How to use Output Parameters in SQL Server Stored Procedure?. Or How to use Output Parameters to return a Value or message from a Stored Procedure with an example.
To output value from the Sql stored procedure, you have to declare a variable along with the OUT or OUTPUT keyword. For this SQL Server Stored Procedure Output Parameters demonstration, we will use the table below.
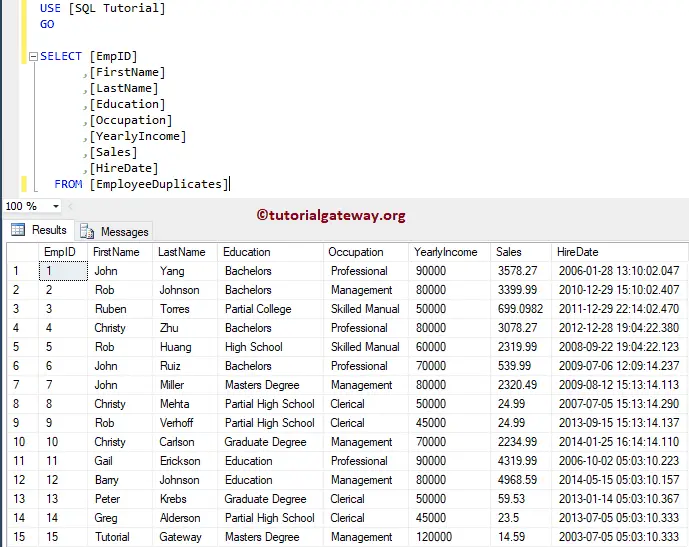
Output Parameters in SQL Stored Procedure Example
In this example, we show you how to use Output Parameters in a Stored procedure. Please see the Select Stored Procedure article to understand how to write the Select statement inside a stored procedure. And also, refer Introduction to Stored Procedure article to understand the basics of the SQL Server stored procedure.
The below statement will create a Stored procedure of Name spEmployeeCount. And we declare a variable called @EmployeeCount of integer Type along with OUTPUT keyword. Within the procedure, we are using the COUNT to find the number of employees in the Employee Duplicate table. Then we assign the value to the Output parameter.
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[spEmployeeCount] @EmployeeCount INT OUTPUT AS BEGIN SELECT @EmployeeCount = COUNT(EmpID)FROM [EmployeeDuplicates] END
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me execute the stored procedure. Here, we have to pass the output parameter @EmployeeCount parameter.
-- Declare a Variable of Type Int. Should match with SP's Output parameter DECLARE @TotalEmployees INT -- Don't forget OUTPUT keyword EXEC [dbo].[spEmployeeCount] @TotalEmployees OUTPUT -- Printing the Output PRINT @TotalEmployees
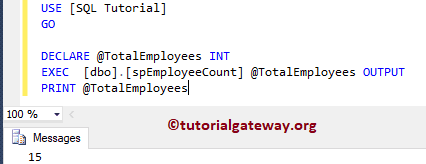
Output Parameters in SQL Stored Procedure Example 2
In this example, we explain to you how to use both Input and Output Parameters in a single Stored procedure. Please refer to the Input Parameters in a Stored Procedure article to know how to use input parameters in a stored procedure.
Here, we declare a variable called @LastName as the input parameter and @EmployeeProfession of Varchar type as an Output parameter. Within the procedure, we find the Occupation of an employee whose last name is equal to the input parameter. Next, we assign the value to the Output parameter.
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[spEmployeeProfession] @LastName VARCHAR(50), @EmployeeProfession VARCHAR(50) OUTPUT AS BEGIN SELECT @EmployeeProfession = [Occupation] FROM [EmployeeDuplicates] WHERE [LastName] = @LastName END
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me execute the stored procedure. Here, we have to pass the value for the @LastName as Gateway.
DECLARE @Profession VARCHAR(50) EXEC [dbo].[spEmployeeProfession] N'Gateway', @Profession OUTPUT PRINT 'Gateway is Working in the ' + @Profession
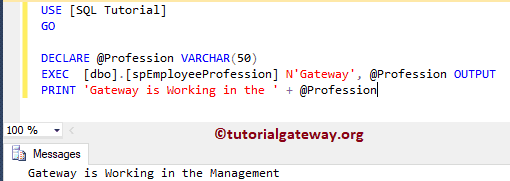
Output Parameters in SP Example 3
Let us see how to use Output Parameters in SQL Stored procedure to return multiple outputs. Here, we declare a variable called @LastName as an input parameter and three Output parameters. Within the procedure, we are finding the Occupation, Education, and yearly Income of an employee whose last name is equal to the input parameter. Next, we assign the value to the Output parameter.
CREATE PROCEDURE [dbo].[spEmployeeProf] @LastName VARCHAR(50), @Profession VARCHAR(50) OUTPUT, @Education VARCHAR(50) OUTPUT, @Income FLOAT OUTPUT AS BEGIN SELECT @Profession = [Occupation], @Education = Education, @Income = YearlyIncome FROM [EmployeeDuplicates] WHERE [LastName] = @LastName END
Messages
--------
Command(s) completed successfully.Let me execute the stored procedure.
-- Example
DECLARE @EmpProfession VARCHAR(50),
@EmpEducation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpIncome FLOAT
EXEC [dbo].[spEmployeeProf] N'Gateway', @EmpProfession OUTPUT,
@EmpEducation OUT,
@EmpIncome OUT
SELECT @EmpProfession AS Profession,
@EmpEducation AS Education,
@EmpIncome AS Income
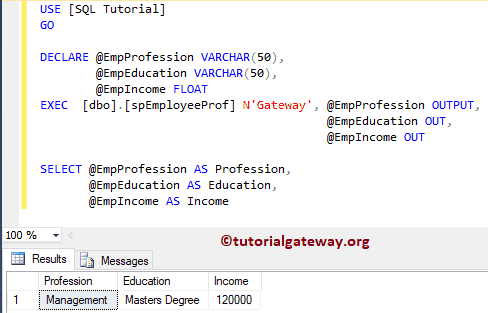
Let me show you, What will happen if you miss the OUTPUT keyword
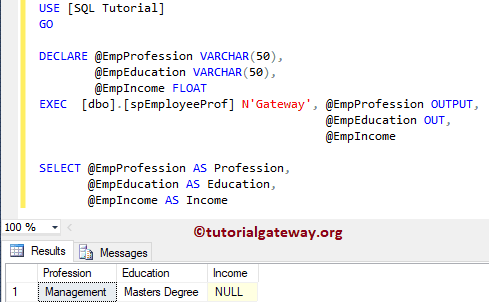
As you can see from the above screenshot, it is returning a NULL value. So, don’t forget the OUTPUT keyword.
