How to write SELECT Stored Procedure in SQL Server?. Or How to write the SELECT Statements inside the Stored Procedure with example. For this SQL Server SELECT Stored Procedure demonstration, we use the below-shown data.
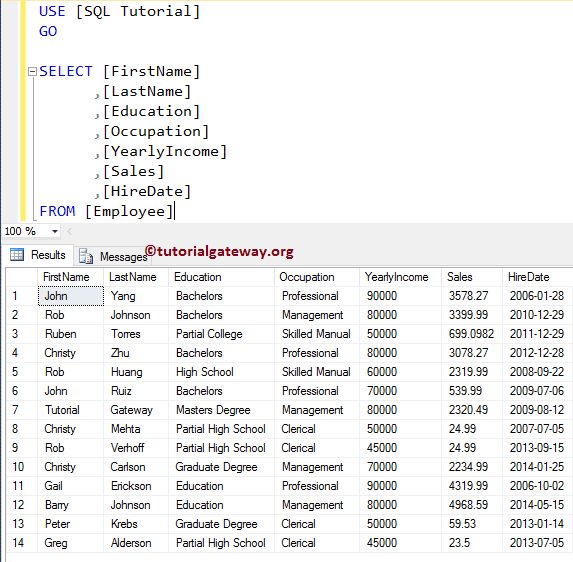
SELECT Stored Procedure in SQL Server Example
In this SQL Server example, we will show you how to use the SELECT Statement inside the Stored procedure. I suggest you refer Introduction to Stored Procedures article to know the basics.
-- Example for SELECT Statement Inside the SQL Stored Procedure
IF OBJECT_ID ( 'SelectStoredProcedureFirstExample', 'P' ) IS NOT NULL
DROP PROCEDURE SelectStoredProcedureFirstExample;
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE SelectStoredProcedureFirstExample
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT [FirstName] + ' ' + [LastName] AS [Full Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [Employee]
END
GO
From the above code snippet, you can see that we are concatenating the First name and second name as Full Name. We are using the SPACE function to provide the space between the First name and last name
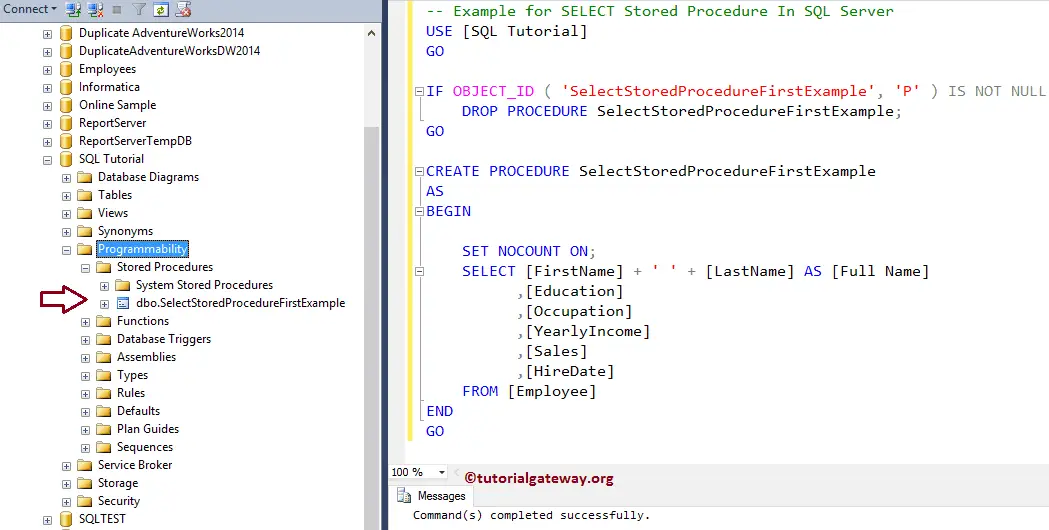
Let me use the EXEC Command (Execute Command) to execute the stored procedure to check the result
EXEC [dbo].[SelectStoredProcedureFirstExample] GO
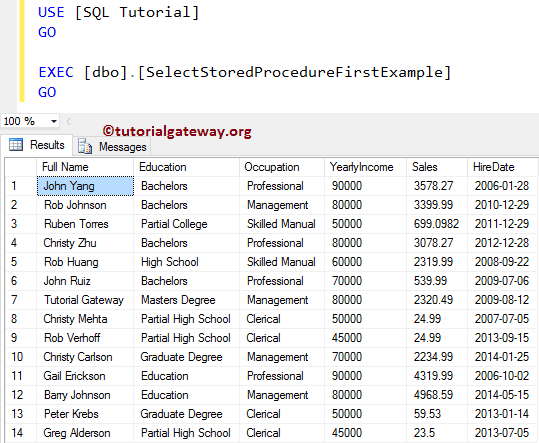
Multiple Select Statements in SQL Stored Procedure
This example will show you how to use Multiple SELECT Statements inside the Stored procedure. From the below code snippet you can see that,
- First, we are selecting the top 6 records from employees order by Sales in Ascending Order.
- Next, we selected the top 4 records from employees, order by Sales in Descending Order.
-- Example for SELECT Statement inside the Stored Procedure In SQL Server
IF OBJECT_ID ( 'SelectStoredProcedureSecondExample', 'P' ) IS NOT NULL
DROP PROCEDURE SelectStoredProcedureSecondExample;
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE SelectStoredProcedureSecondExample
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT TOP 6 [FirstName] + ' ' + [LastName] AS [Full Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [Employee]
ORDER BY [Sales] ASC
SELECT TOP 4 [FirstName] + ' ' + [LastName] AS [Full Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [Employee]
ORDER BY [Sales] DESC
END
GO
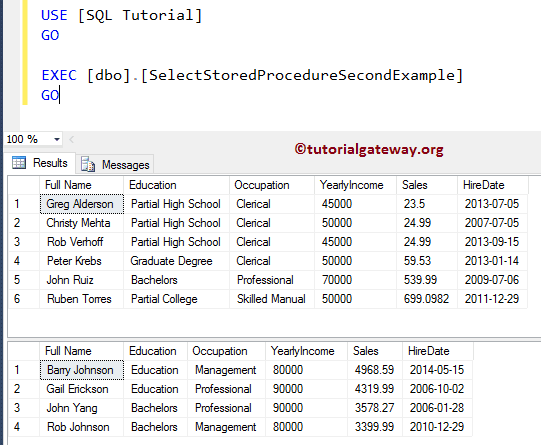
Run the above Multiple Select Statements in a single Stored Procedure query
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me execute the stored procedure to check the result
EXEC [dbo].[SelectStoredProcedureSecondExample] GO
Select Statements With Parameter in Stored Procedure
This example create the Select Stored procedures with parameters.
-- Example for SELECT Statement within the Stored Procedure In SQL Server
IF OBJECT_ID ( 'SelectStoredProcedureThirdExample', 'P' ) IS NOT NULL
DROP PROCEDURE SelectStoredProcedureThirdExample;
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE SelectStoredProcedureThirdExample
@Occupation VARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT [FirstName] + ' ' + [LastName] AS [Full Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [Employee]
WHERE [Occupation] = @Occupation
END
GO
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me execute the Select stored procedure
EXEC [dbo].[SelectStoredProcedureThirdExample] GO
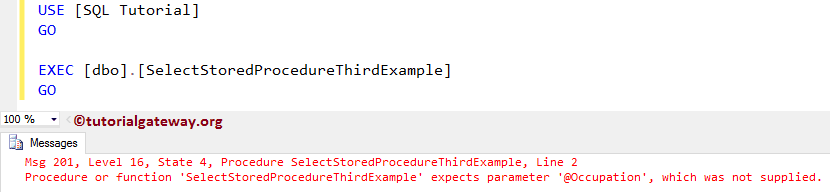
As you can see, it is throwing an error stating that: we haven’t passed the value for the @Occupation parameter. So, let us pass the parameter value using any of the following ways
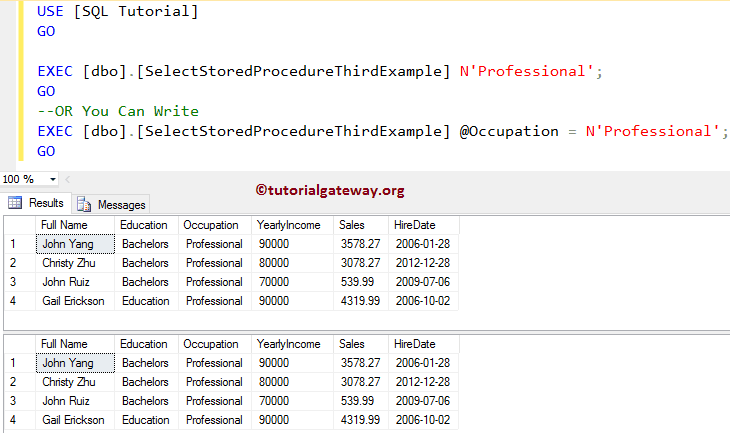
EXEC [dbo].[SelectStoredProcedureThirdExample] N'Professional'; GO --OR You Can Write EXEC [dbo].[SelectStoredProcedureThirdExample] @Occupation = N'Professional'; GO
Select Statements With Multiple Parameter in Stored Procedure
We use the Multiple parameters along with the Select statement inside the stored procedure.
-- Example for SELECT Statement with Stored Procedure in SQL Server
IF OBJECT_ID ( 'SelectStoredProcedureFourthExample', 'P' ) IS NOT NULL
DROP PROCEDURE SelectStoredProcedureFourthExample;
GO
CREATE PROCEDURE SelectStoredProcedureFourthExample
@Education VARCHAR(50),
@Occupation VARCHAR(50)
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
SELECT [FirstName] + ' ' + [LastName] AS [Full Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
,[HireDate]
FROM [Employee]
WHERE [Occupation] = @Occupation OR
[Education] = @Education
END
GO
Messages
--------
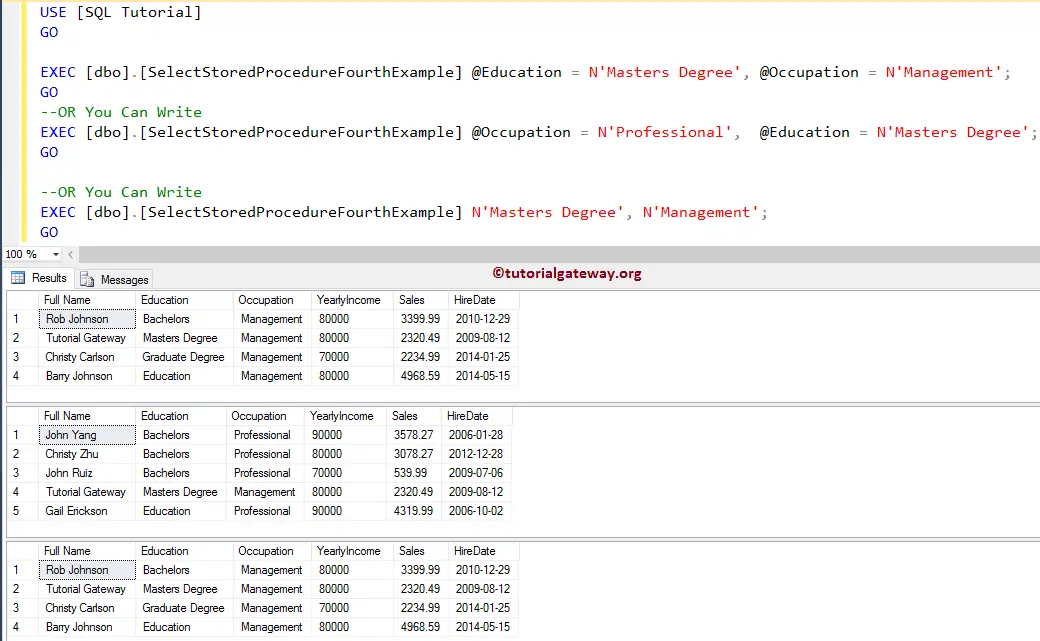
Command(s) completed successfully.The following are the number of ways you can execute the select stored procedure. Let me execute the sp.
EXEC [dbo].[SelectStoredProcedureFourthExample] @Education = N'Masters Degree', @Occupation = N'Management'; GO --OR You Can Write EXEC [dbo].[SelectStoredProcedureFourthExample] @Occupation = N'Professional', @Education = N'Masters Degree'; GO --OR You Can Write EXEC [dbo].[SelectStoredProcedureFourthExample] N'Masters Degree', N'Management'; GO

Comments are closed.