The SQL Server MIN is an Aggregate Function used to find the minimum value from the total records (or rows) selected by the SELECT Statement. The Function will ignore Null values. The syntax of the SQL MIN Function is
SELECT MIN([Column_Name]) FROM [Source]
For this Function, use the below data
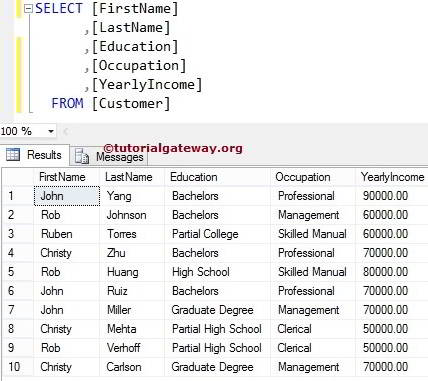
SQL Server MIN Function Example
The Min function returns the Minimum value from the total records present in the specified column. This query finds the Minimum yearly income present in the [Yearly Income] column from the Customers table.
SELECT MIN([YearlyIncome]) AS [Minimum Income] FROM [Customer]
Minimum Income
--------------
50000.00MIN Group By Clause
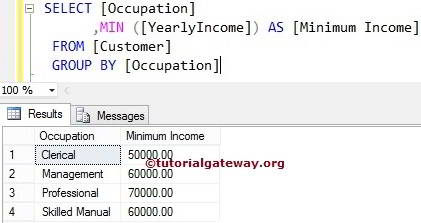
Generally, we usually check the minimum product price (Lowest pricing product) belongs to a particular category or color, etc. In these circumstances, we use the GROUP BY Clause to group the products by color or category. Next, use this to find the Lowest pricing product present in each group. Let us see the SQL Server MIN Function Group By Example.
SELECT [Occupation]
,MIN([YearlyIncome]) AS [Minimum Income]
FROM [Customer]
GROUP BY [Occupation]
Above Server Query will find the Customers associated with the particular Department and SELECT the minimum income in each department
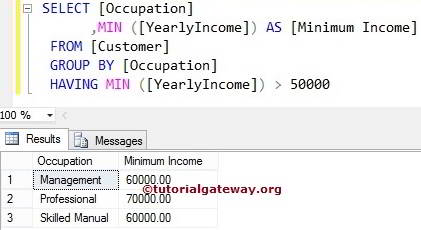
SQL MIN Function in Group By Having Clause
When we are grouping the data in some cases, we usually check for the conditions against the aggregated data. In these conditions, we use the HAVING Clause along with Group By Statement. For instance, the following query groups the Customers by their Occupation. Then finds the Minimum yearly Income present in each group.
The last line of code verifies whether the Minimum Yearly income of each Group is greater than 50000 or not. If this is true, the corresponding records will be displayed.
SELECT [Occupation]
,MIN([YearlyIncome]) AS [Minimum Income]
FROM [Customer]
GROUP BY [Occupation]
HAVING MIN ([YearlyIncome]) > 50000 -- Last Line
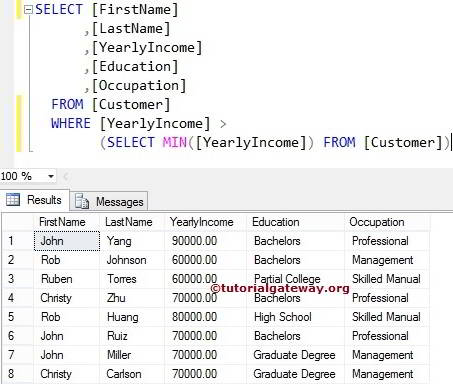
SQL Server Min Function in Subquery
While retrieving the data, in some instances, we check for the conditions against the aggregated data. In these situations, we have to use Subquery in the Where Clause. This minimum function query returns the Customers whose [Yearly Income] is greater than the Minimum yearly income.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
FROM [Customer]
WHERE [YearlyIncome] >
(SELECT MIN([YearlyIncome]) FROM [Customer])
From the first example, see that the Minimum Yearly Income is 50000. So above Aggregate Function query display all the customers whose yearly income is greater than 50000