The SQL Dynamic Cursors are exactly opposite to Static Cursors. You can use this SQL Server Dynamic cursor to perform INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE operations. Unlike static cursors, all the changes made in the Dynamic cursor will reflect the Original data.
Let us see how to Create a Dynamic Cursor in SQL Server, and how to perform both Updates, and delete operations within the dynamic cursor with an example. For this dynamic cursor demonstration, we are going to use the Employee table that holds 14 records
Dynamic Cursor in SQL Server For UPDATE
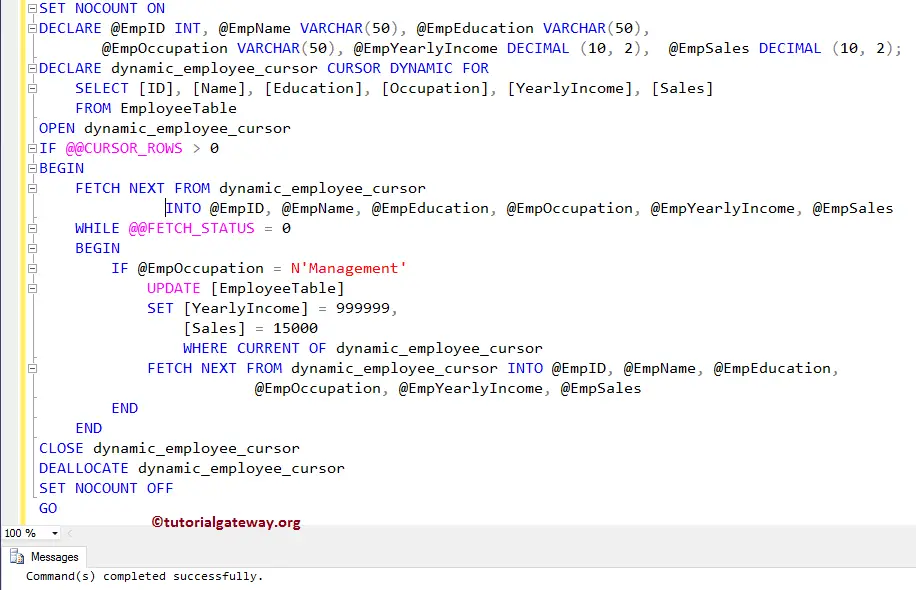
In this example, we will show you how to declare and open a dynamic cursor in SQL Server. And how to perform the Update operation within the SQL dynamic cursor.
For this, we are using the DECLARE CURSOR Statement. Within that Dynamic cursor, we will use the WHILE LOOP to loop over the SQL Server cursor elements and perform updates
SET NOCOUNT ON
-- Declaring the Variables
DECLARE @EmpID INT,
@EmpName VARCHAR(50),
@EmpEducation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpOccupation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpYearlyIncome DECIMAL (10, 2),
@EmpSales DECIMAL (10, 2);
-- SQL Dynamic Cursor Declaration
DECLARE dynamic_employee_cursor CURSOR
DYNAMIC FOR
SELECT [ID]
,[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM EmployeeTable
ORDER BY Occupation
OPEN dynamic_employee_cursor
IF @@CURSOR_ROWS > 0
BEGIN
FETCH NEXT FROM dynamic_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
IF @EmpOccupation = N'Management'
UPDATE [EmployeeTable]
SET [YearlyIncome] = 999999,
[Sales] = 15000
WHERE CURRENT OF dynamic_employee_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM dynamic_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
END
END
CLOSE dynamic_employee_cursor
DEALLOCATE dynamic_employee_cursor
SET NOCOUNT OFF
GO
ANALYSIS
First, we used SET NOCOUNT ON to stop the number of rows affected message from SQL Query. Next, we declared a few variables to hold the data coming from the Cursor. Then, we declared, and open the SQL Server dynamic cursor called dynamic_employee_cursor for all the records in Employee table
Next, we used the @@CURSOR_ROWS within the IF Statement to check whether there are any rows in the Cursor or not
IF @@CURSOR_ROWS > 0
The below statement will fetch the next record from dynamic_employee_cursor into already declared variables.
FETCH NEXT FROM dynamic_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
Then, we used the WHILE LOOP to loop over the cursor elements, and within the loop, FETCH_STATUS is used to check the status of the FETCH statement.
Within the Loop, we used one more IF Statement to check whether Occupation is equal to management or not
IF @EmpOccupation = N'Management'
and if the condition is TRUE, the cursor will use the UPDATE statement to update the yearly Income and Sales Amount.
UPDATE [EmployeeTable]
SET [YearlyIncome] = 999999,
[Sales] = 15000
WHERE CURRENT OF dynamic_employee_cursor
TIP: If your table (here it is Employee table) has the Primary Key, then only you can use the WHERE CURRENT OF statement. Otherwise, it will throw an error.
and then, we used the FETCH NEXT to get the next record from the cursor.
FETCH NEXT FROM dynamic_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
Here, we used the CLOSE, and DEALLOCATE statements to close, and deallocate the cursor.
CLOSE dynamic_employee_cursor DEALLOCATE dynamic_employee_cursor
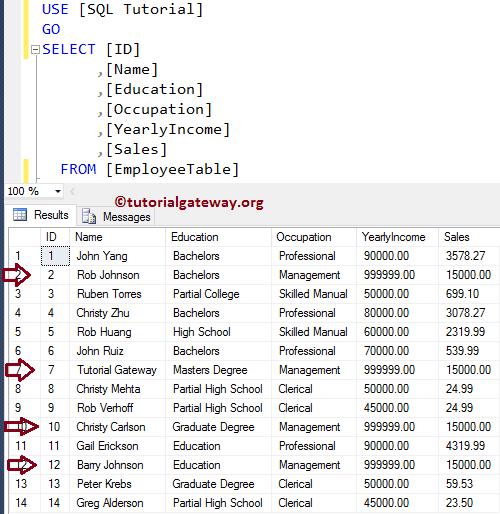
Please use the following SQL Query to check whether the Cursor has updated the records in the Employee table or not.
SELECT [ID]
,[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [EmployeeTable]
From the below screenshot, you can see that the cursor has updated the Income and Sales Amount
Dynamic Cursor in SQL Server for DELETE
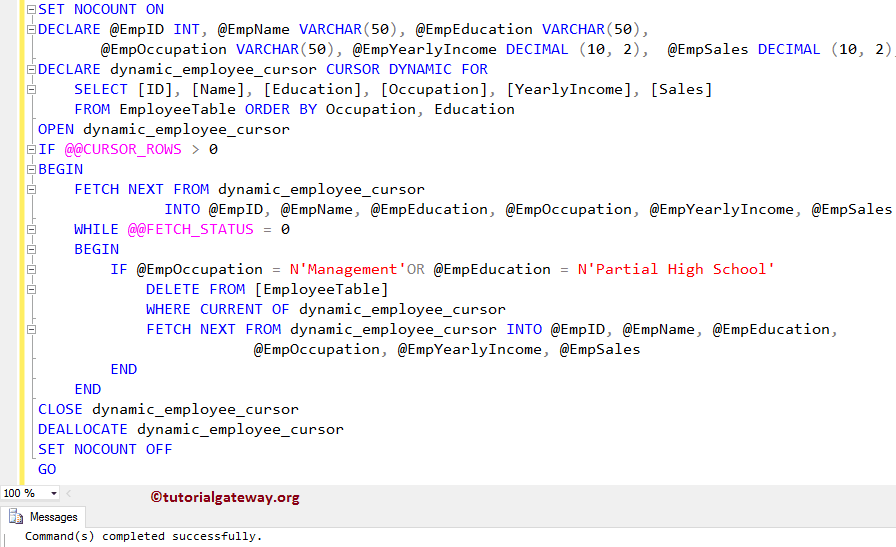
In this example, we will show you how to perform the Delete operations within the dynamic cursor.
-- SQL Server Dynamic Cursor Example
SET NOCOUNT ON
-- Declaring the Variables
DECLARE @EmpID INT,
@EmpName VARCHAR(50),
@EmpEducation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpOccupation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpYearlyIncome DECIMAL (10, 2),
@EmpSales DECIMAL (10, 2);
DECLARE dynamic_employee_cursor CURSOR
DYNAMIC FOR
SELECT [ID]
,[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM EmployeeTable
ORDER BY Occupation, Education
OPEN dynamic_employee_cursor
IF @@CURSOR_ROWS > 0
BEGIN
FETCH NEXT FROM dynamic_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
IF @EmpOccupation = N'Management' OR @EmpEducation = N'Partial High School'
DELETE FROM [EmployeeTable]
WHERE CURRENT OF dynamic_employee_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM dynamic_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
END
END
CLOSE dynamic_employee_cursor
DEALLOCATE dynamic_employee_cursor
SET NOCOUNT OFF
GO
ANALYSIS
We haven’t changed anything in this SQL Server Dynamic Cursor example, except few lines of code, and those lines are:
Within the Loop, we used one more IF Statement to check whether Occupation is equal to Management or Education = Partial High School
IF @EmpOccupation = N'Management' OR @EmpEducation = N'Partial High School'
And if the condition is TRUE, the dynamic cursor will use the DELETE statement to delete that record.
DELETE FROM [EmployeeTable] WHERE CURRENT OF dynamic_employee_cursor
Let us see the Employee table
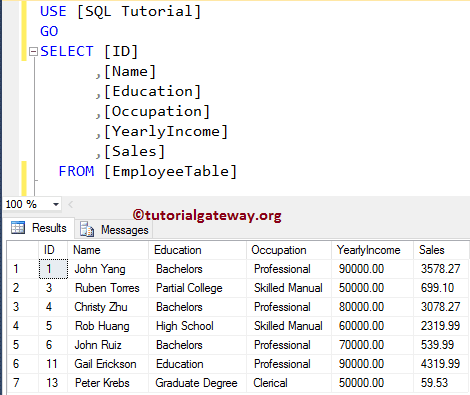
Please refer to Static Cursors, INSERT Statement, DELETE Statement, and UPDATE Statement operations.

Comments are closed.