The Arithmetic operators are some of the C Programming operators which are used to perform arithmetic operations, including operators like Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division, and Modulus.
All these Arithmetic operators are binary operators, which means they operate on two operands. The below table shows all the Arithmetic Operators in C Programming with examples.
| C Arithmetic Operators | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | 10 + 2 = 12 |
| – | Subtraction | 10 – 2 = 8 |
| * | Multiplication | 10 * 2 = 20 |
| / | Division | 10 / 2 = 5 |
| % | Modulus – It returns the remainder after the division | 10 % 2 = 0 (Here remainder is zero). If it is 10 % 3 then it will be 1. |
Arithmetic Operators in C Example
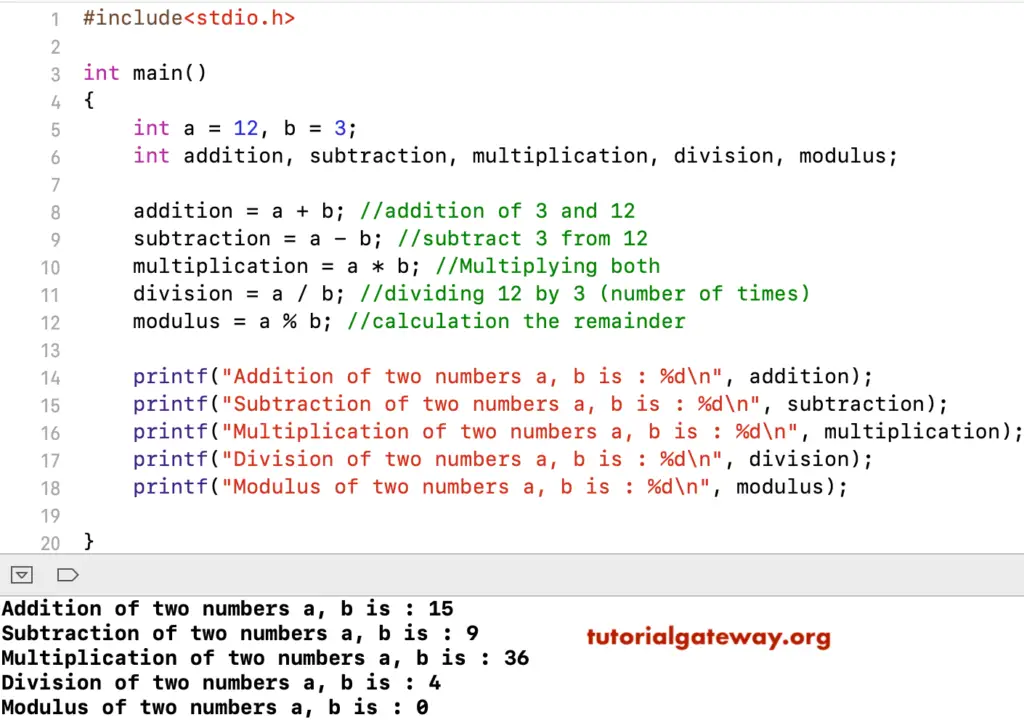
In this C arithmetic operator program, We are using two variables a and b and their values are 12 and 3.
We are going to use these two variables to perform various arithmetic operations present in the Programming Language.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 12, b = 3;
int addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulus;
addition = a + b; //addition of 3 and 12
subtraction = a - b; //subtract 3 from 12
multiplication = a * b; //Multiplying both
division = a / b; //dividing 12 by 3 (number of times)
modulus = a % b; //calculation the remainder
printf("Addition of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", addition);
printf("Subtraction of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", subtraction);
printf("Multiplication of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", multiplication);
printf("Division of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", division);
printf("Modulus of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", modulus);
}
NOTE: When we are using the division (/) operator, the result will completely depend upon the data type it belongs to.
For example, if the data type is an integer, then division arithmetic operators in c will produce the integer value by rounding the value (5 / 2 = 2). If you want the correct result, change the data type to float. Don’t get confused. Let’s see one more example for a better understanding.
C Arithmetic Operators using Float
For this example program, we use two variables, a and b, whose values are 7 and 3. We will use these two variables to show the problems we generally face while performing arithmetic operations on Int and Float Datatype.
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 7, b = 3;
int integerdiv, modulus;
float floatdiv;
integerdiv = a / b; // dividing 7 by 3
modulus = a % b; // calculation the remainder
floatdiv = (float)a / b; // Converting int to float
printf("Division of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", integerdiv);
printf("Modulus of two numbers a, b is : %d\n", modulus);
printf("---------Correct Results is------- \n");
printf("Division of two numbers a, b is : %f\n", floatdiv);
}
Division of two numbers a, b is : 2
Modulus of two numbers a, b is : 1
---------Correct Results is-------
Division of two numbers a, b is : 2.333333Within the above example, If you notice the result, we got two different results for the same calculation. Because for the first result, both a and b are integers, and the output is also an integer (integerdiv). So the compiler neglects the term after the decimal point and shows answer 2 instead of 2.3333, and a % b is 1 because the remainder is 1.
Next, we changed the output data type to float (floatdiv), and also converted the result to float to get our desired result. Please be careful while using the division Operator (Type casting plays a major role here)

Comments are closed.