The JavaScript Assignment operators are used to assign values to the declared variables. Equals (=) operator is the most commonly used assignment operator. For example:
var i = 10;
The below table displays all the JavaScript assignment operators.
| JavaScript Assignment Operators | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| = | x = 15 | Value 15 is assigned to x |
| += | x += 15 | This is same as x = x + 15 |
| -= | x -= 15 | This is same as x = x – 15 |
| *= | x *= 15 | This is same as x = x * 15 |
| /= | x /= 15 | This is same as x = x / 15 |
| %= | x %= 15 | This is same as x = x % 15 |
JavaScript Assignment Operators Example
For this example, We are using two integer variables a, and Total, and their values are 7 and 21. We are going to use these two variables to show you the working functionality of all the Assignment Operators in JS.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> JavascriptAssignmentOperators</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> AssignmentOperations </h1>
<script>
var a = 7, Total = 21;
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total += a) + "<br />");
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total -= a) + "<br />");
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total *= a) + "<br />");
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total /= a) + "<br />");
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total %= a) + "<br />");
</script>
</body>
</html>
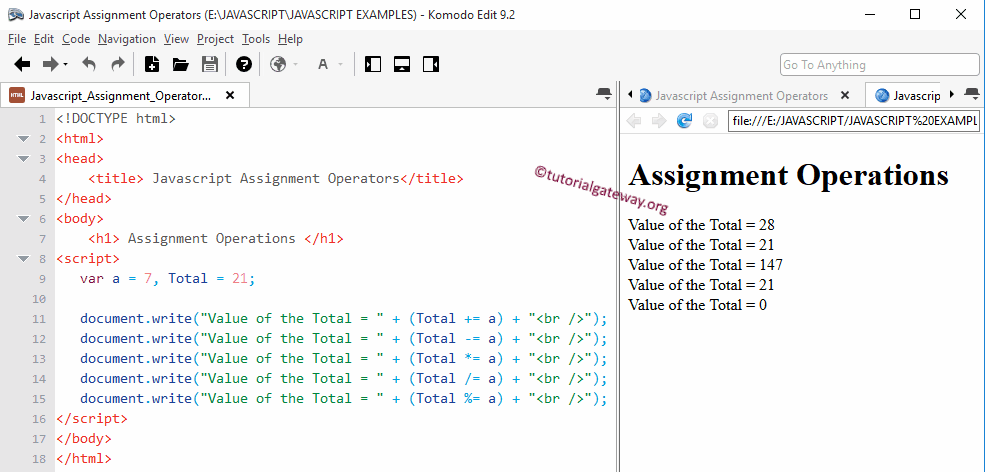
In this JavaScript Assignment Operators program, We declared 2 integer values a, and Total, and we assigned values 7 and 21 respectively. Below statements will perform Assignment operations on a and Total and then write the output to the respective browser.
Let us see the functionality of the JS Assignment Operators
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total += a) + "<br />");
Total += a means
Total = Total + a = 21 + 7 = 28
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total -= a) + "<br />");
Total -= a means
Total = Total – a = 28 – 7 = 21
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total *= a) + "<br />");
Total *= a means
Total = Total * a = 21 * 7 = 147
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total /= a) + "<br />");
Total /= a means
Total = Total / a = 147 / 7 = 21
document.write("Value of the Total = " + (Total %= a) + "<br />")
Total %= a means
Total = Total + a = 21 % 7 = 0 (Remainder of 21/7 is = 0)
JavaScript Assignment Operators Example 2
For this JavaScript example, we are using two integer variables, a and Total, whose values are 7 and 21. We will use these variables to show you, How to display the Assignment Operators output in Paragraphs.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title> Example 2</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Assignment Operations </h1>
<p id = 'add'> Plus Equal to </p>
<p id = 'sub'> Subtraction Equal to </p>
<p id = 'mul'> Multiplication Equal to </p>
<p id = 'div'> Division Equal to </p>
<p id = 'mod'> Modulus Equal to </p>
<script>
var a = 3, Total = 12;
document.getElementById("add").innerHTML = "Value of the Total = " + (Total += a);
document.getElementById("sub").innerHTML = "Value of the Total = " + (Total -= a);
document.getElementById("mul").innerHTML = "Value of the Total = " + (Total *= a);
document.getElementById("div").innerHTML = "Value of the Total = " + (Total /= a);
document.getElementById("mod").innerHTML = "Value of the Total = " + (Total %= a);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Assignment Operations
Value of the Total = 15
Value of the Total = 12
Value of the Total = 36
Value of the Total = 12
Value of the Total = 0