The SQL Server Continue statement is very useful to control the flow of a While loop. Generally, we use this Continue statement inside the While loop. If the execution finds the SQL continue statement inside the While loop, it will stop executing the current loop iteration and starts the new iteration from the beginning.
SQL Continue Example – If we have 15 statements inside the loop. And we want to skip executing a few statements (statement 2 — statement 6, and statement 11 — statement 14) when a specific condition is True. Otherwise, it has to run all 15 statements inside the loop. In this situation, we can place the IF ELSE or ELSE IF to check for the condition. And within the if block puts the continue statement in SQL Server. If the condition is True, it will stop executing statements 2 to 6 and 11 to 14; otherwise, it will run statements from 1 to 15.
SQL Continue Syntax
The syntax of the SQL Server Continue Statement is
CONTINUE;
SQL CONTINUE Statement Example
In this query, we will use the SQL Server Continue statement inside the While loop to control the loop iteration.
-- Example DECLARE @Val INT SET @Val = 1 WHILE @Val <= 10 BEGIN IF (@Val = 3 OR @Val = 7) BEGIN PRINT 'Skipped By Continue Statement = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val) SET @Val= @Val + 1 CONTINUE END PRINT 'Tutorial Gateway Views = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val) SET @Val= @Val + 1 END PRINT 'This statement is Coming from Outside the While Loop' GO
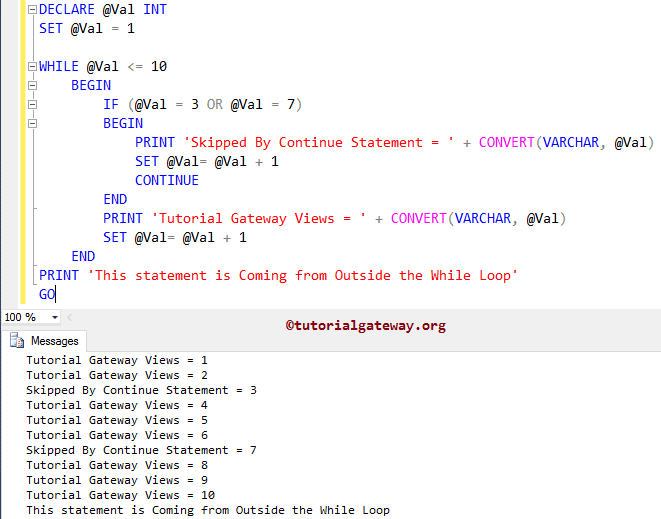
Within this SQL continue statement example, First, we created one variable called @Val and initialized it to 10 using the following statement
DECLARE @Val INT SET @Val = 1
Within the While loop, we check for the condition of whether @Val is less than 10 or not. I suggest you refer to the While Loop article to understand the iteration process.
WHILE @Val <= 10
Inside the While loop, we placed IF ELSE to test whether @Val is equal to 3 or 7 (IF (@Val = 3 OR @Val = 7)). If the condition is false, it will skip the Continue statement and return the following statement as output (In Our case 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10). You can also try ELSE IF for more conditions.
PRINT 'Tutorial Gateway Views = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val)
If this condition is True, the SQL Server Continue statement will execute. Next, the While loop iteration will stop at that number (i.e., 3 and 7) without printing the other statements. For better understanding, we placed the below SQL Server statement inside the If block. So, whenever the iteration break, that value will be printed from this statement.
PRINT 'Skipped By Continue Statement = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val)
The following statement is outside the While Loop and has nothing to do with the expression in the While loop. It means, irrespective of the condition result, this statement will execute.
PRINT 'This statement is Coming from Outside the While Loop'
