The SQL Server @@IDENTITY is a System Function that returns the last inserted identity value. You can use this @@IDENTITY after an INSERT, INTO SELECT, BULK INSERT, or SELECT INTO Statement is completed to find the last generated identity value. And, if no insert operation happens, it will return NULL.
How to write or use this SQL @@IDENTITY Query to extract identity value with an example? For this demonstration, we are going to use the below-shown table data.
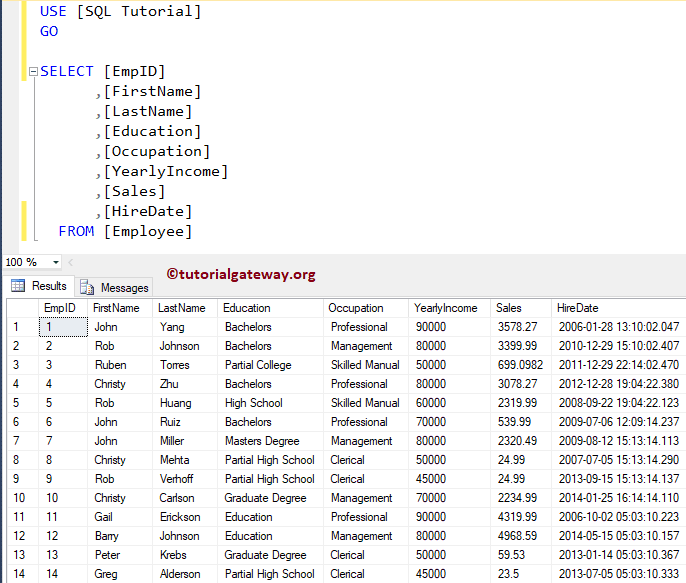
We are creating the following SQL table to insert the data into it.
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[EmployeeDuplicates]( [EmpID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [FirstName] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [LastName] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [Education] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [Occupation] [nvarchar](255) NULL, [YearlyIncome] [float] NULL, [Sales] [float] NULL, [HireDate] [datetime] NULL, CONSTRAINT [PK_EmployeeDuplicates_EmpID] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ( [EmpID] ASC ) )
SQL Server @@IDENTITY Example
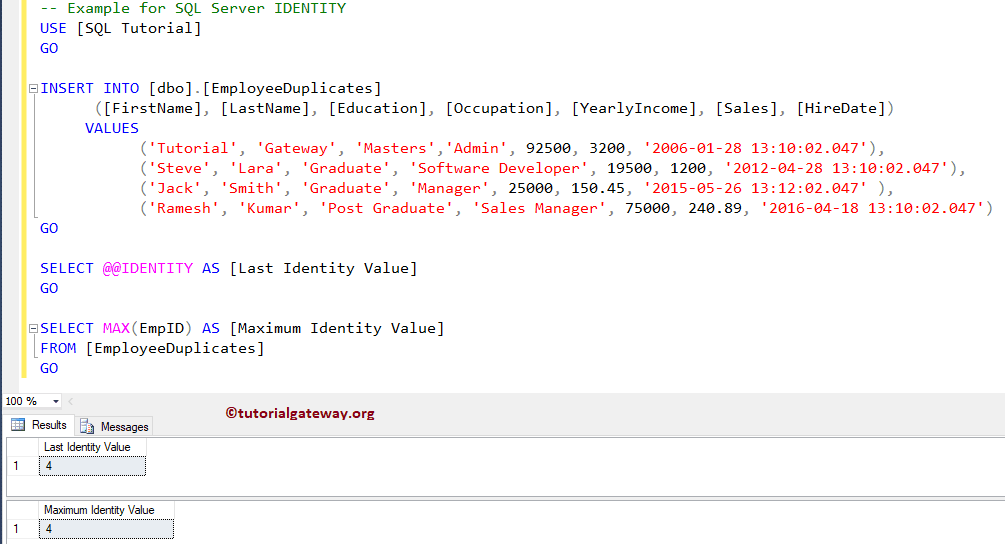
In this example, first, we will load four random records into the Employee Duplicates table. Next, we will extract the last inserted identity value using the SQL @@IDENTITY.
Let me insert a value into the table using the INSERT Statement.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[EmployeeDuplicates]
([FirstName], [LastName], [Education], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales], [HireDate])
VALUES
('Tutorial', 'Gateway', 'Masters','Admin', 92500, 3200, '2006-01-28 13:10:02.047'),
('Steve', 'Lara', 'Graduate', 'Software Developer', 19500, 1200, '2012-04-28 13:10:02.047'),
('Jack', 'Smith', 'Graduate', 'Manager', 25000, 150.45, '2015-05-26 13:12:02.047' ),
('Ramesh', 'Kumar', 'Post Graduate', 'Sales Manager', 75000, 240.89, '2016-04-18 13:10:02.047')
GO
SELECT @@IDENTITY AS [Last Identity Value]
GO
SELECT MAX(EmpID) AS [Maximum Identity Value]
FROM [EmployeeDuplicates]
GO
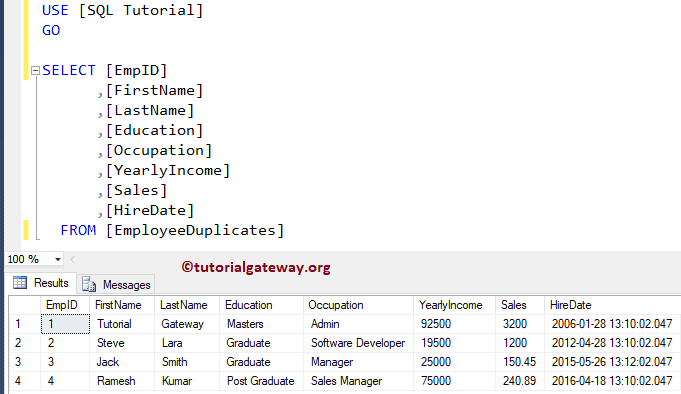
Let me show you the data that we put into the Employee Duplicates tables
In this example, first, we will use the INSERT, INSERT INTO SELECT to insert records from the Employee table into the Employee Duplicates table.
Next, we will extract the last inserted identity value using the SQL @@IDENTITY
INSERT INTO [EmployeeDuplicates] ( [FirstName], [LastName], [Education], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales], [HireDate]) SELECT [FirstName], [LastName], [Education], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales], [HireDate] FROM [Employee] AS Emp WHERE Emp.EmpID > 4 GO SELECT @@IDENTITY AS [Last Identity Value] GO SELECT MAX(EmpID) AS [Maximum Identity Value] FROM [EmployeeDuplicates] GO
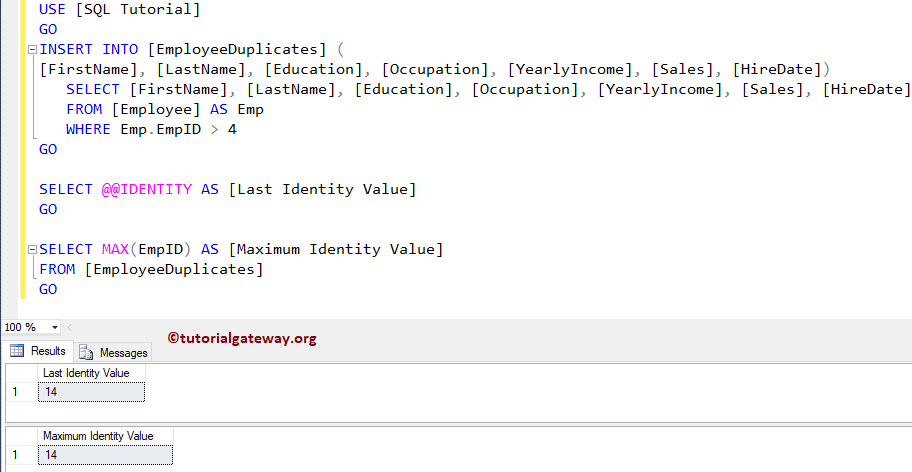
Let me show you the data that we put into the Employee Duplicates tables
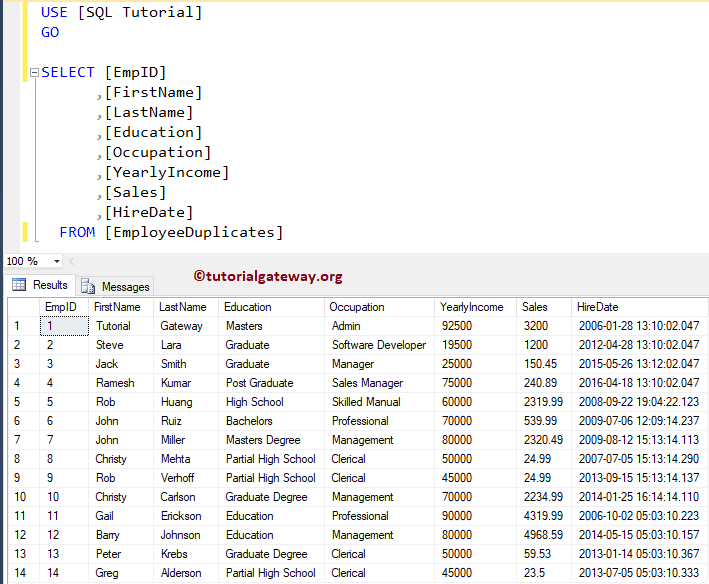
@@IDENTITY Example 3
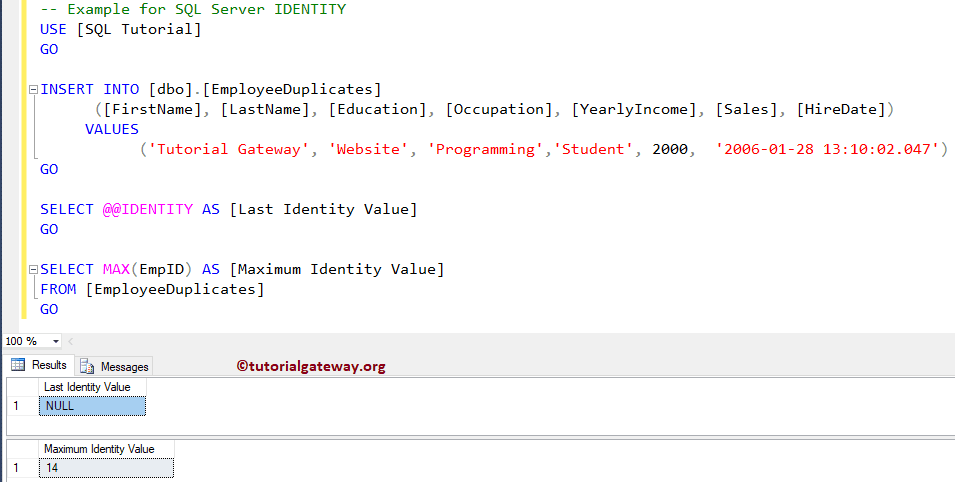
In this SQL @@IDENTITY example, first, we will show you what will happen if the Insert statement fails for some reason. To demonstrate this, we are deliberately failing the load operation.
INSERT INTO [dbo].[EmployeeDuplicates]
([FirstName], [LastName], [Education], [Occupation], [YearlyIncome], [Sales], [HireDate])
VALUES
('Tutorial Gateway', 'Website', 'Programming','Student', 2000, '2006-01-28 13:10:02.047')
GO
SELECT @@IDENTITY AS [Last Identity Value]
GO
SELECT MAX(EmpID) AS [Maximum Identity Value]
FROM [EmployeeDuplicates]
GO
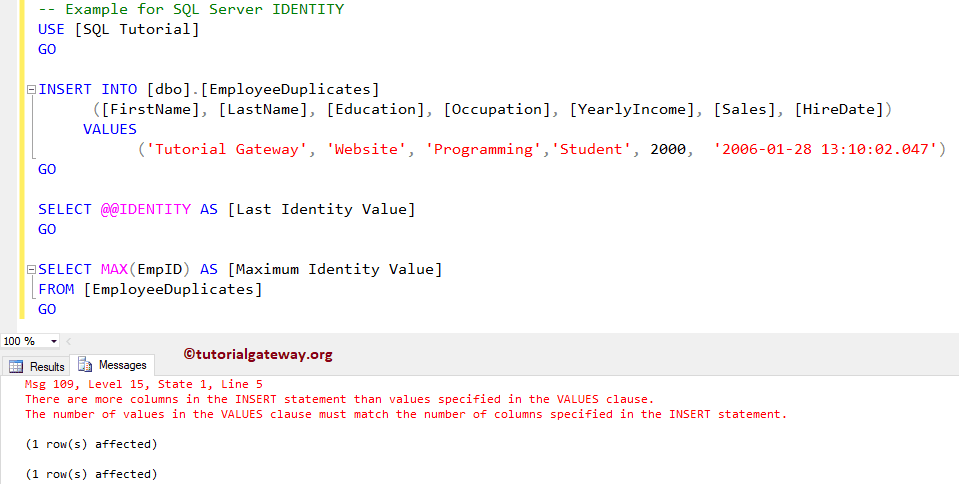
Let me show you the data that we loaded into the Employee Duplicates tables. As you can see, it (the last identity value) returns a NULL value.