C Programming Operators are symbols useful to perform mathematical and logical operations. You can use these Operators on individual values or variables.
The below table will show you the list of available C Programming operators with an example.
| C Programming Operators | Description |
|---|---|
| Arithmetic | Used to perform basic mathematical calculations like Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, and Modulus. |
| Relational | The Relational operators are mostly used either in Loops or If Statements. Use these to check the relationship between the two variables. If the relationship is true, it will return 1. Otherwise, it will return a value of 0. |
| Logical | Used to combine two or more conditions and perform the logical operations using Logical AND (&&), OR (||), and NOT (!). |
| Assignment | Used to assign the values to the declared variables. = (Equals) is the most commonly used one to assign the result. |
| Increment & Decrement | To increase or decrease the value by 1. ++ is used to increase the existing variable value by 1. The decrement operator – – is used to subtract or decrease the existing value by 1. |
| Bitwise | Bitwise operators in C programming are useful for performing bit-level operations. First, the decimal values will convert into a sequence of bits ( binary values), i.e., 0001, 1011, etc. And this will work on these bits like shifting them right to the left etc. |
| Conditional | The Conditional is also known as the Ternary operator. We use them in the decision-making process of true or false. Depending upon the expression result, this operator returns the statement. |
| Sizeof | It is most useful in finding the structure size and array size. |
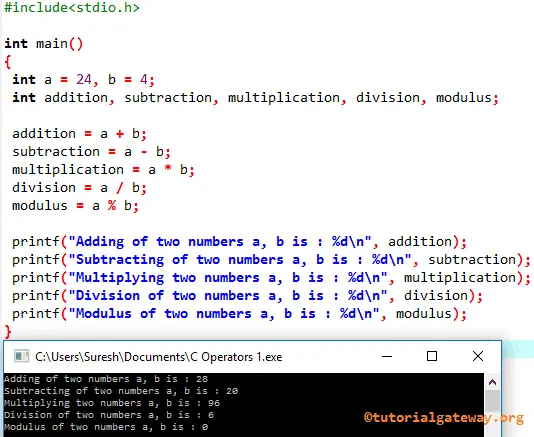
C Programming Arithmetic Operators Example
In this operators example, we will use two variables to perform various arithmetic operations in this C programming Language.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 24, b = 4;
int addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulus;
addition = a + b;
subtraction = a - b;
multiplication = a * b;
division = a / b;
modulus = a % b;
printf("Adding of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", addition);
printf("Subtracting of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", subtraction);
printf("Multiplying two numbers a, b is : %d\n", multiplication);
printf("Division of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", division);
printf("Modulus of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", modulus);
}
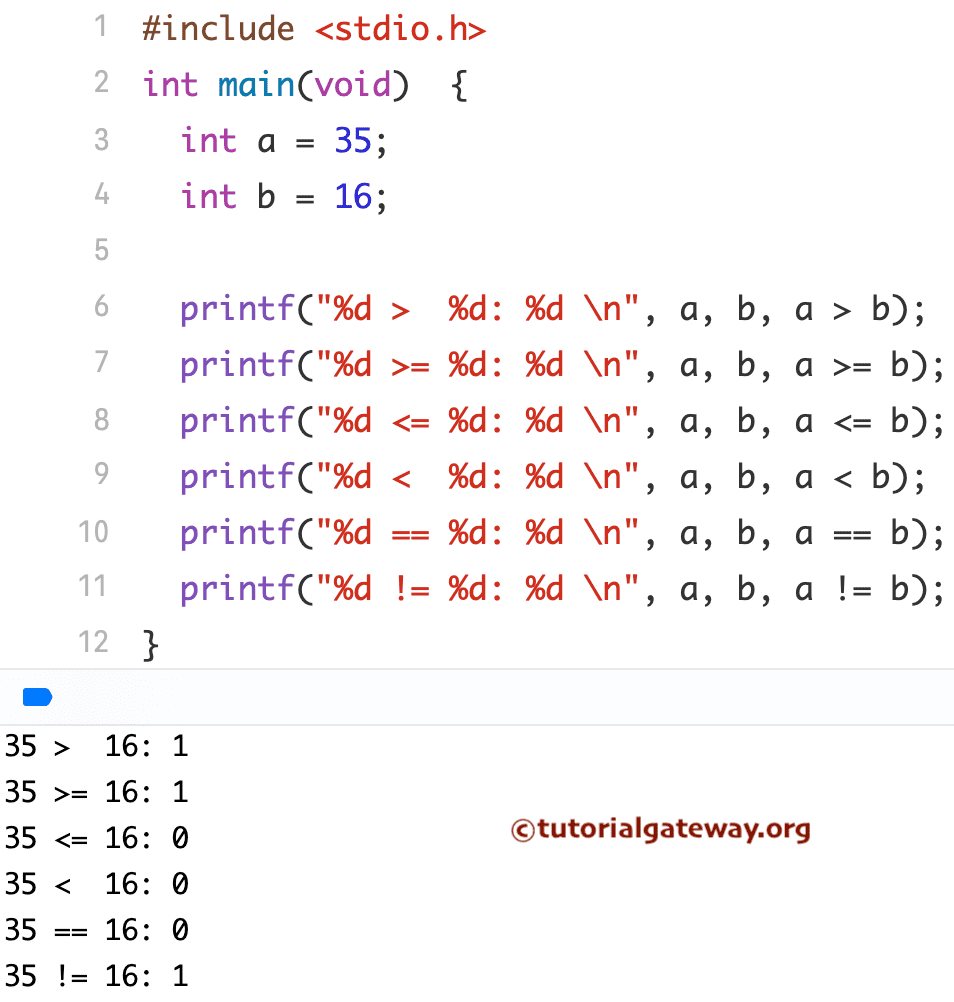
C Relational Operators Example
In this example, we will use two variables, a and b, to perform various relational operations in programming.
// Relational example
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
int a = 35;
int b = 16;
printf("%d > %d: %d \n", a,b, a > b);
printf("%d >= %d: %d \n", a,b, a >= b);
printf("%d <= %d: %d \n", a,b, a <= b);
printf("%d < %d: %d \n", a,b, a < b);
printf("%d == %d: %d \n", a, b, a == b);
printf("%d != %d: %d \n", a, b, a != b);
}
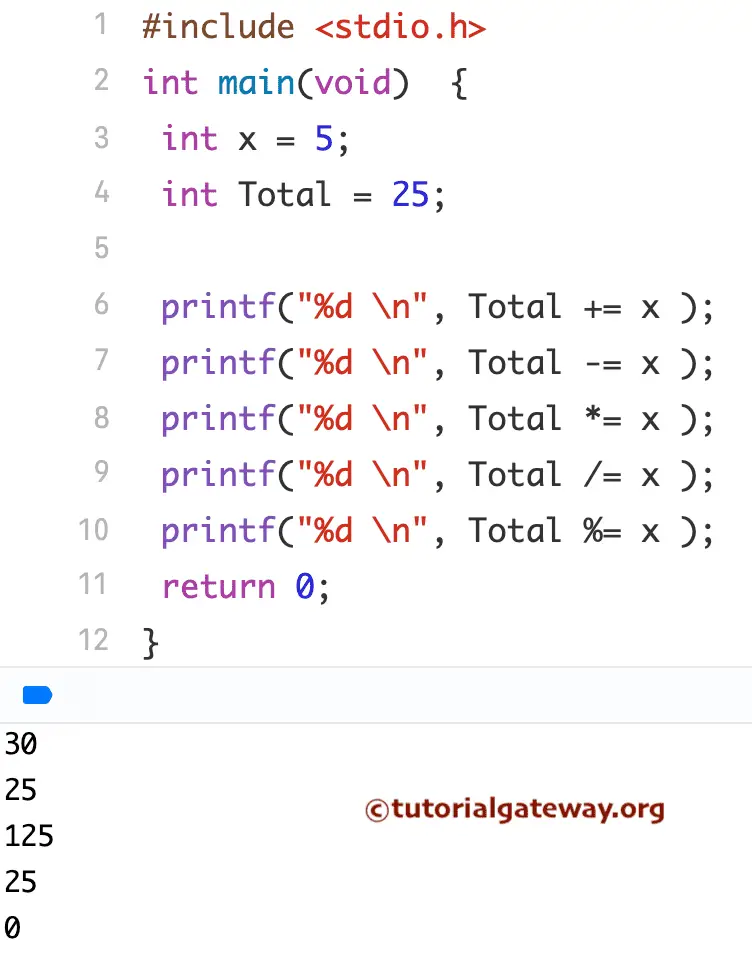
Assignment Example
For this example, We use the two variables x and Total. They will show you the working functionality of all the Assignment Operators in C Programming Language.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x = 5;
int Total = 25;
printf("%d \n", Total += x );
printf("%d \n", Total -= x );
printf("%d \n", Total *= x );
printf("%d \n", Total /= x );
printf("%d \n", Total %= x );
return 0;
}