The box plot or boxplot in R programming is a convenient way to graphically visualize the numerical data group by specific data. Let us see how to Create, Remove outlines, Format their color, add names, add the mean, and draw a horizontal boxplot in R Programming language with an example.
R Boxplot Syntax
The syntax to draw the Boxplot in R Programming is
boxplot(formula, data = NULL,.., subset, na.action = NULL)
The complex syntax behind this R Boxplot function has the following arguments
(x, ....., range = 1.5, width = NULL, varwidth = FALSE,
notch = FALSE, outline = TRUE, col = NULL, log = "",
border = par("fg"), names, plot = TRUE,
pars = list(boxwex = 0.8, staplewex = 0.5, outwex = 0.5),
horizontal = FALSE, add = FALSE, at = TRUE)
There are many arguments supported by the Boxplot in R programming language, and the following are some of the arguments:
- data: Please specify the Data Frame or List that contains the data to draw a boxplot. In this example, it is airquality
- subset: You can restrict the plots by specifying the vector of values. In this example, you can restrict them to August month.
- x: Please specify the data from which you want to draw. Here, you can use a numeric vector or a list containing the numeric vector.
- range: This R Programming boxplot argument decides how far the whisker extends out of the box.
- width: It is optional, use this to specify a vector that contains the widths of each box.
- varwidth: It is a Boolean argument. If it is TRUE, boxes draw with widths proportional to the square roots of the no. of observations in the group.
- border: It is an optional argument. Please specify the vector of color you want to add to the outlines of the boxplot borders.
- plot: It is a Boolean argument. If it is FALSE, it returns the summaries on which the R boxplots are based.
- log: You have to specify a character string of three options. If X-Axis is to be logarithmic, then “x”, If Y-Axis is to be logarithmic “y”, if both X-Axis and Y-Axis are to be logarithmic, then specify either “xy” or “yx”
- add: It is a Boolean argument, and by default, it is FALSE. If it is TRUE, the plot should add to an already existing plot.
- horizontal: It is a Boolean argument. If it is FALSE, the boxplot drew vertically. If it is TRUE, it drew horizontally.
- at: It is a numeric vector, which gives the locations where the boxplot drew. It is very helpful when we are adding a new box to the existing plot region.
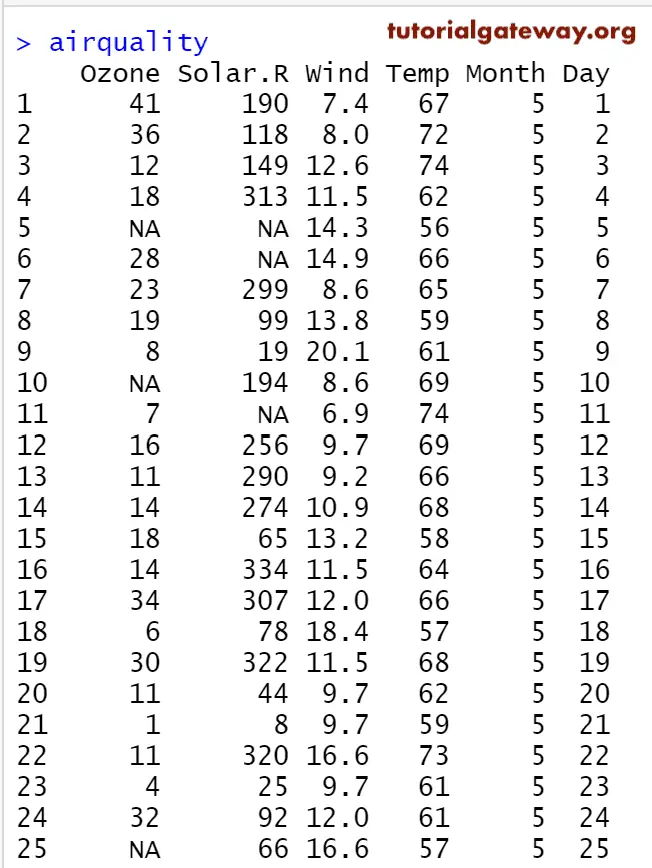
Before we get into the example, let us see the airquality dataset data provided by this R programming, which we are going to use for this boxplot example.
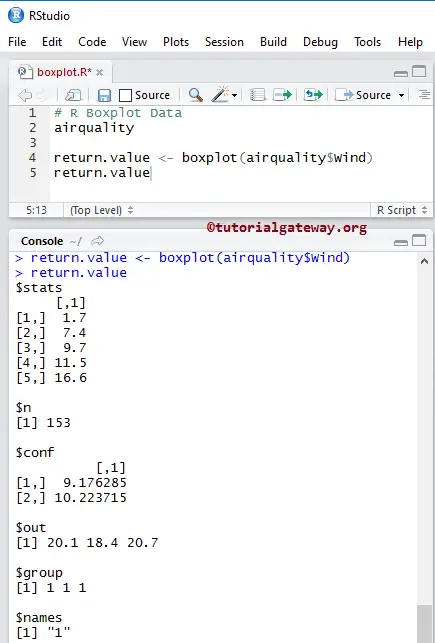
Return Value of a Boxplot in R Programming
In general, before we start creating, let us see how the data is divided. It returns the stats, outliners, groups, and names.
airquality return.value <- boxplot(airquality$Wind) return.value
Create a Boxplot in R Programming
In this example, we create a R Boxplot using the airquality data set, which is provided by the Studio. If you require to import data from external files, then refer to the R Read CSV article to understand the importing of the CSV file.
airquality boxplot(airquality$Wind)
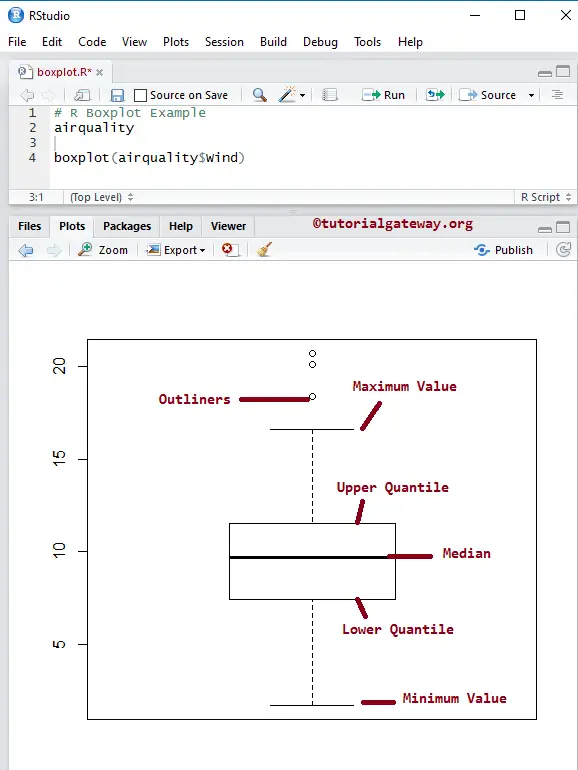
airquality data set returns the output as a List. So, we are using the $ to extract the data from the List.
boxplot(airquality$Wind)
Boxplot using Formula argument
In this example, we create using the formula argument to create a boxplot in r programming.
- formula: It should be something like value~group, where the value is the vector of numeric values, and the group is the column you want to use as a group by. For example, you want to draw the sample size box for countrywide sales, then value = sales and group = country.
airquality boxplot(airquality$Wind~airquality$Month)
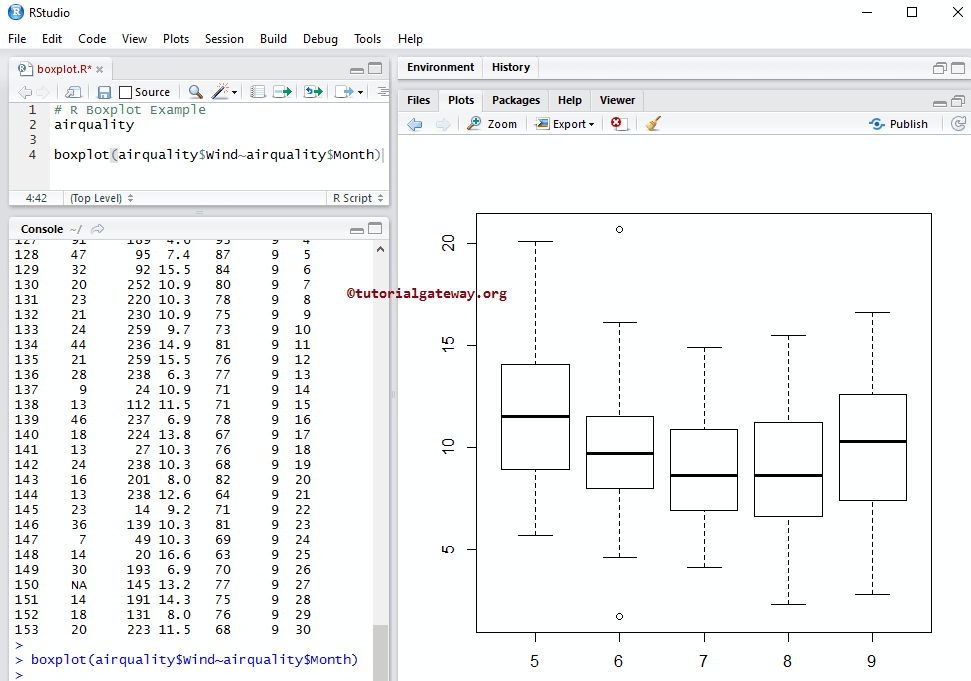
Assigning names to Boxplot
In this example, we assign names to R Boxplot, X-Axis, and Y-Axis using main, xlab, and ylab
- main: You can change or provide the Title.
- xlab: Please specify the label for the X-Axis
- ylab: Please specify the label for the Y-Axis
- las: Used to change the Y-axis values direction.
airquality
boxplot(airquality$Wind~airquality$Month,
main = "Airquality",
xlab = "Months",
ylab = "Wind",
las = 1
)
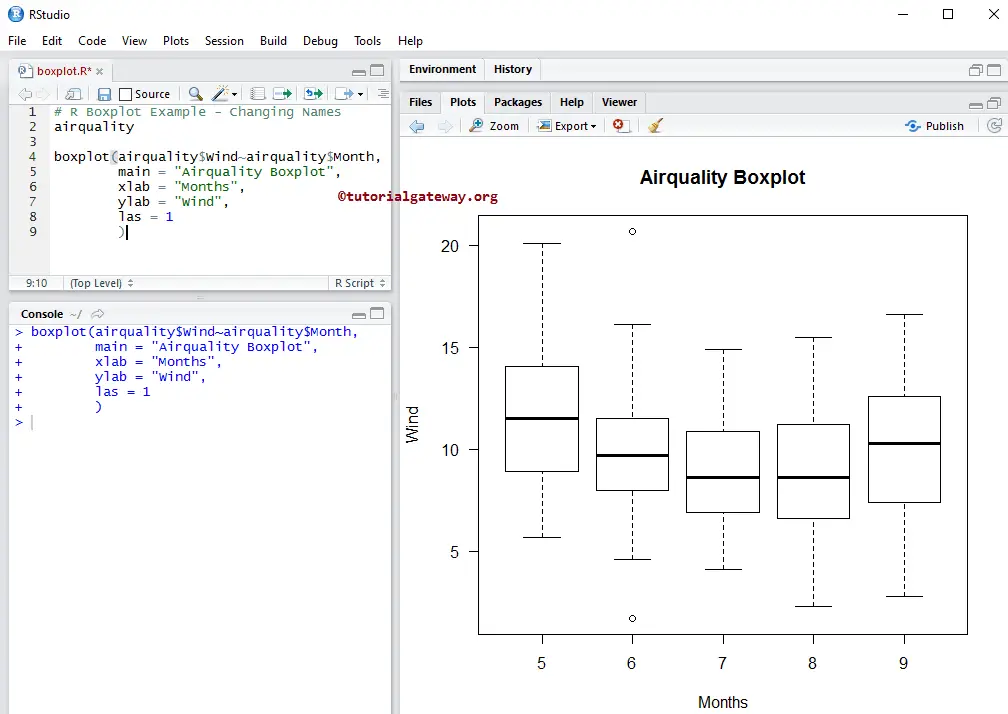
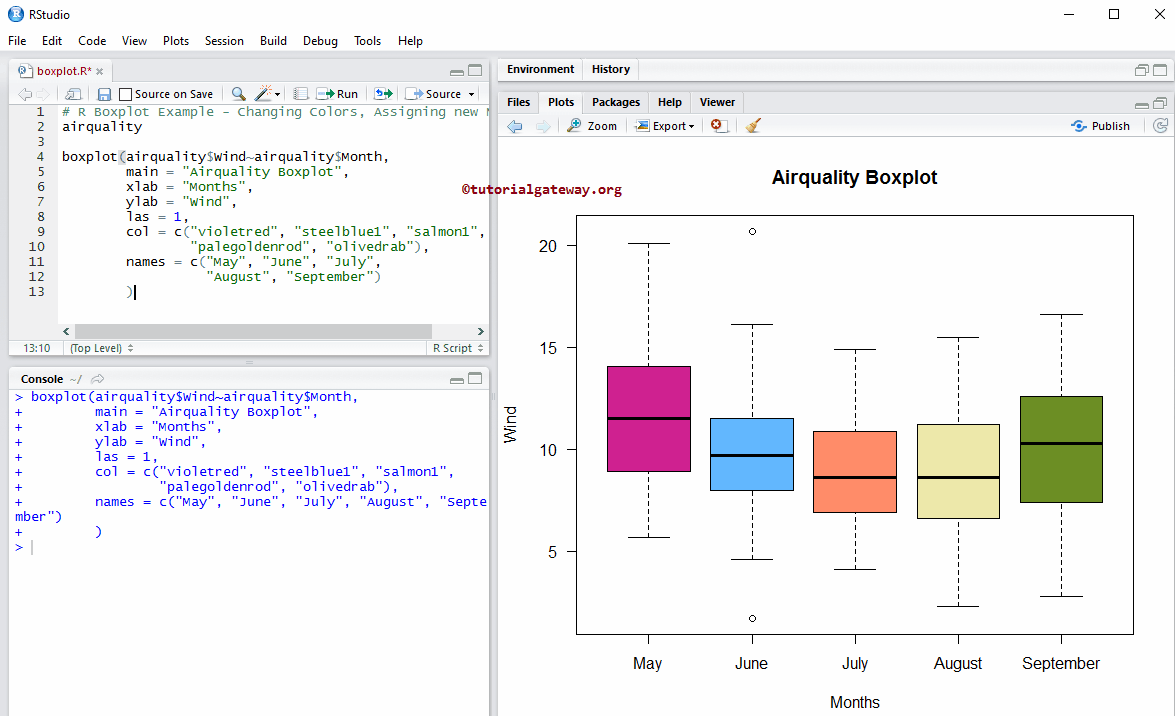
Change Colors of a Boxplot in R
In this R example, we change the Boxplot box colors using the col argument
- col: Please specify the color you want to use. Type colors() in your console to get the list of colors available.
- names: Please specify the names of the boxes. Here, we are changing the Month numbers to Month names.
# Changing Colors, Assigning new Names
airquality
boxplot(airquality$Wind~airquality$Month,
main = "Airquality",
xlab = "Months",
ylab = "Wind",
las = 1,
col = c("violetred", "steelblue1", "salmon1",
"palegoldenrod", "olivedrab"),
names = c("May", "June", "July", "August", "September")
)
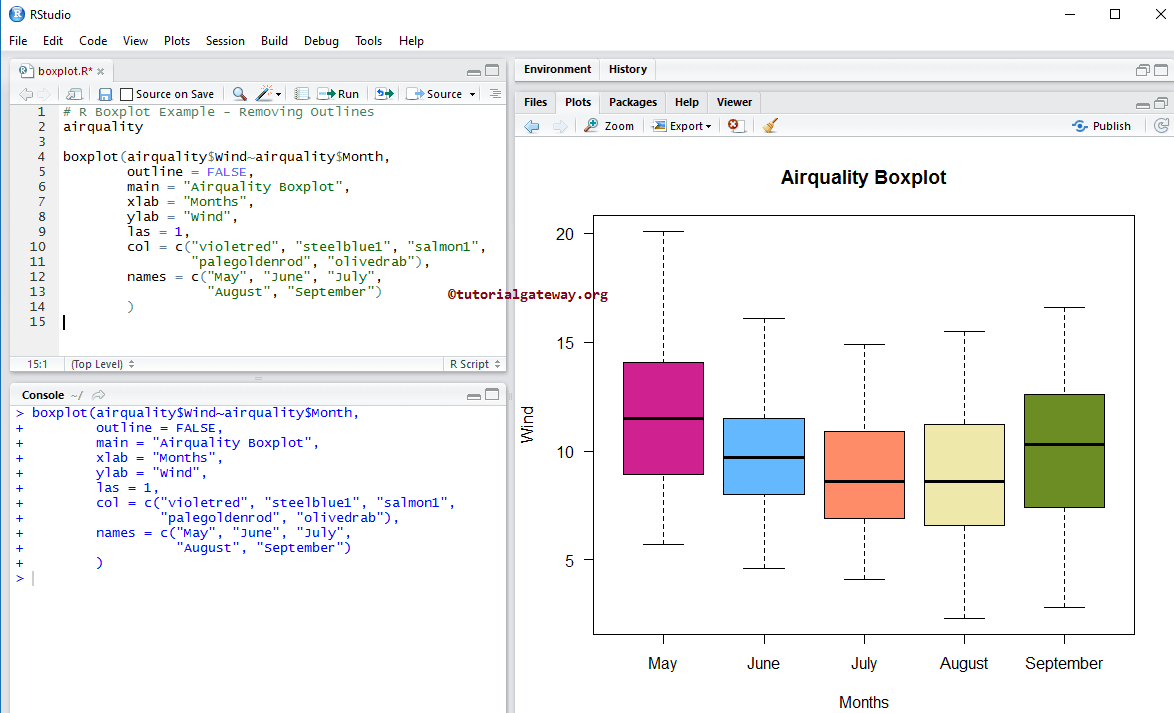
Removing Outlines of Boxplot
In this R Boxplot example, we remove the Outlines using an outline argument.
- outline: It is a Boolean argument. If it is TRUE, it draws the outlines (that are extra dots outside the box), and if it is false, all the outlines are removed.
airquality
boxplot(airquality$Wind~airquality$Month,
outline = FALSE,
main = "Airquality",
xlab = "Months",
ylab = "Wind",
las = 1,
col = c("violetred", "steelblue1", "salmon1",
"palegoldenrod", "olivedrab"),
names = c("May", "June", "July",
"August", "September")
)
Calculating & Adding Mean to Boxplot in R
In this R example, we calculate the Mean of each box and how to add those mean values to the existing boxplot using the points function.
airquality
boxplot(airquality$Wind~airquality$Month,
main = "Airquality",
xlab = "Months",
ylab = "Wind",
las = 1,
col = c("violetred", "steelblue1", "salmon1",
"palegoldenrod", "olivedrab"),
names = c("May", "June", "July",
"August", "September")
)
meanval <- by(airquality$Wind, airquality$Month, mean)
points(meanval, col = "white", pch = 8, cex = 1.5)
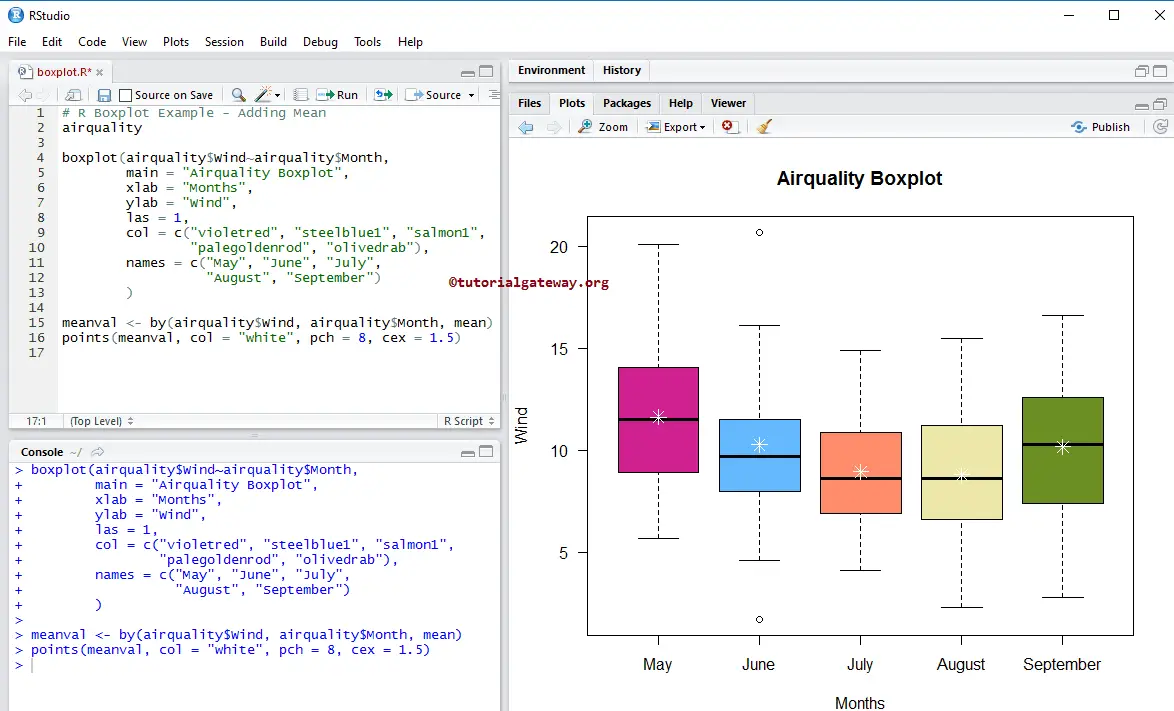
The following statement finds the mean value of Wind, grouped by Month numbers.
meanval <- by(airquality$Wind, airquality$Month, mean)
The following statement adds that means value to the boxes. pch = 8 means star character, cex is the size of the character, and col is for color.
points(meanval, col = "white", pch = 8, cex = 1.5)
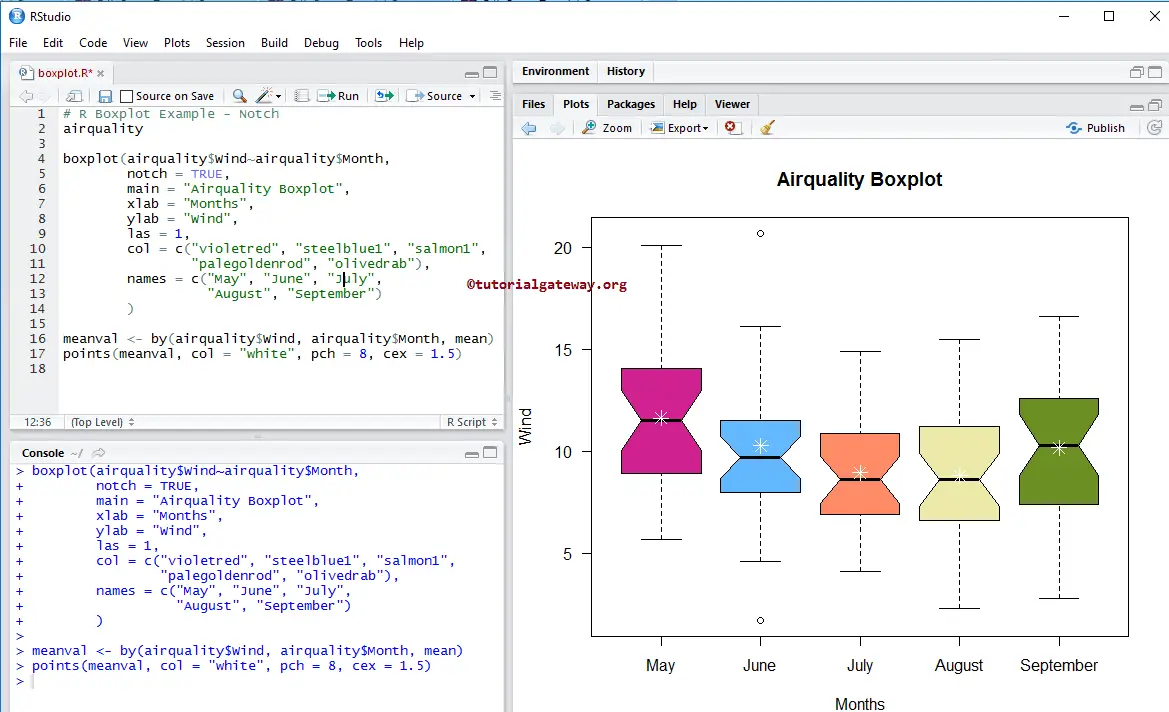
Notch argument in R Boxplot
In this example, we draw a line on each side of the boxes using the notch argument.
- notch: It is a Boolean argument. If it is TRUE, a notch is drawn on each side of the box. If the notches of 2 plots overlapped, then we could say that the medians of them are the same. Otherwise, they are different.
# Notch
airquality
boxplot(airquality$Wind~airquality$Month,
notch = TRUE,
main = "Airquality",
xlab = "Months",
ylab = "Wind",
las = 1,
col = c("violetred", "steelblue1", "salmon1",
"palegoldenrod", "olivedrab"),
names = c("May", "June", "July",
"August", "September")
)
meanval <- by(airquality$Wind, airquality$Month, mean)
points(meanval, col = "white", pch = 8, cex = 1.5)
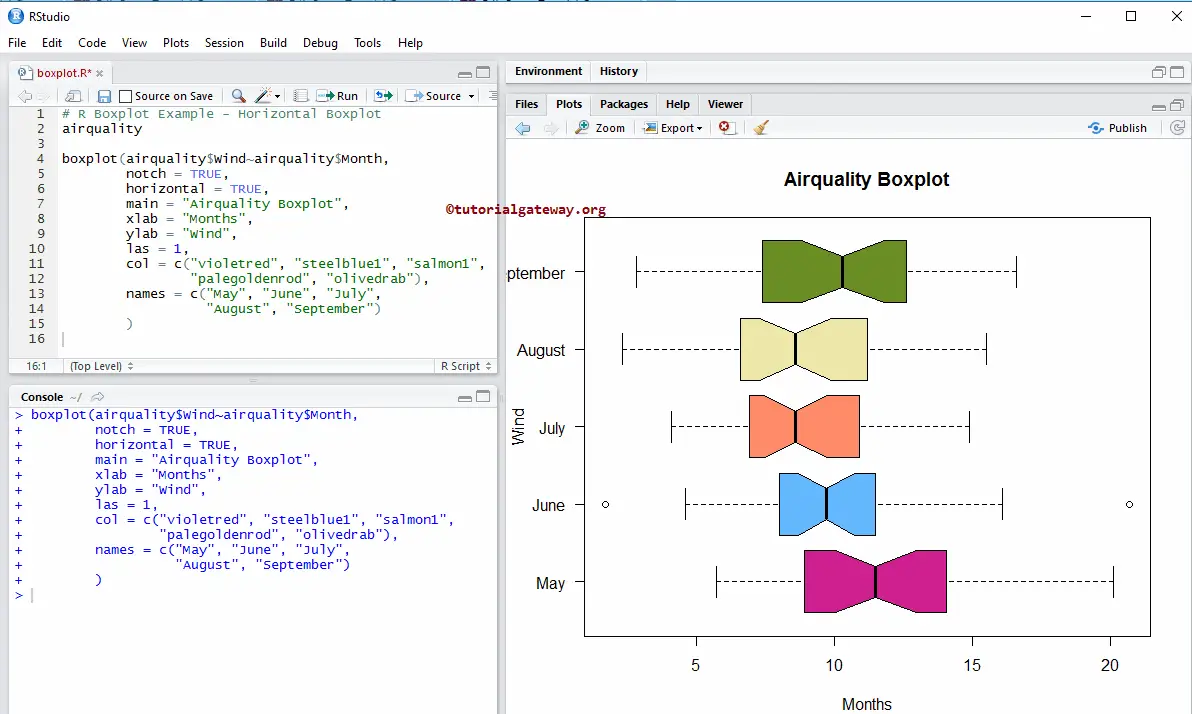
Horizontal Boxplot in R Programming
We change the default vertical boxplot into a horizontal box plot in this R example using a horizontal argument.
airquality
boxplot(airquality$Wind~airquality$Month,
notch = TRUE,
horizontal = TRUE,
main = "Airquality",
xlab = "Months",
ylab = "Wind",
las = 1,
col = c("violetred", "steelblue1", "salmon1",
"palegoldenrod", "olivedrab"),
names = c("May", "June", "July",
"August", "September")
)
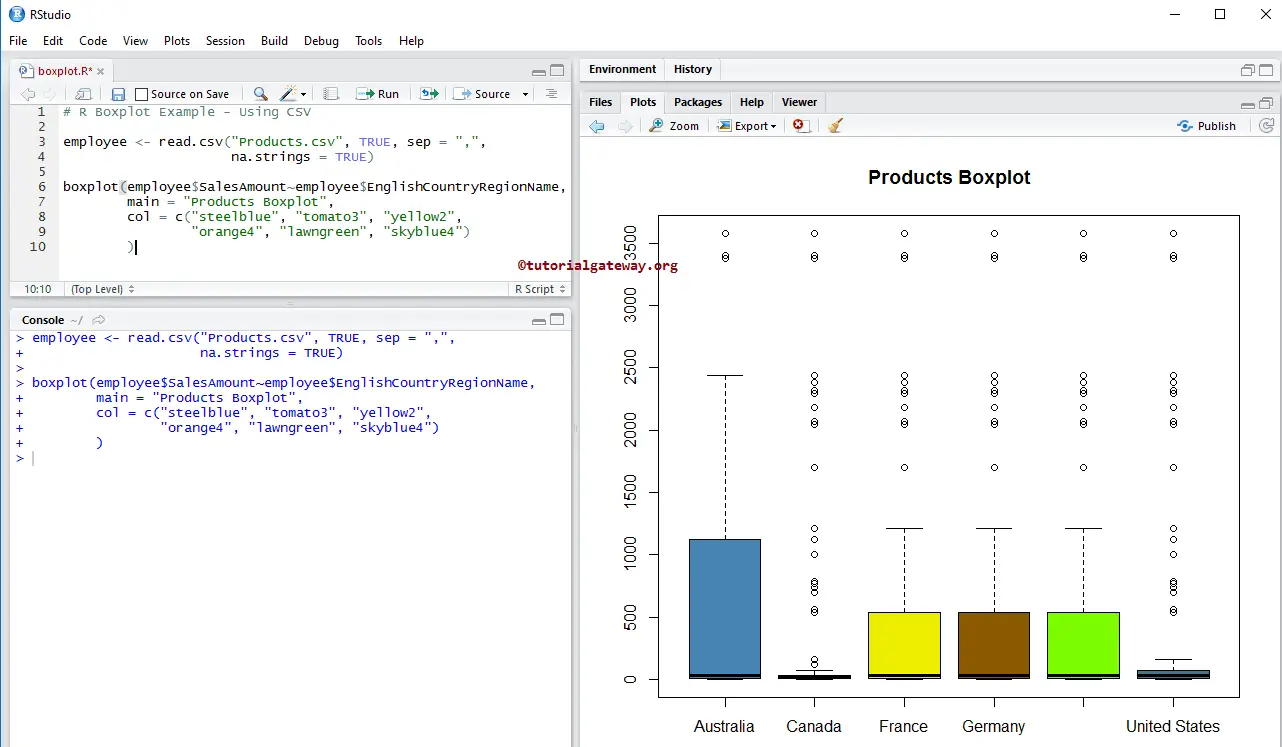
Creating R Boxplot using CSV File
Let us see how to create the R Boxplot using external data. For this, we are importing data from the CSV file using the read.csv function. Refer to the Read CSV article to import the CSV file.
employee <- read.csv("Products.csv", TRUE, sep = ",",
na.strings = TRUE)
boxplot(employee$SalesAmount~employee$EnglishCountryRegionName,
main = "Products",
col = c("steelblue", "tomato3", "yellow2",
"orange4", "lawngreen", "skyblue4")
)
The above code snippet will draw the boxplot for the Sales Amount, grouped by Country.