The SQL Server SYSUTCDATETIME function is one of the Date Functions, which is useful to return the current system timestamp as a datetime2 value. The return value of this SYSUTCDATETIME function is the current Coordinated Universal Time (UTC time). And it derives from the operating system (OS) of the computer on which the SQL Server instance is running.
NOTE: This function is similar to the GETUTCDATE function, and the differences are:
- SYSUTCDATETIME returns the fractional seconds precision up to 7, whereas the GETUTCDATE returns up to 3
- The SYSUTCDATETIME returns datetime2 as the data type, whereas the GETUTCDATE returns DateTime
SQL SYSUTCDATETIME Syntax
The syntax of the SYSUTCDATETIME is
SYSUTCDATETIME()
SQL Server SYSUTCDATETIME Function Example
The SQL Server SYSUTCDATETIME function returns datetime2 data type, and the format is: ‘yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss.nnnnnnn’. From the below screenshot, you can see that the fractional seconds precision = 7).
SELECT SYSUTCDATETIME() AS [Current_Date]
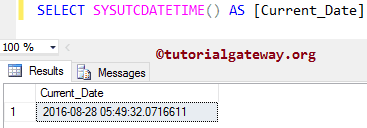
SYSUTCDATETIME Function Example 2
This SQL Server function returns the current system timestamp of type datetime2. Here, we are going to show you the SQL Server SYSUTCDATETIME function with examples.
SELECT 'Today' AS 'TODAY', SYSUTCDATETIME() AS [Current_Date]; SELECT 'Milli Seconds' AS 'MILLISECOND', DATEPART(millisecond, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [MilliSeconds_Value]; SELECT 'Micro Seconds' AS 'MICROSECOND', DATEPART(microsecond, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [MicroSeconds_Value]; SELECT 'Nano Seconds' AS 'NANOSECOND', DATEPART(nanosecond, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [NanoSeconds_Value]; SELECT 'Day' AS 'DAY', DATENAME(WEEKDAY, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [Day_Name]; SELECT 'Tomorrow' AS 'DAY', DATEADD(day, 1, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [Next_Date];
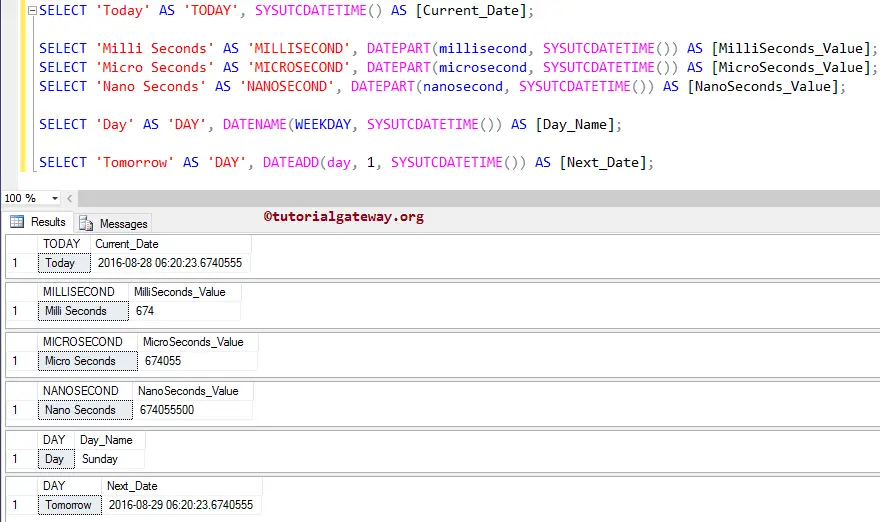
We used the SQL DATEPART function to display the Microsecond, Milliseconds, and Nanoseconds from today’s date & time.
SELECT 'Milli Seconds' AS 'MILLISECOND', DATEPART(millisecond, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [MilliSeconds_Value]; SELECT 'Micro Seconds' AS 'MICROSECOND', DATEPART(microsecond, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [MicroSeconds_Value]; SELECT 'Nano Seconds' AS 'NANOSECOND', DATEPART(nanosecond, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [NanoSeconds_Value];
Next, We used the DATENAME function to display the weekday name from today’s date & time.
SELECT 'Day' AS 'DAY', DATENAME(WEEKDAY, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [Day_Name];
We used the DATEADD function to display Tomorrow’s date & time
SELECT 'Tomorrow' AS 'DAY', DATEADD(day, 1, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [Next_Date];
SYSUTCDATETIME Function Example 3
In this SQL Server SYSUTCDATETIME function example, we are going to find the differences in Minutes, Seconds, and Milliseconds between the variable and Current Date & time. For this, we are using the DATEDIFF function.
DECLARE @dtime DATETIME2 SET @dtime = '2016-08-27 03:54:27.5301234' SELECT 'Minutes_Difference' AS 'MINUTE', DATEDIFF(MINUTE, @dtime, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [Number of Minutes]; SELECT 'Seconds_Difference' AS 'SECOND', DATEDIFF(SECOND, @dtime, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [Number of Seconds]; SELECT 'Millisecond_Diff' AS 'MILLISECOND', DATEDIFF(MILLISECOND, @dtime, SYSUTCDATETIME()) AS [Number of MilliSeconds];
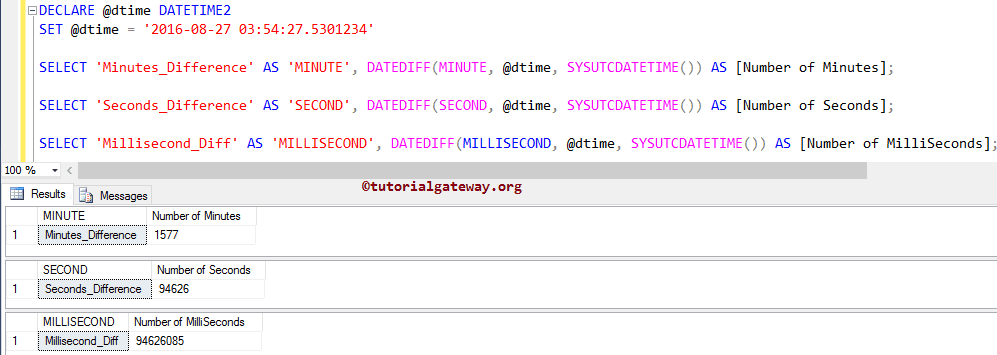
From the above, you can observe that we used the DATEDIFF Date and Time Function to find the difference between the current date and time and the @dtime variable that we declared.
