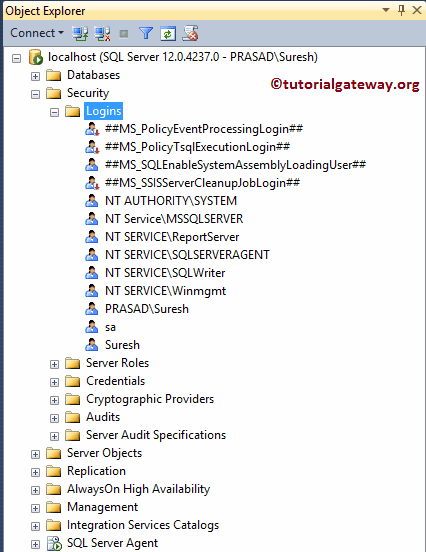
There are two approaches to create SQL Server Widows Login authentications: Management Studio and Transact query. This article explains both these approaches with an example. Before we start creating new windows login in SQL Server, let me show you the list of available logins in our Management Studio.
Create Windows Login in SQL Server Management Studio
To create SQL Server Windows login, please expand the Security folder, and right-click on the Login folder to open the context menu. Please select the New Login.. option to create a login.
- Guide to Management Studio, Install SSMS, and Uninstall SSMS.
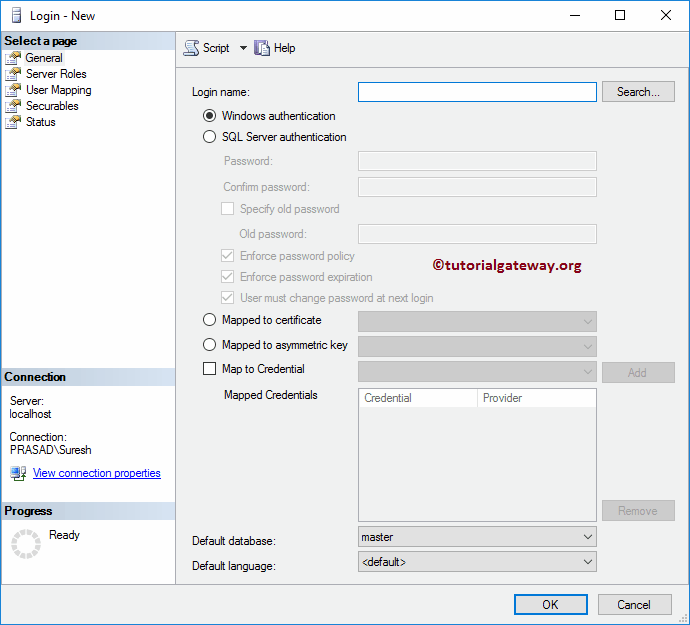
Once you choose the New Login.. option, the below-shown window will open. By default, Windows Authentication selected by SQL Server, and you don’t need to change anything.
- Login Name: Please select the Windows User that you are going to use to login to the Database Engine.
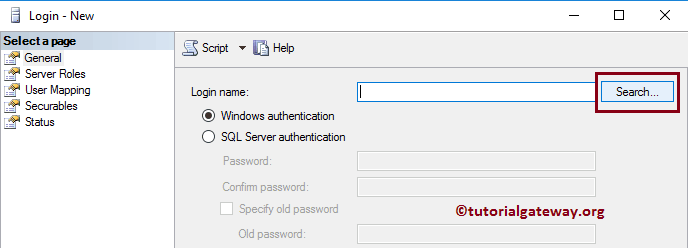
If you know the login name, type the name inside the Login name text box. Otherwise, click on the Search button beside the Login Name
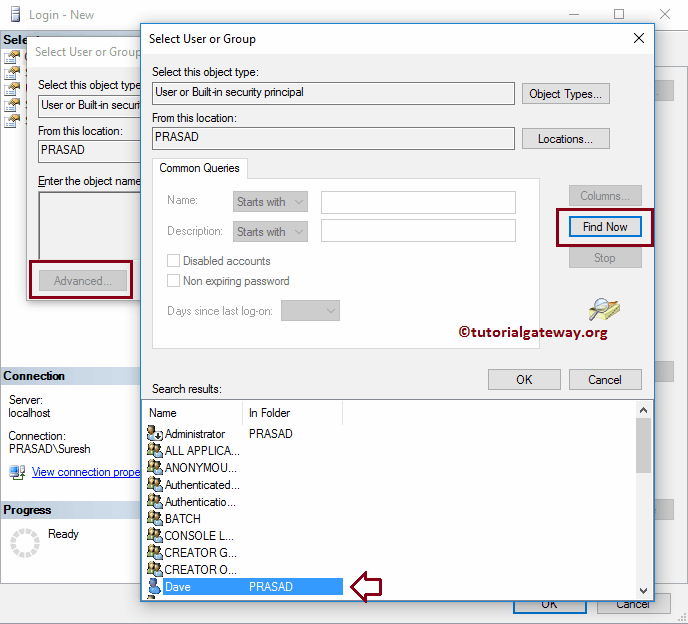
Once you click on the Search button, the following window will open.
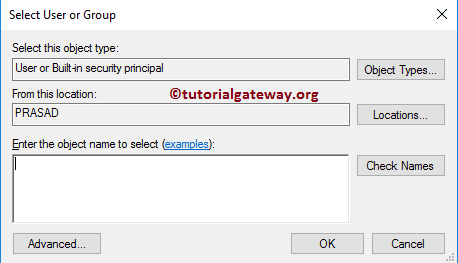
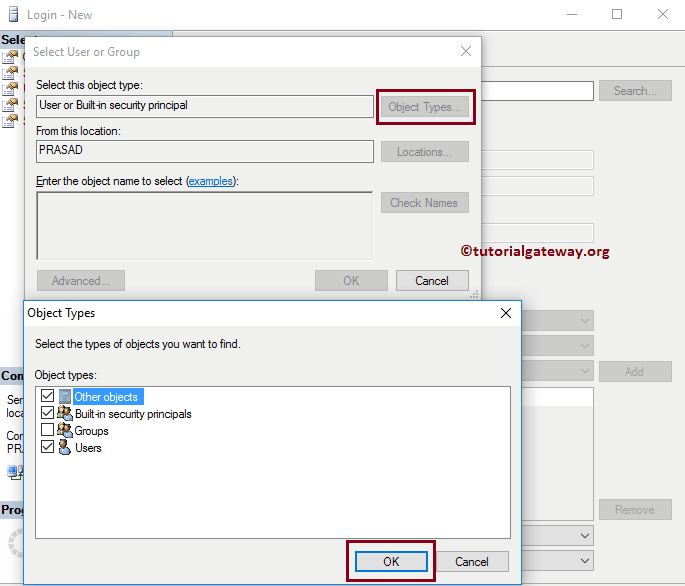
If you want to change the Object Types, click the Object Types.. button
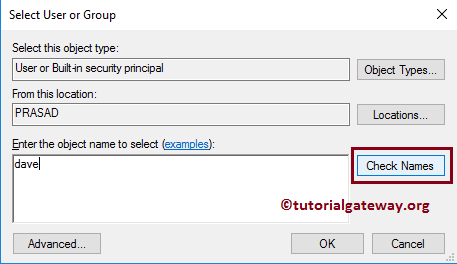
If you know the name, write it inside the text box and click Check Names button
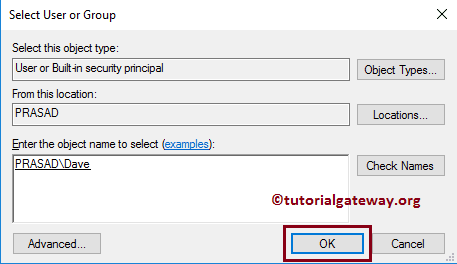
As you can see, it is automatically retrieving the windows account information
If you don’t know the name, click the Advanced button and click the Find Now button. It displays all the existing users
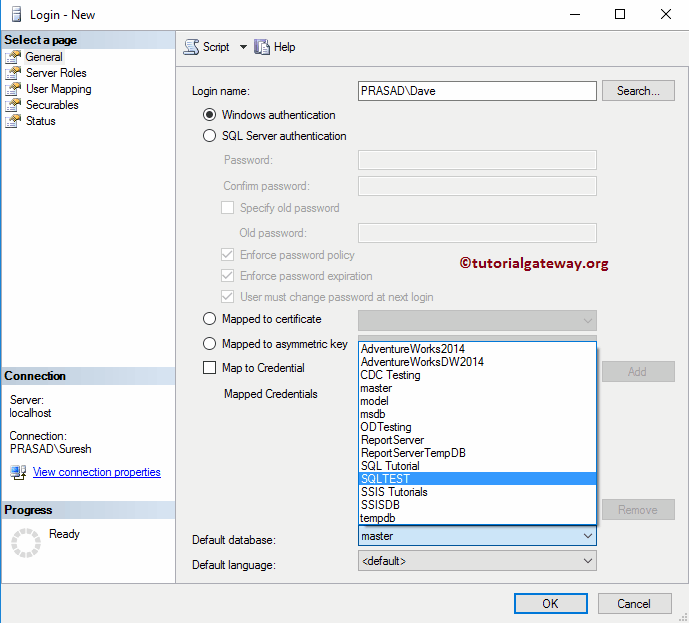
Default Database: Select the default Database that you need to assign to this Windows Login user and for now, we are choosing the SQL Test database.
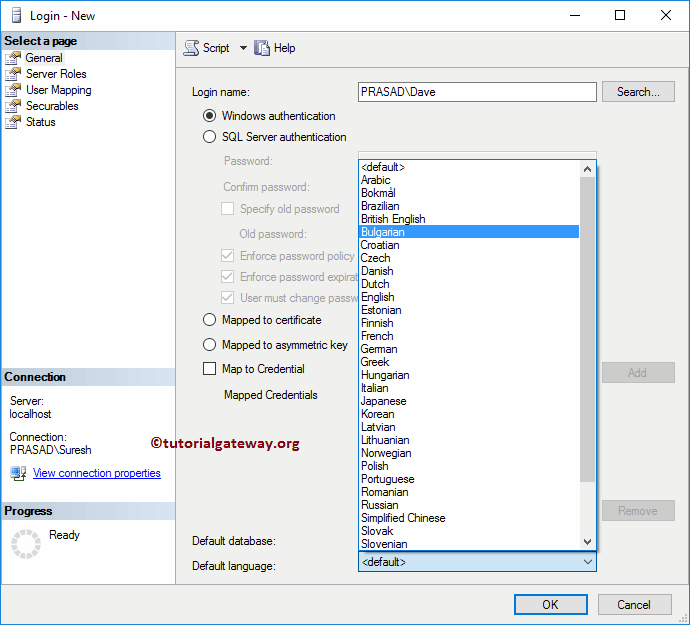
Default Language: Select the default language. For now, let us keep it default, which is English.
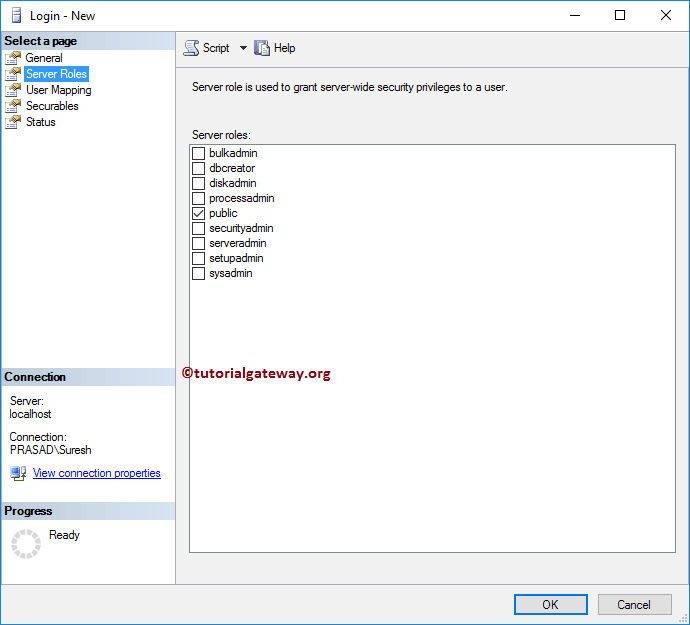
Server Roles: Use this to specify the Server Roles. Please refer to the Create Server Roles article. For now, we chose the default Public option.
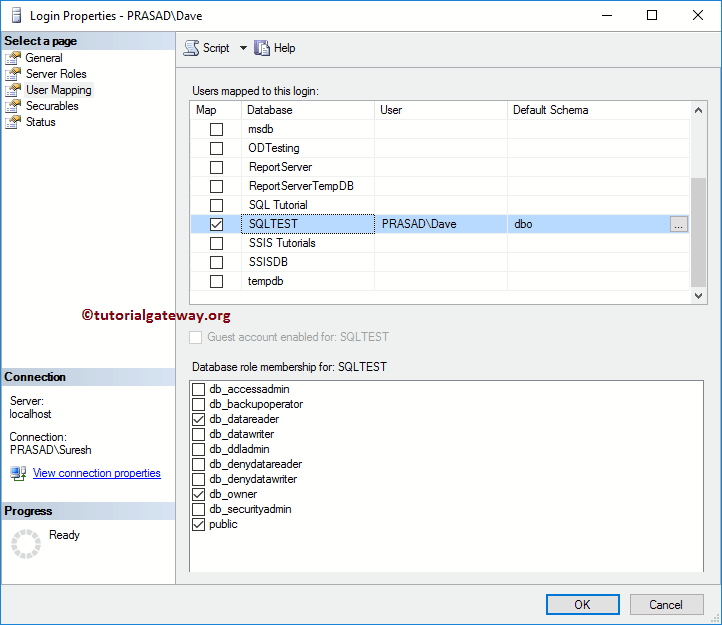
User Mapping: Use this to pick the database and assign database roles. Since we chose the SQL Test as the default database, Windows Login has automatically mapped the user to this database.
Let me select the database roles as default Public, db_datareader, and db_Owner option.
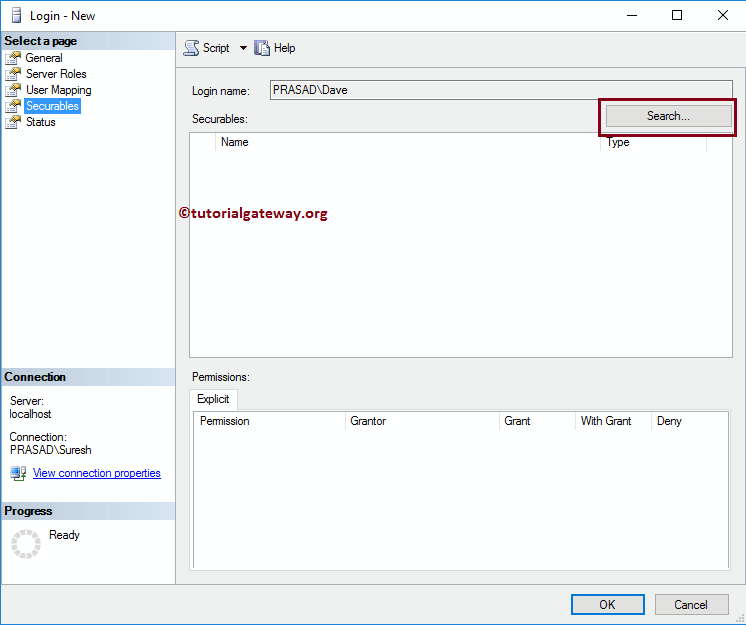
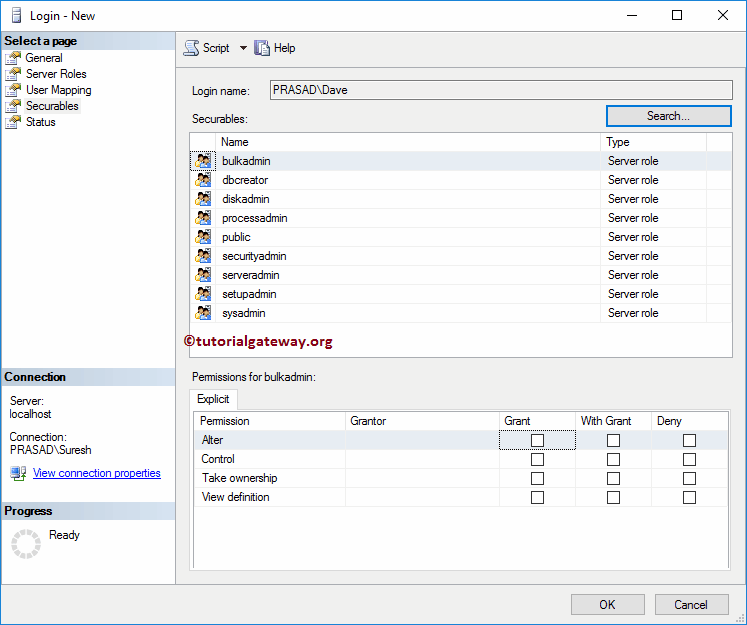
Securables: Use the Search button to search for Objects.
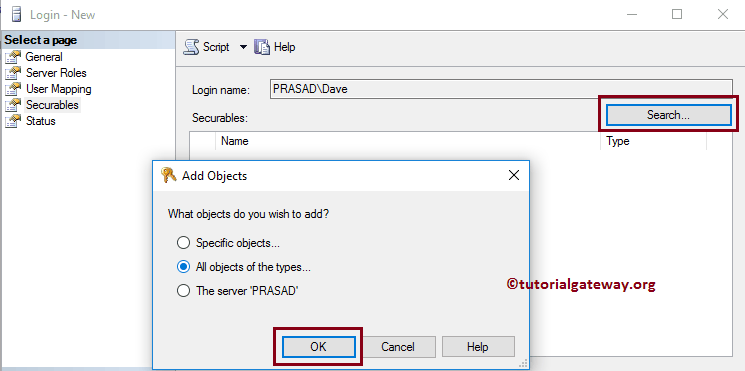
For now, we are selecting the All Objects of the types.. option
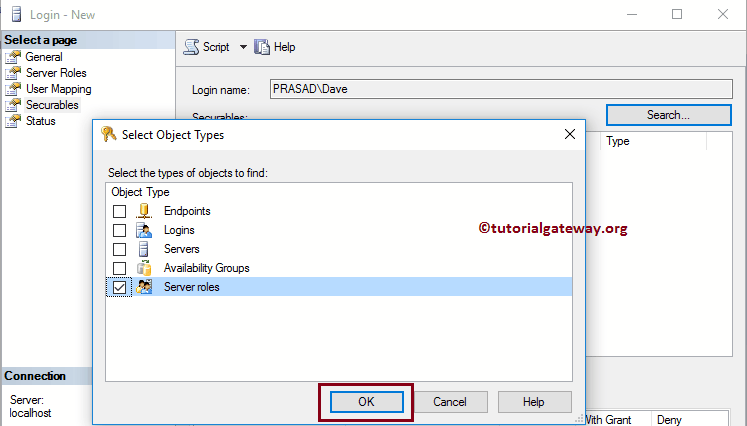
And then, we are choosing the Server Roles. It means this particular server role will control all the server roles.
You can select the server role and use the Grant, With Grant, and Deny options to grant permissions, or to deny. For now, we are leaving it without any changes.
Status: In this tab we had two options:
- Permission to connect to database Engine: If you want to give, then select the Grant; otherwise, Deny.
- Login: If you need this user to login to Database Manager, pick Enabled otherwise, Disabled.
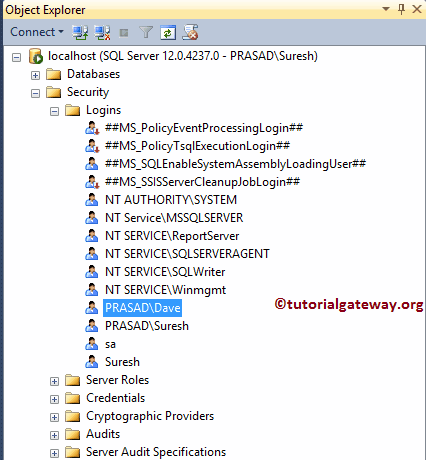
From the below screenshot, you can see our newly created widows Login in SQL Server.
Create Windows Login
The basic syntax to create Windows login in SQL Server is:
CREATE LOGIN [Domain_Name\Login_Name] -- This is the User that you use for login FROM WINDOWS DEFAULT_DATABASE = [Database Name], -- This is Optional DEFAULT_LANGUAGE = [Language Name];-- This is Optional
Below code snippet will create a new windows login Kishore in SQL Server using CREATE LOGIN with default settings.
CREATE LOGIN [PRASAD\Kishore] -- This is the User that you use for login FROM WINDOWS
Run the above create login query
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Below screenshot will show our newly created window login
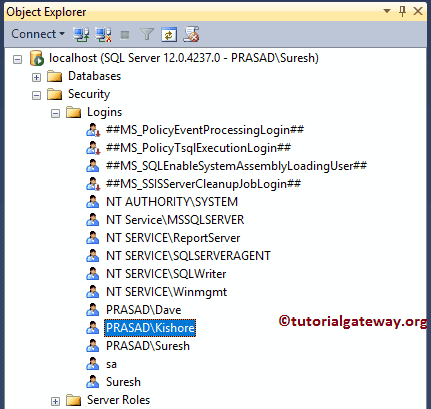
Please go to its properties to view or edit the login properties. As you can see, this login is pointing to the master database.
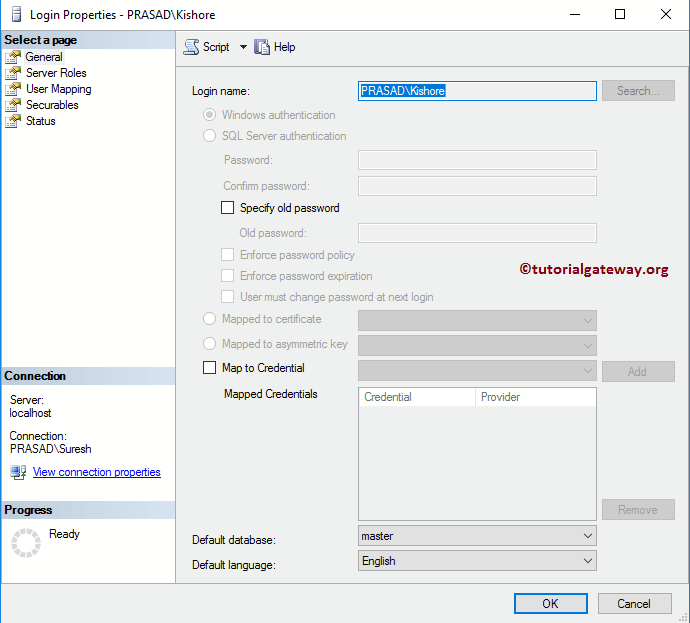
Below code snippet will create a new windows login PRASAD\Kishore, and his default database is a shown below.
CREATE LOGIN [PRASAD\Kishore] -- This is the User that you use for login FROM WINDOWS DEFAULT_DATABASE = [SQL Tutorial] -- This is Optional
Execute the above create login for windows query
Messages
--------
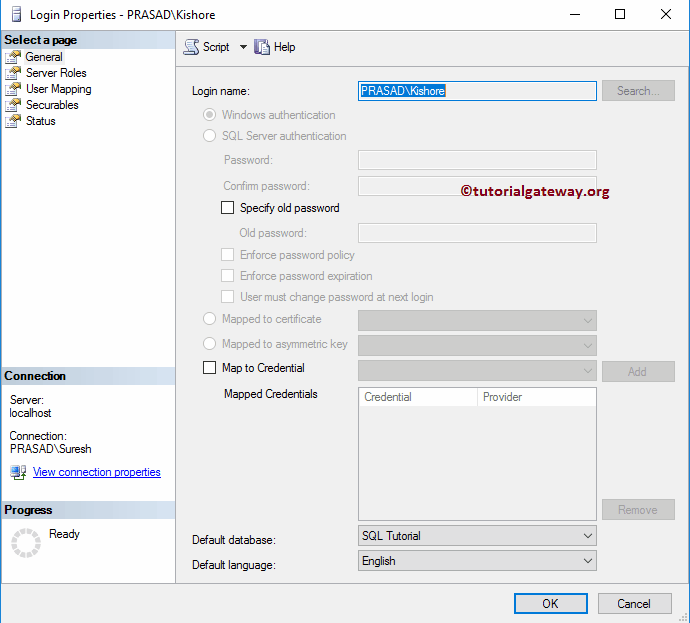
Command(s) completed successfully.You can see the same in its properties.
Edit Windows Login in SQL Server
To edit the existing SQL Server widows login, Please go to the Logins folder to select the required Login name. Right-click on the widows login name that you want to edit and select Properties option.
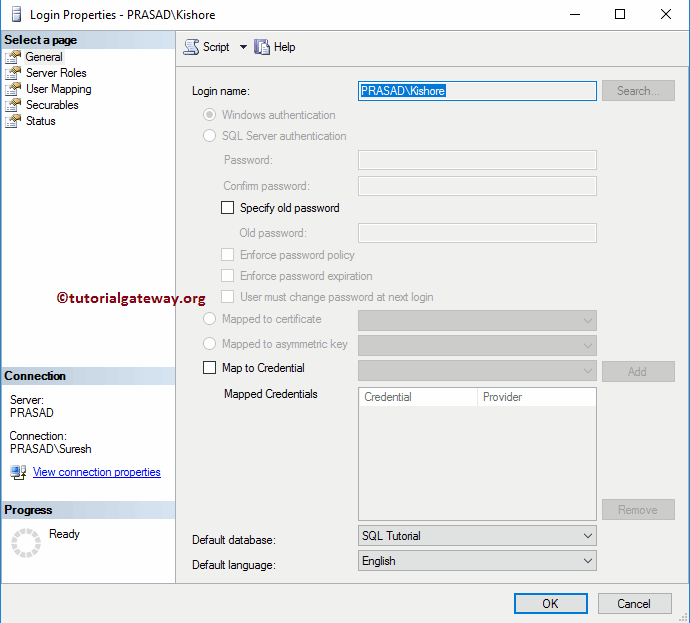
Once you pick the Properties option, the following window will open. Use this windowpane to alter the Default Language, Default Database, User mappings, Server Roles, Securables, and Status.
Delete Windows Login in SQL Server using SSMS
Please extend the SQL Server Logins folder to choose the required windows Login name. Right-click on the name that you want to delete and select Delete option from the context menu.
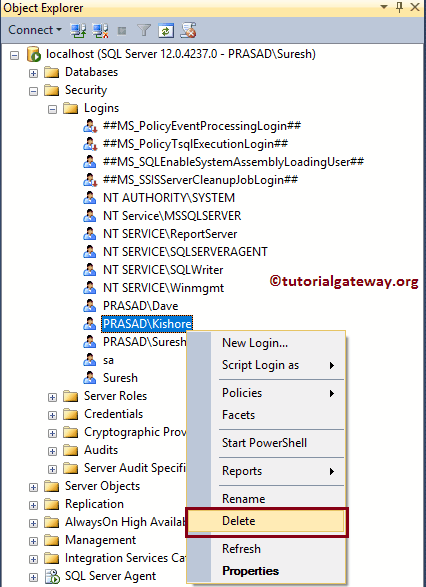
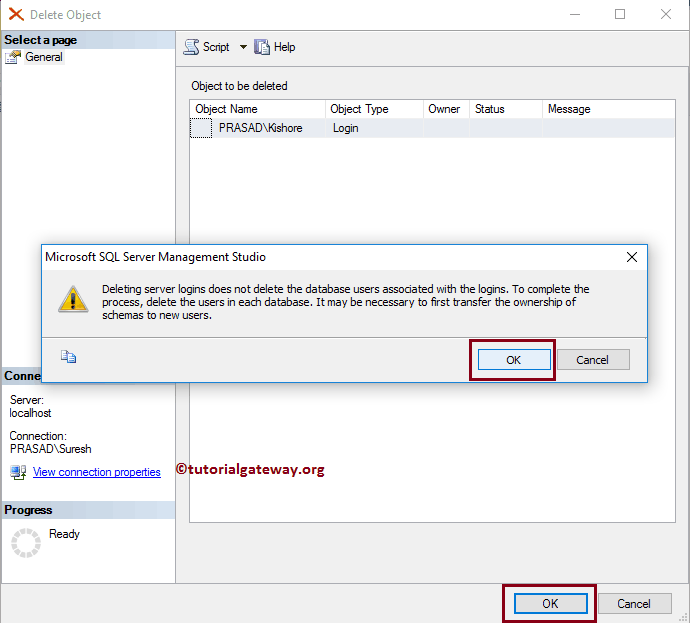
Once you select the Delete option, the below-shown window opened. Click OK to delete the windows login
Delete Windows Login in SQL Server using DROP LOGIN
In this example, we show you how to use the DROP LOGIN statement to delete the windows login in SQL Server.
DROP LOGIN [PRASAD\Kishore]
Execution result
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.