The SQL Server left function returns the leftmost characters from a given expression. This function uses its second argument to decide how many left characters it should return, and the syntax of it in SQL Server is
SELECT LEFT (Character_Expression, Value) FROM [Source]
- Character_Expression: It will write the leftmost characters from this expression.
- Value: How many characters do you want to extract from the Character_Expression?
The index position in SQL Server LEFT Function will start from 1, Not 0. For this example, we use the below-shown data
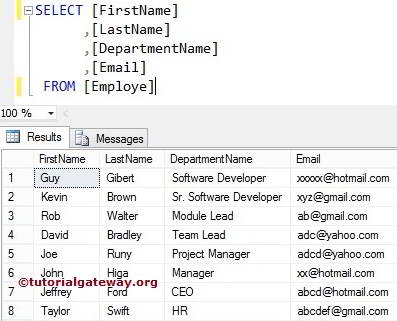
SQL Server LEFT Function Example
The LEFT function returns the specified number of leftmost characters from the given string. The following query returns leading most 3 and 20 characters.
In the first statement, we used LEFT Function to return five leftmost characters from the @Character_Expression variable.
In the next line, We assigned 20 to the second argument, which is greater than the string length. So, it will return all the letters from the @Character_Expression
DECLARE @Charcater_Expression varchar(50) SET @Charcater_Expression = 'Learn SQL Server' --Using Positive Integer 3 SELECT LEFT(@Charcater_Expression, 5) AS 'SQLLEFT' --Searching from specific position – 20 SELECT LEFT(@Charcater_Expression, 20) AS 'SQLLEFT'
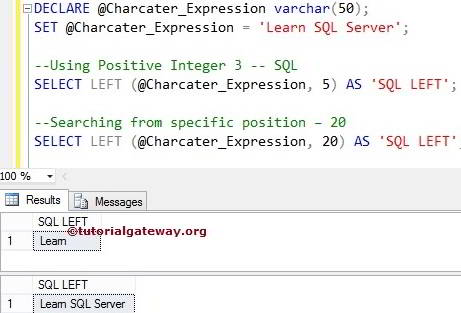
LEFT Function Example 2
The SQL Server Left function also allows you to select the leftmost characters from the column values. In this Server example, we will return the leading four words of all the records present inside the Department Name column.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[DepartmentName]
,LEFT([DepartmentName], 4) AS [SQLLEFT]
FROM [Employe]
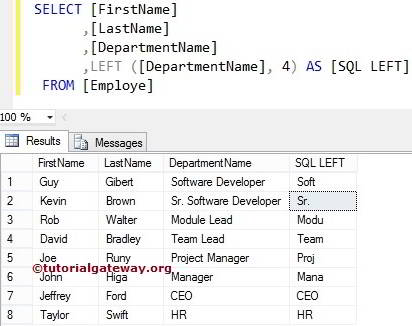
NOTE: If you observe the second record, there is an Empty space after the Sr.
Let us find the index position of a @ symbol present in the Email column using the CHARINDEX function. Next, this String method will extract the leading letters up to @ symbol.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[DepartmentName]
,[Email]
,LEFT(
[Email]
,CHARINDEX ('@', [Email]) - 1
) AS [SQLLEFT]
FROM [Employe]
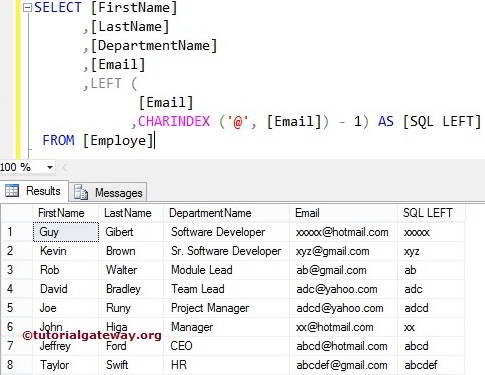
The below LEFT statement returns the index position of the @ symbol. It suggests the CHARINDEX method finds the index position of @ sign in every record.
CHARINDEX ('@', [Email])
We reduced the index position by 1, using the below statement. If you miss this, the output includes @ symbol as well.
CHARINDEX ('@', [Email]) - 1
