The KEYSET Cursor in SQL Server can only move from the first row to last and last to first. When the Sql Server KEYSET cursor is open, the order of the rows and the membership fixed. And the set of a key that identifies the rows uniquely will be stored in a table under tempdb database.
Remember to use the SQL Keyset cursor on a table with a unique key. Otherwise, this cursor will act like any other static cursor. Once you Open the SQL KEYSET Cursor on Employee, any INSERT operations on that table will not reflect in the Cursor. But both DELETE and UPDATE operations will reflect.
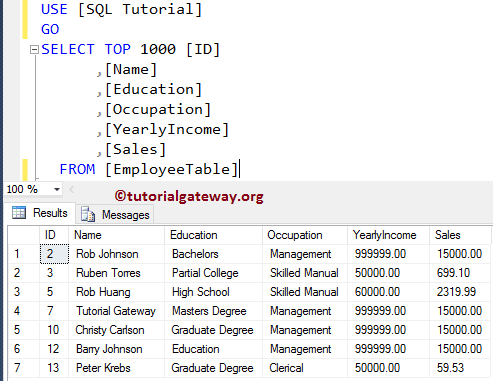
For this SQL Server keyset Cursor demonstration, We use the below shown Employee table, which holds 14 records
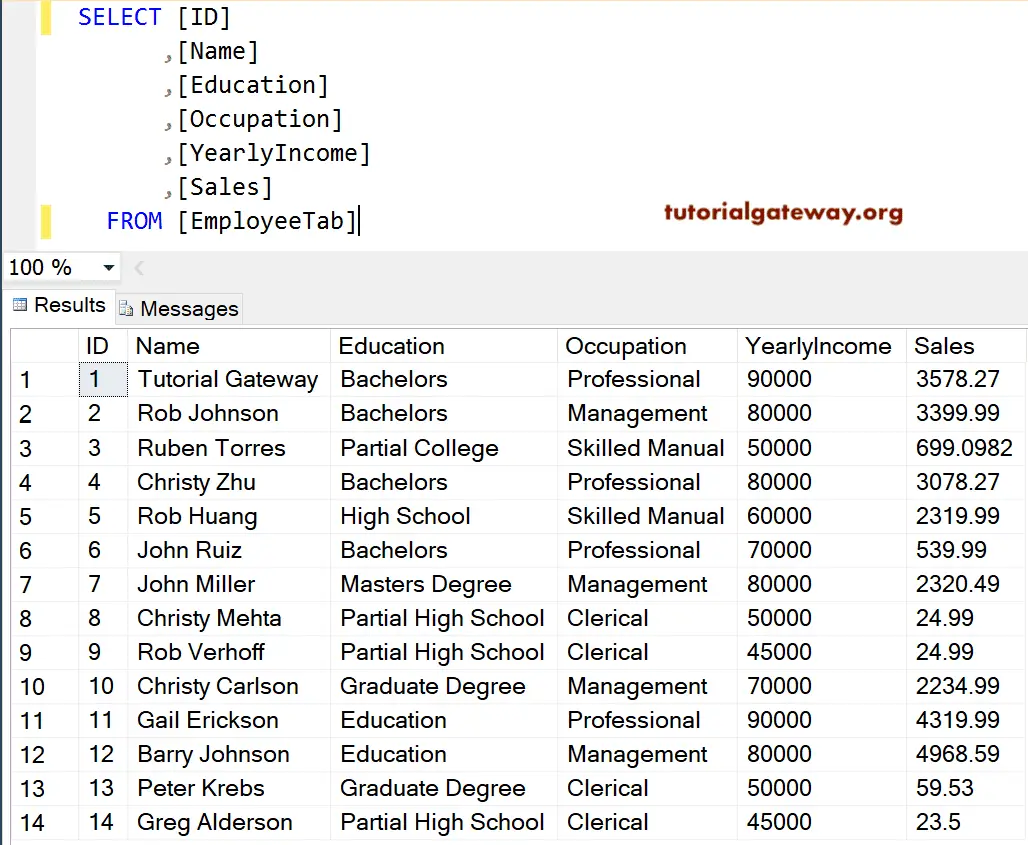
KEYSET Cursor in SQL Server Example 1
Let us see how to declare and open a keyset cursor in SQL Server and how to fetch rows from the cursor. In this example, we will use the WHILE LOOP to loop over the SQL Server cursor elements and print them as output.
Remember, if you apply SQL keyset cursor on any table that does not have at least one unique column then it will act as STATIC CURSOR
SET NOCOUNT ON
-- Declaring the Variables
DECLARE @EmpID INT,
@EmpName VARCHAR(50),
@EmpEducation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpOccupation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpYearlyIncome DECIMAL (10, 2),
@EmpSales DECIMAL (10, 2);
DECLARE keyset_employee_cursor CURSOR
KEYSET FOR
SELECT [ID]
,[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM EmployeeTable
OPEN keyset_employee_cursor
IF @@CURSOR_ROWS > 0
BEGIN
FETCH NEXT FROM keyset_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
PRINT 'ID = '+ CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), @EmpID)+', Full Name = '+ @EmpName
+', Education = '+ @EmpEducation +', Occupation = '+ @EmpOccupation
+ ', Yearly Income = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10),@EmpYearlyIncome)
+ ', Sales Amount = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10),@EmpSales)
FETCH NEXT FROM keyset_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
END
END
CLOSE keyset_employee_cursor
DEALLOCATE keyset_employee_cursor
SET NOCOUNT OFF
If you observe the cursor declaration, we are using the KEYSET cursor, while declaring the cursor. We already explained the remaining steps in Static Cursor in SQL Server example.
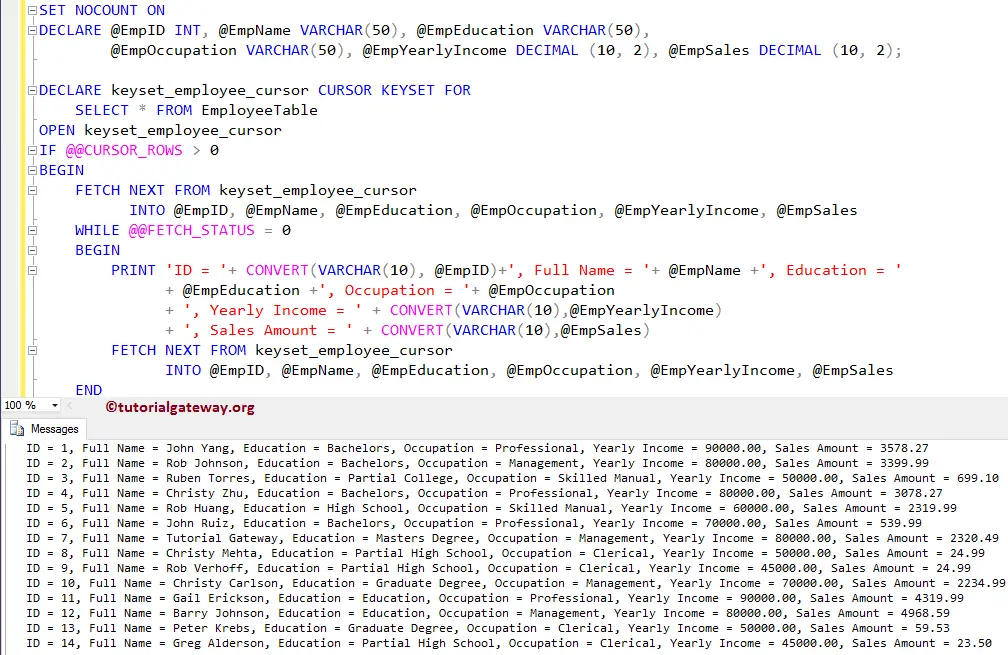
Let me add the WAITFOR DELAY ’00:00:05′ to delay the execution of the query, and PRINT @@FETCH_STATUS to print the FETCH status (-2 to 0)

KEYSET Cursor in SQL Server Example 2
What will happen when you perform INSERT operation while the Cursor is Open?
SET NOCOUNT ON
-- Declaring the Variables
DECLARE @EmpID INT,
@EmpName VARCHAR(50),
@EmpEducation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpOccupation VARCHAR(50),
@EmpYearlyIncome DECIMAL (10, 2),
@EmpSales DECIMAL (10, 2);
DECLARE keyset_employee_cursor CURSOR
KEYSET FOR
SELECT TOP 5 [ID]
,[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM EmployeeTable
OPEN keyset_employee_cursor
IF @@CURSOR_ROWS > 0
BEGIN
FETCH NEXT FROM keyset_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:05'
PRINT 'ID = '+ CONVERT(VARCHAR(10), @EmpID)+', Full Name = '+ @EmpName
+', Education = '+ @EmpEducation +', Occupation = '+ @EmpOccupation
+ ', Yearly Income = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10),@EmpYearlyIncome)
+ ', Sales Amount = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR(10),@EmpSales)
FETCH NEXT FROM keyset_employee_cursor
INTO @EmpID, @EmpName, @EmpEducation,
@EmpOccupation, @EmpYearlyIncome, @EmpSales
PRINT @@FETCH_STATUS
END
END
CLOSE keyset_employee_cursor
DEALLOCATE keyset_employee_cursor
SET NOCOUNT OFF
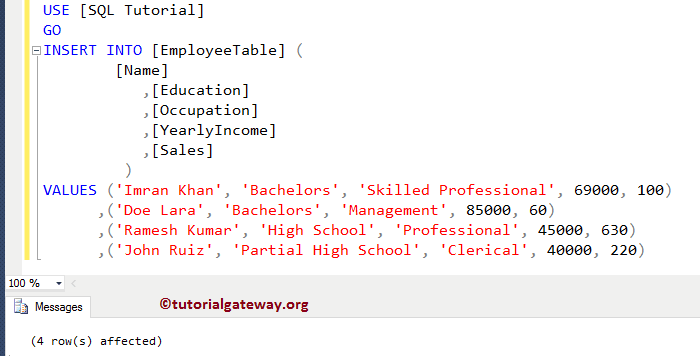
while the Cursor is Open, let me insert few records using the following query
INSERT INTO [EmployeeTable] (
[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
)
VALUES ('Imran Khan', 'Bachelors', 'Skilled Professional', 69000, 100)
,('Doe Lara', 'Bachelors', 'Management', 85000, 60)
,('Ramesh Kumar', 'High School', 'Professional', 45000, 630)
,('John Ruiz', 'Partial High School', 'Clerical', 40000, 220)
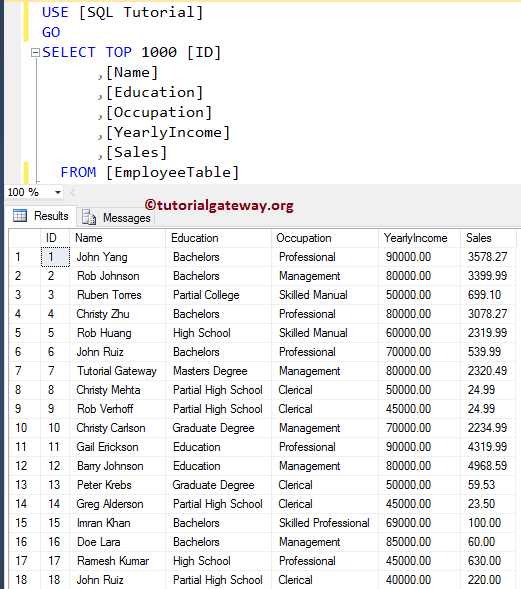
If you observe the below screenshot, though we have inserted four new records into our Employee table, the keyset cursor is returning the top 5 records. Because, once the cursor is open, it will fix the key value, and an insert operation by another user will not reflect inside the cursor.

Please use the following SQL Query to check whether the new records inserted into the Employee table or not.
SELECT [ID]
,[Name]
,[Education]
,[Occupation]
,[YearlyIncome]
,[Sales]
FROM [EmployeeTable]
KEYSET Cursor in SQL Server Example 3
What happens when you perform UPDATE operation while the Cursor is Open. For this, we are using the definition of the cursor that we used earlier. And here, we are selecting all the columns instead of Top 5.
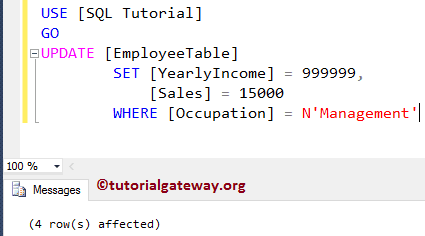
While the Cursor is Open, let me Update the yearly Income and Sales amount of the Employees whose occupation is management using the following query
UPDATE [EmployeeTable]
SET [YearlyIncome] = 999999,
[Sales] = 15000
WHERE [Occupation] = N'Management'
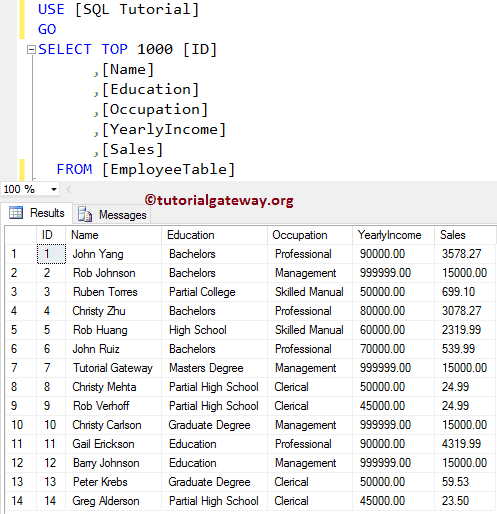
If you see, though the keyset cursor is open, it is showing the Updated values from our Employee table. Because, even though the cursor is open, it can read the updated values (values updated by another user).

Let me check the Employee table, whether the Update has happened at the server level or not.
KEYSET Cursor in SQL Server Example 4
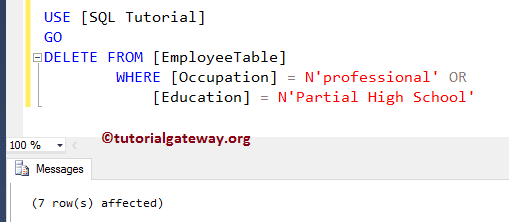
Perform DELETE operation while the KEYSET Cursor is Open. For this, let me delete the employees whose Occupation is Professional, or Education is Partial High School while the Cursor is Open
DELETE FROM [EmployeeTable]
WHERE [Occupation] = N'professional' OR
[Education] = N'Partial High School'
Although the Sql Server keyset cursor is open, it terminated after it reaches 3rd record because the 4th record has the Occupation = Professional, so the fetch status is returning -2. Try to increase the Time delay to get the correct result.
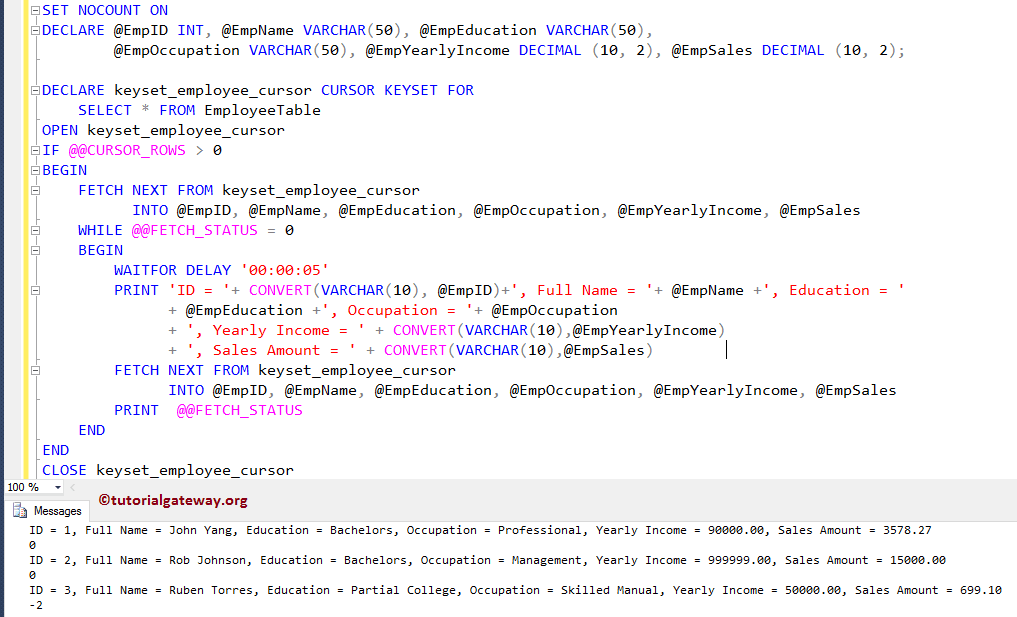
Let me check the Employee table, whether the delete has happened on the original table or not.