In Python, we have the random module used to generate random numbers of a given type using the PRNG algorithm. Here, we are going to discuss the list of available functions to generate a random array in Python.
Python random array using rand
The Numpy random rand function creates an array of random numbers from 0 to 1. Here, you have to specify the shape of an array.
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.rand(7)
print('-----Generated Random Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.rand(10)
print('\n-----Using rand----')
print(arr2)
Generating random array using numpy rand function
-----Generated Random Array----
[0.72324285 0.902257 0.19086646 0.9848013 0.30726131 0.75984849
0.11788513]
-----Using rand----
[0.14238328 0.76333895 0.00358847 0.98198312 0.5848289 0.56392288
0.35347529 0.18018618 0.01869014 0.77321169]Python numpy 2D Random Array
Here, we are using this random rand function to generate a two dimensional array.
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.rand(2, 2)
print('-----Generated Two Dimensional Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.rand(4, 5)
print('\n-----Generated Two Dimensional Array----')
print(arr2)
2D random numpy Array
-----Generated Two Dimensional Array----
[[0.05429576 0.8120831 ]
[0.36443455 0.46820556]]
-----Generated Two Dimensional Array----
[[0.53800077 0.70044703 0.25007049 0.24959807 0.05361196]
[0.47492029 0.52460608 0.52157766 0.82260612 0.69135087]
[0.05602937 0.97118117 0.10938115 0.05648402 0.05137225]
[0.8724333 0.10477049 0.39284046 0.6794777 0.05015464]]Python Numpy 3D Random Array
Let us create a three-dimensional array using the Python random rand function.
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.rand(2, 2, 2)
print('-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.rand(2, 4, 5)
print('\n-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr2)
3D random Array output
-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----
[[[0.47091454 0.00534269]
[0.31374026 0.72377206]]
[[0.35134082 0.81840205]
[0.43662241 0.74013157]]]
-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----
[[[0.1361512 0.7146421 0.19965805 0.9579547 0.53017549]
[0.85335786 0.78601753 0.92519525 0.28573707 0.82727768]
[0.13179852 0.31101528 0.39261411 0.96552699 0.41586368]
[0.00234082 0.94735564 0.04102073 0.79654052 0.21729369]]
[[0.45856543 0.34984498 0.49087227 0.18287609 0.99288025]
[0.27352962 0.81479204 0.53724292 0.58885669 0.73794929]
[0.51417471 0.81165201 0.91994261 0.02474345 0.80619796]
[0.96855789 0.91635793 0.00951753 0.08579405 0.58610143]]]Python numpy random randn
The Python Numpy randn function generates random arrays of one, 2D, and 3D Arrays.
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randn(5)
print('-----Generated Random Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.randn(8)
print('\n-----Generated Random Array----')
print(arr2)
The Python numpy random randn function output
-----Generated Random Array----
[ 0.83523213 -1.01096736 -0.7414885 2.09988314 0.91615544]
-----Generated Random Array----
[-1.38702799 1.38481935 -2.72106855 -0.36215012 -2.37834684 2.03501968
-0.47954383 -1.32138939]This time we are generating two dimensional and three-dimensional arrays using the Numpy random randn function.
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randn(5, 4)
print('-----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.randn(2, 3, 5)
print('\n-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr2)
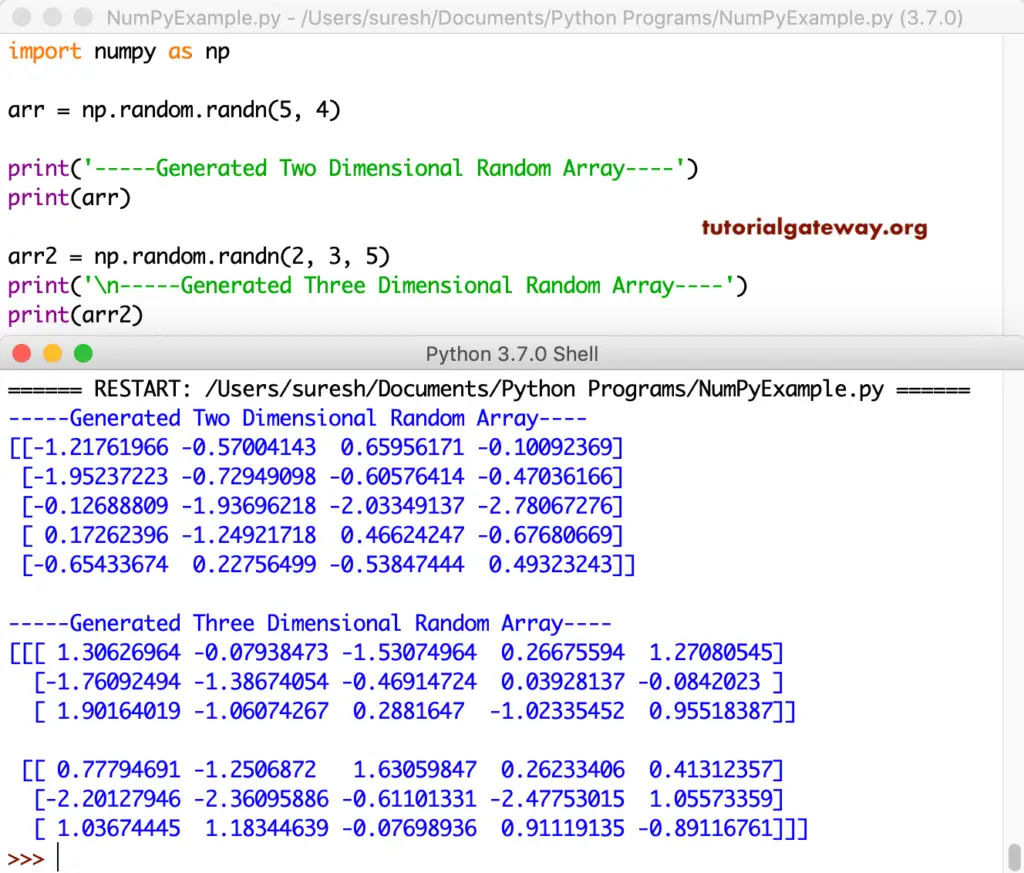
numpy Array using random function
We are using the Numpy random function available in the module to generate an array of numbers of length 6 and 8
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.random(5)
print('-----Generated Random Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.random((4, 5)) # Array size 4 * 5
print('\n-----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr2)
arr3 = np.random.random((2, 3, 5)) # Array size 2 * 3 * 5
print('\n-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr3)
The Python Numpy random function output
-----Generated Random Array----
[0.64137581 0.52893567 0.97619638 0.58440911 0.02690007]
-----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array----
[[0.80152396 0.57538786 0.66899029 0.38246115 0.33088933]
[0.4770973 0.50341904 0.37849585 0.23645669 0.27725212]
[0.80437494 0.21056882 0.30182026 0.05074108 0.45707601]
[0.01345951 0.67492805 0.58910196 0.50513836 0.74921775]]
-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----
[[[0.97499028 0.65040763 0.40997138 0.8118288 0.81487291]
[0.49658275 0.09282607 0.83938535 0.45125944 0.3039278 ]
[0.73293826 0.78006654 0.5849649 0.87548218 0.83538677]]
[[0.85536797 0.45816044 0.78535175 0.94308075 0.10670098]
[0.70658212 0.13714645 0.0630409 0.93133062 0.30178682]
[0.60449303 0.02822692 0.71913424 0.99570444 0.61137136]]]Python Numpy random randint
The Numpy random randint function returns an integer array from low value to high value of given size. The syntax of this Numpy function in Python is.
numpy.random.randint(low, high = None, size = None, type = ‘l’)
Let us see the Python Numpy random randint function example
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.randint(0, 5, size = 4)
print('-----Generated Random Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.randint(10, 50, size = (5, 10))
print('\n-----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr2)
arr3 = np.random.randint(1, 40, size = (2, 3, 7))
print('\n-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr3)
Python Numpy random randint function output
-----Generated Random Array----
[2 4 1 2]
-----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array----
[[19 39 22 48 21 34 46 39 12 15]
[43 21 20 28 48 29 28 15 29 17]
[36 28 30 35 17 44 33 38 11 18]
[17 15 28 33 20 33 24 33 10 11]
[25 33 37 44 42 20 24 39 24 14]]
-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----
[[[19 21 23 9 15 15 16]
[21 26 4 13 2 28 23]
[29 23 31 19 38 10 2]]
[[22 8 39 22 8 3 34]
[30 2 37 37 3 24 11]
[13 32 15 20 24 13 3]]]Python Numpy random normal
The Python Numpy random normal function generates numbers from a normal distribution. This Numpy normal accepts the size of an array then fills that array with normally distributed values.
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.normal(size = 4)
print('-----Generated Random Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.normal(size = (5, 5))
print('\n-----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr2)
arr3 = np.random.normal(size = (2, 3, 4))
print('\n-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr3)
Python Numpy random normal function output
-----Generated Random Array----
[-1.66160437 0.43505717 -0.74522529 0.34173931]
-----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array----
[[ 0.72445103 1.36516852 -1.59542701 -0.10782248 -0.59504893]
[-1.19228485 -0.6238485 1.46698494 -0.38137906 0.59017025]
[ 0.51707764 1.49834983 -0.54709123 -0.15535543 -0.87678266]
[ 1.346151 0.25772929 -0.00213373 0.58543647 -0.35374876]
[-0.39468152 0.96079429 -1.17187586 0.16560043 0.4487743 ]]
-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----
[[[ 0.99622715 -1.0571159 -0.11373001 1.19205186]
[ 1.39198314 -0.50049901 -1.42638241 -0.14458897]
[-1.5632502 0.41946535 1.11285195 0.90216863]]
[[ 0.45639877 0.34153265 1.63991247 0.49005306]
[-0.00269497 0.71291156 -0.17187131 -0.05854396]
[-0.23710731 -2.21511024 0.31094798 -1.01123501]]]Python Numpy random uniform
The Python Numpy random uniform function generates a uniform distribution of numbers. This uniform accepts the array size and fills that array with uniform distributed values.
import numpy as np
arr = np.random.uniform(size = 5)
print('-----Generated Random Array----')
print(arr)
arr2 = np.random.uniform(size = (5, 5))
print('\n-----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr2)
arr3 = np.random.uniform(size = (2, 3, 4))
print('\n-----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array----')
print(arr3)
The Python Numpy random uniform function output.
-----Generated Random Array---- [0.86094927 0.63186883 0.39364783 0.32536411 0.52483433] -----Generated Two Dimensional Random Array---- [[0.88119145 0.51605353 0.26713714 0.34346039 0.34707231] [0.15778072 0.39243675 0.9420596 0.5071728 0.51497773] [0.78287236 0.00228852 0.48127646 0.27556824 0.18581121] [0.72273377 0.98540534 0.38654194 0.78345594 0.20423307] [0.87925609 0.9183766 0.11937258 0.98181138 0.25497945]] -----Generated Three Dimensional Random Array---- [[[0.74953189 0.16232027 0.51204284 0.45291307] [0.37186809 0.03543589 0.9230671 0.35753014] [0.41904844 0.82840975 0.7316515 0.29189283]] [[0.94959779 0.54924972 0.15773098 0.38614272] [0.2739566 0.70382872 0.10895882 0.20279987] [0.48210976 0.87194087 0.50062708 0.03436968]]]
