The Aggregate Transformation in SSIS performs two main tasks:
- Applying Aggregate Operations on your input data
- It allows you to group your data based on values in your input columns.
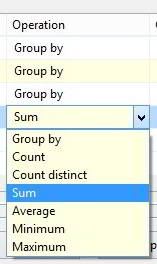
Aggregate Transformation in SSIS performs a function similar to the SQL Agg functions. The operations include the following:
- GROUP BY: Just like the GROUP BY Clause in SQL SELECT queries.
- COUNT: It will Count the number of values in this column. Null values are included in the count if you select (*) as the input column. Otherwise, null values are ignored.
- COUNT DISTINCT: It will count the number of Distinct values in this column.
- SUM: Calculate the Sum of the Column values.
- AVERAGE: Calculate the Average of the Column values.
- MINIMUM: Calculate the Minimum of Column values.
- MAXIMUM: Calculate the Maximum of Column values.
The Aggregate transformation in SSIS can be configured in Basic or Advanced mode. In Basic mode, the Aggregate transformation has one output. In Advanced mode, it can have more than one output, each containing the result of a different aggregation.
Let us see how to configure the Aggregate transformation in SSIS to produce a single output with an example.
TIP: Please refer to the Transformation in Advanced Mode article to know How to Configure multiple outputs in Aggregate Transformation. For more Transformations >> Click Here.
IsBig Property
The Aggregate transformation in SSIS includes the IsBig property, which is used on the output columns to handle big or high-precision numbers. If any of the column values may exceed 4 billion, then IsBig should be set to 1. By setting the IsBig property to 1, Aggregation Transformation Will:
- Use the DT_R8 data type instead of the DT_R4 data type.
- Use the DT_UI8 data type to store the Count results.
- You can use the DT_UI4 data type to store the Distinct count results.
Aggregate Transformation in SSIS Basic Mode Example
For instance, If we want to find the sum of the sales amount for each Color, then we can use this SSIS Aggregate Transformation. In this example, we will perform all the Aggregate Transformation operations on DimGeography and FactResellerSales tables present in AdventureworkDW2014.
STEP 1: Open BIDS and Drag and drop the data flow task from the toolbox to control flow and name it Aggregate Transformation.
Double-click on it will open the data flow tab.
STEP 2: Drag and drop OLE DB Source, Aggregate Transformation from an SSIS toolbox to data flow region
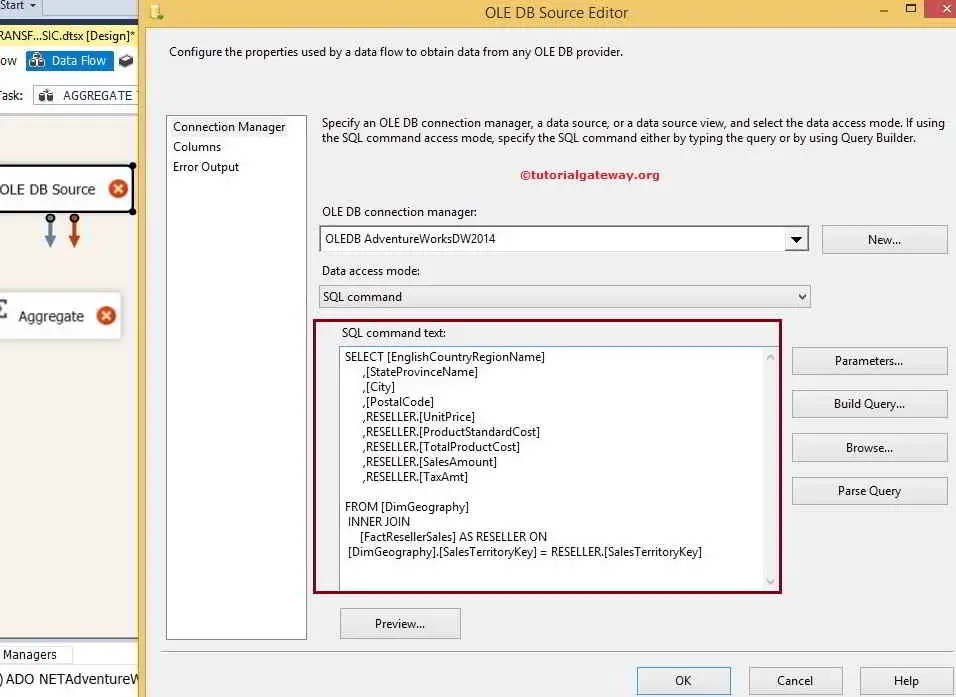
STEP 3: Double click on the OLE DB source in the data flow region. It will open the connection manager settings and provide space to write our statement. Here, we are using DimGeography and [FactResellerSales] present in the AdventureworkDW2014
The command we are using to retrieve data for SSIS aggregate transformation basic mode is:
USE [AdventureWorksDW2014]
GO
SELECT [EnglishCountryRegionName]
,[StateProvinceName]
,[City]
,[PostalCode]
,RESELLER.[UnitPrice]
,RESELLER.[ProductStandardCost]
,RESELLER.[TotalProductCost]
,RESELLER.[SalesAmount]
,RESELLER.[TaxAmt]
FROM [DimGeography]
INNER JOIN
[FactResellerSales] AS RESELLER ON
[DimGeography].[SalesTerritoryKey] = RESELLER.[SalesTerritoryKey]
STEP 4: Click on the columns tab to verify the columns. In this tab, we can uncheck the unwanted columns also.
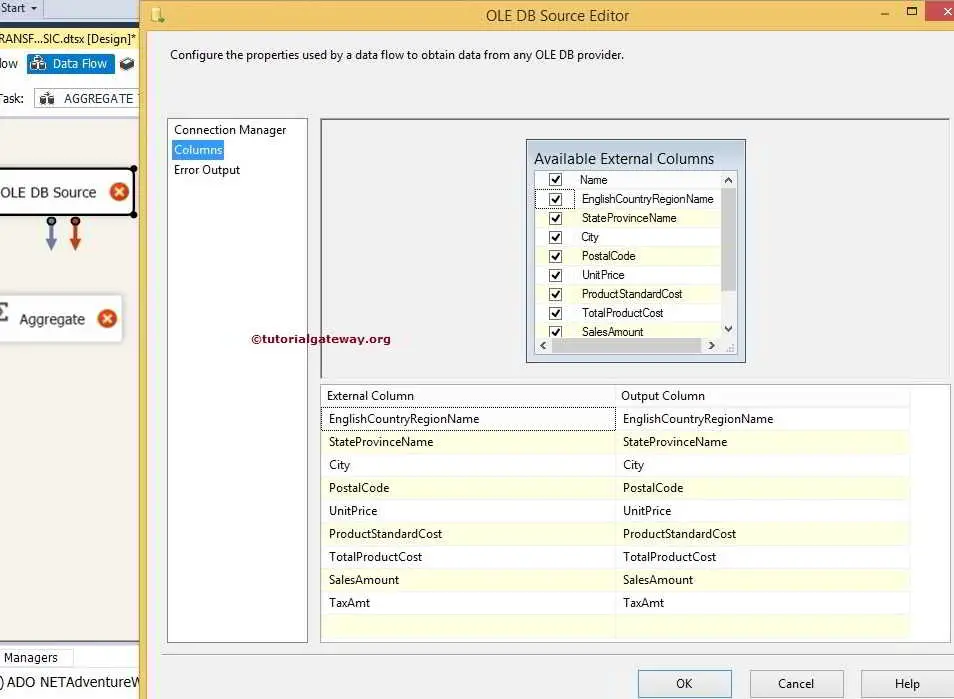
Drag and drop the blue arrow from OLE DB Source to Aggregate Transformation to connect the data.
SSIS Aggregate Transformation Editor
STEP 5: Double-click the SSIS Aggregate Transformation to open the editor. Next, in the lower pane, we select the required columns to perform Aggregate Transformation operations by checking them in Available Input Columns.
Once you check the required columns, those column names will appear in the Input Column located in the lower pane.
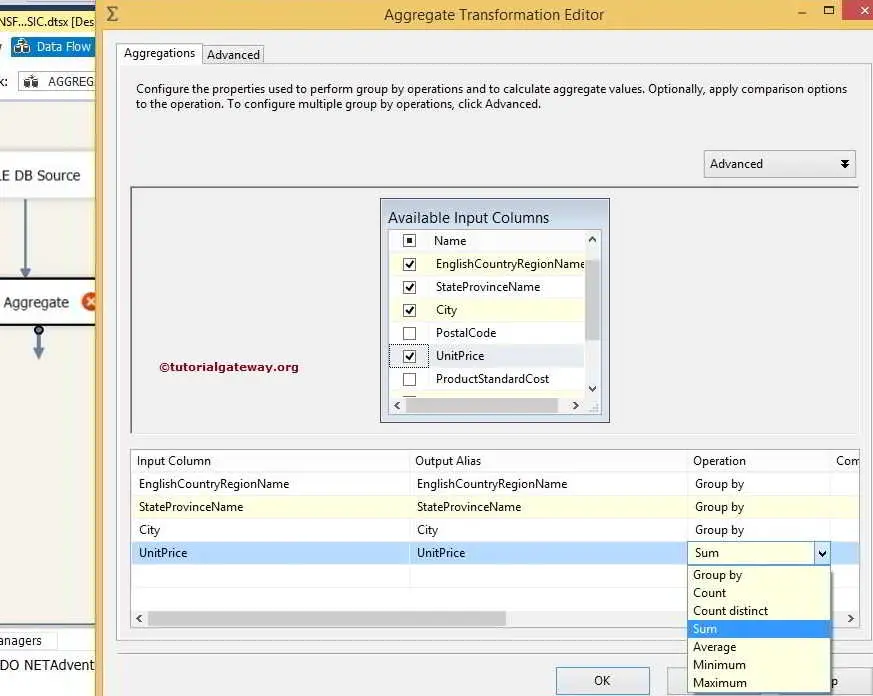
- Input Columns: Column we received from the OLE DB source.
- Output Alias: This is the same as the Alias column. Here, we can change the column name as per the project requirements.
- Operations: We already discussed this above.
For this SSIS Aggregate Transformation example, we will use most of the Aggregate functions below.
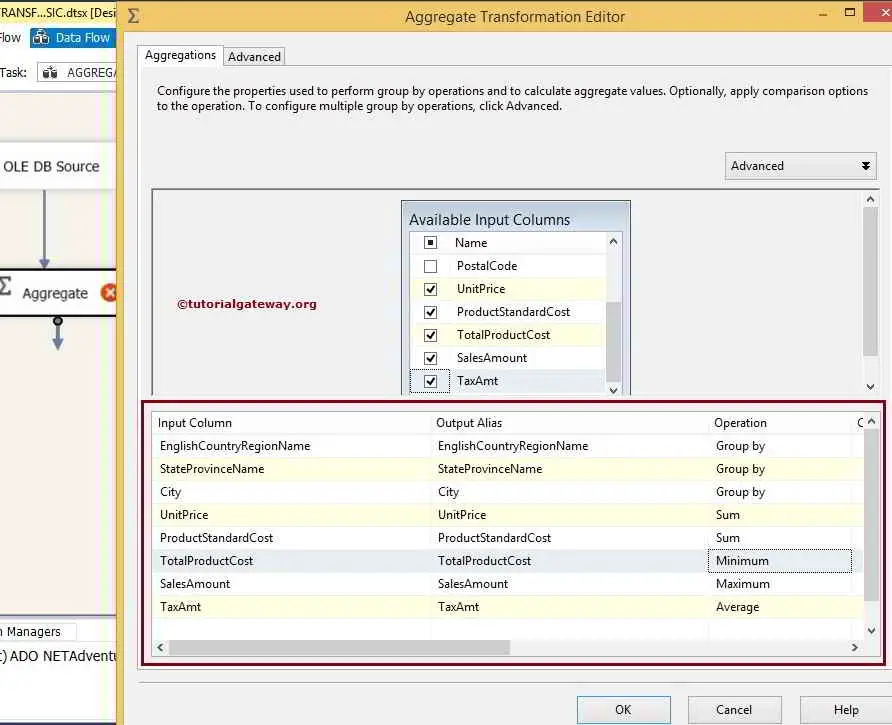
From the above SSIS aggregate transformation screenshot, you can observe that we measure the Sum of Unit Price, Product Standard Cost, Minimum Total Product Cost, Maximum Sales Amount, and Average Tax Amount. And Group by English Country Region, Then by State Province Name, and Then by City.
NOTE: If your input column is a string type, you will not see Sum, Average, and other aggregate functions but only Group by. Always make sure to convert the column’s data type to the proper data type before providing input to Aggregate Transformation.
Click ok.
STEP 6: Drag and drop the OLE DB Destination into the data flow region and drag the blue arrow from Aggregate Transformation to OLE DB Destination
STEP 7: Now, we have to provide the Server, database, and table details of the destination. So, double-click on the OLE DB Destination and provide the required information.
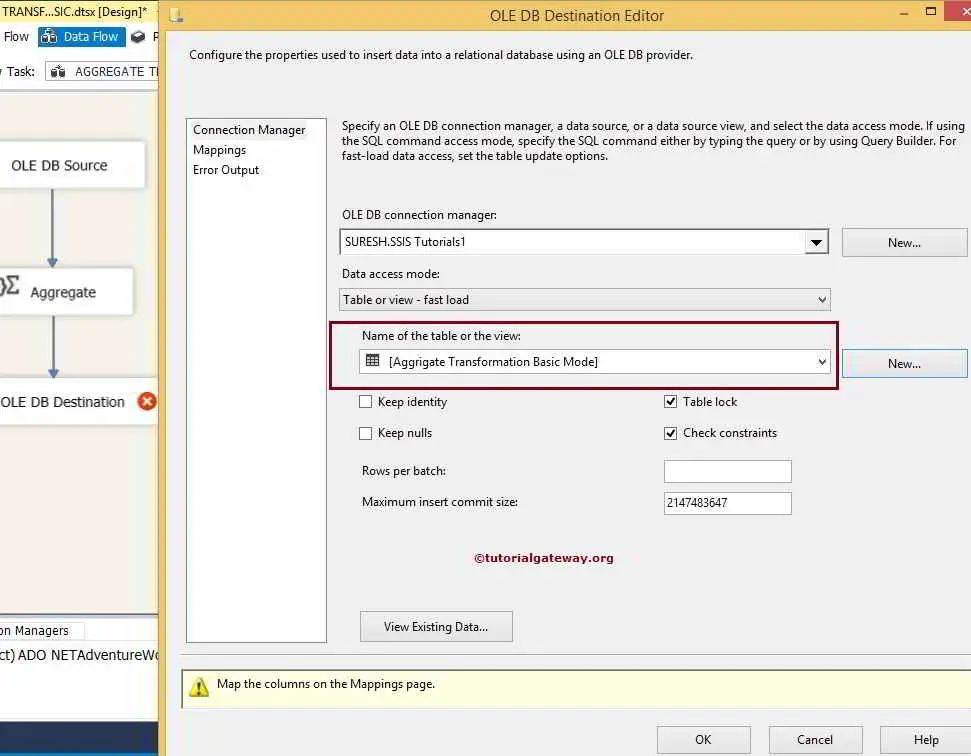
Here, we pointed to our destination database. For the time being, I used the New button to create a destination table for me and named it Aggregate Transformation Basic Mode. But in reality, you should not design your table like this.
STEP 8: Click on the SSIS Aggregate Transformation Mappings tab to check whether the source columns are exactly mapped to the destination columns.
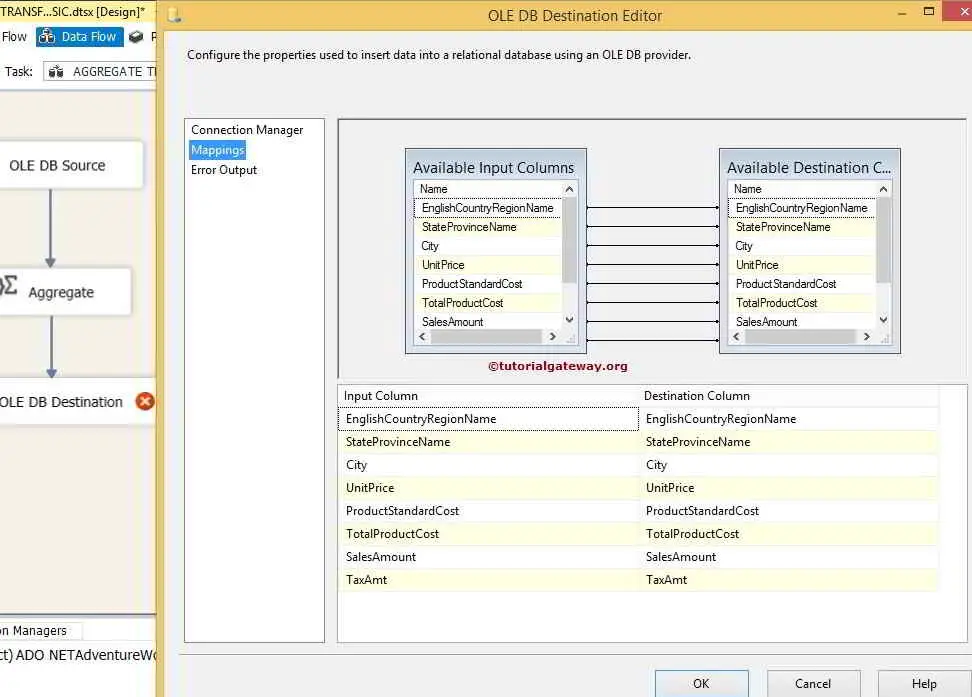
Click ok to finish our Aggregate Transformation in SSIS package design. Let us run the package.
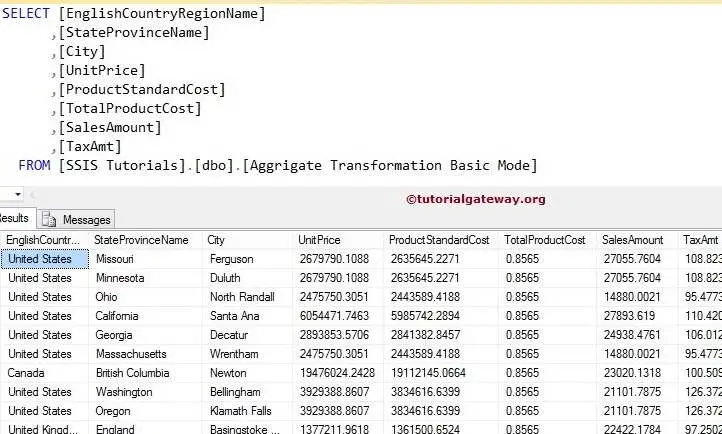
Let’s open the SQL Server Management Studio and write the below statement to check the results.
SELECT [EnglishCountryRegionName]
,[StateProvinceName]
,[City]
,[UnitPrice]
,[ProductStandardCost]
,[TotalProductCost]
,[SalesAmount]
,[TaxAmt]
FROM [Aggrigate Transformation Basic Mode]
SSIS Aggregate Transformation Advanced Option
The Aggregate Transformation supports multiple outputs. It means Aggregate Transformation can read the data from the source for once. And then, we can create various outputs, and each output may have a different set of aggregations. Here, we show you how to configure multiple outputs in aggregate transformation in SSIS advanced mode with an example.
The Aggregate Transformation in SSIS includes a set of properties in the Advanced tab in the Editor. By setting these properties, we can increase the performance of the Aggregate Transformation.
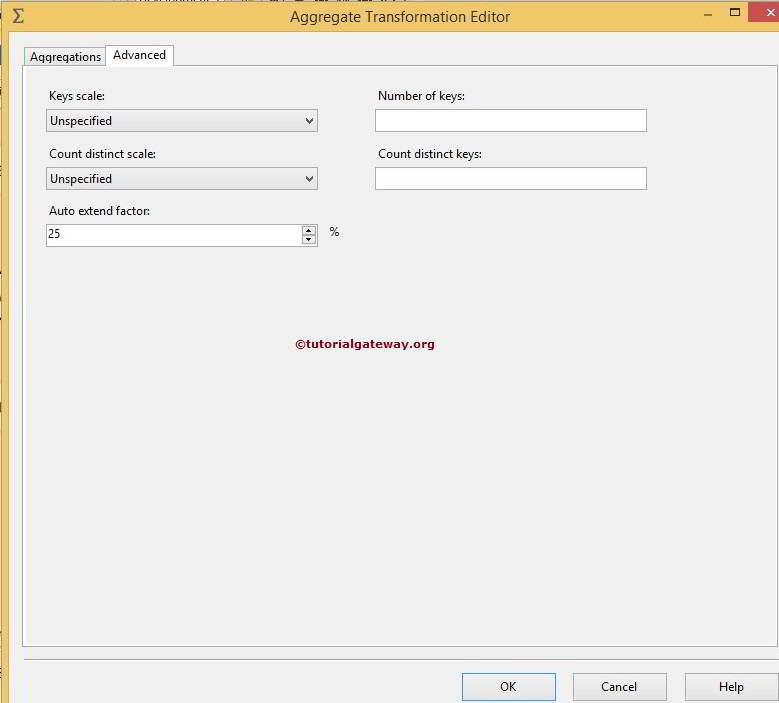
Key Scale: In this option, specify the approximate number of keys an aggregation can write. By default, the value of this option is Unspecified.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| Unspecified | The Key Scale property is not used. |
| Low | Aggregation can write nearly 500,000 keys. |
| Medium | Aggregation can write nearly 5,000,000 keys. |
| High | Aggregation may write more than 25,000,000 keys. |
- Keys: Specifying the exact number of keys an aggregation can write. Keys refers to the number of groups expected to result from a Group by the operation. If both the Key Scale and Keys properties are set, the Keys value takes precedence.
- Count Distinct Scale: We can specify the approximate number of distinct values an aggregation can write.
- Count Distinct Keys: In this, We can specify the exact number of distinct values that the aggregation can write. If both CountDistinctScale and CountDistinctKeys are specified, CountDistinctKeys takes priority.
- Auto extend factor: In this SSIS Aggregate Transformation option, We can specify the percentage of memory it can extend in the aggregation process. We can choose the values from 1 to 100. By default, the value of this option is 25%.
Aggregate Transformation in SSIS Advanced Mode example
STEP 1: Open BIDS and Drag and drop the data flow task from the toolbox to control flow and rename it Aggregate Transformation.

STEP 2: Drag and drop OLE DB Source, Aggregate Transformation from the toolbox to the SSIS data flow region

Double click on the OLE DB source in the data flow region will open the connection manager settings and provide space to write our SQL statement. Here, we are using DimGeography and [FactResellerSales] present in the AdventureworkDW2014

The SQL command we used in the above screenshot to retrieve data is:
SELECT [EnglishCountryRegionName]
,[StateProvinceName]
,[City]
,[PostalCode]
,RESELLER.[UnitPrice]
,RESELLER.[ProductStandardCost]
,RESELLER.[TotalProductCost]
,RESELLER.[SalesAmount]
,RESELLER.[TaxAmt]
FROM [DimGeography]
INNER JOIN
[FactResellerSales] AS RESELLER ON
[DimGeography].[SalesTerritoryKey] = RESELLER.[SalesTerritoryKey]
STEP 4: Click on the columns tab to verify the columns. In this tab, we can uncheck the unwanted columns also.

STEP 5: Double-click on the Aggregate Transformation to open the editor. The upper pane has a button to toggle between the SSIS Aggregate Transformation Basic and Advanced Mode. In this example, we want to configure multiple outputs, so select the Advance mode.
Once you click on the Advanced mode button, a new pane will be opened to configure multiple outputs.
- Aggregate Name: Specify the aggregate name.
- Group By Columns: Here, it shows the list of columns we used for grouping.
Next, in the lower pane, we select the required columns to perform Aggregate Transformation operations by checking them in Available Input Columns.
Once you check the required columns, those column names will appear in the Input Column located in the lower pane, as shown in the figure below.
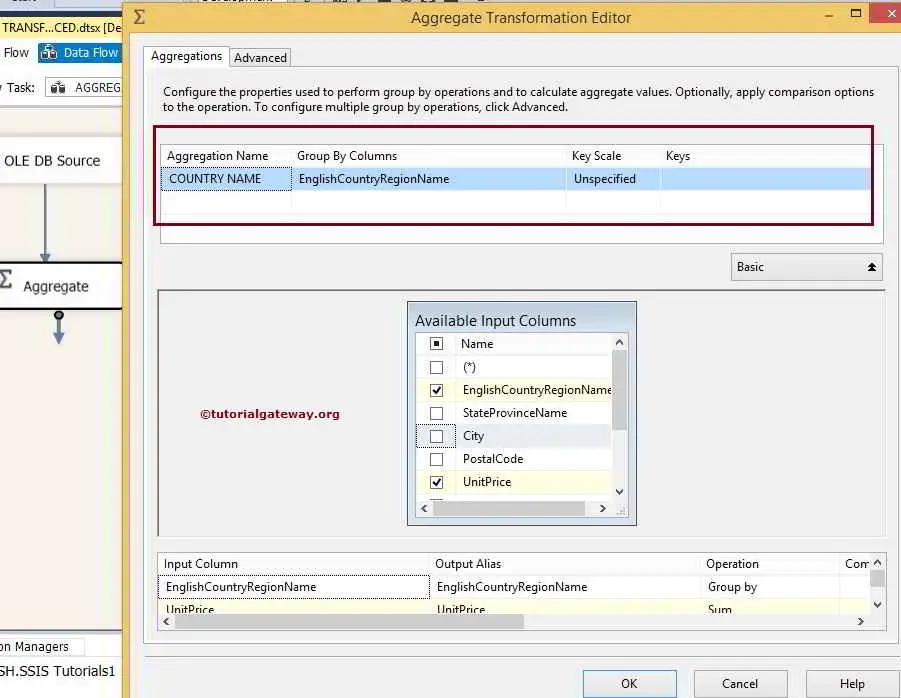
From the above screenshot, you can observe that we were assigning the Aggregation name as COUNTRY NAME and Group by as EnglishCountryRegionName.
Let us add one more aggregation and assign the name STATE NAME and Group by EnglishCountryRegionName and StateProvinceName.
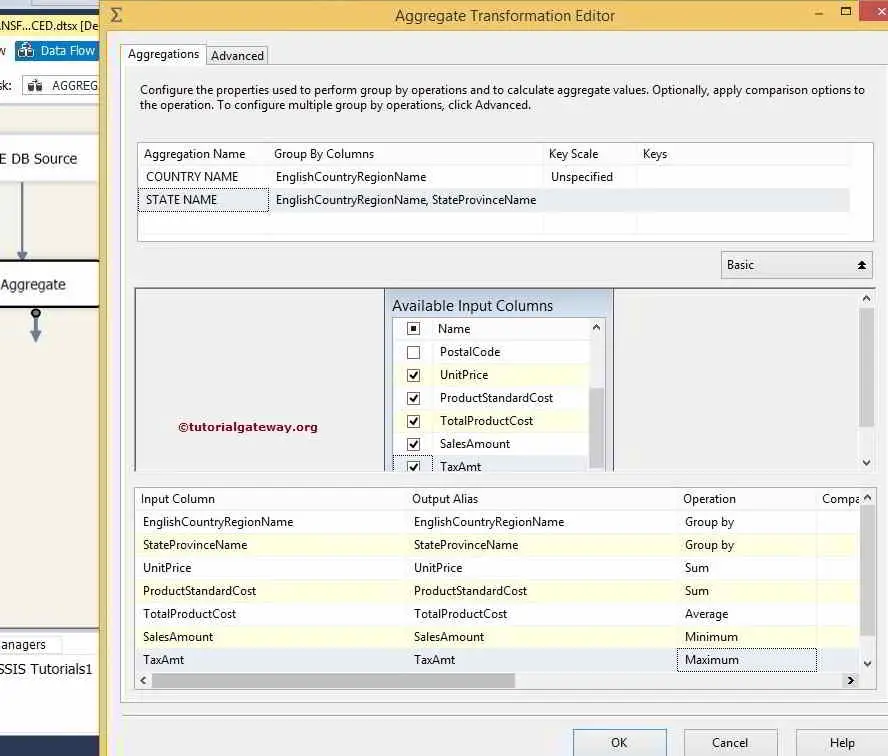
From the above screenshot, we are calculating the Sum of the Unit Price, the Sum of the Product Standard Cost, the Average Total Product Cost, the Minimum Sales Amount, and the Maximum Tax Amount. And Group by English Country Region, then by State Province Name.
Let us add one more aggregation and assign the name CITY and Group as EnglishCountryRegionName, StateProvinceName, and City.
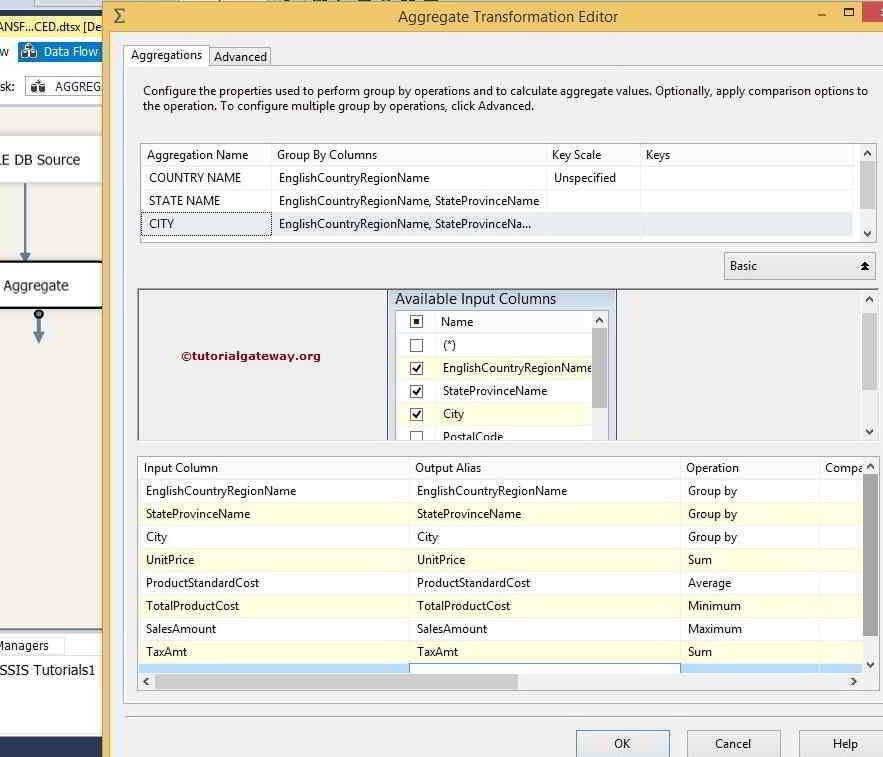
From the above, we are calculating the Sum of Unit Price, Average of Product Standard Cost, Minimum of Total Product Cost, Maximum Sales Amount, and Sum of Tax Amount. And Group by English Country Region, Then by State Province Name, and Then by City.
STEP 6: Drag and drop 3 OLE DB destinations from the toolbox to the data flow region to configure the three outputs we get from Aggregate transformation.
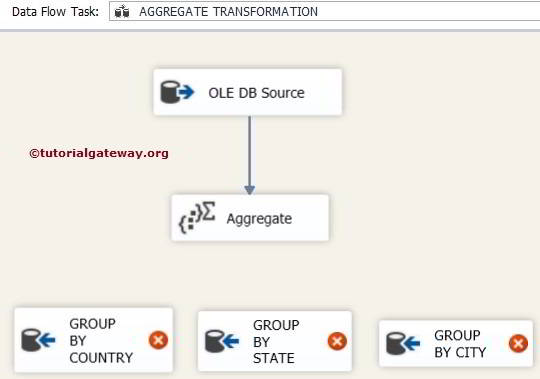
We renamed the OLEDB destinations from the above to Group By Country, Group By State, and Group By City.
STEP 7: When you drag the Aggregate transformation output arrow to the OLE DB destination, an Input Output Selection window will open to select one of the outputs, and here we are selecting COUNTRY NAME.
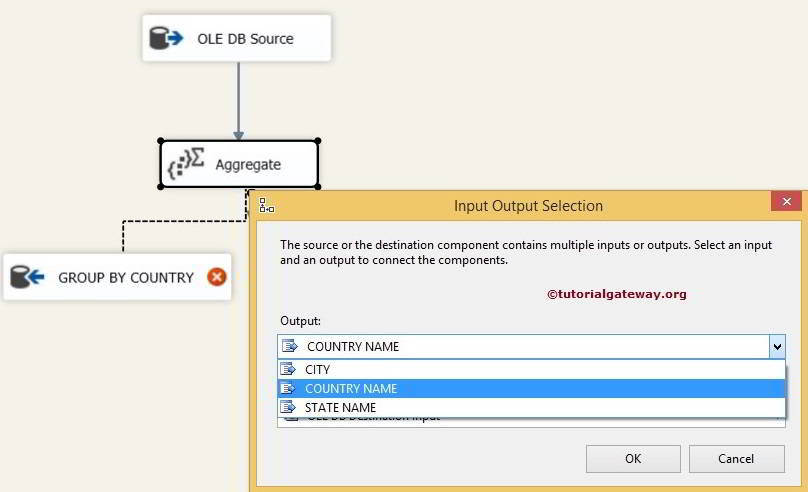
Let us assign the State name output to the second OLE DB destination.
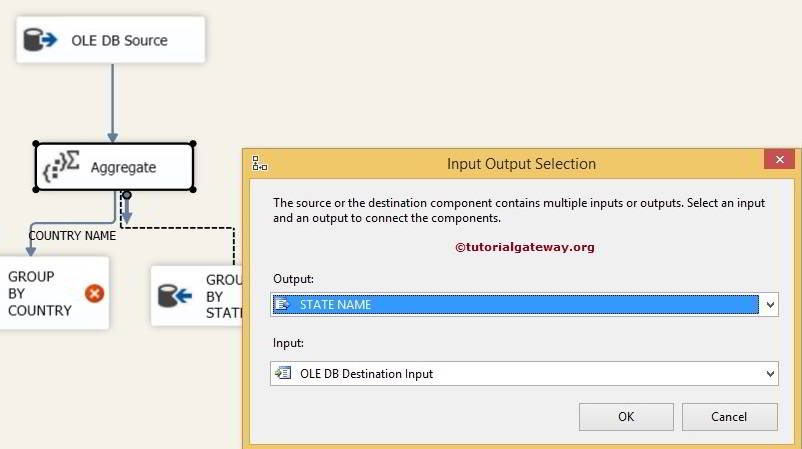
We have one more output (CITY) left, so when we drag the green arrow from SSIS aggregate transformation to the 3rd OLE DB Destination, it automatically assigns to City.
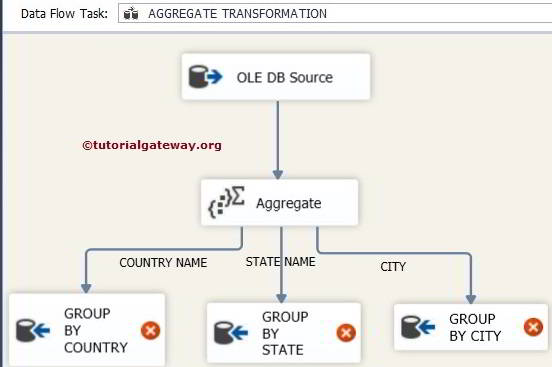
STEP 8: Now, we have to configure the OLE DB destination for the country name. So, double-click on the OLE DB Destination and provide the required information.
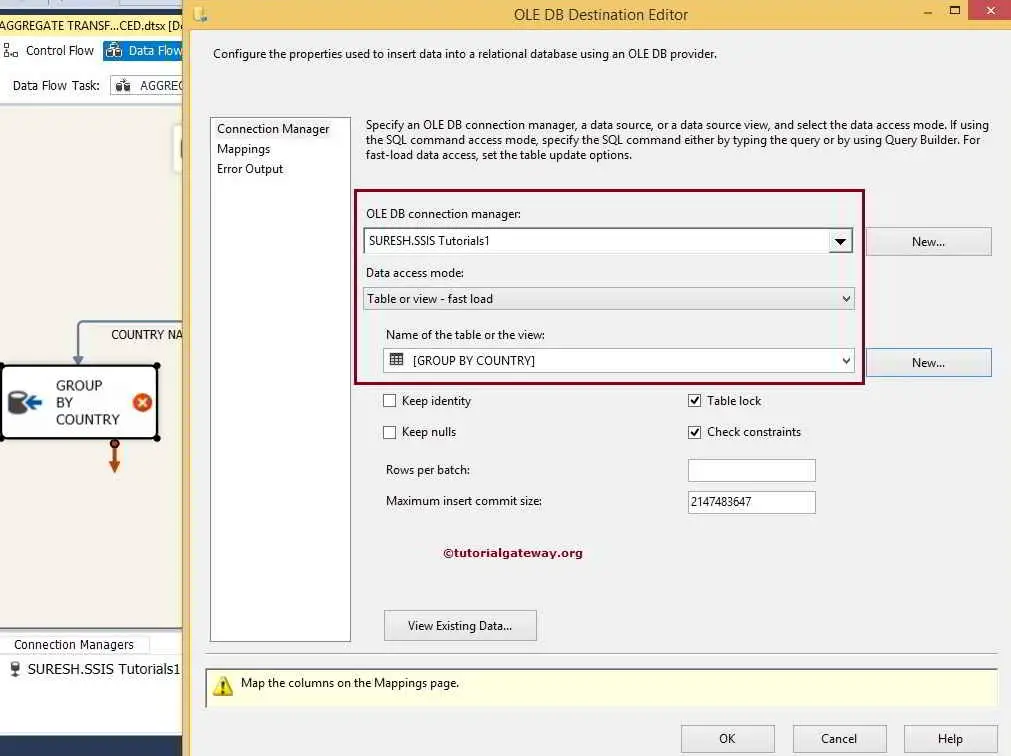
Here, we are selecting the following database as the destination database and the [Group By Country] table as the destination table.
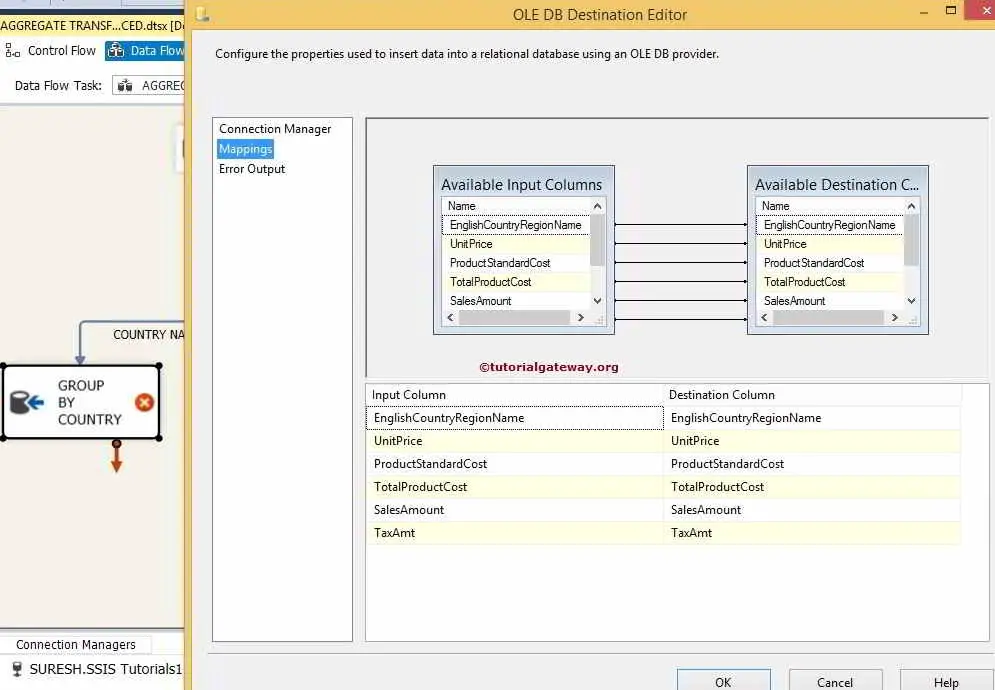
STEP 9: Click on the Mappings tab to check whether the aggregate source columns are exactly mapped to the destination columns.
STEP 10: Now, we have to configure the OLE DB destination for the group by state aggregation output. So, double-click on the OLE DB Destination and provide the required information.
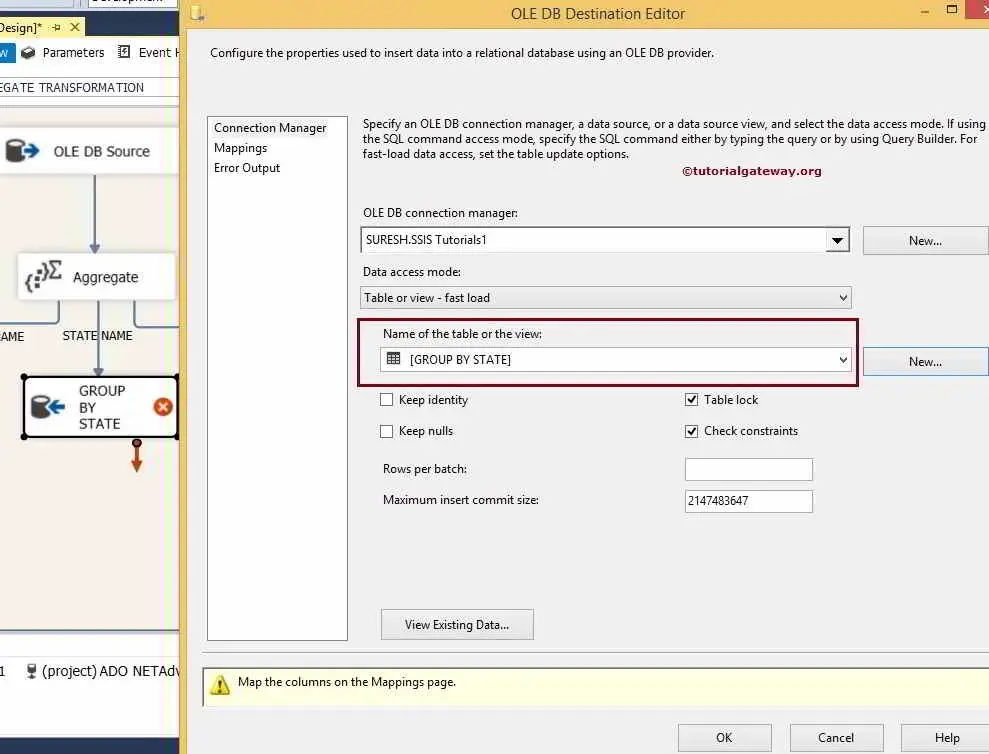
Here, we are selecting the following database as the destination database and [Group By State] table as the destination table
Repeat Step 9
STEP 12: We have to configure the OLE DB destination for the city output rows. So, double-click on the OLE DB Destination and provide the required information.
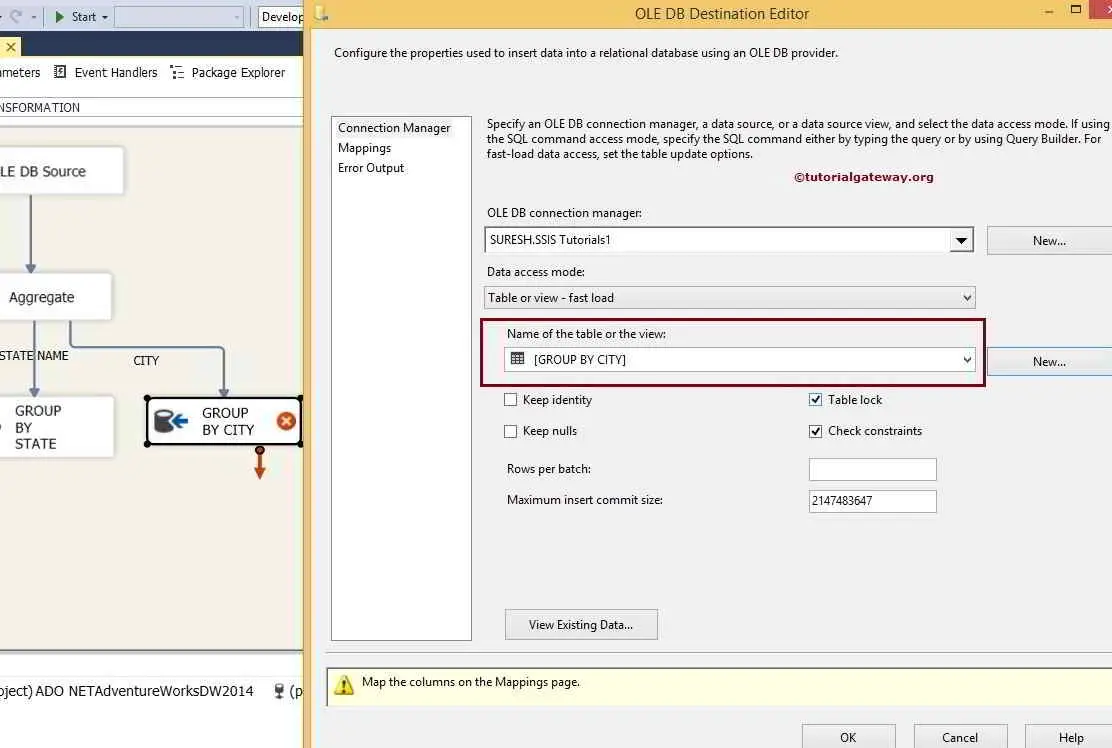
Here, we select the [Group By City] table as the destination table.
Repeat Step 9.
Click ok to finish our package design. Let us run the package
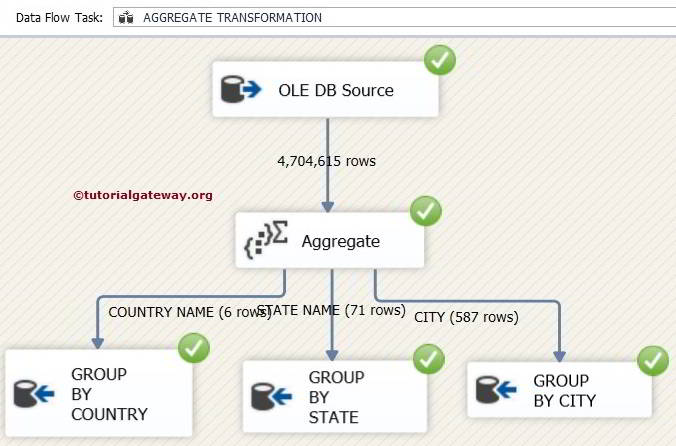
Let us see the result of the Group By English Country Region Name. For this, open the Management studio and write the below query
SELECT [EnglishCountryRegionName]
,[UnitPrice]
,[ProductStandardCost]
,[TotalProductCost]
,[SalesAmount]
,[TaxAmt]
FROM [GROUP BY COUNTRY]
OUTPUT
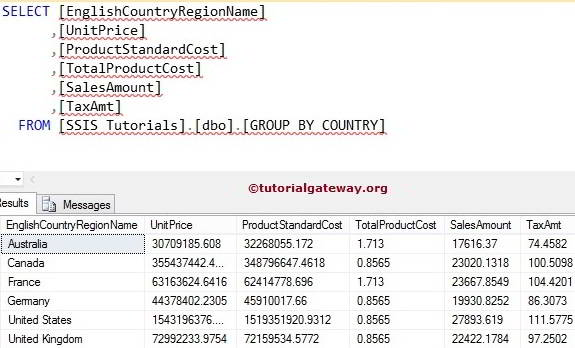
Now, see the result of the Group By English Country Region Name and state Province Name.
SELECT [EnglishCountryRegionName]
,[StateProvinceName]
,[UnitPrice]
,[ProductStandardCost]
,[TotalProductCost]
,[SalesAmount]
,[TaxAmt]
FROM [GROUP BY STATE]
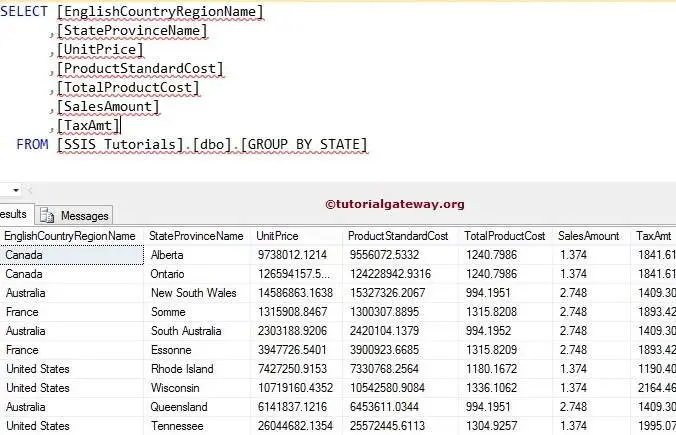
Let us see the result of the Group By English Country Region Name, State Province Name, and City.
SELECT [EnglishCountryRegionName]
,[StateProvinceName]
,[City]
,[UnitPrice]
,[ProductStandardCost]
,[TotalProductCost]
,[SalesAmount]
,[TaxAmt]
FROM [GROUP BY CITY]

Comments are closed.