The SQL SET NOCOUNT ON and OFF is one set function used to stop the number of rows affected message from a query or Stored Procedure to the client.
When you select data from a table, a stored procedure or query will return those records as the result. And it displays the message as Number of Rows affected because of SQL Set Nocount On. For instance, If you INSERT 10 records into any table, then it will return the message as ten records affected, etc.
You can stop the above messages by using this SET NOCOUNT ON. In real-time, it is an extra load to display those messages. So, try to use this function with ON for better performance. Before we get into the SQL Server SET NOCOUNT ON and OFF example, let us see the syntax behind this:
SQL SET NOCOUNT ON OFF Syntax
The basic syntax of the SET NOCOUNT ON and OFF is as shown below:
SET NOCOUNT {ON | OFF }
We are going to use the below-shown data for this demonstration
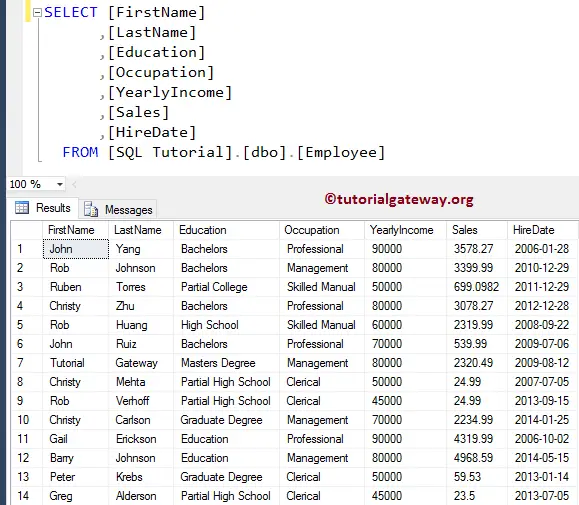
SQL SET NOCOUNT ON Example
In this example, we show you how the SET NOCOUNT ON will affect the queries. Before we get into the main example, let me write a simple SELECT Statement to show you the message that is displayed by the SQL.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Occupation]
,[Education]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Employee]
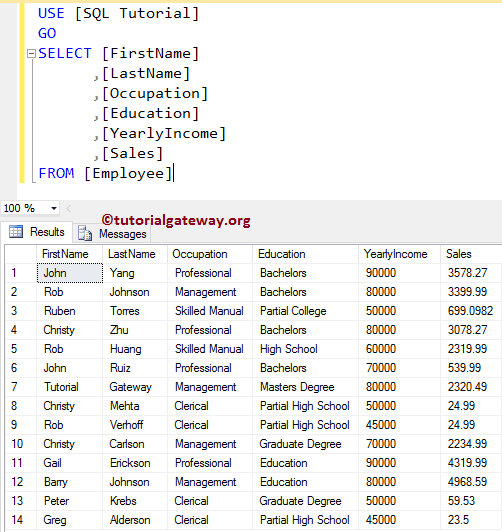
From the above SQL Server screenshot, you can see that the table contains 14 records. Now, let us navigate to Message Tab (besides the Result Tab) to check the information.
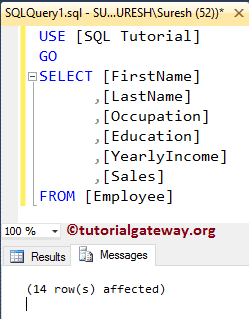
It displays the information as 14 row(s) affected. Let us use the SET NOCOUNT ON Statement.
SET NOCOUNT ON;
GO
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Occupation]
,[Education]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Employee]
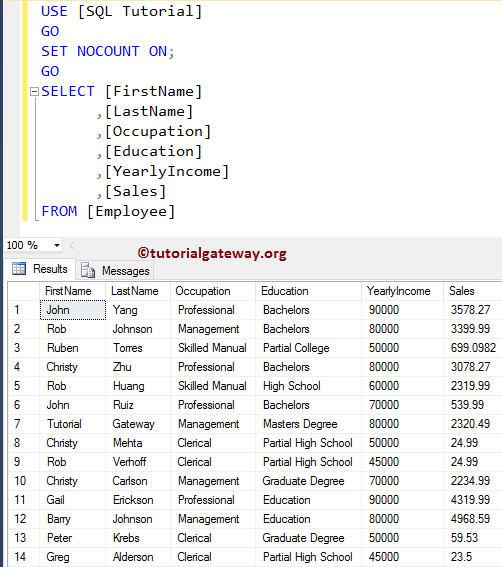
It doesn’t affect the query result. Now, let us go to Message Tab to check for the information.
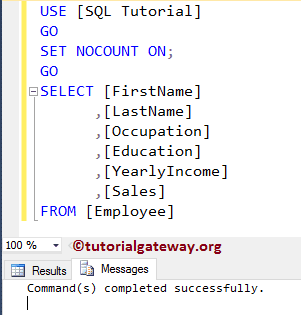
As you see, there is no information such as 14 rows affected. It says Command completed successfully.
SQL SET NOCOUNT OFF
Use the SET NOCOUNT OFF keyword to display the rows that are affected by the message.
SET NOCOUNT OFF;
GO
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[Occupation]
,[Education]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [Employee]
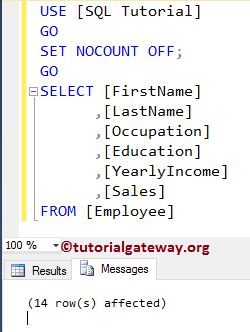
Please refer to the Stored Procedures and Insert Statement articles.
