A series in Python is a kind of one-dimensional array of any data type that we specified in the pandas module. The only difference you can find is that each value in a pandas series is associated with the index. The default index value of it is from 0 to number – 1, or you can specify your own index values.
The following long list of examples helps you understand this Python pandas Series, how to access them, and alter the items, indexes, columns, etc.
Python pandas Series Examples
It is a simple Python pandas Series example. As you can see, it has assigned the default index values from 0 to 3 (4 – 1).
import pandas as pd from pandas import Series arr = Series([15, 35, 55, 75]) print(arr)
0 15
1 35
2 55
3 75
dtype: int64Python Series Values and Index
The Series has two attributes such as values and index. You can use these attributes to get information about them.
- values: This returns the array of actual data or elements in it.
- index: As the name suggests, this object returns the index values.
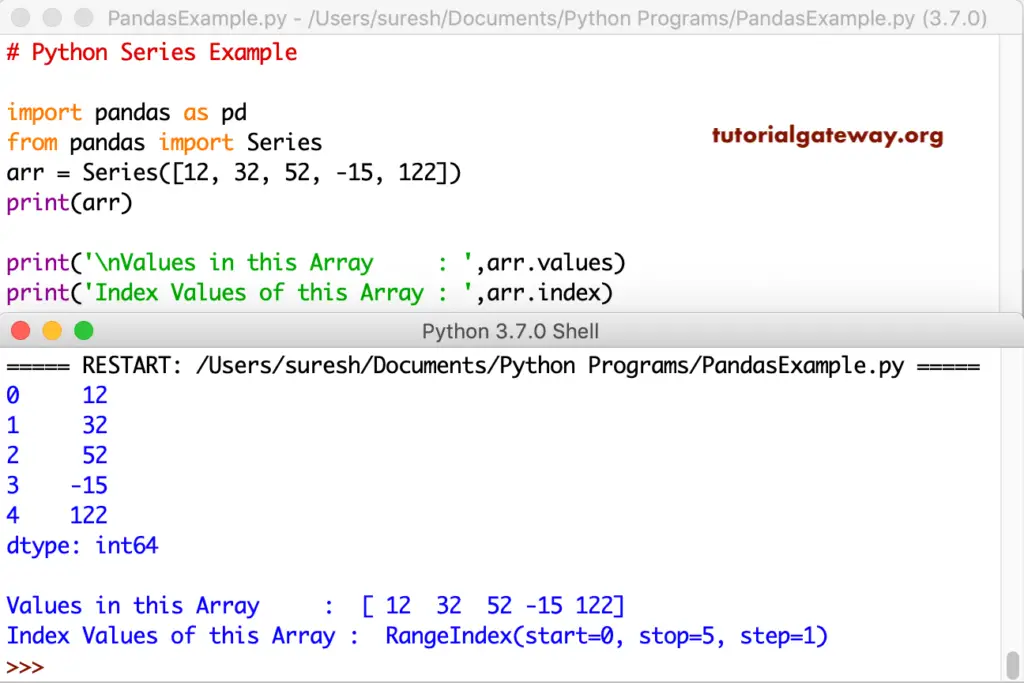
arr = Series([12, 32, 52, -15, 122])
print(arr)
print('\nValues in this Array : ',arr.values)
print('Index Values of this Array : ',arr.index)
Python pandas Series Index
You can use the index attribute to create your own index or assign your own index to the data. It is the handy and best way to identify the data for future analysis.
arr = Series([25, 50, 75, 100, 125], index = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
print(arr)
print('\nValues in this Array : ',arr.values)
print('Index Values of this Array : ',arr.index)
Series Index output
2 25
4 50
6 75
8 100
10 125
dtype: int64
Values in this Array : [ 25 50 75 100 125]
Index Values of this Array : Int64Index([2, 4, 6, 8, 10], dtype='int64')Let me use Alphabets as the index values.
import pandas as pd from pandas import Series arr = Series([2, 33, 66, 70, 15], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u']) arr arr.index
If you use an external file to save this series code, use the below code.
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
arr = Series([2, 33, 66, 70, 15], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'])
print(arr)
print('\nValues in this Array : ',arr.values)
print('Index Values of this Array : ',arr.index)
a 2
e 33
i 66
o 70
u 15
dtype: int64
Values in this Array : [ 2 33 66 70 15]
Index Values of this Array : Index(['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'], dtype='object')Create a Python Series using arange
You can also use the arange function available in the Numpy module to create a pandas series of consecutive numbers from 0 to n-1.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from pandas import Series arr = Series(np.arange(6)) print(arr) # arr # Here, we are assigning the index names. arr1 = Series(np.arange(6), index = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']) print(arr1) #arr1
0 0
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
dtype: int64
a 0
b 1
c 2
d 3
e 4
f 5
dtype: int64Alter Python pandas Series Index
The index function does not only allow you to display the index items, but you can also alter it as well. This example changes the actual index items and places the integer values as the index.
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
new_arr = Series([2, 33, 66, 70, 15], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'])
print(new_arr)
print('\nValues in this Array : ',new_arr.values)
print('Index Values of this Array : ',new_arr.index)
print(' ')
# Assigning New Index Values
new_arr.index = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(new_arr)
print('\nValues in this Array : ',new_arr.values)
print('Index Values of this Array : ',new_arr.index)
Alter Index output
a 2
e 33
i 66
o 70
u 15
dtype: int64
Values in this Array : [ 2 33 66 70 15]
Index Values of this Array : Index(['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'], dtype='object')
1 2
2 33
3 66
4 70
5 15
dtype: int64
Values in this Array : [ 2 33 66 70 15]
Index Values of this Array : Int64Index([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype='int64')Create a Python Series from Dictionary
Python also allows you to create a Series for a dictionary. When you use a dictionary, values become series data, and dictionary keys act as an index.
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
f_dict = {'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries': 6000}
print('Dictionary Items')
print(f_dict)
arr = Series(f_dict)
print('\nArray Items')
print(arr)
Dictionary to pandas Series output
Dictionary Items
{'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries': 6000}
Array Items
apples 500
kiwi 20
oranges 100
cherries 6000
dtype: int64We can also change the order of the index values while converting a dictionary to a Series.
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
f_dict = {'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries': 6000}
new_list = ['apples', 'cherries', 'kiwi', 'oranges']
arr = Series(f_dict, index = new_list)
print('Array Items')
print(arr)
Converting a dictionary and changing the order output
Array Items
apples 500
cherries 6000
kiwi 20
oranges 100
dtype: int64What if we add an index that doesn’t exist in the actual dictionary key, and obviously, it won’t have any value associated with it.
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
f_dict = {'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries': 6000}
new_list = ['apples', 'banana', 'cherries', 'kiwi', 'oranges']
arr = Series(f_dict, index = new_list)
print('Array Items')
print(arr)
From the below object screenshot, you can see it was returning NaN as the value for that index or key
Array Items
apples 500.0
banana NaN
cherries 6000.0
kiwi 20.0
oranges 100.0
dtype: float64series attributes
The Python Series Object has an important attribute called name. You can use this attribute to assign a name for both the data and the indexes.
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
f_dict = {'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries': 6000}
arr = Series(f_dict)
print(arr)
print('\nAssigning Names')
arr.name = 'No of Items'
arr.index.name = 'Fruits'
print(arr)
attributes output
apples 500
kiwi 20
oranges 100
cherries 6000
dtype: int64
Assigning Names
Fruits
apples 500
kiwi 20
oranges 100
cherries 6000
Name: No of Items, dtype: int64Accessing Python Series Items
Like numpy Arrays, we can use the index position or index number to access an item from it.
import pandas as pd from pandas import Series arr = Series([22, 44, 66, 88, 108]) arr
Access the Item at index positions 0, 2, and 4.
arr[0] arr[2] arr[4]
Creating a new or selecting a set of values from an existing one.
arr[[1, 3, 0, 4]]
Accessing items output
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from pandas import Series
>>> arr = Series([22, 44, 66, 88, 108])
>>> arr
0 22
1 44
2 66
3 88
4 108
dtype: int64
>>> arr[0]
22
>>> arr[2]
66
>>> arr[4]
108
>>> arr[[1, 3, 0, 4]]
1 44
3 88
0 22
4 108
dtype: int64
>>> We are accessing the data in it with custom index values. For this, we used Alphabet characters as the index items.
import pandas as pd from pandas import Series arr = Series([2, 4, -6, 8, -10, 12], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'z']) arr arr['a'] arr['u'] arr[['a', 'o', 'z', 'e']]
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from pandas import Series
>>> arr = Series([2, 4, -6, 8, -10, 12], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'z'])
>>> arr
a 2
e 4
i -6
o 8
u -10
z 12
dtype: int64
>>> arr['a']
2
>>> arr['u']
-10
>>> arr[['a', 'o', 'z', 'e']]
a 2
o 8
z 12
e 4
dtype: int64Python pandas Series in Operator
Before we perform anything on the data, it would be nice if we knew whether the index that we are looking for existed or not. For this in operator demo, we have in operator that can check and returns True, if it exists otherwise, False.
import pandas as pd from pandas import Series arr1 = Series([22, 33, 44, 55], index = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']) arr1 'b' in arr1 'c' in arr1 'f' in arr1
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from pandas import Series
>>> arr1 = Series([22, 33, 44, 55], index = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])
>>> arr1
a 22
b 33
c 44
d 55
dtype: int64
>>> 'b' in arr1
True
>>> 'c' in arr1
True
>>> 'f' in arr1
FalseLet me use the Dictionary as an array input and use the in operator.
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
f_dict = {'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries':6000}
arr2 = Series(f_dict)
arr2
'kiwi' in arr2
'banana' in arr2
'oranges' in arr2
in operator against it output
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from pandas import Series
>>> f_dict = {'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries':6000}
>>> arr2 = Series(f_dict)
>>> arr2
apples 500
kiwi 20
oranges 100
cherries 6000
dtype: int64
>>> 'kiwi' in arr2
True
>>> 'banana' in arr2
False
>>> 'oranges' in arr2
TruePython pandas Series Nulls
Python pandas module has isnull and notnull functions used to identify the Null and returns a Boolean True or False. To demonstrate the isnull and notnull functions, we use the same dictionary we used above.
import pandas as pd
from pandas import Series
dict_items = {'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries': 6000}
f_list = ['apples', 'banana', 'cherries', 'kiwi', 'oranges']
arr = Series(dict_items, index = f_list)
arr
It returns True if it is NULL or NA otherwise, False.
pd.isnull(arr) arr.isnull()
It returns False if the value is NaN, Null, or NA; otherwise, True.
pd.notnull(arr) arr.notnull()
pandas isnull, notnull output
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from pandas import Series
>>> dict_items = {'apples': 500, 'kiwi': 20, 'oranges': 100, 'cherries': 6000}
>>> f_list = ['apples', 'banana', 'cherries', 'kiwi', 'oranges']
>>> arr = Series(dict_items, index = f_list)
>>> arr
apples 500.0
banana NaN
cherries 6000.0
kiwi 20.0
oranges 100.0
dtype: float64
>>> pd.isnull(arr)
apples False
banana True
cherries False
kiwi False
oranges False
dtype: bool
>>> arr.isnull()
apples False
banana True
cherries False
kiwi False
oranges False
dtype: bool
>>> pd.notnull(arr)
apples True
banana False
cherries True
kiwi True
oranges True
dtype: bool
>>> arr.notnull()
apples True
banana False
cherries True
kiwi True
oranges True
dtype: boolPython pandas Series Arithmetic Operations
The Python pandas Series allows you to perform arithmetic operations on its data. You can use any of the operators to perform on all the items. This example shows you the pandas Series arithmetic operations.
import pandas as pd from pandas import Series arr = Series([2, 4, -6, 8, -7], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u']) arr
Add 3 to each item in it.
arr + 3
Subtracting 2 from items.
arr - 2
We are multiplying each item with 10.
arr * 10
Returns a subset of it whose values are greater than 0.
arr[arr > 0]
Arithmetic Operations output
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from pandas import Series
>>> arr = Series([2, 4, -6, 8, -7], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'])
>>> arr
a 2
e 4
i -6
o 8
u -7
dtype: int64
>>> arr + 3
a 5
e 7
i -3
o 11
u -4
dtype: int64
>>> arr - 2
a 0
e 2
i -8
o 6
u -9
dtype: int64
>>> arr * 10
a 20
e 40
i -60
o 80
u -70
dtype: int64
>>> arr[arr > 0]
a 2
e 4
o 8
dtype: int64Python Series Mathematical Function
You can use the math function that is supported by the numpy module on it.
from pandas import Series import numpy as np arr = Series([2, 4, -6, 8, -7], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u']) arr
Calculate the Power Of E
np.exp(arr)
Absolute Positive Value
np.fabs(arr)
The square root of each item in it
np.sqrt(arr)
Mathematical Functions on pandas
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> from pandas import Series
>>> import numpy as np
>>> arr = Series([2, 4, -6, 8, -7], index = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'])
>>> arr
a 2
e 4
i -6
o 8
u -7
dtype: int64
>>> np.exp(arr)
a 7.389056
e 54.598150
i 0.002479
o 2980.957987
u 0.000912
dtype: float64
>>> np.fabs(arr)
a 2.0
e 4.0
i 6.0
o 8.0
u 7.0
dtype: float64
>>> np.sqrt(arr)
a 1.414214
e 2.000000
i NaN
o 2.828427
u NaN
dtype: float64