The SQL CHARINDEX function is a String method that finds the index position of a given expression from existing records. The index position will start from 1, Not 0
SQL CHARINDEX Function Syntax
The syntax of the CHARINDEX Function is
SELECT CHARINDEX(ExpressionToFind, ExpressionToSearch, Starting_Position) FROM [Source]
- ExpressionToFind: This SQL CHARINDEX function will search for this expression. If it finds the expression, it returns the index position. Otherwise, it will return 0.
- ExpressionToSearch: Expression on which you want to perform the search operation. It will search this expression within ExpressionToFind.
- Starting: It is an optional argument. If you specify the start location, it will start searching for this character position. Otherwise, it starts searching from the beginning and returns to its position.
It returns NULL if ExpressionToFind or expressionToSearch is NULL. For this SQL Server CHARINDEX Function example, we will use the below-shown data.
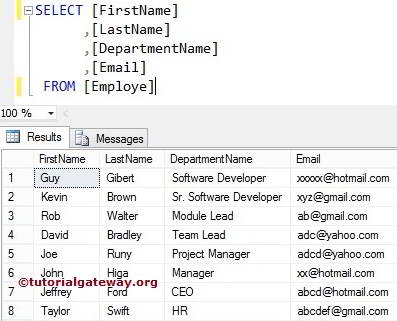
SQL Server CHARINDEX Function Example
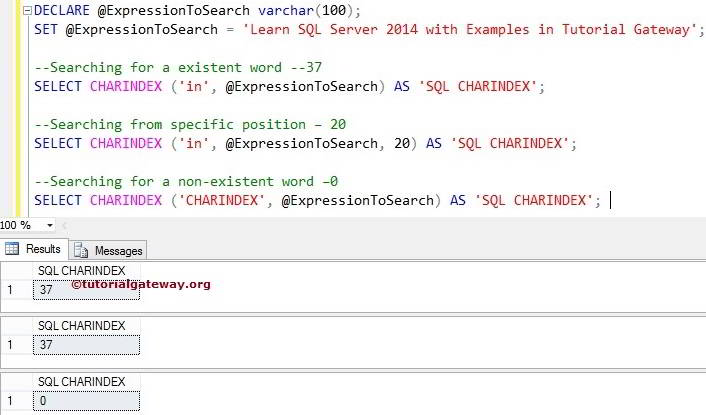
The following CHARINDEX function query finds the index position of existing and non-existing items from the start and specified positions. First, We are finding the position of ‘in’ from the variable @ExpressionToSearch.
In the next line, We used the starting argument of the SQL Server CHARINDEX function. It means the String method will start the search for ‘in’ from 20, reducing the load on the server. The query execution will become faster.
Next, we searched for the following word, which does not exist inside the variable. That’s why it is returning 0.
DECLARE @ExpressionToSearch varchar(100)
SET @ExpressionToSearch = 'Learn SQL Server 2014 with Examples in Tutorial Gateway'
--Searching for a existent word --37
SELECT CHARINDEX('in', @ExpressionToSearch) AS 'SQLCHARINDEX'
--Searching from specific position – 20
SELECT CHARINDEX('in', @ExpressionToSearch, 20) AS 'SQLCHARINDEX'
--Searching for a non-existent word –0
SELECT CHARINDEX('CHARINDEX', @ExpressionToSearch) AS 'SQLCHARINDEX'
CHARINDEX Example 2
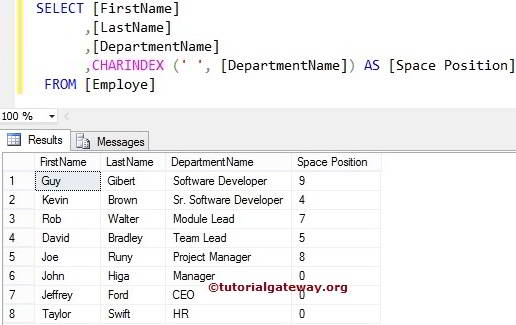
The SQL CHARINDEX function also allows you to search for substrings in a string within the column values. In this SQL Server example, we will find the index position of an Empty Space inside the Department Name column.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[DepartmentName]
,CHARINDEX(' ', [DepartmentName]) AS [Space Position]
FROM [Employe]
If you observe the second record, Although it has Empty space at multiple locations, it displayed the value 4. It is because SQL Server CHARINDEX will display the location of a first occurrence and does not care about the other occurrences.
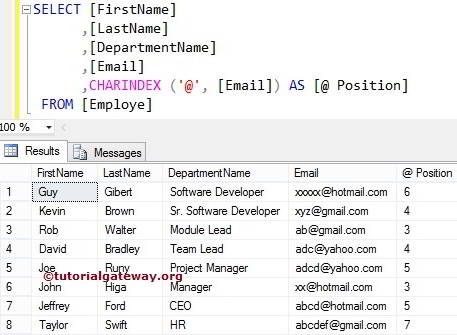
How to find Email @ Position using SQL CHARINDEX?
In this example, we will find the index position of a @ symbol present in the Email address column using the string CHARINDEX.
SELECT [FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[DepartmentName]
,[Email]
,CHARINDEX('@', [Email]) AS [@ Position]
FROM [Employe]
NOTE: We can’t use this function on Image, Text, and NText Data Types.
