The one-dimensional array of characters followed by a null character \0 is called a string in C Programming. Let us see how to declare a string array in C, access elements or characters, and print characters with examples.
C string Syntax
The syntax of a string declaration in C Programming is as follows:
char Name [Size];
- Name: Please specify the name. For example, full_name, employee_name, etc
- Size: Number of characters required for this plus one (\0). For instance, if Size =10, it can hold 9 characters.
For Example, char full_name[50];. Here, full_name is the name, and the size equals 50. It means this allows a maximum of 49 characters
C String Initialization
There are multiple ways to initialize a string in C programming language.
char name[] = “Tutorial Gateway”; // Declare without Size
char name[50] = “Tutorial Gateway”; // Declare with Size
Declare C string Characters Array.
char name[] = {‘T’, ‘u’, ‘t’, ‘o’, ‘r’, ‘i’, ‘a’, ‘l’, ‘G’, ‘a’, ‘t’, ‘e’, ‘w’, ‘a’, ‘y’, ‘\0’};
char name[16] = {‘T’, ‘u’, ‘t’, ‘o’, ‘r’, ‘i’, ‘a’, ‘l’,’ G’, ‘a’, ‘t’, ‘e’, ‘w’, ‘a’, ‘y’, ‘\0’};
You can also declare it using pointers
char *str;
char *name = “hello world”;
C Program to Declare and Print Strings
In this program, We are declaring the character array in possible ways. Next, we are using the printf statement to print the char array. I suggest you refer Arrays article.
You must use %s to display the sentence or text as output. Or you use C Programming puts function.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
// Without Size
char name1[] = "Tutorial Gateway";
// With Size
char name2[50] = "Tutorial Gateway";
// Declare Characters Array
char name3[] = {'T','u','t','o','r','i','a','l','G','a','t','e','w','a','y', '\0'};
char name4[16] = {'T','u','t','o','r','i','a','l','G','a','t','e','w','a','y', '\0'};
printf("Name1: %s \n", name1);
printf("Name2: %s \n", name2);
printf("Name3: %s \n", name3);
printf("Name4: %s \n", name4);
return 0;
}
Name1: Tutorial Gateway
Name2: Tutorial Gateway
Name3: TutorialGateway
Name4: TutorialGateway Allow Users to enter Text from the Command line
In this C program, we are allowing users to enter their own string. Next, we print that user’s given sentences as output.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
char name1[50];
printf("Please enter the Name : ");
scanf("%s", name1);
printf("Name: %s \n", name1);
return 0;
}
Please enter the Name : TutorialGateway
Name: TutorialGateway Access Elements of Strings in C programming
You can use indexes to access individual letters. By this C index, you can insert, delete, or update any string character at any given position.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
char name[50];
int i = 0;
printf("Please enter the Name : ");
scanf("%s", name);
while (name[i] != '\0')
{
printf("The Character at %d Index Position = %c \n", i, name[i]);
i++;
}
return 0;
}
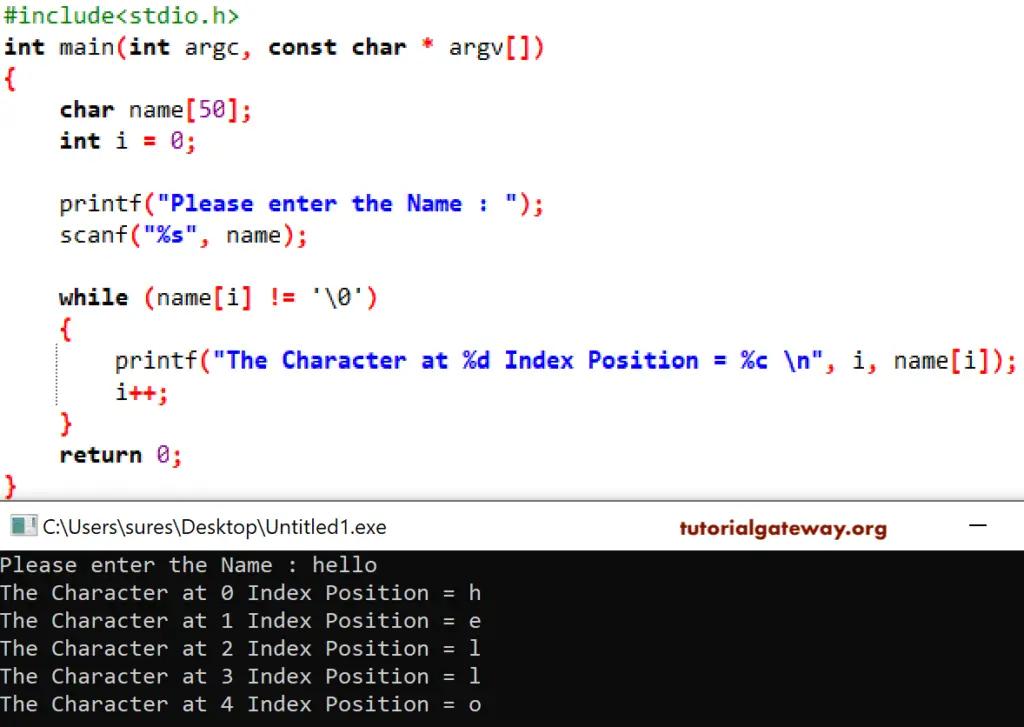
The analysis of the character array iteration-wise is shown below.
First Iteration : while (name[i] != ‘\0’)
Here, i value is 0. It means, name[0] = h So, condition is True
It will print that letter along with the index position.
Next, i value will increment
Second Iteration: while (name[1] != ‘\0’)
while (e != ‘\0’) – Condition True
C string Third Iteration: while (name[2] != ‘\0’)
while (l != ‘\0’) – It means, Condition was True
Fourth Iteration: while (name[3] != ‘\0’)
while (l != ‘\0’) – Condition True
Fifth Iter: while (name[4] != ‘\0’)
while (0 != ‘\0’) – This condition is True
Sixth Iteration:while (name[5] != ‘\0’)
while (\0 != ‘\0’) – Condition is False. So, the Compiler will exit from the While loop
C String length
In this program, we are using the built-in function strlen to find the length of a char array.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
char nam[50];
printf("Enter the Name : ");
scanf("%s", nam);
float len;
len = strlen(name);
printf("The Length = %.f \n", len);
return 0;
}
Enter the Name : sample
Length = 6 C String Functions
The following is the list of available string functions in this C Programming language.
- memchr: Find the first occurrence of a character and returns a pointer to it.
- strcat: To concat or combine
- strncat: This is the same as above. However, you can restrict the characters to add. It appends user-specified characters to the end.
- strcmp: Used to compare two and check whether they are equal or not.
- strncmp: This function is the same as strcmp. However, you can restrict the total number of characters to compare.
- strcpy: Used to shallow copy
- strncpy: This is the same as strcpy. However, you can restrict the number of characters to copy.
- strcoll: Using LC_COLLATE settings, it will compare the two.
- strlen: Finds the total characters or length of it.
- strlwr: Converts to lowercase
- strpbrk: It finds the first character in the first one that matches any character in the second one.
- strrev: Use this to reverse.
- strupr: Converts it to uppercase
- strtok
- strrchr
- strchr
- strstr
