The SQL VAR Function is an Aggregate Function, which is used to determine the statistical Variance of entire records (or rows) selected by the SELECT Statement. The syntax of the SQL Server VAR Function is
SELECT VAR ([Column_Name]) FROM [Source]
SQL Var Function Formula
Sql Server VAR Function will only work on Numeric Columns, and it ignores Nulls. The mathematical formulas behind the function to calculate the Sql Server Statistical Variance is
--Calculating the Mean or Average Mean = Sum of each individual/Total number of items --Calculating the Statistical Variance Variance = ((OriginalValue – Mean)² + (OriginalValue – Mean)² +.... )/(Total number of items - 1)
For this SQL VAR function demo, we use the below-shown data
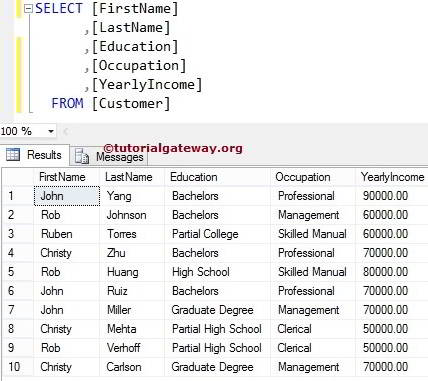
SQL Server VAR Example
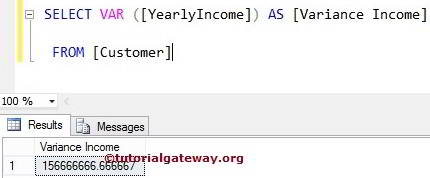
The VAR returns the Variance of the total number of records present in the specified column. For example, the following query will calculate the variance of total records present in the [Yearly Income] column from the Customers table.
SELECT VAR ([YearlyIncome]) AS [Variance Income] FROM [Customer]
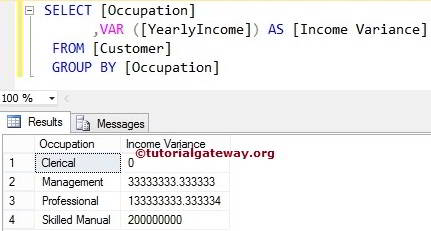
SQL Variance with Group By Clause
In most cases, we usually calculate the variance of products belonging to a particular category or color, etc. In these situations, we use GROUP BY Clause to group the products by color or category. Then use the Var Function to calculate the variance of products present in each group. Let us see the Aggregate Function Example
SELECT [Occupation]
,VAR ([YearlyIncome]) AS [Income Variance]
FROM [Customer]
GROUP BY [Occupation]
Above SQL Server Query will find, the Customers associated with the particular Department and calculates their income variance
It is too big to show the Mean and Variance calculations for everything. So, We are taking the Skilled Manual profession and showing you the output.
--Calculating Mean Mean = (60000 + 80000) / 2 Mean = 70000 --Calculating Variance Variance = ( (60000 - 70000) + (80000 - 70000) ) / (2 -1) Variance = 200000000
SQL VAR in Having Clause
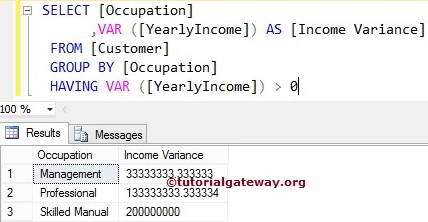
When we are grouping the data, in some cases, we usually check for the conditions against the aggregated data. In these situations, we use the HAVING Clause along with Group By Statement. For example, the following query will group the Customers by their Occupation and then finds the Income variance of each group.
SELECT [Occupation]
,VAR ([YearlyIncome]) AS [Income Variance]
FROM [Customer]
GROUP BY [Occupation]
HAVING VAR ([YearlyIncome]) > 0
Below lines of code will check whether the aggregated amount (Variance of Yearly income for each Group) is greater than 0 or not. If this is True, then corresponding records or rows will display.
HAVING VAR ([YearlyIncome]) > 0