The SQL Server GOTO statement is used to alter the flow of a program. When the execution reaches the SQL GOTO statement, it will jump unconditionally to the label specified in it.
The syntax of the SQL Server GOTO Statement is
GOTO label ........ ........ label: statements
The label specified after the goto statement is the location where we place the code to execute.
SQL Server Goto Statement Example
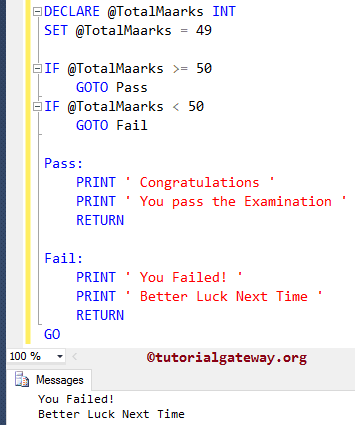
This program will check whether the person is pass or failed using the SQL Goto Statement.
TIP: Unlike the Break and Continue, the GOTO statement doesn’t require any If condition to perform.
DECLARE @TotalMaarks INT SET @TotalMaarks = 49 IF @TotalMaarks >= 50 GOTO Pass IF @TotalMaarks < 50 GOTO Fail Pass: PRINT ' Congratulations ' PRINT ' You pass the Examination ' RETURN Fail: PRINT ' You Failed! ' PRINT ' Better Luck Next Time ' RETURN GO
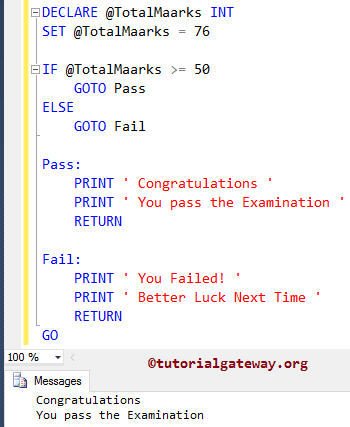
Let us replace the @TotalMarks value with 76, and we replaced the second If condition with the ELSE block.
IF @TotalMaarks >= 50 GOTO Pass ELSE GOTO Fail
In the above SQL Server code, we used Pass and Fail labels. First, we declared the integer variable @Totalmarks and assigned value 49 to it.
DECLARE @TotalMaarks INT SET @TotalMaarks = 49
In the next line, we used IF ELSE to check whether @Totalmarks is greater than or equal to 50 or not.
IF @TotalMaarks >= 50
If the above condition is TRUE, then the Sql Server Goto statement inside the If block will take the execution to the Pass label and execute the print messages inside the Pass label.
PRINT ' Congratulations ' PRINT ' You pass the Examination '<br>
When the condition is FALSE (Else block executed). It means the Else block will take the execution to the Fail label and execute the messages inside it.
PRINT ' You Failed! ' PRINT ' Better Luck Next Time '
NOTE: Although it supports the GOTO, it is always good practice to avoid using it or at least minimize its usage.
