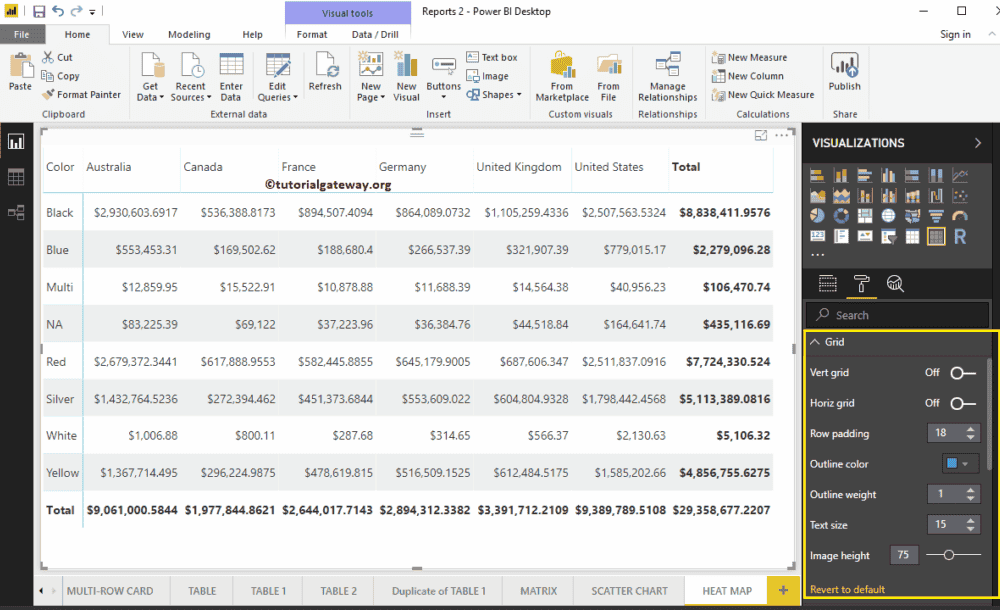
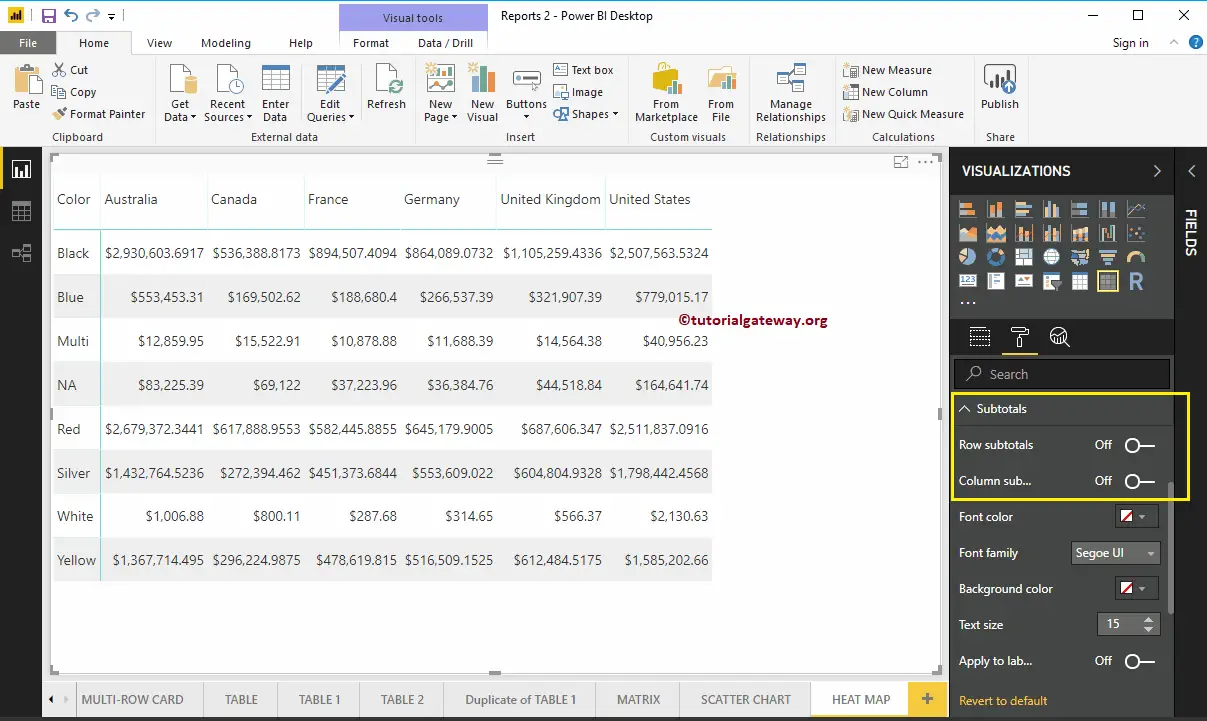
By toggling Row subtotals and column subtotals under the Subtotals section to Off, you can remove the Totals completely. So, let me remove them.
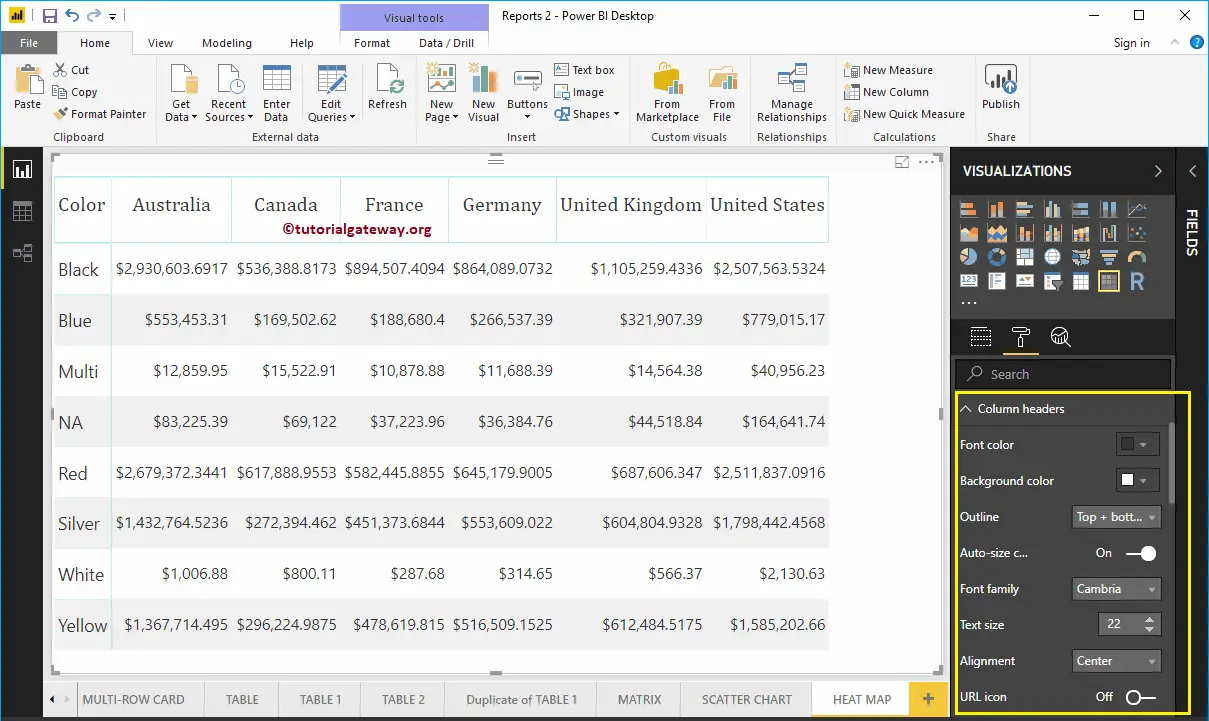
The column Header section of Power BI Heatmap helps us to alter the Headers. As you can see from the screenshot below, we changed the Font Family to Cambria. Next, Outline to Top + Bottom (Outline added to the top and bottom of a Header), Text Size to 22, and Header text alignment to center.
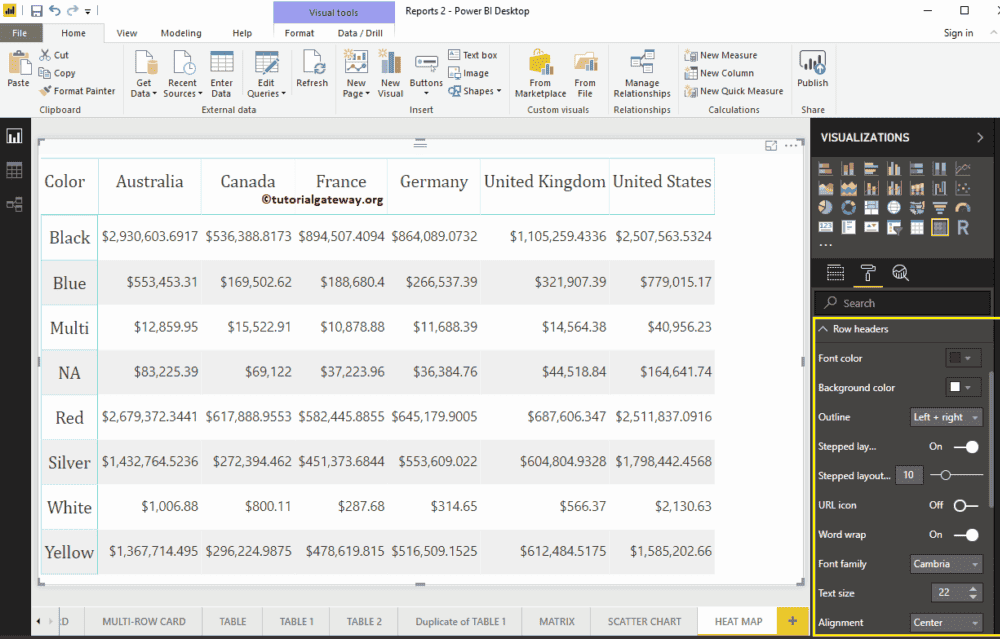
Heatmap’s row Header section helps us format the Row Headers section. Here, we changed the Outline to Left + Right (Outline added to the Left and Right of Header Column, i.e., Color). Next, the Font Family to Cambria, the Text Size to 22, and the text alignment to the center.
Power BI Heatmap Example
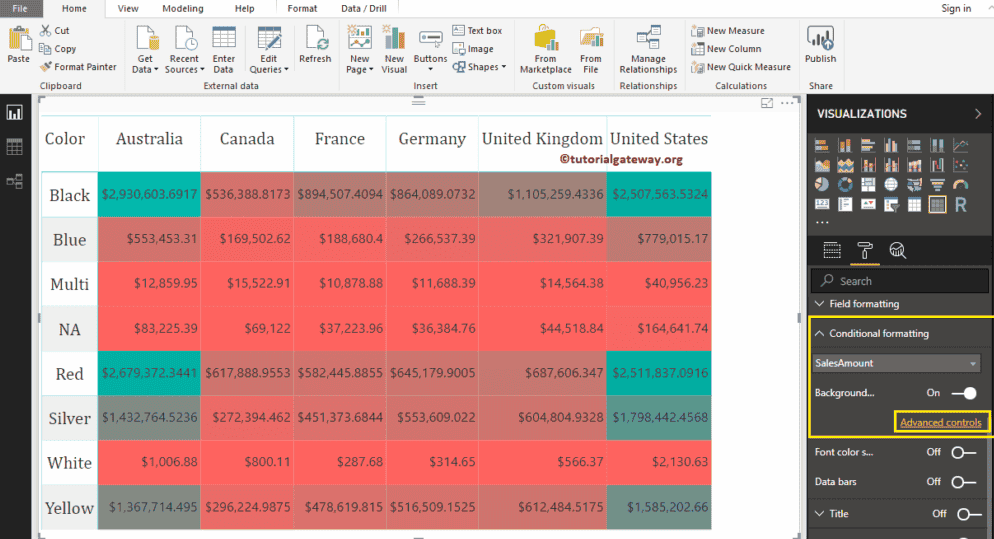
To connect that matrix to the heatmap, go to the Conditional Formatting section to add colors to the Matrix Numeric column.
As you can see from the screenshot below, we selected the Sales Amount as the field and toggled the background color scale property to On. It adds a default color to the matrix. I mean, the default color to Heatmap.
Change Power BI Heatmap Color
Click on the Advanced option to change the Power BI heat map color. It will open the following window. If you are interested in two colors, select the Minimum and maximum colors.
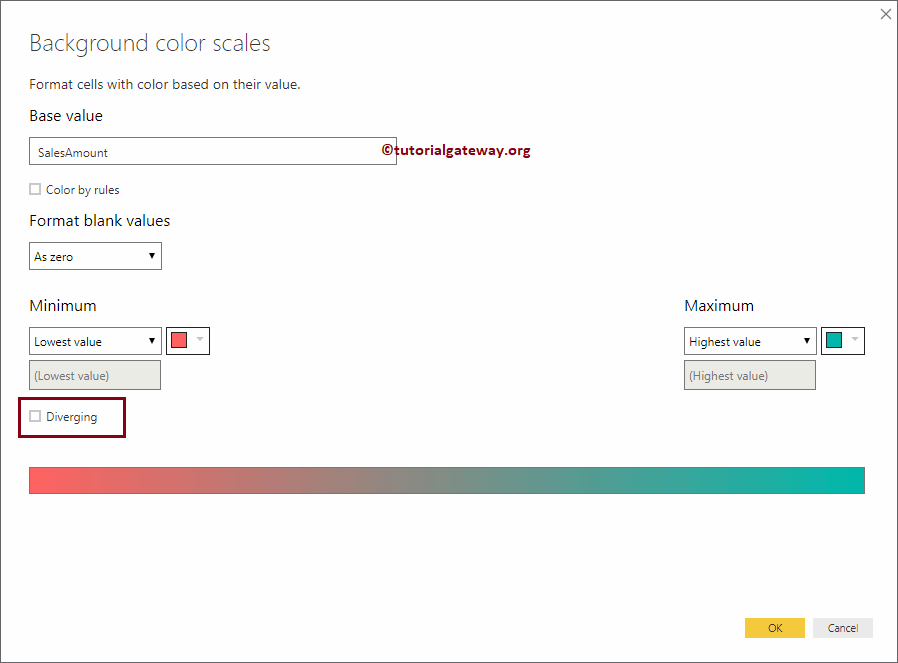
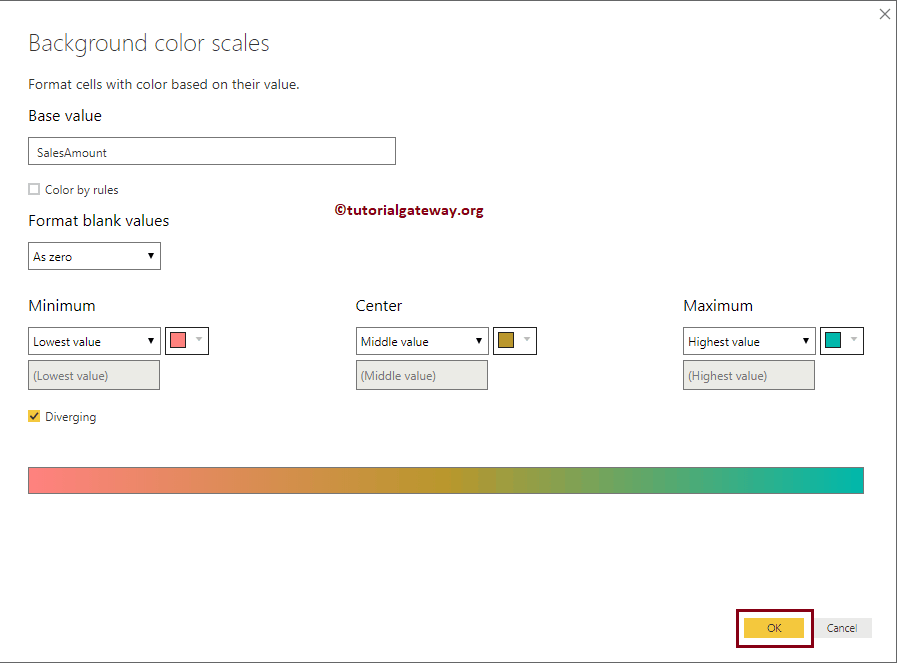
We check-marked the Diverging option. Next, we selected some random colors as the minimum, Center, and Maximum values.
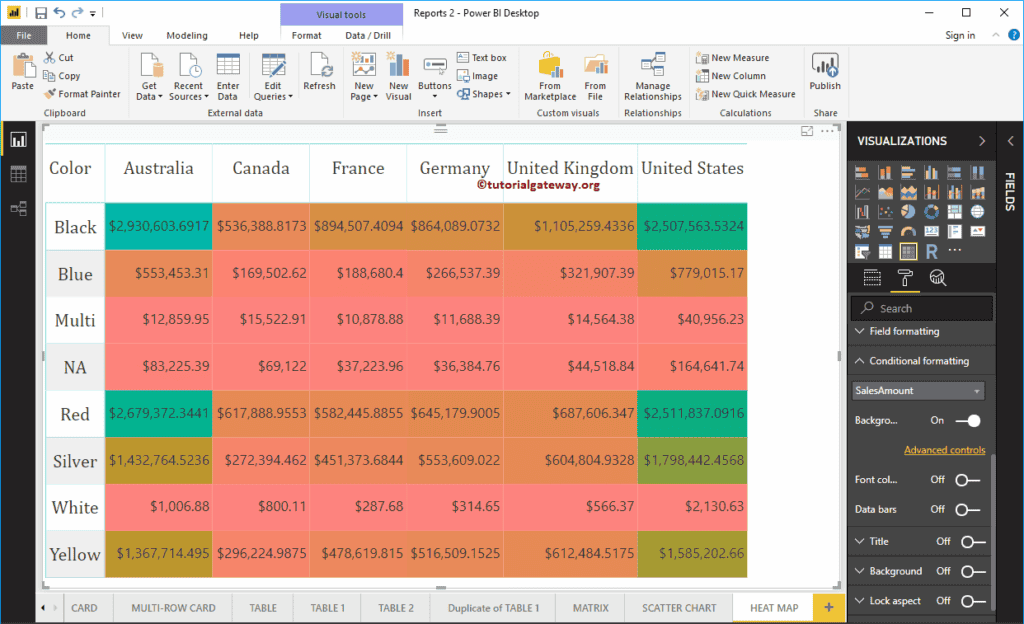
Now, you see the Power BI Heat map with the selected colors.
FAQ’s
Heat maps, also known as density maps, use different colors to display data density. If you use it on a map, it shows the color density at each location. For instance, state or postcode-wise visits, sales, or orders. The most common one is displaying cyclone or hurricane movement.
Yes. Either get it from the marketplace or use any file from the system.
If you are using the marketplace heat map, click on the icon. Then, add geographic data (State, City, Country, Postal Code) to the Location ID and Numeric Measure to the values section. You have an option for the Latitudes.
If converting a standard table to a heat map, use the conditional formatting option of the measure value.
Heat maps use colors to represent the data graphically. The thickness of the color means more (high) data in that region.
It shows the popularity of the data in color-coded. A heat map helps easily identify which month, state, or zone has good and bad profits.

Comments are closed.