The Python Iterator is an Object which contains a countable number of values or elements. You can use this one to Traverse all those elements. The Python iterator uses special methods called __iter__() and __next__() methods to traverse the object elements.
Python Iterator Vs Iterables
If we can get the iterators from it, then we call that object iterable. So far, we have seen objects called Lists, Tuples, Sets, and Dictionaries. From these objects, you can call Iter. This section explains how to use this Python class and create our own infinity iterators with practical examples.
Python String Iterator Example
In python, strings are iterable objects. Here, we use for loop to loop each character in a string and return that character. By default, or say, For loop implements the Iterator object concept without your knowledge.
stri = 'tutorialgateway'
for x in stri:
print(x, end = ' ')
t u t o r i a l g a t e w a yFor loop Iterator Example
In this example, we used both for loop and this. In this Python programming language, we must use the next() function to return an element or value from an iterator.
Remember, the next() method returns one item at a time. So, for n number of items, you have to use n next() statements. Here, we used the next() for one time. So, it returns the first character from a string.
stng = 'tutorialgateway'
for x in stng:
print(x, end = ' ')
print("\n**** Output *****")
itr = iter(stng)
print(next(itr))
t u t o r i a l g a t e w a y
**** Output *****
tLet me use next() to traverse all the characters in a string. This time, the Python iterators write the completed string.
sting = 'tutorialgateway'
for x in sting:
print(x, end = ' ')
print("\n**** Example *****")
itr = iter(sting)
print(next(itr))
print(next(itr))
print(next(itr))
print(next(itr))
print(next(itr))
print(next(itr))
print(next(itr))
print(next(itr))
t u t o r i a l
**** Example *****
t
u
t
o
r
i
a
lPython List Iterator example
In this example, we show how to traverse List items and print them.
numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] itr = iter(numbers) print(next(itr)) print(next(itr)) print(next(itr)) print(next(itr)) print(next(itr))
10
20
30
40
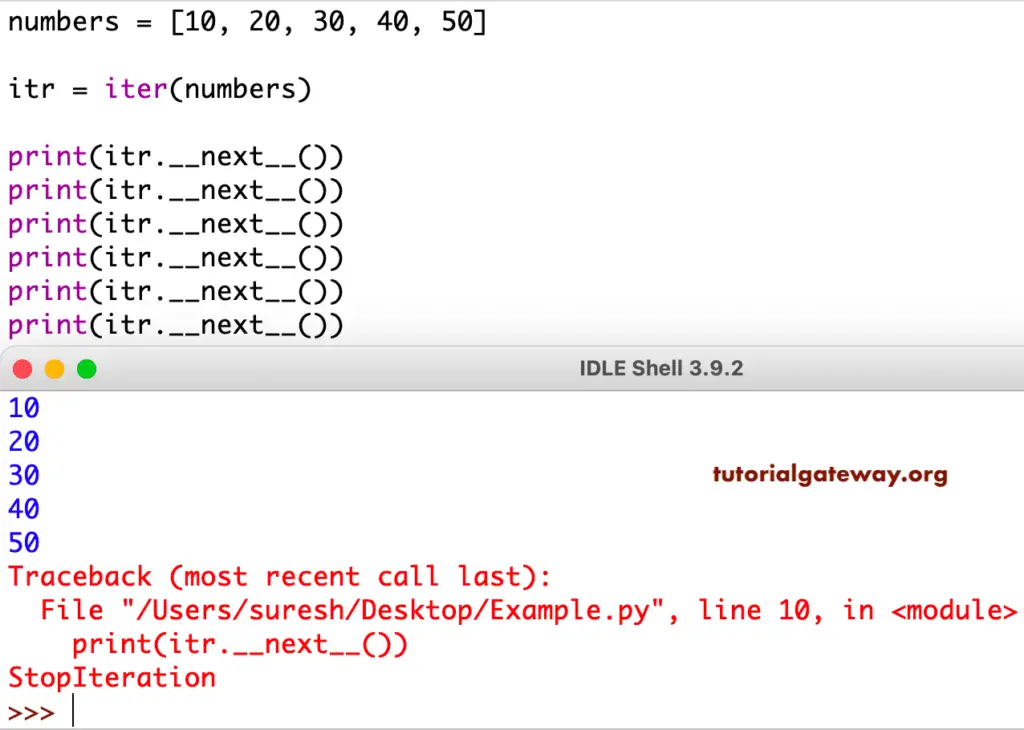
50We used the __next__() special method in this example. If you observe the last statement, we are trying to return the next element that doesn’t exist. That’s why Iter is called StopIteration.
numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] itr = iter(numbers) print(itr.__next__()) print(itr.__next__()) print(itr.__next__()) print(itr.__next__()) print(itr.__next__()) print(itr.__next__())
Python Set Iterator Example
You can use this to traverse the set items and returns the object. This program traverses the numbers in a Set and prints each one of them.
mySet = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
ittr = iter(mySet)
print(ittr.__next__())
print(ittr.__next__())
print(ittr.__next__())
print(ittr.__next__())
print(ittr.__next__())
1
2
3
4
5Tuple Example
The Python iterator object can also allow you to use it on Tuples. This program iterates Tuple items and prints each item in a tuple.
fruits = ('Apple', 'Orange', 'Grape', 'Banana', 'Kiwi')
fruit_itr = iter(fruits)
print(next(fruit_itr))
print(next(fruit_itr))
print(next(fruit_itr))
print(next(fruit_itr))
print(next(fruit_itr))
Apple
Orange
Grape
Banana
KiwiCreate Own Iterator in Python
It is a simple class called Counter. In this example, we first declared a maximum value within the __init__ method. The __iter__ method to initialize the value of an iterable object. For now, we set the number to 0. It means Iter starts at 0.
The __next__ method is to select the next element from an Object. Within this method, we used the If Else Statement to check whether the next number is greater than the maximum value. If True, a StopIteration error is raised. Otherwise, the number incremented.
class Counter:
def __init__(self, maximum):
self.maximum = maximum
def __iter__(self):
self.number = 0
return self
def __next__(self):
number = self.number
if number > self.maximum:
raise StopIteration
else:
self.number = number + 1
return number
numbers = Counter(10)
a = iter(numbers)
print(next(a))
print(next(a))
print(next(a))
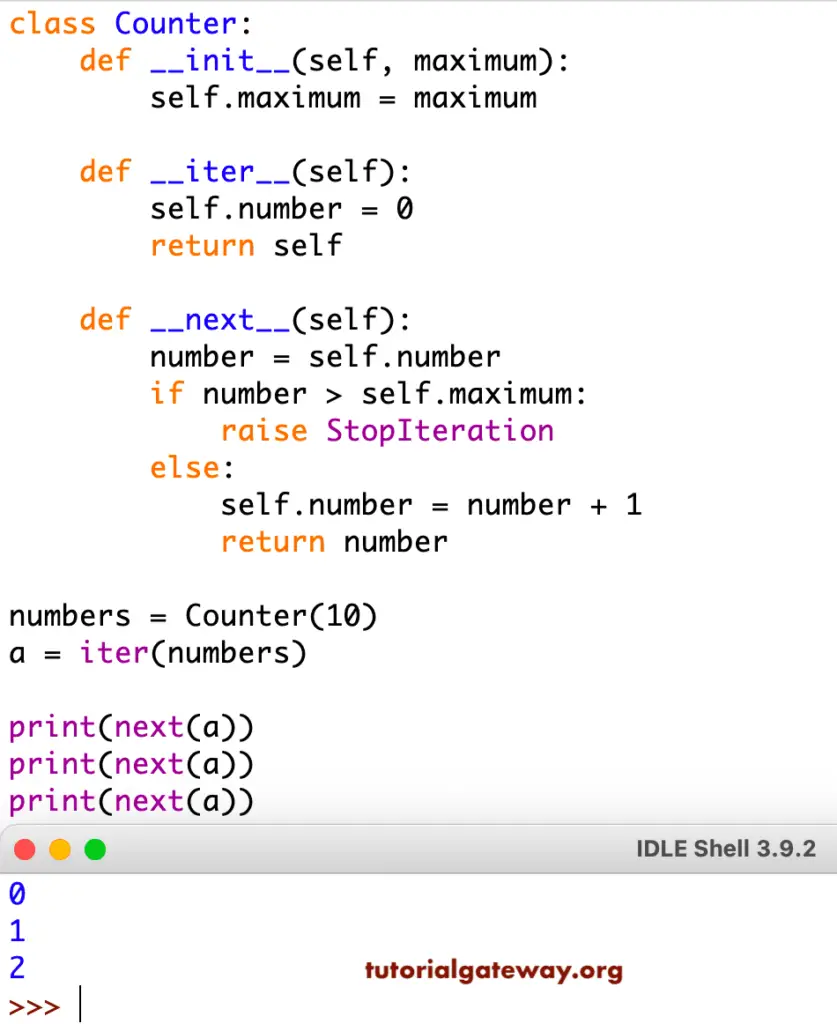
The above code displays numbers from 0 to 2. It is because we used next(a) three times only. In this Python iterator program, we used for loop to iterate the Counter class with the maximum value of 10. This prints the values from 0 to 10. __iter__() starts at 0, and __next__() print elements up to 10.
class Counter:
def __init__(self, maximum):
self.maximum = maximum
def __iter__(self):
self.number = 0
return self
def __next__(self):
number = self.number
if number > self.maximum:
raise StopIteration
else:
self.number = number + 1
return number
for t in Counter(10):
print(t)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10Python Infinity Iterator class
While you create your own iter, you should always be careful with Infinity loops. If you forget to raise the error, you end up in infinity loops. It is a simple example of an infinity iterator object. It is the same as above, but we removed the If statement.
class Counter:
def __iter__(self):
self.number = 0
return self
def __next__(self):
number = self.number
self.number = number + 1
return number
numbers = Counter()
a = iter(numbers)
print(next(a))
print(next(a))
print(next(a))
0
1
2Although the above example is an infinite iter, you might not have noticed it. It is because we used the next() three times only. So, let me use the Counter class for loop to an iter function. Please refer to the Dictionary article.
class Counter:
def __iter__(self):
self.num = 0
return self
def __next__(self):
num = self.num
self.num = num + 1
return num
for t in Counter():
print(t)
Now you can see the infinity object. This executes continuously.
267
268
269
270
271
272
273