SQL Server DATENAME function is used to extract or display specified date parts from the existing date. This SQL DATENAME function always returns String data. For example, If you want to extract the month name or day name (Sunday .. Saturday) from the existing Date, use this Datename function.
SQL DATENAME Syntax
The basic syntax of Sql Server Datename
DATENAME (Datepart, Date)
Datepart: It is part of a given date that we are going to display as output. The following table will display the list of available datepart arguments in the SQL Server
| Datepart | Abbreviations | Description |
|---|---|---|
| year | yy,yyyy | This will display the Millisecond’s Value. |
| quarter | qq, q | Display the quarter value from the given date. |
| month | mm, m | Display the month name from the given date. |
| dayofyear | dy, y | The day of a year numbers from 1 to 365. |
| day | dd, d | The day of the year numbers from 1 to 365. |
| week | wk, ww | Display the Weekdays name from the given date (Sunday to Saturday). |
| weekday | dw, w | Minute Value present on the specified date. |
| hour | hh | It returns the Hour value. |
| minute | mi, n | Minute Value present on the specified date. |
| second | ss, s | This will display the Millisecond’s Value. |
| millisecond | ms | This will display the Milliseconds Value. |
| microsecond | mcs | This Datename will display the microsecond Value available. |
| nanosecond | ns | This argument in sql datename function will display the Nanoseconds Value. |
| TZOffset | tz | This will display the Time Zone Offset Value. |
| ISO_WEEK | isowk, isoww | This will display the Iso Week Number. |
Date: Please specify the valid date as the second argument in this SQL datename function. It can be a column, an expression, or any variable.
SQL DATENAME Example
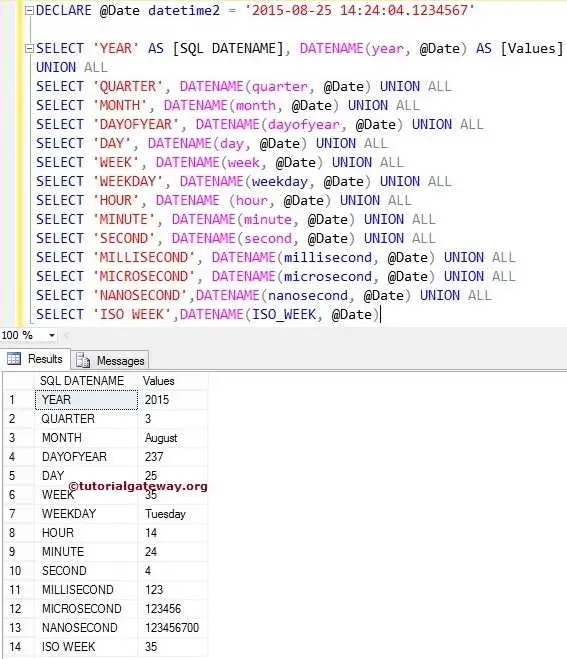
In this Date function example, we are going to declare a variable of datetime2 data type. Let us assign a valid date to that variable and perform all the available SQL DATENAME operations.
First, we declared one variable and assigned the date and time to that variable. The first SQL Server Datename statement will display the year number, and the following statement prints the month.
DECLARE @Date datetime2 = '2015-08-25 14:24:04.1234567' SELECT 'YEAR' AS [SQLDATENAME], DATENAME(year, @Date) AS [Values] UNION ALL SELECT 'QUARTER', DATENAME(quarter, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'MONTH', DATENAME(month, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'DAYOFYEAR', DATENAME(dayofyear, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'DAY', DATENAME(day, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'WEEK', DATENAME(week, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'WEEKDAY', DATENAME(weekday, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'HOUR', DATENAME (hour, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'MINUTE', DATENAME(minute, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'SECOND', DATENAME(second, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'MILLISECOND', DATENAME(millisecond, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'MICROSECOND', DATENAME(microsecond, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'NANOSECOND',DATENAME(nanosecond, @Date) UNION ALL SELECT 'ISO WEEK',DATENAME(ISO_WEEK, @Date)
DATENAME Function Example 2
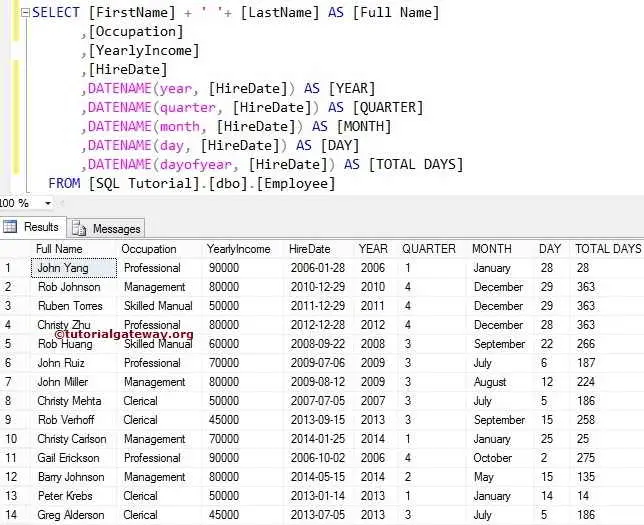
In this SQL Server example, we use one of the custom tables to perform Datename operations on the HireDate column.
The Datename function will print the Year value from the HireDate Column for the fifth line. And the sixth line will display the Quarter value from the HireDate Column.
SELECT [FirstName] + ' '+ [LastName] AS [Full Name]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[HireDate]
,DATENAME(year, [HireDate]) AS [YEAR]
,DATENAME(quarter, [HireDate]) AS [QUARTER]
,DATENAME(month, [HireDate]) AS [MONTH]
,DATENAME(day, [HireDate]) AS [DAY]
,DATENAME(dayofyear, [HireDate]) AS [TOTAL DAYS]
FROM [Employee]