SQL Server Pivot is one of the most useful operators to convert the Row values into Column names or, say, rotating tables. While rotating the table or the Pivot Table, the remaining column values must be involved in Grouping or Aggregation.
We use the below query to convert rows into columns using the SQL Pivot Table.
USE AdventureWorks2014
GO
SELECT PROD.Name,
YEAR(OrdHead.OrderDate) AS [Order Year],
SUM(Details.OrderQty) AS [Order Quantity]
FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail AS Details
INNER JOIN
Production.Product AS PROD ON
Details.ProductID = PROD.ProductID
INNER JOIN
Sales.SalesOrderHeader AS OrdHead ON
Details.SalesOrderID = OrdHead.SalesOrderID
GROUP BY
PROD.Name,
YEAR(OrdHead.OrderDate)
ORDER BY [Order Year]
Although it is easy to understand the above query, we are copying the data to a new table to avoid further complications. It will also allow you to concentrate more on the SQL Server Pivot clause.
To do this, we are using the SELECT INTO Statement. The below screenshot shows our new table data. We use this SQL PIVOT function to convert row data into Columns.
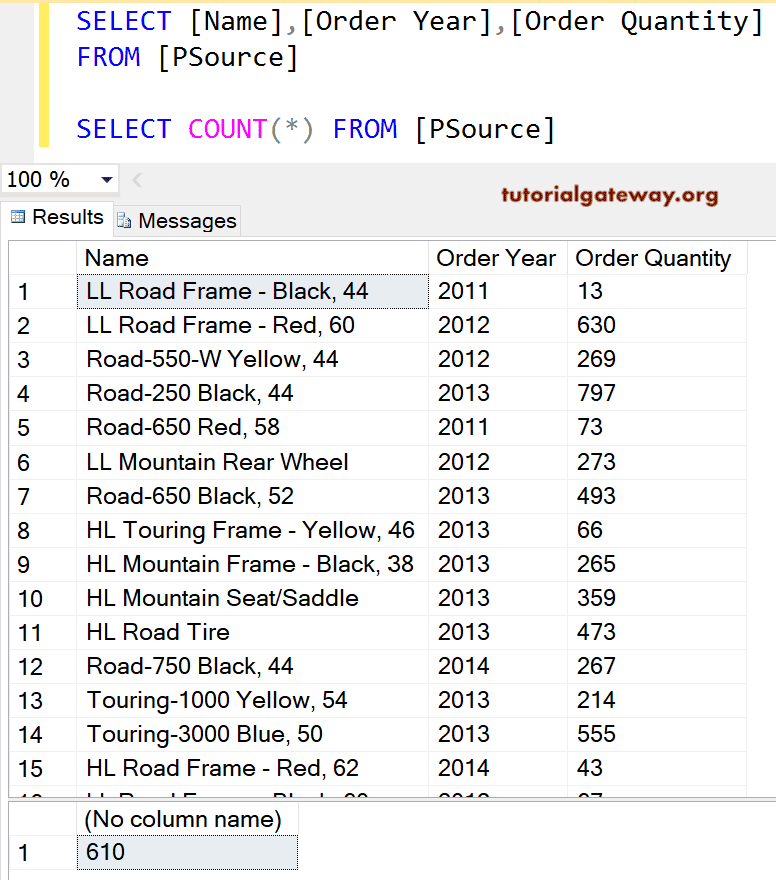
SQL Server PIVOT Operator Example
This example will convert the calendar year information in rows to separate columns. Here, the Name column will remain the same, and the Order quantity will separate based on the Year.
SELECT Name,[2011], [2012], [2013], [2014]
FROM (
SELECT [Name]
,[Order Year]
,[Order Quantity]
FROM [PSource]
) AS SOURCE
PIVOT
(
SUM([Order Quantity]) FOR [Order Year]
IN ([2011], [2012], [2013], [2014])
) AS [Result]
ORDER BY Name
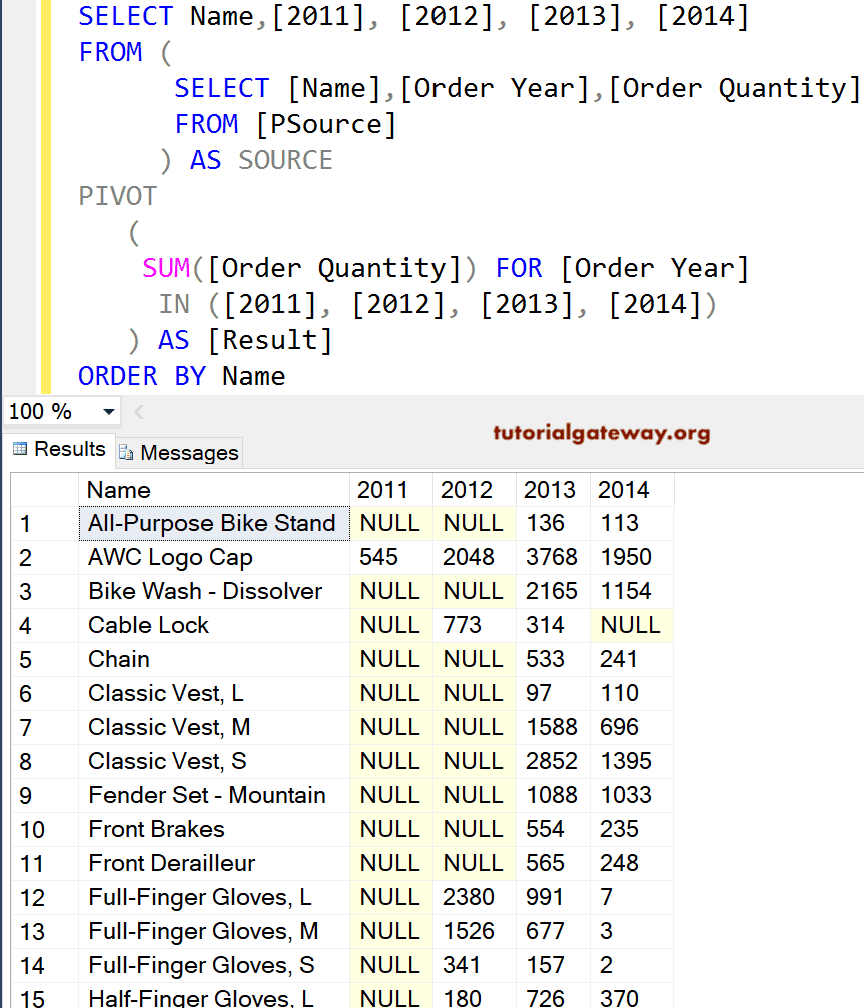
The Select query unto SOURCE will execute first, extracting name, OrderYear, and OrderQuantity information from the table. Please refer to the Select Statement and SELECT INTO Statement in the SQL Server.
Next, the remaining query after the SOURCE will convert the rows into columns using the aggregated function sum and SQL Pivot. Within this query, the below statement will display the output.
SELECT Name,[2011], [2012], [2013], [2014]
If you want to apply the same functionalities to your original data, You have to use the following query.
USE AdventureWorks2014
GO
SELECT Name,[2011], [2012], [2013], [2014]
FROM
(
SELECT PROD.Name,
YEAR(OrdHead.OrderDate) as OrderYear,
SUM(Details.OrderQty) AS OrderQuantity
FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail AS Details
INNER JOIN Production.Product AS PROD
ON Details.ProductID = PROD.ProductID
INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeader AS OrdHead
ON Details.SalesOrderID = OrdHead.SalesOrderID
GROUP BY PROD.Name,YEAR(OrdHead.OrderDate)
) AS SOURCE
PIVOT( SUM(OrderQuantity) FOR OrderYear
IN ([2011], [2012], [2013], [2014])
) AS Result
ORDER BY Name
SQL PIVOT Approach 2
Suppose you are getting all your source information from one table. And if the data doesn’t include any Joins and Grouping, use the following query on the source table. It is a short version of Approach 1.
SELECT Name,[2011], [2012], [2013], [2014]
FROM [PSource]
PIVOT
(
SUM([Order Quantity]) FOR [Order Year]
IN ([2011], [2012], [2013], [2014])
) AS [Result]
ORDER BY Name
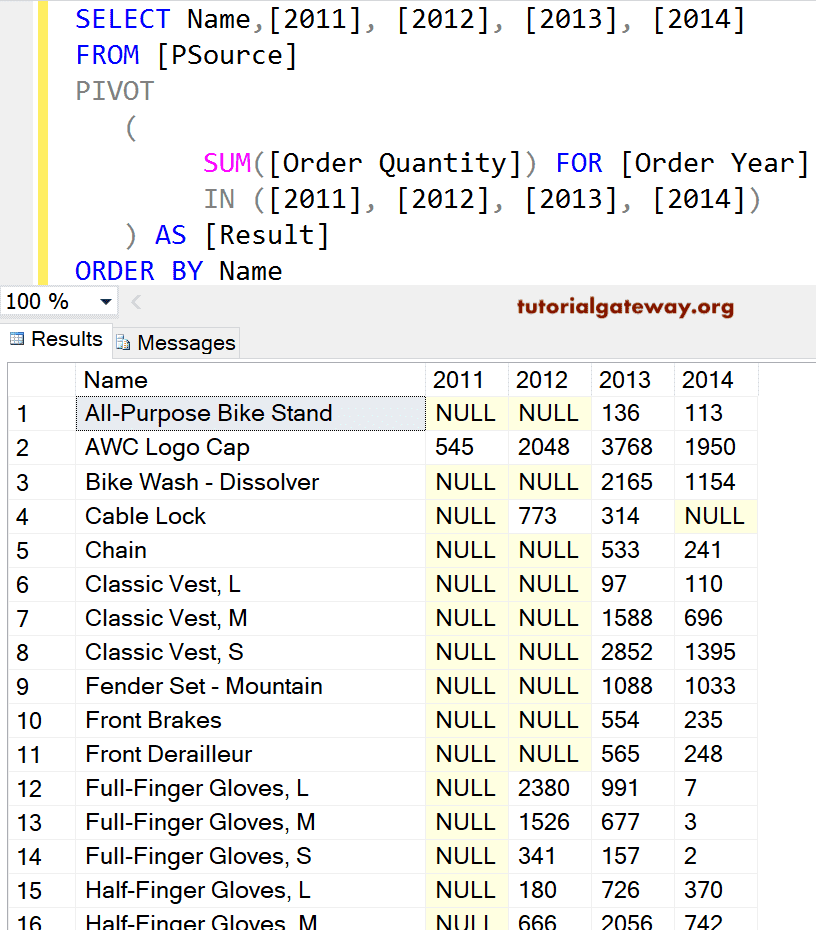
SQL Server PIVOT Alternative
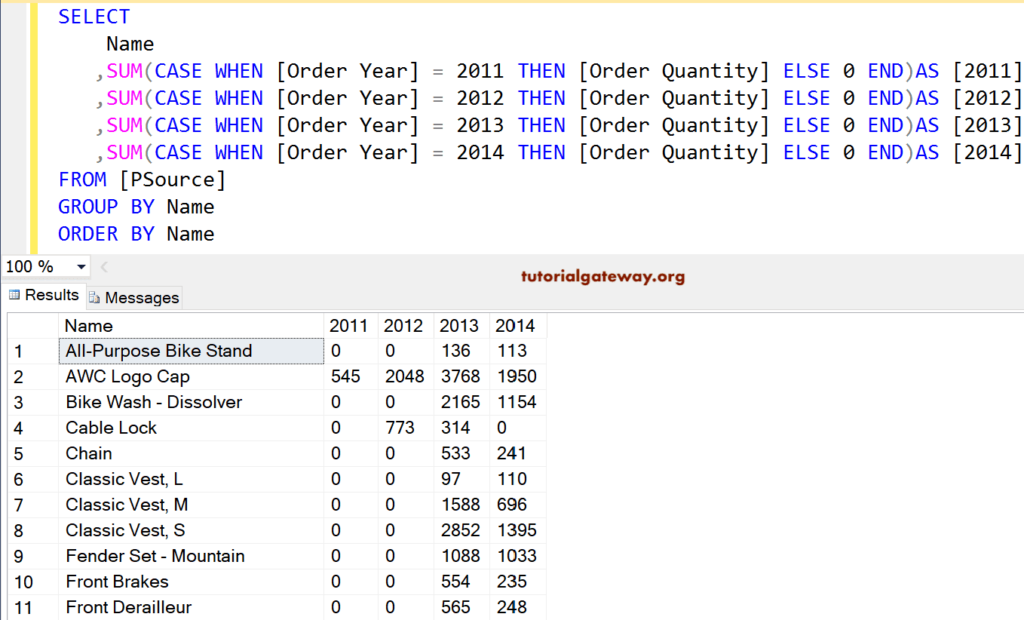
This alternative query example is purely for interview purposes. Usually, To test your coding skills in the interview, they might ask you a question: How to convert rows to columns without using it?
SELECT
Name
,SUM(CASE WHEN [Order Year] = 2011 THEN [Order Quantity] ELSE 0 END)AS [2011]
,SUM(CASE WHEN [Order Year] = 2012 THEN [Order Quantity] ELSE 0 END)AS [2012]
,SUM(CASE WHEN [Order Year] = 2013 THEN [Order Quantity] ELSE 0 END)AS [2013]
,SUM(CASE WHEN [Order Year] = 2014 THEN [Order Quantity] ELSE 0 END)AS [2014]
FROM [PSource]
GROUP BY Name
ORDER BY Name
If you want to apply the same functionality to your original data, You have to use the following query.
USE AdventureWorks2014
GO
SELECT
PROD.Name
,SUM(CASE WHEN YEAR(OrdHead.OrderDate) = 2011 THEN (Details.OrderQty) ELSE 0 END)AS [2011]
,SUM(CASE WHEN YEAR(OrdHead.OrderDate) = 2012 THEN (Details.OrderQty) ELSE 0 END)AS [2012]
,SUM(CASE WHEN YEAR(OrdHead.OrderDate) = 2013 THEN (Details.OrderQty) ELSE 0 END)AS [2013]
,SUM(CASE WHEN YEAR(OrdHead.OrderDate) = 2014 THEN (Details.OrderQty) ELSE 0 END)AS [2014]
FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail AS Details
INNER JOIN Production.Product AS PROD
ON Details.ProductID = PROD.ProductID
INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeader AS OrdHead
ON Details.SalesOrderID = OrdHead.SalesOrderID
GROUP BY PROD.Name
ORDER BY Name

Comments are closed.