Let us see how to use Power BI DAX Date Functions with examples. Microsoft Power BI DAX provides various Date Functions such as Year, Month, Day, Calendar, date, time, datediff, now, today, utcnow, utctoday, datevalue, timevalue, etc.
To demonstrate these Power BI DAX Date functions, we use the below-shown data. As you can see, there are 15 records in this table.
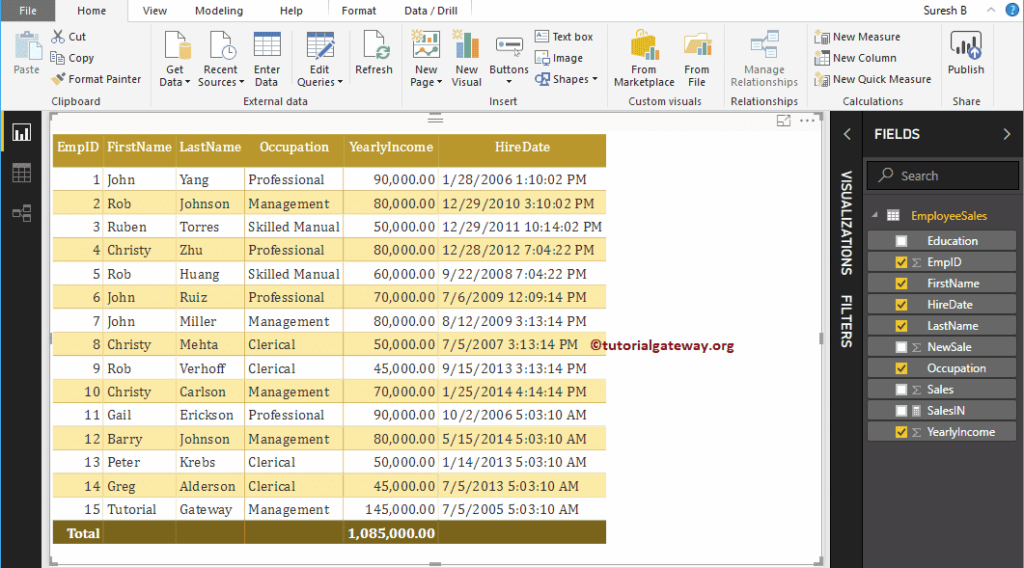
Power BI DAX Date Functions
The following series of examples shows the list of DAX Date Functions.
DAX NOW Function
The DAX Now is one of the date function, used to return the current date and time. The syntax of this DAX NOW is
NOW()
To demonstrate the Power BI DAX NOW functions, we have to use the Calculated column. In order to create a column, please click on the New Column option under the Home tab, or Modeling tab.
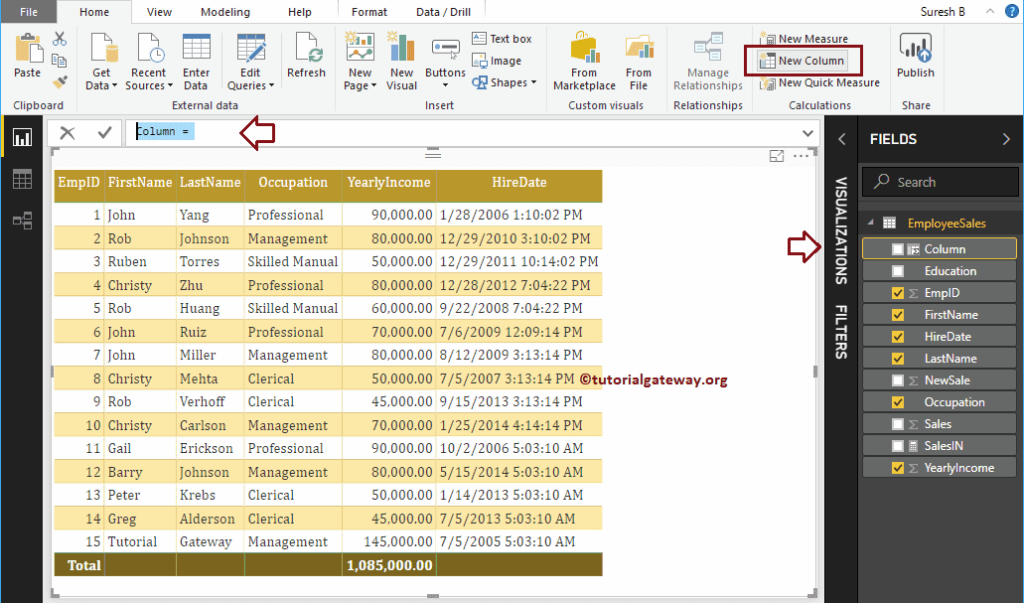
We renamed the default column name as Today. As you can see from the screenshot below, while I was typing, it is showing the suggestions.
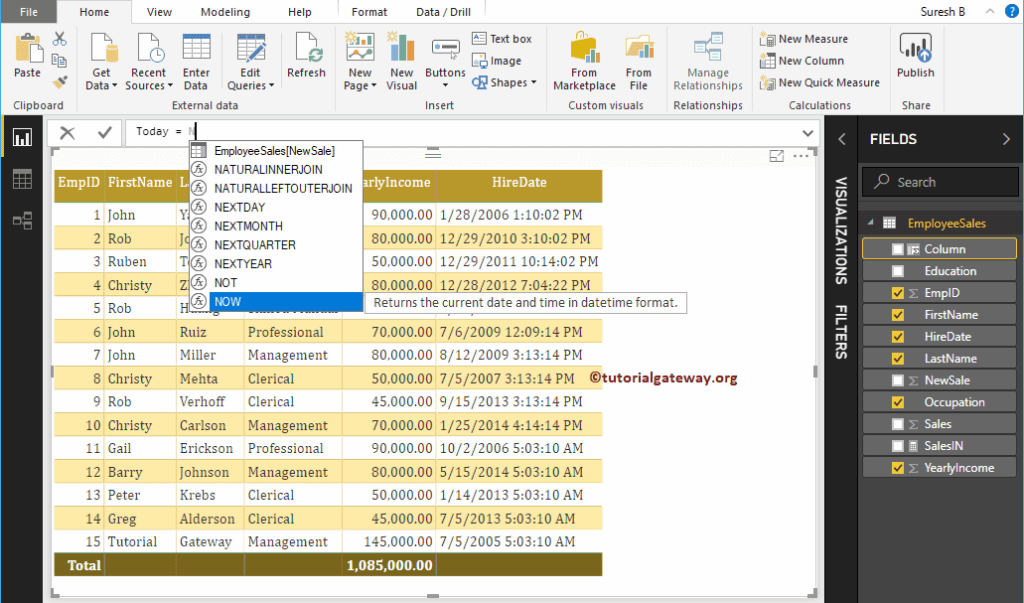
By clicking the enter or any key, a new column created.
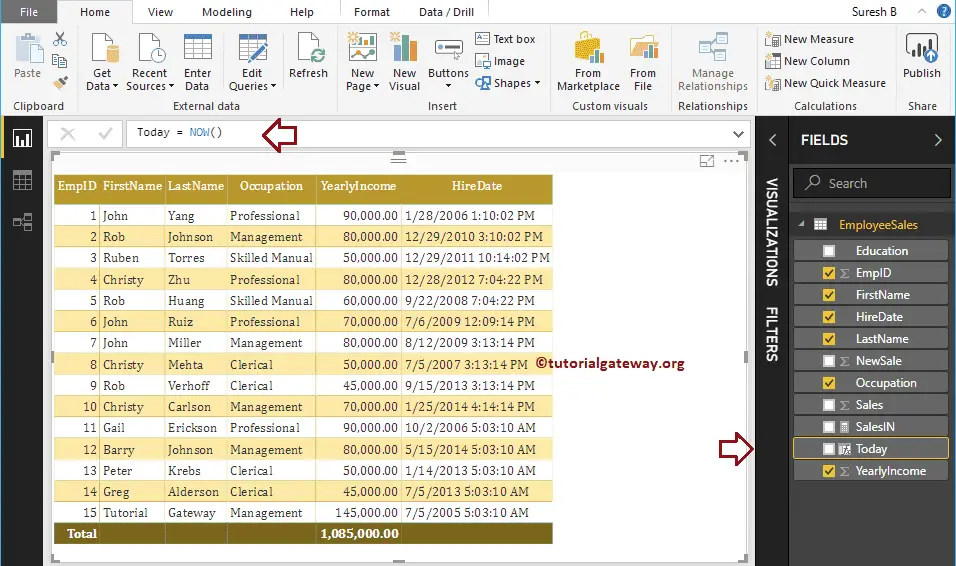
Let me add this column to the table that we created earlier. Please refer to Create Table Report article to understand the steps involved in creating a table
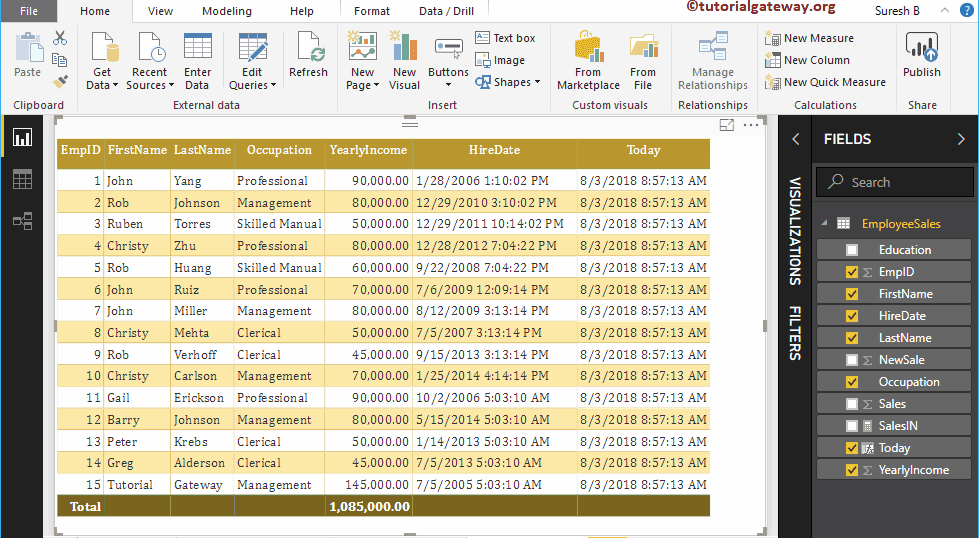
As you can see from the above screenshot, it displays today’s date and time.
DAX DAY Function
The Power BI DAX DAY function extract or return Day number from the given date and the DAX DAY Function syntax is
DAY(Date)
Let me create a column to return Day number from the Hire date column
DayinDate = DAY(EmployeeSales[HireDate])
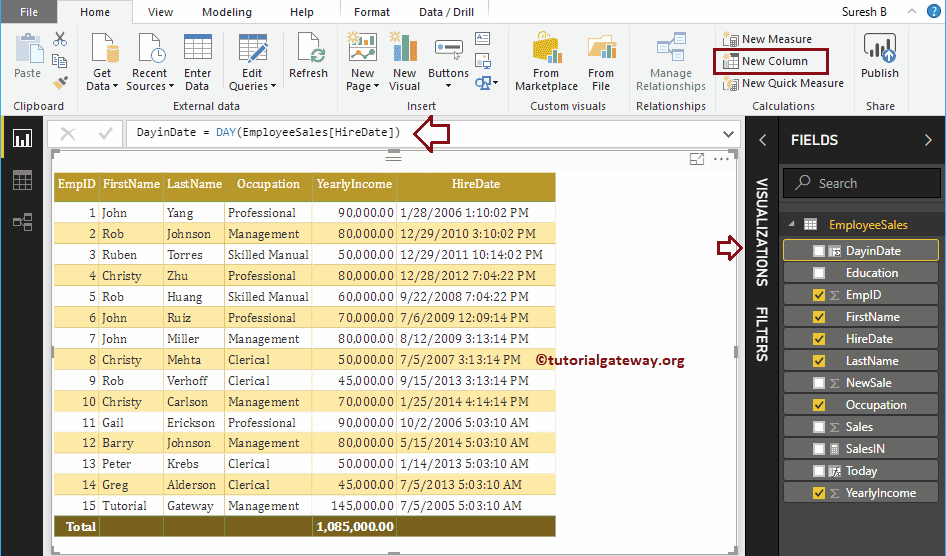
DAX MONTH Function
The Power BI DAX Month function returns Month number from a given date. The DAX MONTH Function syntax is
MONTH(Date)
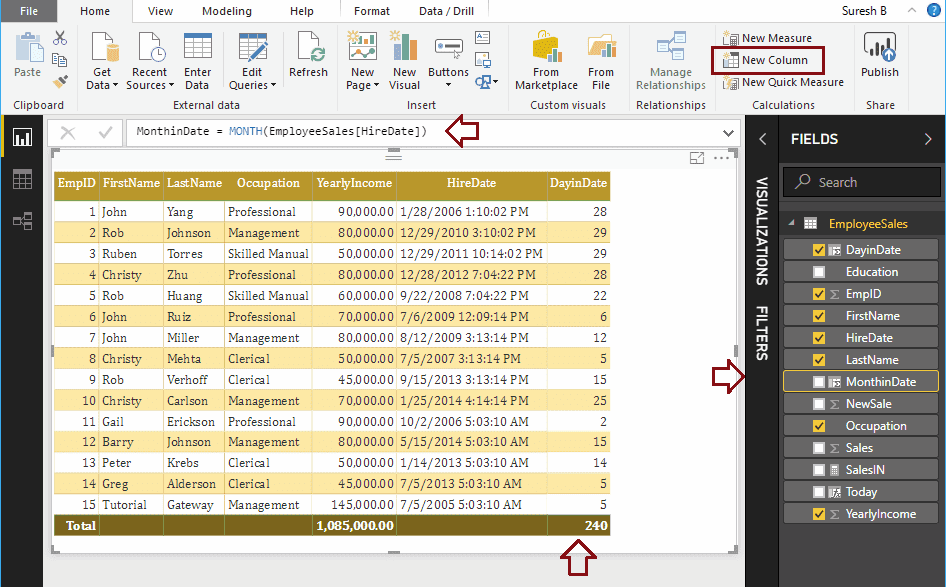
Let me create a column to return Month number from Hire date column
MonthinDate = MONTH(EmployeeSales[HireDate])
Here, we added the result of a previous function (day Function) to the Table.
DAX YEAR Function
The Power BI DAX YEAR function extract or return year number from the given date. The syntax of this DAX YEAR:
YEAR(Date)
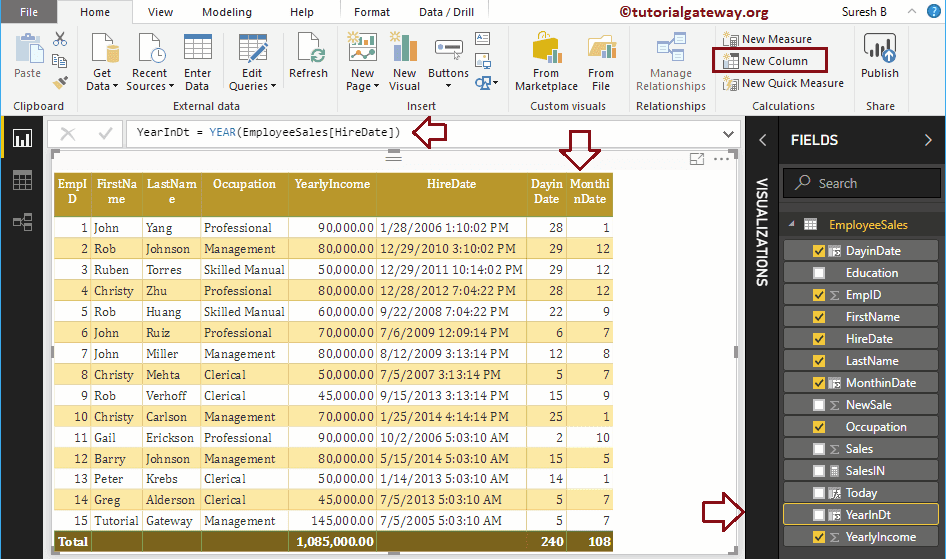
Let me create a column to return Year from Hire date column
YearInDt = YEAR(EmployeeSales[HireDate])
DAX HOUR Function
The Power BI DAX HOUR function returns Hours (in 24 hours format) from a given date. The DAX HOUR Function syntax is:
HOUR(DateTime)
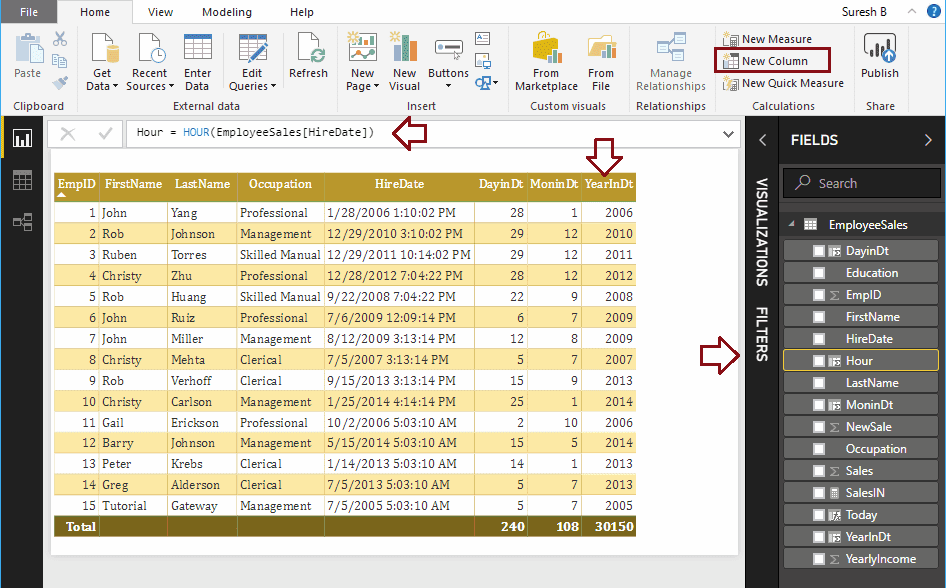
Let me create a column to return Hours from Hire date column
Hour = HOUR(EmployeeSales[HireDate])
DAX MINUTE Function
The Power BI DAX MINUTE function returns the number of minutes. The syntax of this DAX MINUTE is:
MINUTE(DateTime)
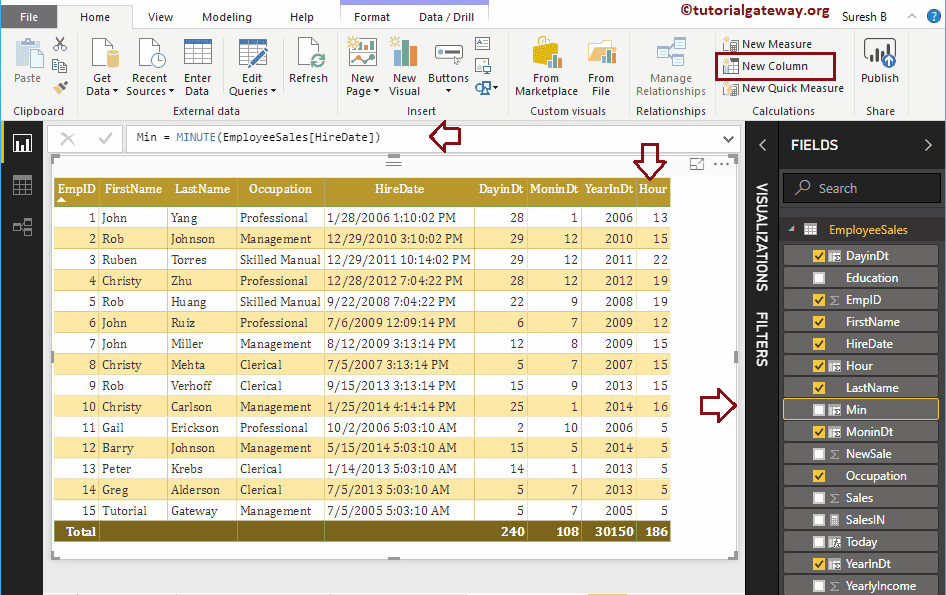
Let me create a column to return the number of minutes from the Hire date column
Min = MINUTE(EmployeeSales[HireDate])
DAX SECOND Function
The Power BI DAX SECOND function returns the number of seconds and the syntax of this is:
SECOND(DateTime)
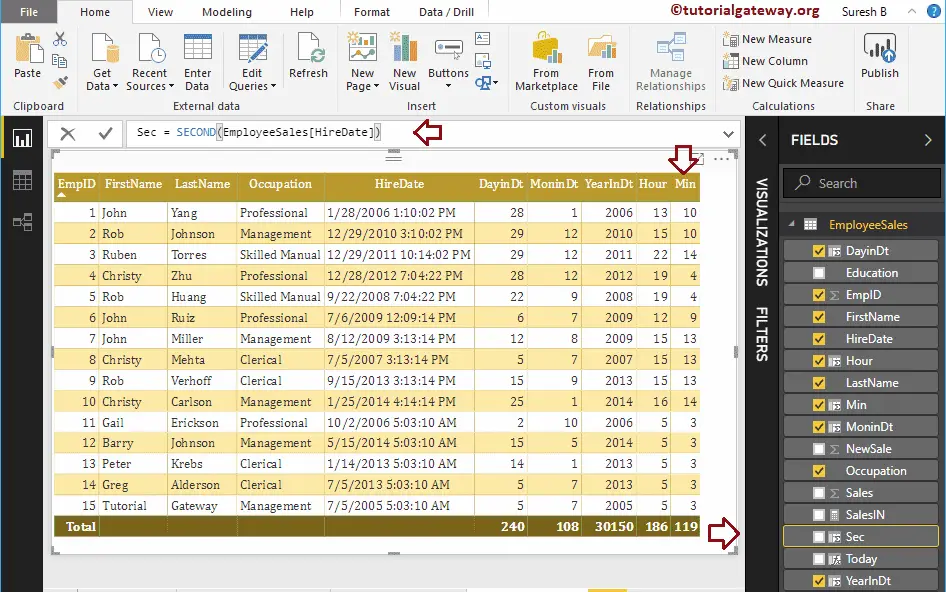
Let me create a column to return the number of seconds from the Hire date column
Sec = SECOND(EmployeeSales[HireDate])
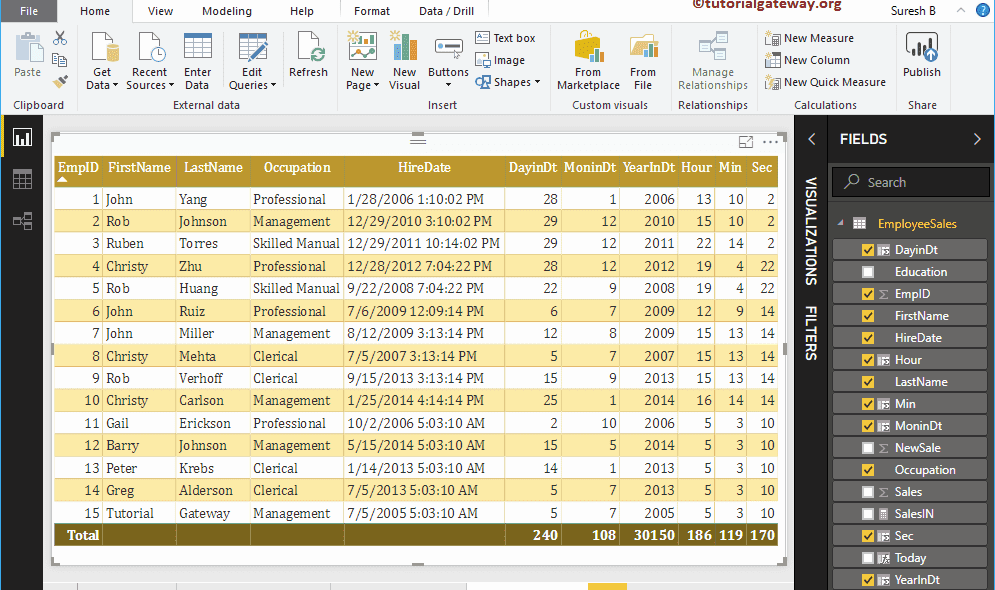
Let me add the results of Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, and Second function results to the table.
DAX TODAY Function
The Power BI DAX Today function returns today’s date with default system time and the syntax of this DAX Today is:
TODAY()
Let me create a column to display today’s date
Today 2 = TODAY()
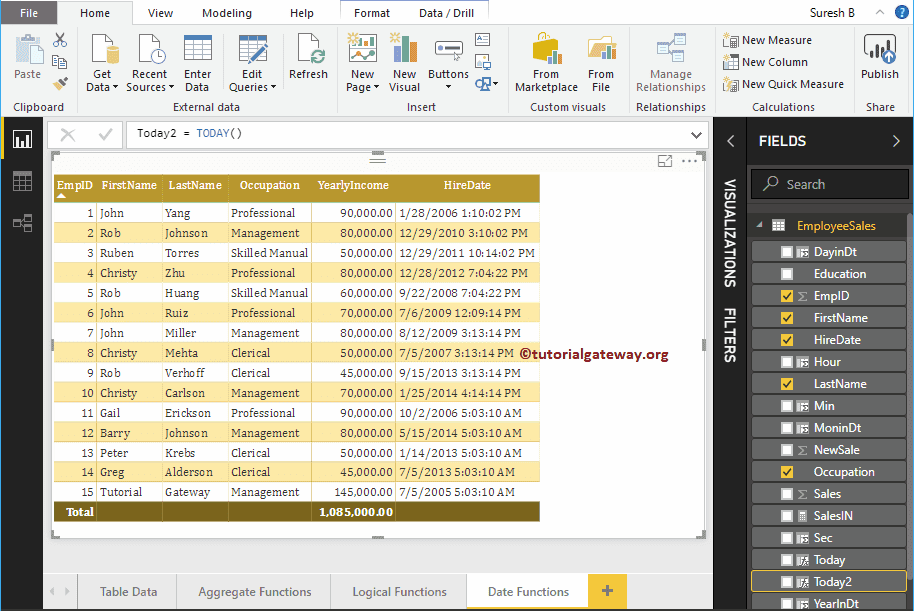
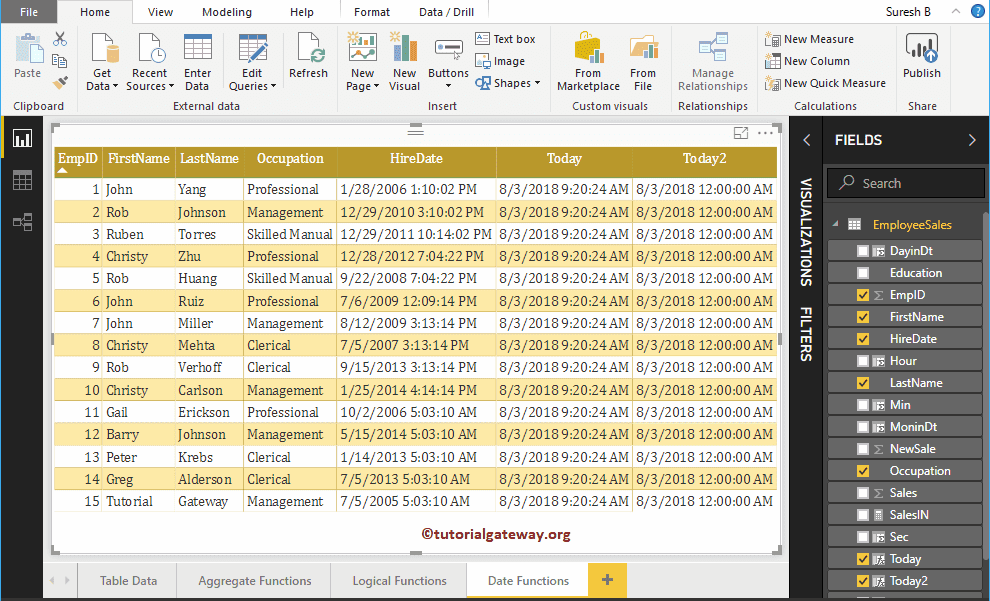
Let me compare both NOW() and TODAY().
From the screenshot below, you can see there is a time difference between the two of them.
DAX DATE Function
The Power BI DAX Date function is useful to return date from the year, month, and day. The DAX Date function syntax is:
DATE(year, month, day)
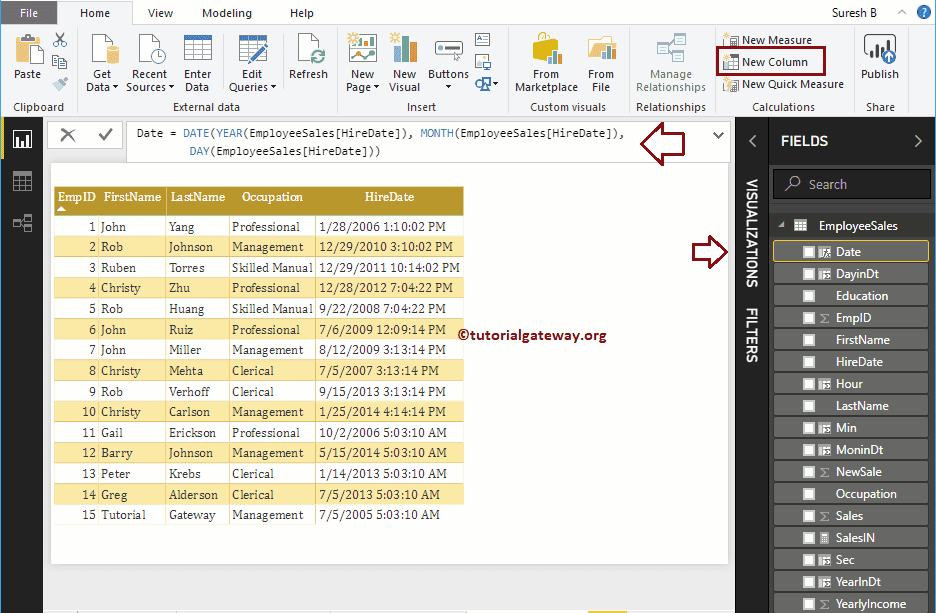
Let me create a single column to create a date from the year, month and day
Date = DATE(YEAR(EmployeeSales[HireDate]), MONTH(EmployeeSales[HireDate]),
DAY(EmployeeSales[HireDate]))
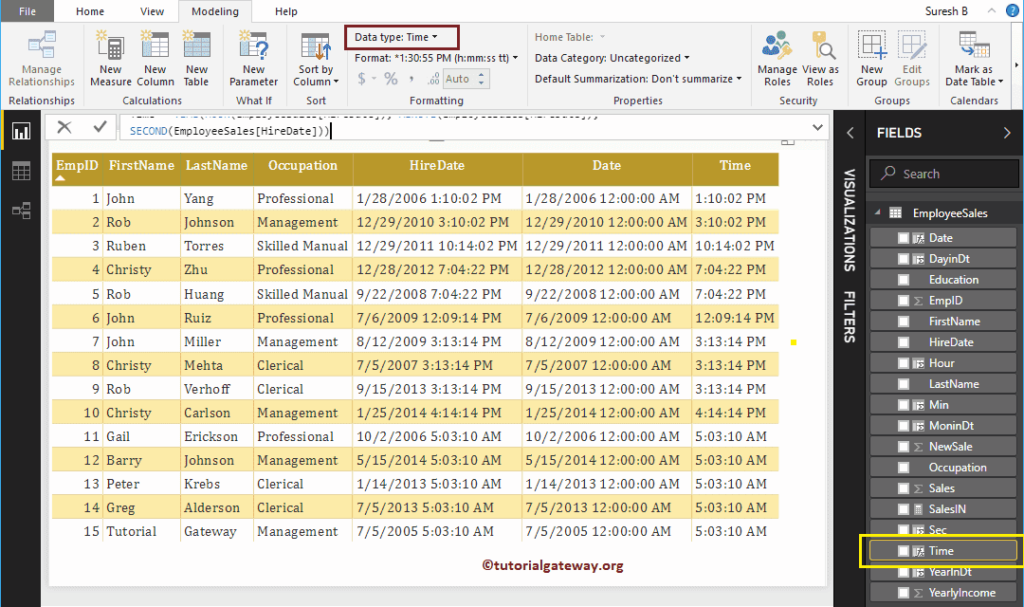
DAX TIME Function
The Power BI DAX Time function returns time from specified hour, minute, and seconds. The syntax of this DAX Time function is:
TIME(hour, minute, second)
Let me create one column to create time from hour, minute, and seconds
Time = TIME(HOUR(EmployeeSales[HireDate]), MINUTE(EmployeeSales[HireDate]),
SECOND(EmployeeSales[HireDate]))
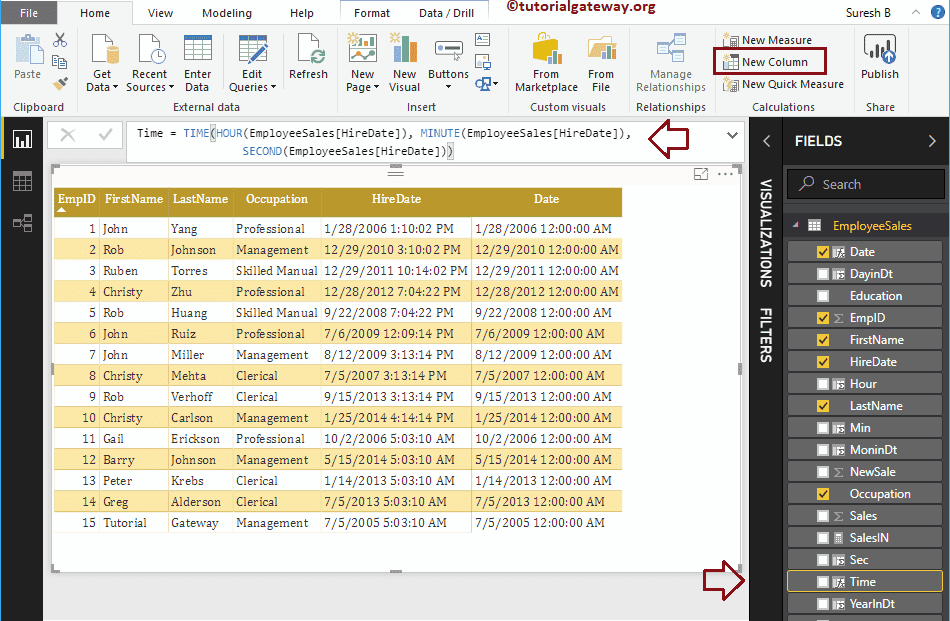
Let me add DAX Time function result to the table report. If you find the output as the default date with the time, then change the data type from date/Time to Time.
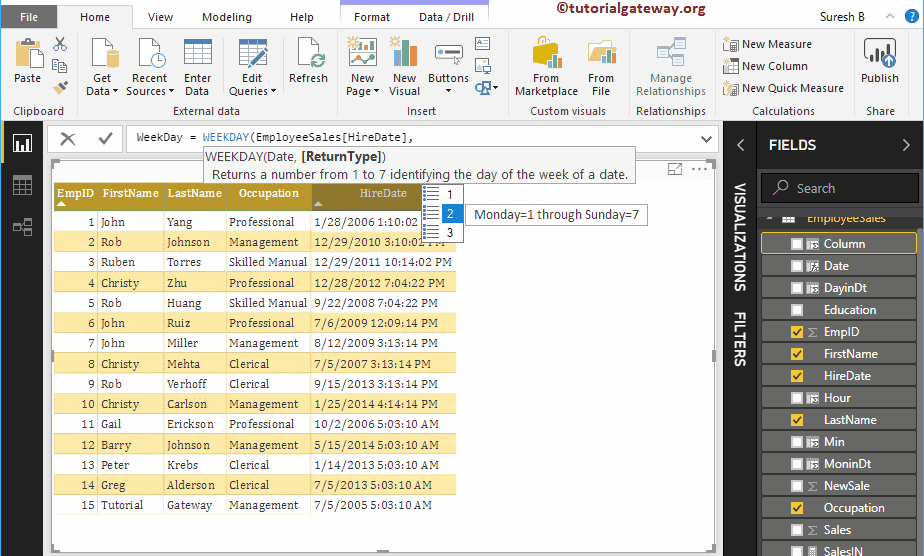
DAX Weekday Function
The Power BI DAX Weekday function returns numbers from 1 to 7, where 1 as of Sunday, and 7 as of Monday. The DAX Weekday function syntax is:
WEEKDAY(Date, Number)
- If Number = 1 then 1 as of Sunday
- If Number = 2 then 1 as of Monday
- and Number = 3 then 0 as of Monday
Let me create a column to find the weekday number
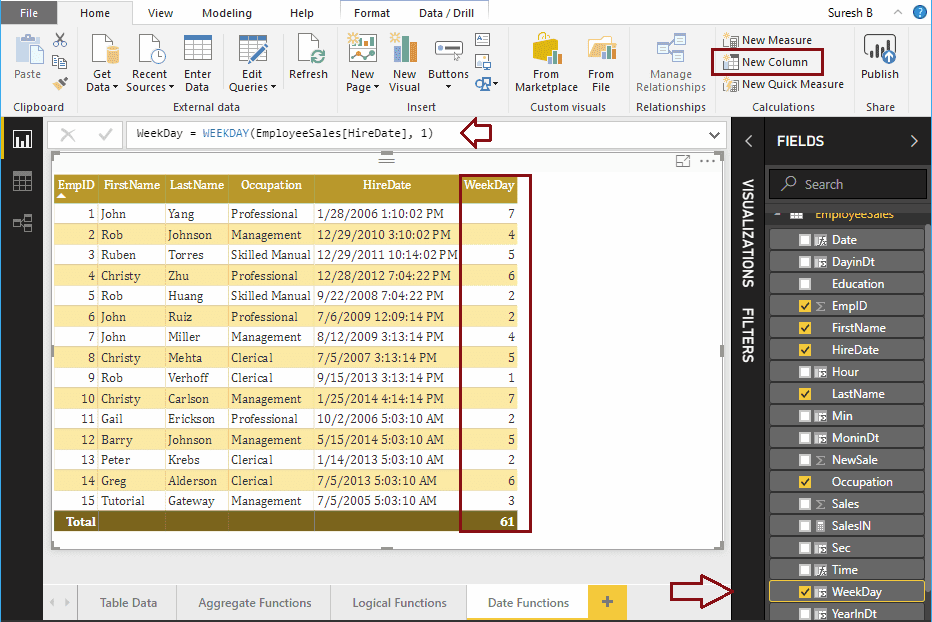
WeekDay = WEEKDAY(EmployeeSales[HireDate], 1)
You can see the Week numbers
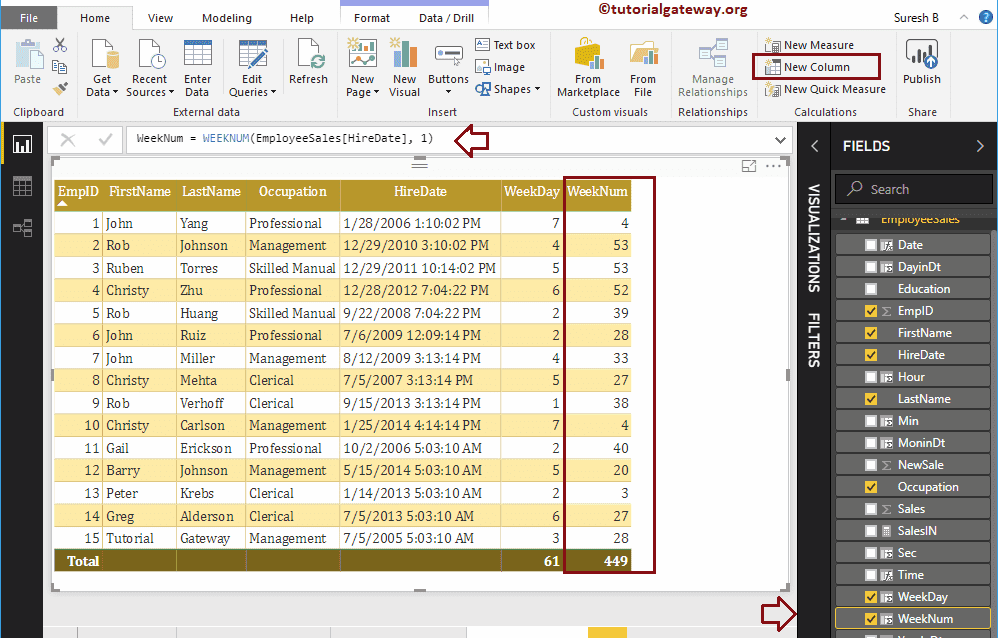
DAX WeekNum Function
The Power BI DAX WeekNum function returns the week number ( 1 as January first week). The syntax of this DAX Weeknum function is:
WEEKNUM(Date, Number)
If Number = 1 Week begins on Sunday, and If Number = 2, then Week begins on Monday. Let me create a column to find the week number
WeekNum = WEEKNUM(EmployeeSales[HireDate], 1)
DAX UTCNOW Function
The DAX UTCNOW function is the same as the Power BI DAX NOW function. However, it returns date and time along with UTC. The syntax of this DAX UTCNOW function is:
UTCNOW()
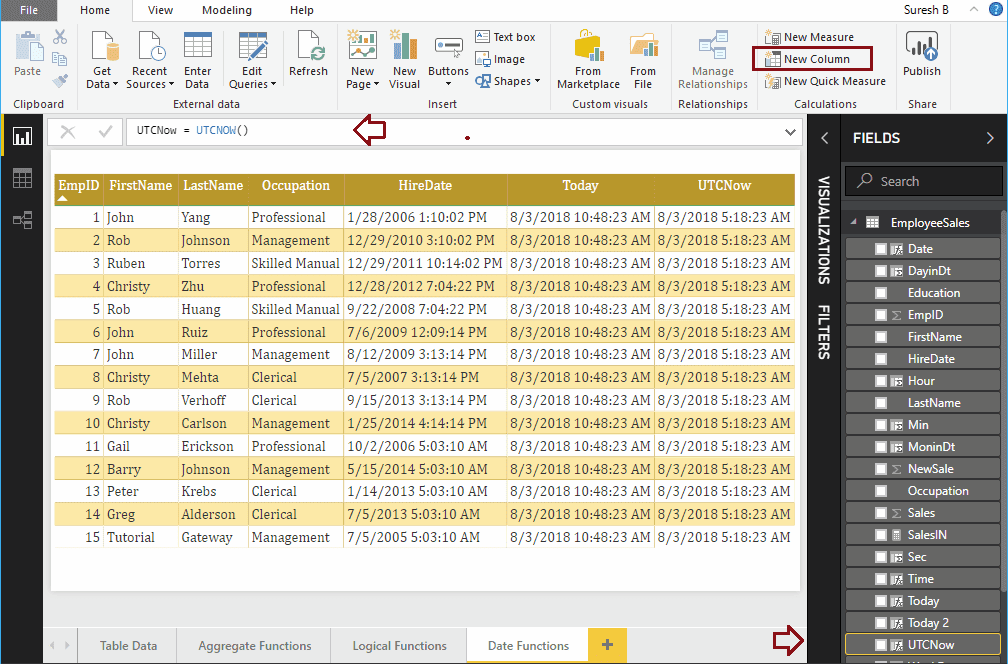
Let me create one column to find the date and time along with UTC
UTCNow = UTCNOW()
DAX UTCTODAY Function
The Power BI DAX UTCTODAY function is the same as the ODAY function. However, it returns date with default time along with UTC. The syntax of this DAX UTCTODAY is:
UTCTODAY()
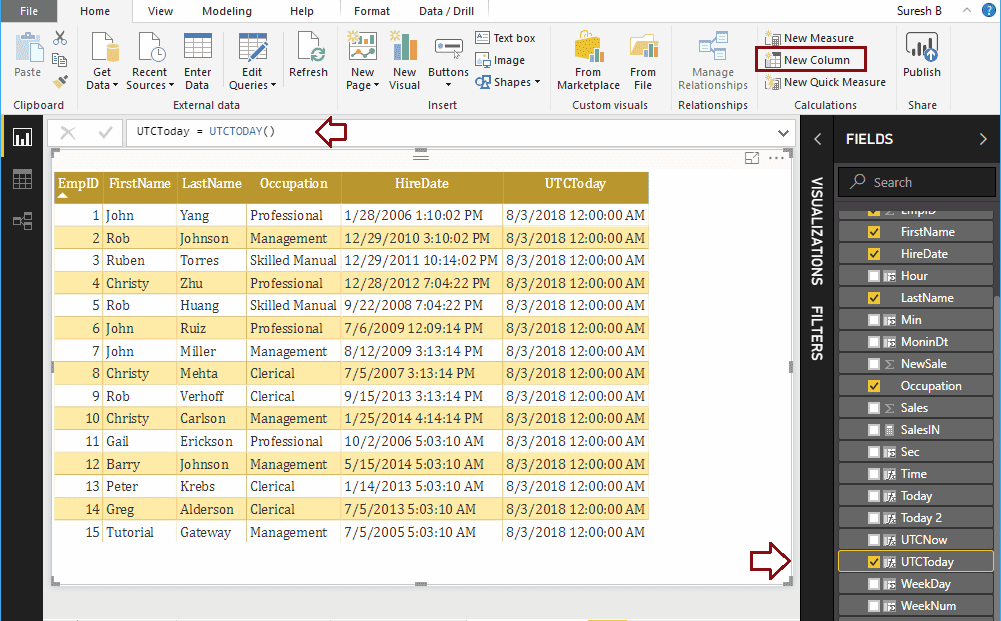
Let me create a column to find the date with UTC
UTCToday = UTCTODAY()
DAX YEARFRAC Function
The Power BI DAX YEARFRAC function returns the fractional difference between the start date and end date. The syntax of the DAX YEARFRAC is:
YEARFRAC(Start_Date, End_Date)
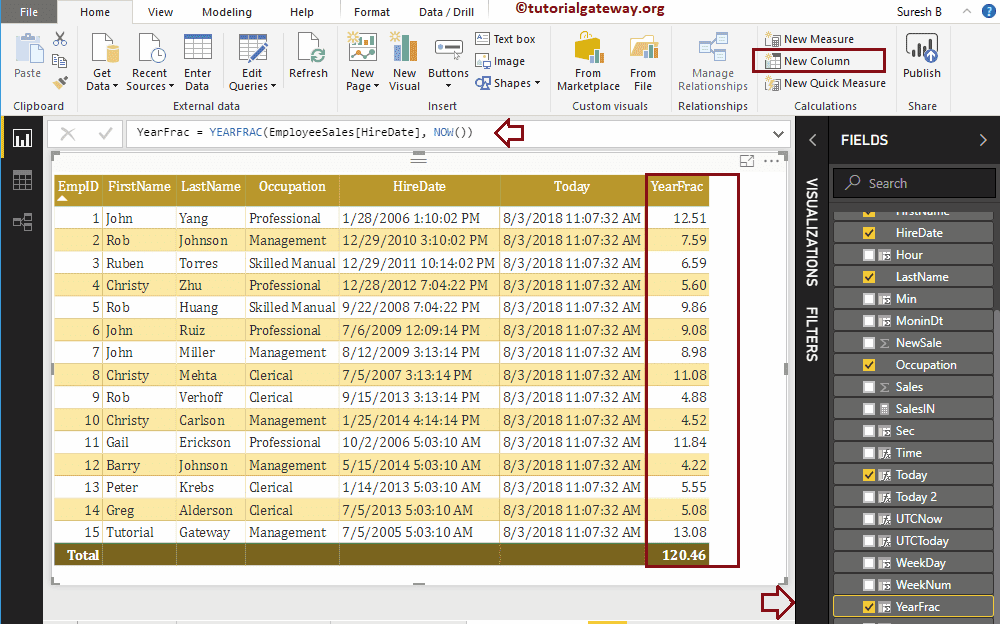
Let me find the exact number of years difference in-between Hire Date and Today
YearFrac = YEARFRAC(EmployeeSales[HireDate], NOW())
DAX EDATE Function
The Power BI DAX EDATE function returns previous dates or future dates. For example, policy mature date by adding 24 as the second argument, etc. The syntax of this DAX EDATE function is:
EDATE(Start_Date, Months)
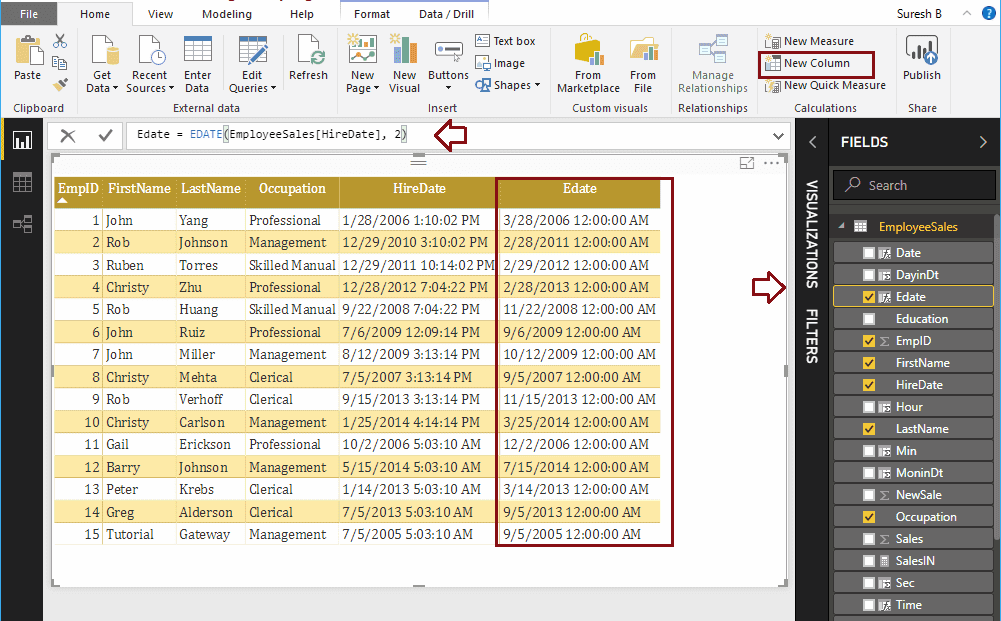
Let me add 2 months to Hire Date
Edate = EDATE(EmployeeSales[HireDate], 2)
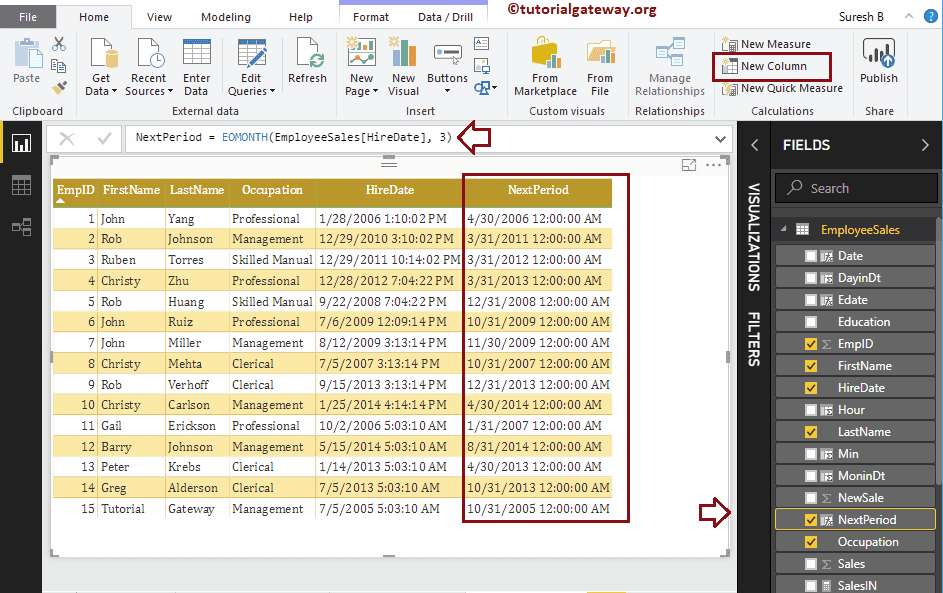
DAX EOMONTH Function
The Power BI DAX EOMONTH function (EOMONTH means the end of the month) display the last day in a month. You can use the second argument to return previous dates or future dates. The syntax of this DAX EDATE is:
EOMONTH(Start_Date, Months)
Let me add 3 months to Hire Date. The below statement first adds three months to Hire date and then returns the last day of that month.
Eomonth = EOMONTH(EmployeeSales[HireDate], 3)
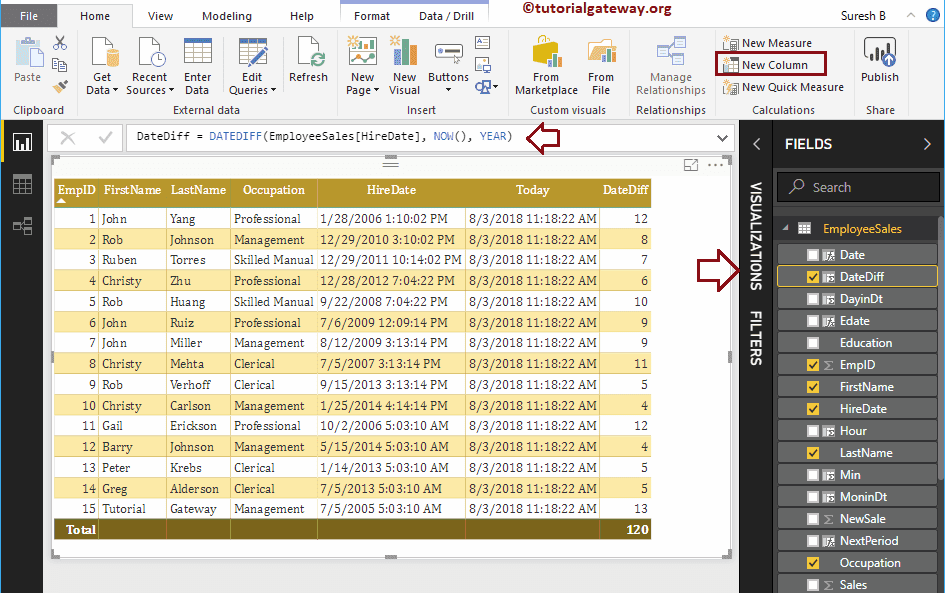
DAX DATEDIFF Function
The Power BI DAX DATEDIFF function returns the date difference between the start date and end date. You can use the DAX DATEDIFF function third argument to select the difference value.
The DAX DATEDIFF function accepts YEAR, MONTH, DAY, SECOND, MINUTE, HOUR, QUARTER, WEEK. For example, if you select the MONTH, then the DateDiff function returns the number of month difference between a start date and end date.
The syntax of this DAX DATEDIFF function is:
DATEDIFF(Start_Date, End_Date, Difference_Value)
Let me check the difference between Hire date and Today in years.
DateDiff = DATEDIFF(EmployeeSales[HireDate], NOW(), YEAR)
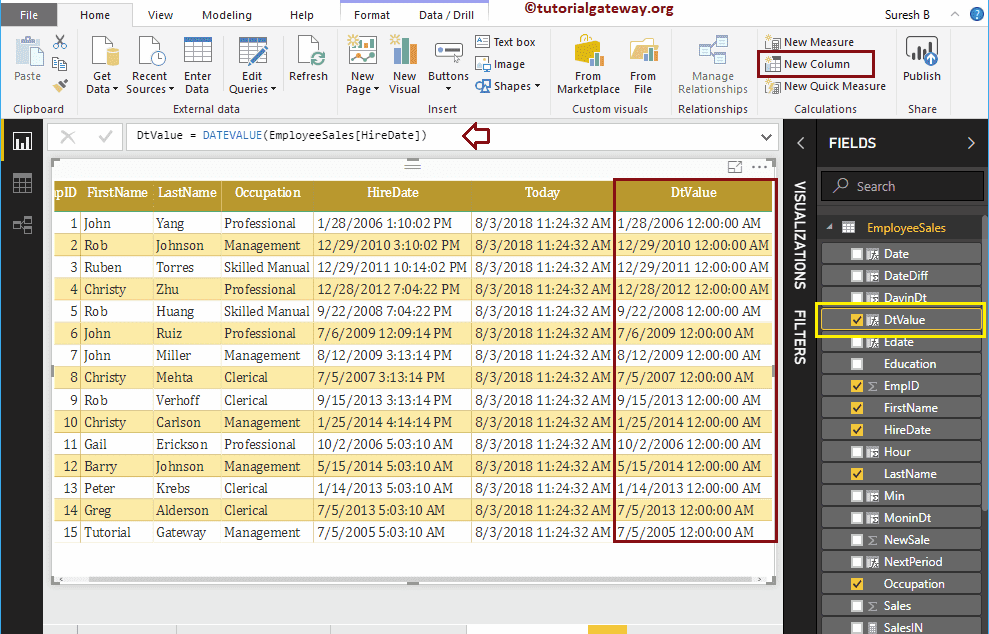
Power BI DAX DATEVALUE Function
The DAX DATEVALUE function returns the date with system time and the syntax of this DATEVALUE is:
DATEVALUE(Date)
Let me return the Date from Hire date.
DtValue = DATEVALUE(EmployeeSales[HireDate])
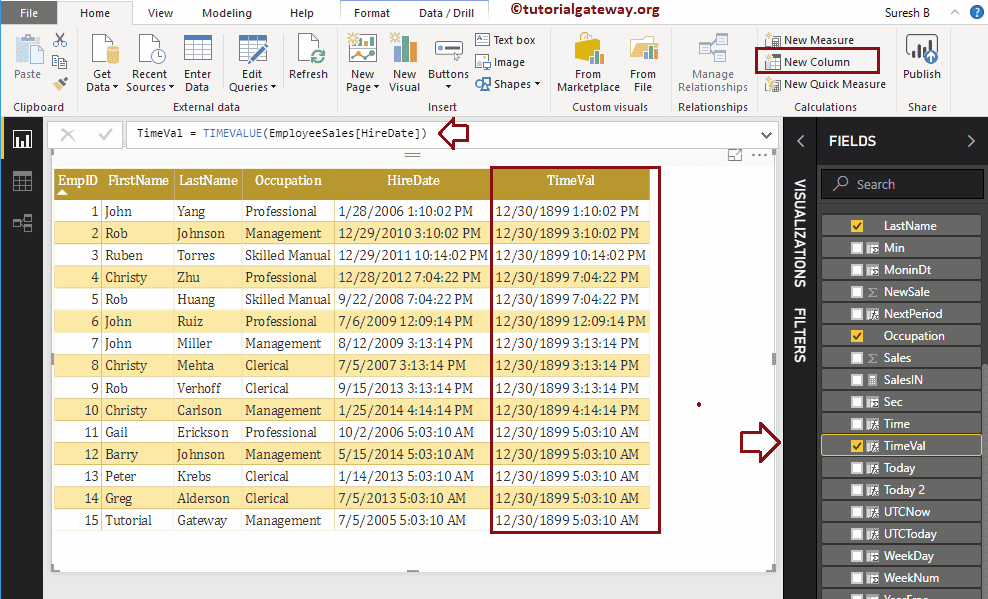
DAX TIMEVALUE Function
The Power BI DAX TIMEVALUE function returns the time with the system default date and the TIMEVALUE function syntax is:
TIMEVALUE(Date)
Let me return the Time value from the Hire date. Remember, 12/30/1899 is the default generated date.
TimeVal = TIMEVALUE(EmployeeSales[HireDate])
DAX CALENDAR Function
The Power BI DAX CALENDAR function returns a table of dates from the start date to the end date. The syntax of a DAX CALENDAR function is:
CALENDAR(Start_Date, End_Date)
The below DAX CALENDAR function returns dates from Jan 1, 2018, to January 15, 2018. I suggest you refer to Create a calculated table article to understand the process of creating a new table.
Calender = CALENDAR(DATE(2018,1, 1), DATE(2018, 1, 15))
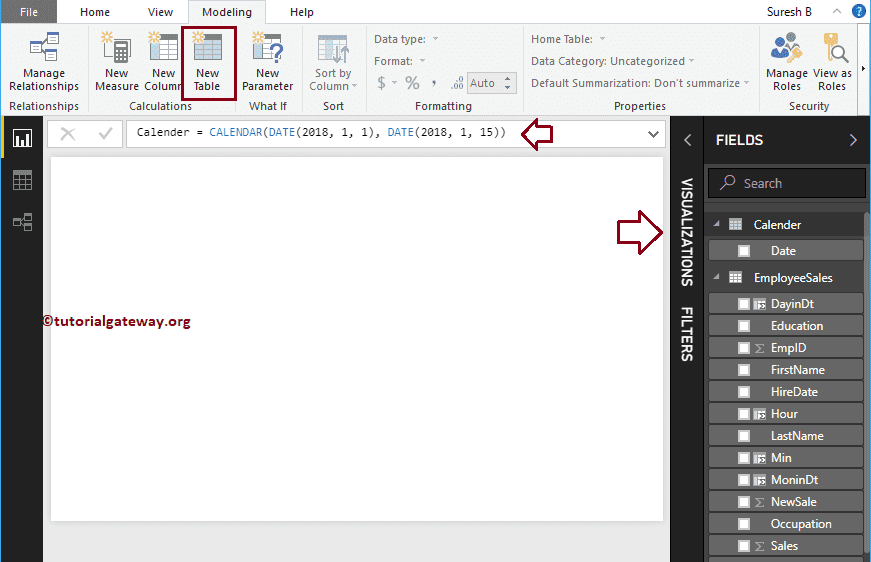
Let me create a table using this output
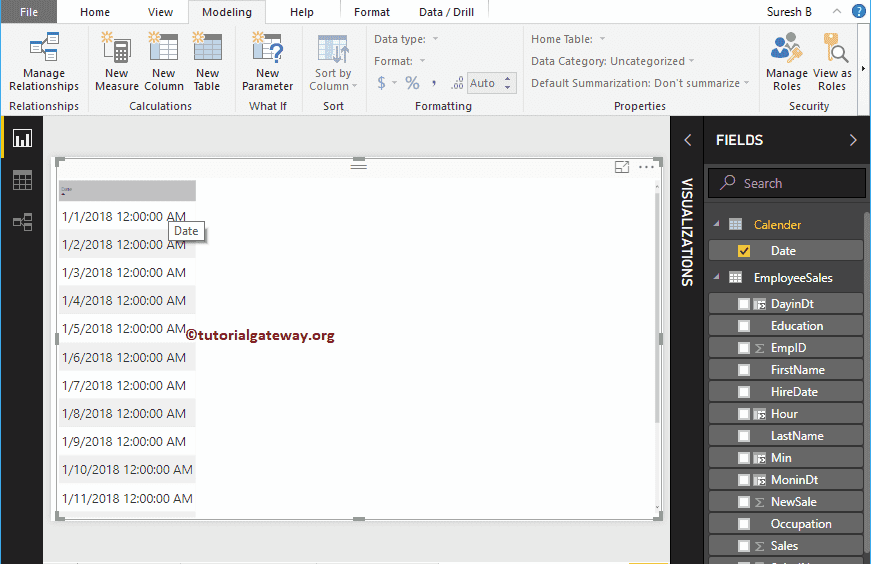
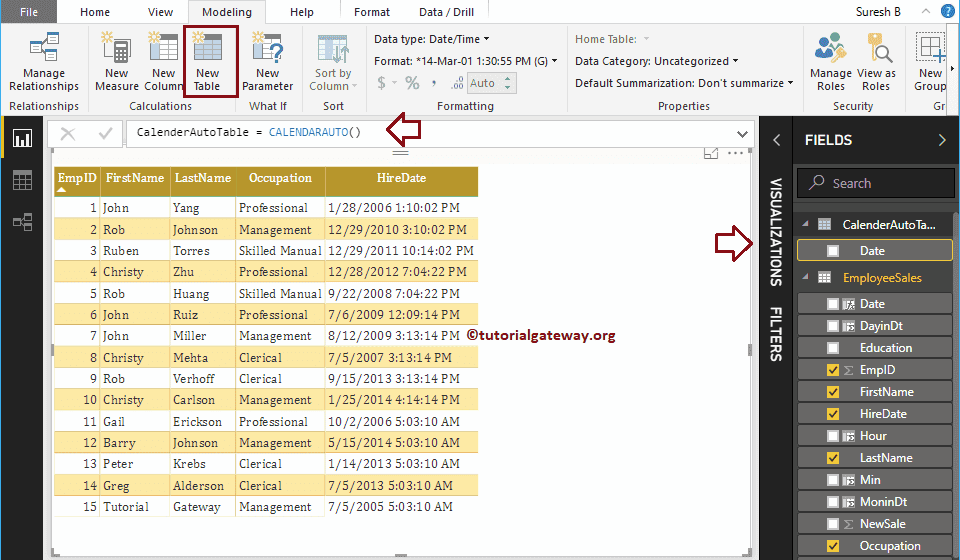
Power BI DAX CALENDARAUTO Function
The DAX CALENDARAUTO function, which returns continues dates using the data model date and the syntax of a CALENDARAUTO is:
CALENDARAUTO(year_end_month)
The argument value is an option for this DAX CALENDARAUTO function. It accepts numbers from 1 to 12 months, and if you omit, it treats the value as 12 (default)
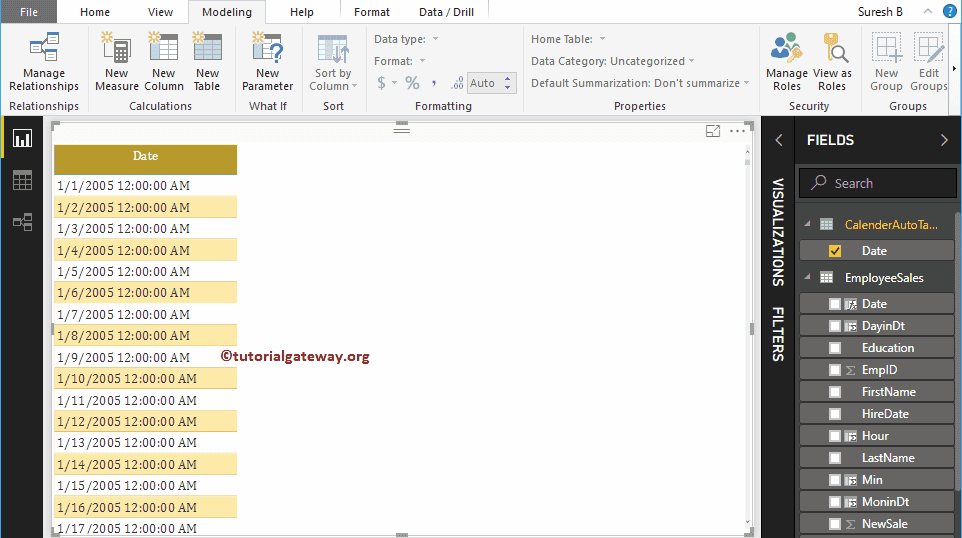
CalenderAutotable = CALENDARAUTO()
You can see the output of this date function

Comments are closed.